Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnostic evaluation of hemorrhage involves various laboratory tests and imaging studies to confirm the presence, source, extent, and effects of bleeding. Some common tests include:
- Complete blood count (CBC), including hemoglobin, hematocrit, red blood cell (RBC) count, white blood cell (WBC) count, and platelet count. These tests measure the amount and quality of blood cells and indicate the degree of blood loss and anemia.
- Coagulation studies, including prothrombin time (PT), international normalized ratio (INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), fibrinogen level, D-dimer test, and thrombin time (TT). These tests measure the ability of blood to clot and indicate the presence of coagulation disorders or anticoagulant therapy.
- Blood type and crossmatch. This test determines the compatibility of blood for transfusion and prevents transfusion reactions.
- Serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and liver function tests (LFTs). These tests measure the levels of electrolytes and metabolic waste products in the blood and indicate the effects of bleeding on the kidney and liver function.
- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. This test measures the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in the blood and indicates the effects of bleeding on the acid-base balance and tissue perfusion.
- Urinalysis. This test detects the presence of blood, protein, glucose, ketones, or bacteria in the urine and indicates the effects of bleeding on the urinary system.
- Endoscopy. This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera and light into the gastrointestinal tract to visualize the source and extent of bleeding and perform interventions such as cauterization, clipping, or banding.
- Colonoscopy. This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera and light into the colon to visualize the source and extent of bleeding and perform interventions such as polypectomy, cauterization, or injection.
- Angiography. This procedure involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels and taking X-rays to visualize the source and extent of bleeding and perform interventions such as embolization or stenting.
- Ultrasound. This procedure involves using sound waves to create images of the internal organs and structures and detect the presence of fluid, masses, or abnormalities.
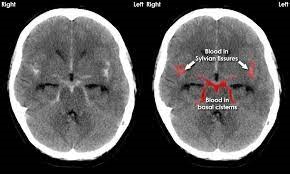
- Computed tomography (CT) scan. This procedure involves using X-rays and a computer to create cross-sectional images of the body and detect the presence of fluid, masses, or abnormalities.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. This procedure involves using a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the body and detect the presence of fluid, masses, or abnormalities.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Questions on Diagnostic Evaluation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Search Here
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
