Memory and Secondary Immune Response:
A. Memory Cells: Both B cells and T cells can form memory cells, which "remember" previous encounters with specific antigens and mount a faster and stronger response upon re-exposure.
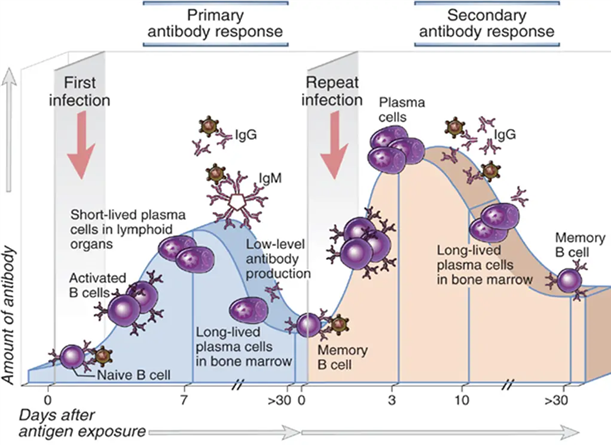
B. Secondary Immune Response: If the body encounters the same antigen again, memory cells rapidly differentiate into effector cells, leading to a more robust and rapid immune response.
Nursing Test Bank
Test Bank #1: RN Pharmacology Exams
Test Bank #2: RN Medical-Surgical Exams
Test Bank #3: RN Fundamentals Exams
Test Bank #4: RN Maternal-Newborn Exams
Test Bank #5: RN Anatomy and Physiology Exams
Test Bank #6: RN Obstetrics and Pediatrics Exams
Test Bank #7: RN Fluid and Electrolytes Exams
Test Bank #9: RN Adult Health
Test Bank #10: RN Dosage Calculation
Test Bank #11: RN Community Health Exams
Test Bank #12: RN Psychology Exams
Test Bank #13: RN Nursing Care Of Children
Test Bank #14: RN Foundations of Nursing Exams
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Exam #1: RN Comprehensive predictor 2023 proctored exam
Exam #2: Ati rn vati comprehensive predictor proctored exam
Exam #3: Ati Rn Comprehensive Predictor Proctored Exam 2023
Exam #4: Rn Comprehensive Predictor 2023 Proctored Exam - St. Joseph
Exam #5: RN Comprehensive Predictor Proctored Exam (National U CA San Diego)
Exam #6: Ati rn comprehensive predictor 2023 retake proctored exam
Exam #7: RN Hesi Exit Proctored Exam
Exam #8: Hesi RN Exit proctored exam
Exam #9: Hesi rn exit proctored exam
Exam #10: Hesi Rn compass exit B proctored exam
Questions on Memory and Secondary Immune Response:
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Memory cells are a type of immune cell that are formed during the body's initial encounter with a pathogen. They "remember" the specific antigen of the pathogen and allow the immune system to respond more rapidly and effectively if the same pathogen is encountered again in the future. Memory cells are responsible for providing long-term immunity.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
<p>Vaccinations are made from either weakened or killed pathogens or parts of pathogens, which cannot cause the disease they are meant to protect against. However, they stimulate the body's immune system to produce a protective response, providing immunity against the specific disease.</p>
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
<p>Producing memory cells after exposure to a pathogen is part of the adaptive immune response and contributes to long-term immunity, not passive immunity.</p>
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
<p>Memory B cells are formed during the primary immune response and play a critical role in the secondary immune response. When re-exposed to the same antigen, memory B cells quickly differentiate into plasma cells that produce large quantities of specific antibodies, leading to a rapid and robust immune response.</p>
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to dry eyes and dry mouth, but it does not typically present with a "butterfly rash" or skin lesions.VII. Vaccination and Immunization:
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Antibodies are proteins produced by B cells in response to the presence of antigens. They play a vital role in recognizing and neutralizing foreign substances in the body.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
<p>While the immune system is designed to fight off infections, it is not capable of fighting off all types of infections equally. The immune response is specific to the type of pathogen encountered.</p>
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Cytokines are signaling molecules released by immune cells to regulate the immune response but are not the primary means of distinguishing self from non-self.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Crohn's disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the gastrointestinal tract, not the central nervous system.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The production of hormones that control bodily functions is primarily the responsibility of the endocrine system, not the immune system.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The meningococcal vaccine protects against meningococcal infections, not certain types of cancer.Conclusion xx
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
<p>The regulation of the immune response is mainly the function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and other immune regulatory mechanisms, not the primary role of B cells.IV. T Lymphocytes (T Cells) and Cell-Mediated Immunity:</p>
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
<p>Herd immunity is the indirect protection that occurs when a large percentage of a population becomes immune to a disease, either through vaccination or previous infection, reducing the likelihood of transmission to susceptible individuals.True or False: Vaccines can cause autism in children.Explanation: Numerous scientific studies have found no link between vaccines and autism. The notion that vaccines cause autism was based on a discredited and fraudulent study, and subsequent research has shown no evidence of such a link.</p>
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine protects against pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria, not hepatitis B.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
<p>Macrophages are phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy pathogens and debris in the body. While they play a crucial role in immune responses, they do not produce antibodies.I. Components of the Immune System:A. Innate Immunity:B. Adaptive Immunity:</p>
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Red blood cells do not have a direct role in antigen recognition or the immune response. Their primary function is to transport oxygen throughout the body.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Directly attacking and killing infected cells is the role of cytotoxic T cells during cell-mediated immunity, not B cells during the humoral immune response.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
<p>Allergic reactions are primarily mediated by a different type of T cells called helper T cells (CD4+ T cells), not cytotoxic T cells.</p>
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
<p>The primary immune response is characterized by the production of IgM antibodies initially, but during the secondary immune response, the production of IgG antibodies predominates, which are more effective in neutralizing antigens.</p>
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
<p>Phagocytosis of pathogens is mainly carried out by macrophages and neutrophils, not B cells.</p>
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
<p>Antibodies do not play a role in maintaining body temperature during infections; instead, fever is a response triggered by the release of certain chemicals called pyrogens during infections.</p>
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
No explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Perforin is a protein released by cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells to create pores in the membrane of infected cells, leading to cell death. B cells do not produce perforin.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
<p>Cell-mediated immunity is another component of adaptive immunity, where T cells directly attack infected or abnormal cells.</p>
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
<p>Acquired immunity is a general term that includes both active and passive immunity, but it does not specifically describe the type of immunity acquired through vaccination or exposure to a specific pathogen.</p>
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The immune response is a complex system of defense mechanisms that aim to protect the body from pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. It involves the activation of various immune cells, production of antibodies, and other immune components to recognize and eliminate the invading pathogens.
<p>The varicella vaccine is usually administered at 12 months of age, not at 2 months.True or False: Vaccinations can cause the diseases they are designed to prevent.Explanation: Vaccinations are made from either weakened or killed pathogens or parts of pathogens, which cannot cause the disease they
The secondary immune response provides long-lasting immunity because of the presence of memory B cells and memory T cells. These memory cells "remember" the specific antigen and can quickly mount a strong and effective immune response upon re-exposure to the same antigen, providing long-term protect
<p>The ability of B cells to produce antibodies is an essential part of the primary immune response, but it is not specific to memory in the immune system.</p>
The production of memory cells after exposure to a pathogen is also a characteristic of active immunity, as it allows the body to recognize and respond more quickly to future infections with the same pathogen.
Natural killer cells are a type of lymphocyte involved in the innate immune response and can directly kill infected or abnormal cells, but they do not primarily function as phagocytes like macrophages.
<p>Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, not the small intestine.</p>
<p>Natural killer cells are part of the innate immune response and can directly kill infected or abnormal cells. They do not participate in the adaptive immune response.II. Immune Response and Antigen Recognition:</p>
Herd immunity is the indirect protection that occurs when a large percentage of a population becomes immune to a disease, either through vaccination or previous infection, reducing the likelihood of transmission to susceptible individuals.
<p>Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell involved in the innate immune response. They do not release antibodies, as that function is primarily carried out by B cells and plasma cells.III. B Lymphocytes (B Cells) and Antibody-Mediated Immunity:</p>
<p>Passive immunity. Passive immunity is acquired when preformed antibodies are transferred from one individual to another. In this case, the mother's antibodies are transferred to her baby through breast milk, providing temporary protection against certain infections.</p>
Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to dry eyes and dry mouth.True or False: Immune disorders can be caused by both genetic and environmental factors.Explanation: Immune disorders can result from a combination of genetic pred
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell involved in the innate immune response. They primarily target and destroy bacteria and other foreign invaders in the body, but they do not have the specific recognition capabilities of T cells.
The HPV vaccine is recommended for adolescents and young adults, not older adults, and does not protect against pneumonia.
Natural killer cells are a type of lymphocyte involved in the innate immune response. They do not produce antibodies but can directly kill infected or abnormal cells.
<p>Memory cells are formed after the immune system encounters an antigen and are not directly involved in antigen presentation.</p>
<p>Recognizing and responding to specific antigens. T cells are a type of lymphocyte that plays a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They recognize and respond to specific antigens presented by infected or abnormal cells, leading to their destruction.</p>
Toxoid vaccines use inactivated toxins produced by the pathogen, not weakened forms of the pathogen itself.
<p>Regulatory T cells (suppressor T cells) are involved in regulating the immune response to prevent excessive inflammation and tissue damage, not cytotoxic T cells.V. Memory and Secondary Immune Response:</p>
Suppressor T cells (regulatory T cells) are involved in down-regulating the immune response to prevent excessive inflammation and tissue damage, not in enhancing immune cell activity.
<p>Antibodies do not regulate body temperature. Body temperature regulation is mainly controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain.</p>
No explanation
Booster doses do not reduce the number of required vaccine doses; they are additional doses given to maintain immunity over time.
<p>Macrophages are phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy foreign substances, including pathogens, but they are not the primary cells responsible for recognizing and attacking cancer cells.</p>
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin, and it is not related to the salivary and lacrimal glands.
B cells recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells like macrophages, but their primary function is to produce antibodies, not to recognize antigens directly.
<p>Numerous scientific studies have found no link between vaccines and autism. The notion that vaccines cause autism was based on a discredited and fraudulent study, and subsequent research has shown no evidence of such a link.</p>
Natural immunity refers to the immunity that is acquired through natural exposure to a pathogen and the subsequent development of an immune response. This includes both active immunity from natural infection and passive immunity from maternal antibodies passed to the baby during childbirth or breast
Search Here
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
