Please set your exam date
Blood and Cardiovascular Disorders
Study Questions
Hypertension
A nurse is providing education to a client about hypertension. Which statement made by the nurse is accurate?
Explanation
Rationale:
A) This statement is incorrect. Hypertension is characterized by elevated blood pressure levels, not low blood pressure levels.
B) This statement is incorrect. Regular screenings for hypertension are essential, even in the absence of symptoms, to detect and manage the condition early.
C) Correct answer. Hypertension is often asymptomatic in its early stages, which makes routine screenings crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention.
D) This statement is incorrect. While a family history of hypertension is a risk factor, there are other non-modifiable and modifiable risk factors that can contribute to the development of hypertension.
A nurse is discussing modifiable risk factors for hypertension with a client. Which factor should the nurse include in the discussion?
Explanation
Rationale:
A) This option is incorrect. Age is a non-modifiable risk factor for hypertension.
B) This option is incorrect. Family history is a non-modifiable risk factor for hypertension.
C) Correct answer. Smoking is a modifiable risk factor that can contribute to the development of hypertension. Smoking causes vasoconstriction and damages the blood vessel walls, leading to elevated blood pressure.
D) This option is incorrect. Genetics is a non-modifiable risk factor for hypertension.
A nurse is explaining the pathophysiology of hypertension to a client. Which process is primarily responsible for elevated blood pressure in hypertension?
Explanation
Rationale:
A) This option is incorrect. In hypertension, there is often vasoconstriction and increased sodium retention, leading to elevated blood pressure.
B) Correct answer. Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is a key mechanism in hypertension. It leads to vasoconstriction and increased water and sodium retention, elevating blood pressure.
C) This option is incorrect. In hypertension, sympathetic nervous system activity is often increased, not decreased.
D) This option is incorrect. In hypertension, there is reduced nitric oxide production, which contributes to arterial stiffness and elevated blood pressure.
A nurse is assessing a client suspected of having hypertension. Which clinical manifestation may be present in the early stages of hypertension?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Severe headaches are more commonly associated with hypertensive crises, not the early stages of hypertension.
B) This option is incorrect. Blurred vision may occur in severe hypertension but is not a typical early-stage manifestation.
C) This option is incorrect. Chest pain may be related to other cardiovascular conditions but is not a common manifestation of early-stage hypertension.
D) Correct answer. Hypertension is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making routine screenings crucial for early detection.
A nurse is reviewing diagnostic tests for hypertension with a client. Which test directly measures blood pressure levels for 24 hours?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. An electrocardiogram (ECG) measures electrical activity in the heart, not blood pressure levels.
B) This option is incorrect. A blood glucose test measures blood sugar levels, not blood pressure.
C) Correct answer. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) is a diagnostic test that measures blood pressure levels at regular intervals over 24 hours, providing a comprehensive view of a client's blood pressure variations.
D) This option is incorrect. A renal function panel assesses kidney function, not blood pressure levels.
A nurse is discussing complications of hypertension with a client. Which target organ damage is related to hypertensive retinopathy?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Heart complications of hypertension include heart failure, myocardial infarction, and arrhythmias.
B) This option is incorrect. Kidney complications of hypertension include nephrosclerosis and chronic kidney disease.
C) This option is incorrect. Brain complications of hypertension include stroke and transient ischemic attacks (TIA).
D) Correct answer. Hypertensive retinopathy refers to damage to the blood vessels in the eyes due to hypertension, leading to vision problems and potential vision loss.
A nurse is providing education on hypertension management to a client. Which statement by the nurse accurately reflects a lifestyle modification for managing hypertension?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. A high-sodium diet can exacerbate hypertension by causing fluid retention and raising blood pressure.
B) This option is incorrect. Smoking is a risk factor for hypertension and can lead to vasoconstriction, increasing blood pressure.
C) This option is incorrect. Regular physical activity is recommended for hypertension management as it can help improve cardiovascular health and lower blood pressure.
D) Correct answer. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise are important lifestyle modifications for managing hypertension. Weight reduction and physical activity can help improve blood pressure control and overall cardiovascular health.
Questions
A nurse is discussing non-modifiable risk factors for hypertension with a client. Which factor should the nurse include in the discussion?
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Age is a non-modifiable risk factor for hypertension. As individuals get older, the risk of developing hypertension increases.
B) This option is incorrect. A sedentary lifestyle is a modifiable risk factor for hypertension, as regular physical activity can help lower blood pressure.
C) This option is incorrect. High sodium intake is a modifiable risk factor for hypertension. Reducing sodium intake can help prevent and manage hypertension.
D) This option is incorrect. Obesity is a modifiable risk factor for hypertension. Weight reduction through lifestyle changes can contribute to blood pressure control.
A nurse is discussing modifiable risk factors for hypertension with a client. Which factor should the nurse include in the discussion?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. A family history of hypertension is a non-modifiable risk factor.
B) This option is incorrect. Ethnicity, such as being African-American, is a non-modifiable risk factor for hypertension.
C) Correct answer. Tobacco use is a modifiable risk factor for hypertension. Smoking causes vasoconstriction and damages blood vessels, contributing to elevated blood pressure.
D) This option is incorrect. Advancing age is a non-modifiable risk factor for hypertension.
A nurse is providing education on hypertension risk factors to a group of clients. Which client statement indicates a need for further clarification?
Explanation
A. Limiting alcohol intake is a well-known strategy to reduce the risk of hypertension. Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure, so this statement is accurate and does not need further clarification.
B. Family history is a significant risk factor for hypertension. If a person has a family history of hypertension, their chances of developing it are higher. This statement is incorrect and indicates a need for further clarification.
C. Regular exercise is beneficial for lowering blood pressure. Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and improves heart health, making this statement correct.
D. Reducing stress levels can help prevent hypertension. Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure, so managing stress is a valid preventive measure.
A client asks the nurse about the relationship between hypertension and salt intake. What should the nurse explain?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. High salt intake is a significant risk factor for hypertension, and reducing salt intake is important for blood pressure management.
B) Correct answer. Reducing salt intake can indeed help lower blood pressure and decrease the risk of developing hypertension. High salt intake can lead to fluid retention and increased blood pressure.
C) This option is incorrect. Salt intake is a concern for everyone, regardless of family history, as it can impact blood pressure levels.
D) This option is incorrect. Salt intake is relevant for individuals of all ages, not just older adults. Excessive salt intake can affect blood pressure at any age.
A nurse is conducting a hypertension risk assessment for a client. Which question is most relevant in identifying a modifiable risk factor?
Explanation
A) This question is not relevant to identifying a modifiable risk factor, as family history is a non-modifiable risk factor.
B) This question is not relevant to identifying a modifiable risk factor, as age is a non-modifiable risk factor.
C) Correct answer. This question is relevant in identifying a modifiable risk factor. Regular physical activity is a lifestyle choice that can impact blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health.
D) This question is not relevant to identifying a modifiable risk factor, as ethnicity is a non-modifiable risk factor.
A client with hypertension asks the nurse if stress could be contributing to their condition. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Stress can have a significant impact on blood pressure, especially in individuals with hypertension.
B) This option is incorrect. Stress can be a significant factor in the development and worsening of hypertension, not just a temporary effect.
C) Correct answer. Stress can lead to elevated blood pressure, as it activates the sympathetic nervous system and increases the release of stress hormones like cortisol, contributing to hypertension.
D) This option is incorrect. Stress can affect blood pressure in all individuals, regardless of family history. It is a modifiable risk factor that can be managed through stress-reduction techniques.
Questions
A client asks the nurse about common symptoms associated with hypertension. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While severe headaches and visual disturbances can occur in hypertensive crises, they are not typical symptoms of hypertension in its early stages.
B) This option is incorrect. Chest pain and shortness of breath are not common symptoms of hypertension.
C) Correct answer. Hypertension is often asymptomatic in its early stages, earning it the nickname "silent killer." Occasionally, clients may experience nosebleeds and fatigue, but many individuals with hypertension do not exhibit any noticeable symptoms.
D) This option is incorrect. Palpitations and increased heart rate are not typical symptoms of hypertension. These may be indicative of other cardiac conditions.
A nurse is assessing a client with hypertension. Which symptom should the nurse be particularly vigilant about, as it could indicate a hypertensive emergency?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Blurred vision may be a symptom of hypertension, but it is not specific to hypertensive emergencies.
B) Correct answer. Severe headache is a concerning symptom that could indicate a hypertensive emergency, such as malignant hypertension or hypertensive encephalopathy.
C) This option is incorrect. Occasional dizziness is not specific to hypertensive emergencies, although it may be associated with uncontrolled hypertension.
D) This option is incorrect. Mild chest discomfort is not a typical symptom of a hypertensive emergency. However, any chest pain should be evaluated promptly as it may be indicative of other cardiac issues.
A nurse is assessing a client with long-standing uncontrolled hypertension. Which clinical manifestation should the nurse anticipate as a result of target organ damage?
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Proteinuria (presence of protein in urine) and edema (swelling) are common signs of kidney damage (nephrosclerosis) resulting from long-standing uncontrolled hypertension.
B) This option is incorrect. Weight loss and increased appetite are not typical manifestations of target organ damage in hypertension.
C) This option is incorrect. Improved exercise tolerance is not associated with target organ damage in hypertension.
D) This option is incorrect. Reduced urine output is not typically associated with target organ damage in hypertension. However, reduced urine output may occur in acute hypertensive emergencies, such as hypertensive nephropathy.
A nurse is educating a client about complications of uncontrolled hypertension. Which complication should the nurse emphasize as a common result of hypertension-induced arterial damage?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Visual disturbances are more commonly associated with hypertensive crises, not arterial damage.
B) This option is incorrect. Peripheral neuropathy is not a common complication of hypertension.
C) This option is incorrect. Peripheral edema is often associated with heart failure, not arterial damage resulting from hypertension.
D) Correct answer. Atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, is a common complication of uncontrolled hypertension. Hypertension can cause chronic damage to the blood vessel walls, promoting the development of atherosclerotic plaques, which further narrows and stiffens the arteries.
A nurse is conducting a health screening for hypertension in a community setting. Which question should the nurse ask to assess for potential hypertension-related symptoms?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Sudden weight loss or gain is not typically associated with hypertension-related symptoms.
B) Correct answer. Fatigue and tiredness can be symptoms of hypertension, especially if it is uncontrolled or has led to target organ damage.
C) This option is incorrect. Abdominal pain or discomfort is not commonly associated with hypertension.
D) This option is incorrect. Changes in skin texture or color are not typical symptoms of hypertension.
A client with hypertension reports occasional episodes of nosebleeds. What information should the nurse provide to the client regarding this symptom?
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Occasional nosebleeds are typically unrelated to hypertension and are commonly caused by dry air, nasal irritation, or other factors.
B) This option is incorrect. While nosebleeds can occur in individuals with hypertension, they are not specific to hypertension and do not necessarily indicate worsening of the condition.
C) This option is incorrect. Nosebleeds are not an early warning sign of hypertensive crisis. Severe headache, shortness of breath, and neurological symptoms are more indicative of hypertensive crisis.
D) This option is incorrect. Nosebleeds, in isolation, are not usually indicative of severe hypertension. However, chronic uncontrolled hypertension can lead to target organ damage and potentially life-threatening complications.
A nurse is assessing a client with hypertension. Which clinical manifestation should the nurse recognize as a possible consequence of hypertensive encephalopathy?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Increased appetite and weight gain are not typical manifestations of hypertensive encephalopathy.
B) Correct answer. Hypertensive encephalopathy is characterized by visual disturbances, severe headaches, and neurological symptoms resulting from uncontrolled hypertension and cerebral edema.
C) This option is incorrect. Pain and tingling in the extremities are not directly associated with hypertensive encephalopathy.
D) This option is incorrect. Reduced urine output and fatigue are more likely related to kidney damage and heart failure, respectively, rather than hypertensive encephalopathy.
Questions
A client asks the nurse about the primary purpose of measuring blood pressure in hypertension diagnosis. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While measuring blood pressure can provide insight into the severity of hypertension-related complications, it is not the primary purpose of blood pressure measurement in hypertension diagnosis.
B) This option is incorrect. While hypertension is a significant risk factor for other cardiovascular diseases, blood pressure measurements are not primarily used to confirm the presence of those diseases.
C) This option is incorrect. Monitoring blood pressure is indeed important to assess the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications and medication in managing hypertension. However, it is not the primary purpose of blood pressure measurement in the initial diagnosis of hypertension.
D) Correct answer. Blood pressure measurement is essential in diagnosing and classifying hypertension accurately. It helps healthcare professionals determine if a person's blood pressure is within the normal range or meets the criteria for hypertension diagnosis.
A nurse is preparing a client for Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM). Which instruction should the nurse provide to the client regarding this test?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While the client should avoid excessive movement during blood pressure measurements, they do not need to remain perfectly still during the entire 24-hour monitoring period of ABPM.
B) Correct answer. The client can remove the blood pressure cuff briefly for activities like showering or bathing. However, it is essential to reapply the cuff promptly after these activities to ensure continuous monitoring.
C) This option is incorrect. Mild physical activities, such as walking, are generally allowed during ABPM, but strenuous exercise should be avoided.
D) This option is incorrect. The client is not required to record daily activities and symptoms during the 24-hour monitoring period for ABPM. Instead, the device automatically records blood pressure readings at regular intervals throughout the day and night.
A nurse is explaining the purpose of blood tests for hypertension diagnosis to a client. Which parameter should the nurse indicate as essential in assessing kidney function?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While electrolyte levels are essential in assessing overall health, they are not specifically used to evaluate kidney function in the context of hypertension diagnosis.
B) This option is incorrect. Cholesterol profile evaluation is essential for assessing cardiovascular health, but it is not the primary purpose of blood tests in hypertension diagnosis.
C) This option is incorrect. Blood glucose levels are vital for diagnosing and managing diabetes, but they are not directly related to kidney function assessment for hypertension diagnosis.
D) Correct answer. Creatinine and BUN (blood urea nitrogen) levels are essential markers used to assess kidney function in the context of hypertension diagnosis. Hypertension can lead to kidney damage, and these blood tests help identify any impairment in kidney function.
A client asks the nurse about the difference between an electrocardiogram (ECG) and Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM). How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. An ECG records the heart's electrical activity, not blood pressure. ABPM is used to continuously monitor blood pressure for 24 hours.
B) Correct answer. An ECG measures the heart's electrical activity by recording the electrical signals generated during each heartbeat. On the other hand, ABPM monitors blood pressure over a 24-hour period to assess blood pressure variations during different activities and times of day.
C) This option is incorrect. While both ECG and ABPM record physiological data over 24 hours, an ECG focuses on the heart's electrical activity, while ABPM is specifically for blood pressure monitoring.
D) This option is incorrect. An ECG is used to assess the heart's electrical activity, regardless of exercise. ABPM, as previously explained, monitors blood pressure continuously over 24 hours, including during periods of rest and activity.
A nurse is explaining the importance of an electrocardiogram (ECG) in the diagnosis of hypertension. Which statement should the nurse include in the discussion?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While hypertension is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis, an ECG primarily assesses the heart's electrical activity, not arterial blockages.
B) Correct answer. An ECG is essential in diagnosing and assessing heart abnormalities, such as left ventricular hypertrophy, which can result from the strain caused by hypertension.
C) This option is incorrect. An ECG is not directly used to diagnose kidney damage. Blood tests like creatinine and BUN are more specific for assessing kidney function in the context of hypertension.
D) This option is incorrect. An ECG does not provide information on blood levels of sodium and potassium. Blood tests are used for evaluating electrolyte levels, not ECG results.
A client is scheduled for a renal function panel to evaluate hypertension-related kidney damage. Which lab values should the nurse expect to be included in this panel?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Liver enzymes (ALT and AST) are not relevant to assessing kidney function or hypertension-related kidney damage.
B) Correct answer. A renal function panel typically includes creatinine and BUN levels, as they are essential markers used to evaluate kidney function in the context of hypertension.
C) This option is incorrect. Blood glucose and HbA1c levels are related to diabetes assessment and management, not kidney function in hypertension.
D) This option is incorrect. Prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized
ratio (INR) are coagulation tests used to evaluate blood clotting, not kidney function or hypertension-related kidney damage.
A nurse is educating a client about the significance of self-monitoring blood pressure at home. Which benefit should the nurse emphasize?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Home blood pressure monitoring may not identify the specific underlying causes of hypertension, as it primarily focuses on monitoring blood pressure levels.
B) Correct answer. Self-monitoring blood pressure at home allows individuals to track their blood pressure trends over time, observe the effects of lifestyle changes and medication, and communicate this information with their healthcare providers for effective management.
C) This option is incorrect. While home blood pressure monitoring can provide valuable data to determine target blood pressure ranges, healthcare providers play a crucial role in establishing appropriate targets and making treatment adjustments.
D) This option is incorrect. Home blood pressure monitoring is a valuable complement to regular medical check-ups, but it does not replace the need for healthcare visits. Regular medical check-ups are essential for comprehensive hypertension management and monitoring other health parameters.
QUESTIONS
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While hypertension can lead to kidney damage, it does not directly cause liver dysfunction.
B) This option is incorrect. While hypertension can impact blood vessels in the eyes, leading to hypertensive retinopathy, it does not increase the risk of cataracts.
C) This option is incorrect. Peripheral neuropathy is not a common complication of hypertension. Heart failure is a potential complication, but it is not directly related to peripheral neuropathy.
D) Correct answer. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to various complications, including stroke (brain damage due to reduced blood flow), heart attack (damage to the heart muscle), and kidney damage (nephrosclerosis). These are among the most serious and common complications of hypertension.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Proteinuria (presence of protein in urine) is not directly related to hypertensive retinopathy.
B) Correct answer. Blurred vision is a common symptom of hypertensive retinopathy, a condition characterized by damage to the blood vessels in the retina due to hypertension.
C) This option is incorrect. Peripheral edema is a sign of fluid retention and may be related to heart failure or kidney problems but is not specifically associated with hypertensive retinopathy.
D) This option is incorrect. Tingling in the extremities is not a typical manifestation of hypertensive retinopathy. It may be related to other conditions, such as peripheral neuropathy.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Hypertensive encephalopathy results from severe and uncontrolled hypertension, causing brain swelling. It is not directly associated with hypertensive heart disease.
B) This option is incorrect. Atherosclerosis is a common complication of hypertension but is not specifically related to hypertensive heart disease.
C) Correct answer. Hypertensive heart disease refers to changes in the heart muscle structure due to chronic high blood pressure. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a common consequence of uncontrolled hypertension, where the left ventricle of the heart becomes thickened and enlarged.
D) This option is incorrect. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is caused by atherosclerosis in the peripheral arteries and is not directly related to hypertensive heart disease.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Hypertension is not directly associated with pancreas damage.
B) This option is incorrect. Hypertension does not cause liver cirrhosis. Liver damage can occur in some cases of severe hypertension, but cirrhosis is typically caused by chronic liver disease, alcohol abuse, or viral hepatitis.
C) Correct answer. Hypertension is a significant risk factor for kidney dysfunction, including nephrosclerosis (hardening of the kidney arteries) and chronic kidney disease. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to long-term damage to the kidneys.
D) This option is incorrect. Bone fractures are not directly related to hypertension or its complications.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Hypertensive crises are characterized by a sudden and severe increase in blood pressure, not sudden drops.
B) This option is incorrect. During a hypertensive crisis, blood pressure levels can rise to extremely high levels, not remain stable.
C) Correct answer. Hypertensive crises involve severely high blood pressure levels, which can lead to acute organ damage and require immediate medical intervention.
D) This option is incorrect. Hypertensive crises are medical emergencies and require prompt medical intervention to lower blood pressure and prevent potential complications.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Peripheral neuropathy is not directly associated with hypertensive nephropathy.
B) This option is incorrect. Hypertensive nephropathy primarily affects the kidneys and does not directly impair liver function.
C) This option is incorrect. Heart valve abnormalities are not typical complications of hypertensive nephropathy.
D) Correct answer. Hypertensive nephropathy refers to kidney damage caused by chronic high blood pressure. It can lead to chronic kidney disease (CKD), a progressive loss of kidney function over time.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Reduced lung function is not directly related to hypertensive retinopathy.
B) Correct answer. Hypertensive retinopathy refers to damage to the blood vessels in the retina caused by uncontrolled high blood pressure. It can lead to vision impairment and, in severe cases, blindness.
C) This option is incorrect. Gastrointestinal bleeding is not a typical complication of hypertensive retinopathy.
D) This option is incorrect. Hypertensive retinopathy does not cause thyroid dysfunction.
QUESTIONS
A client with hypertension asks the nurse about ways to reduce stress to improve blood pressure. Which relaxation technique should the nurse recommend?
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Deep-breathing exercises are a relaxation technique that can help reduce stress and lower blood pressure. Deep breathing triggers the relaxation response, leading to decreased heart rate and blood pressure.
B) This option is incorrect. While regular exercise is beneficial for managing hypertension, high-intensity workouts may not be the best choice for stress reduction. Low to moderate-intensity exercises are more effective in promoting relaxation.
C) This option is incorrect. Consuming alcohol can have negative effects on blood pressure and overall health. It is not a recommended relaxation technique.
D) This option is incorrect. Social interactions and maintaining a support system are essential for mental well-being. Limiting social interactions may lead to increased stress and feelings of isolation.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Taking antihypertensive medications on an empty stomach may lead to gastrointestinal irritation and is not the recommended approach.
B) This option is incorrect. While taking medication with a meal can help reduce potential stomach upset, it is not the primary consideration when timing antihypertensive medications.
C) Correct answer. It is essential to take antihypertensive medications at the same time every day to maintain consistent blood levels and ensure effectiveness. Consistency in medication administration is critical for controlling blood pressure.
D) This option is incorrect. Some antihypertensive medications, such as diuretics, may be best taken in the morning to avoid nighttime urination. However, the timing of medications should be discussed with the prescribing healthcare provider based on the specific medication regimen.
A nurse is conducting a health education session for a group of clients with hypertension. Which dietary modification should the nurse recommend to reduce sodium intake?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Processed and canned foods often contain high levels of added sodium. Reducing sodium intake involves choosing fresh, whole foods and minimizing processed food consumption.
B) This option is incorrect. Including a variety of salty snacks would lead to an increase in sodium intake, which is not recommended for managing hypertension.
C) Correct answer. Using herbs and spices as alternatives to salt is an effective way to reduce sodium intake while adding flavor to meals. This dietary modification is beneficial for individuals with hypertension.
D) This option is incorrect. Salty cheeses and processed meats are high in sodium and should be limited in the diet of individuals with hypertension.
A nurse is caring for a client with hypertension who is prescribed a thiazide diuretic. Which instruction should the nurse include when educating the client about this medication?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Thiazide diuretics are best taken in the morning to prevent nighttime urination and disturbances in sleep.
B) Correct answer. Thiazide diuretics can cause potassium loss in some individuals, so it is essential to monitor potassium levels and, if necessary, increase potassium intake through dietary sources or supplements.
C) This option is incorrect. Thiazide diuretics are not known to significantly affect blood glucose levels.
D) This option is incorrect. Thiazide diuretics may cause increased urination initially, but this effect usually diminishes over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
A nurse is caring for a client with hypertension and instructs them on self-monitoring blood pressure at home. What should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Checking blood pressure once a week is insufficient for effective monitoring, as it may not provide a comprehensive view of blood pressure trends.
B) This option is incorrect. Using the arm with the highest blood pressure reading consistently is not recommended. Blood pressure should be measured in the arm with the higher reading only if there
is a significant difference between the arms.
C) This option is incorrect. To obtain accurate blood pressure readings, the client should rest for at least 5 minutes in a comfortable seated position with their feet flat on the floor and arms supported at heart level. Crossing the legs may affect blood flow and accuracy of the reading.
D) Correct answer. Recording blood pressure readings and any symptoms in a journal is essential for effective self-monitoring. It provides valuable information for the healthcare provider to assess blood pressure control and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
A client with hypertension asks the nurse about the role of salt substitutes in managing blood pressure. What should the nurse advise the client?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While salt substitutes are often low in sodium, they may contain other minerals like potassium. Using them freely without considering their composition can have adverse effects.
B) Correct answer. Salt substitutes often contain potassium chloride as a replacement for sodium chloride. Clients taking certain medications, especially potassium-sparing diuretics or potassium supplements, should use salt substitutes with caution to avoid excessive potassium intake.
C) This option is incorrect. Some salt substitutes can effectively reduce sodium intake and contribute to blood pressure management when used appropriately.
D) This option is incorrect. Replacing regular table salt with salt substitutes may lead to increased potassium intake, which can be problematic for individuals taking medications that affect potassium levels. The client should use salt substitutes with caution and consult their healthcare provider if they have any concerns.
Questions
A client with hypertension asks the nurse about the potential complications of uncontrolled high blood pressure. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While hypertension can lead to kidney damage, it does not directly cause liver dysfunction.
B) This option is incorrect. While hypertension can impact blood vessels in the eyes, leading to hypertensive retinopathy, it does not increase the risk of cataracts.
C) This option is incorrect. Peripheral neuropathy is not a common complication of hypertension. Heart failure is a potential complication, but it is not directly related to peripheral neuropathy.
D) Correct answer. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to various complications, including stroke (brain damage due to reduced blood flow), heart attack (damage to the heart muscle), and kidney damage (nephrosclerosis). These are among the most serious and common complications of hypertension.
A client asks the nurse about the role of genetics in developing hypertension. What should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Genetics can significantly influence the risk of developing hypertension, and lifestyle factors may exacerbate or mitigate this risk.
B) This option is incorrect. While genetics play a role in hypertension, lifestyle changes can still have a significant impact on prevention and management.
C) Correct answer. Both genetics and lifestyle factors contribute to the development of hypertension. While genetics can predispose individuals to hypertension, lifestyle choices like diet and exercise play a crucial role in its occurrence and progression.
D) This option is incorrect. Hypertension is influenced by both genetic and lifestyle factors, and poor dietary habits can exacerbate the risk.
Congenital Heart Disease
A nurse is teaching a client about congenital heart diseases. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further education?
Explanation
A. This statement is incorrect because congenital heart diseases are not acquired during childhood; they are structural heart defects that are present at birth due to genetic or environmental factors during fetal development.
B. This statement is accurate and describes the nature of congenital heart diseases as being present from birth and affecting the heart's structure or function.
C. This statement is correct as certain congenital heart diseases can indeed be diagnosed prenatally using fetal echocardiography, allowing for early intervention and planning.
D. This statement is true, as treatment options for congenital heart diseases often include medications, surgical interventions, or other medical therapies, depending on the specific condition and its severity.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Middle-aged adults are not considered a high-risk population for congenital heart diseases. These conditions are primarily present from birth.
B) This option is incorrect. Elderly individuals are not at high risk for congenital heart diseases since these conditions are typically diagnosed at birth or during childhood.
C) This option is incorrect. While prenatal diagnosis of certain congenital heart diseases is possible through fetal echocardiography, pregnant women themselves are not at a higher risk for developing these conditions.
D) Correct answer. Neonates and infants are the highest-risk population for congenital heart diseases because these conditions are typically present from birth and may become apparent shortly after delivery or during infancy.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While some individuals with congenital heart diseases may remain asymptomatic, others can experience symptoms depending on the type and severity of the condition.
B) This option is incorrect. Congenital heart diseases are present from birth, and symptoms may manifest shortly after birth or during infancy, childhood, or adolescence.
C) Correct answer. Common symptoms of congenital heart diseases can include cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin or lips due to poor oxygenation), fatigue, and shortness of breath. These symptoms may arise due to poor blood circulation and oxygenation.
D) This option is incorrect. Congenital heart diseases do not typically present with mild cold-like symptoms and fever. These are more indicative of common respiratory infections, unrelated to heart conditions.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While early detection and treatment can improve outcomes, complete resolution of congenital heart diseases is not always possible.
B) This option is incorrect. Timely intervention and treatment are essential for managing congenital heart diseases in affected individuals, but they do not prevent the occurrence of these conditions in future pregnancies.
C) Correct answer. Early management of congenital heart diseases is crucial in minimizing complications, improving the quality of life for affected individuals, and enhancing long-term outcomes.
D) This option is incorrect. While early treatment can significantly improve life expectancy and overall health outcomes, it may not guarantee a "normal" life expectancy for all individuals with congenital heart diseases, as outcomes depend on the specific condition and severity.
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Genetic factors and chromosomal abnormalities are among the primary causes of congenital heart diseases. These conditions often arise due to errors in heart development during fetal growth.
B) This option is incorrect. While certain environmental factors may increase the risk of congenital heart diseases, they are not the leading cause of these conditions.
C) This option is incorrect. Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as smoking and alcohol consumption, may contribute to heart diseases in adults, but they are not the primary cause of congenital heart diseases.
D) This option is incorrect. Vaccination is important for preventing certain infections, but it is not directly related to the cause or prevention of congenital heart diseases.
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Regular prenatal care, including fetal echocardiography, allows for early detection of certain congenital heart diseases in the fetus. This enables appropriate management and planning for the baby's care after birth.
B) This option is incorrect. While prenatal care is essential for overall maternal and fetal health, it is not related to heart transplant considerations.
C) This option is incorrect. Congenital heart diseases can be detected during pregnancy through fetal echocardiography and other diagnostic tests.
D) This option is incorrect. Prenatal care involves monitoring the health and development of the fetus and aims to address potential issues to ensure a healthy pregnancy and baby, including the early detection and management of congenital heart diseases.
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Advanced maternal age and maternal obesity are among the known risk factors for congenital heart diseases. These factors may increase the likelihood of certain heart abnormalities during fetal development.
B) This option is incorrect. Exposure to common childhood illnesses during pregnancy is not a recognized risk factor for congenital heart diseases. The causes are primarily genetic and developmental in nature.
C) This option is incorrect. While genetic factors play a significant role in the development of congenital heart diseases, there are other recognized risk factors, such as maternal age and obesity.
D) This option is incorrect. There are known risk factors for congenital heart diseases, as mentioned in option A. While some cases may occur sporadically without identifiable risk factors, many cases have associated factors that can be addressed through prenatal care and management.
Questions
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Family history of congenital heart diseases is a significant risk factor. If a close family member has had a congenital heart defect, the risk of recurrence in subsequent pregnancies may be higher.
B) Correct answer. Exposure to certain infections during pregnancy, such as rubella (German measles), can increase the risk of congenital heart diseases in the baby. Rubella is known to be teratogenic, meaning it can cause birth defects.
C) This option is incorrect. While a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy is important for overall maternal and fetal health, it is not the primary risk factor for congenital heart diseases.
D) This option is incorrect. While genetic factors play a significant role in the etiology of congenital heart diseases, there are other identifiable risk factors, as mentioned in option B.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Maintaining a sedentary lifestyle during pregnancy is not recommended, as moderate exercise can be beneficial for both maternal and fetal health.
B) This option is incorrect. Prenatal check-ups and ultrasounds are essential for monitoring the health and development of the fetus and identifying any potential issues, including congenital heart diseases.
C) Correct answer. Genetic counseling can help assess the risk of congenital heart diseases based on the family history and provide guidance and recommendations for future pregnancies. This counseling can assist in making informed decisions about prenatal care and potential interventions.
D) This option is incorrect. While a family history of congenital heart diseases may increase the risk, seeking appropriate medical guidance and prenatal care can help manage and address these risks.
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Gestational diabetes is associated with an increased risk of congenital heart diseases in the baby. Poorly controlled diabetes during pregnancy can affect fetal development and increase the likelihood of birth defects, including heart defects.
B) This option is incorrect. While preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication, it is not specifically linked to an increased risk of congenital heart diseases.
C) This option is incorrect. Hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid gland during pregnancy, may pose risks to both the mother and baby, but it is not directly associated with congenital heart diseases.
D) This option is incorrect. Iron deficiency anemia can affect maternal and fetal health, but it is not considered a risk factor for congenital heart diseases.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Not all medications are safe to use during pregnancy, and some may pose risks to the developing baby, including potential congenital heart defects.
B) Correct answer. Some medications, like certain antihypertensives and medications with known teratogenic effects, can increase the risk of congenital heart diseases if used during pregnancy. It is essential for pregnant individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage any medical conditions and choose safe medications during pregnancy.
C) This option is incorrect. Some vaccinations are recommended during pregnancy to protect both the mother and the baby from certain infections. Properly administered vaccinations during pregnancy are generally safe and do not significantly impact heart development.
D) This option is incorrect. Medication use during pregnancy can have various effects on the developing baby, and certain medications may increase the risk of congenital heart diseases.
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Ethnic background and cultural practices can influence the risk of congenital heart diseases. Some genetic and environmental factors that contribute to heart defects may vary among different ethnic groups.
B) This option is incorrect. While prenatal vitamin and mineral supplementation is important for maternal and fetal health, it is not a specific risk factor for congenital heart diseases.
C) This option is incorrect. Fetal movements and kicking patterns are important indicators of fetal well-being, but they are not directly related to the risk of congenital heart diseases.
D) This option is incorrect. Employment and work-related stress levels are not known risk factors for congenital heart diseases.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Maternal age is a non-modifiable risk factor. However, it is important to educate parents about other factors they can control during pregnancy.
B) This option is incorrect. Family history of heart diseases is a non-modifiable risk factor since it relates to the genetic predisposition for certain conditions.
C) Correct answer. Exposure to environmental toxins can be a modifiable risk factor if expectant parents take appropriate measures to avoid exposure to harmful substances during pregnancy. This may include avoiding certain chemicals, pollutants, and teratogenic agents.
D) This option is incorrect. Genetic inheritance is a non-modifiable risk factor for congenital heart diseases, as it relates to the transmission of genes from parents to their children.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can have significant adverse effects on fetal development, including an increased risk of congenital heart diseases. Even moderate alcohol consumption is not safe during pregnancy.
B) Correct answer. Alcohol consumption during pregnancy is a known risk factor for congenital heart diseases and other birth defects. It is best to avoid alcohol completely during pregnancy to protect the developing baby.
C) This option is incorrect. The impact of alcohol on the baby's heart development is generally negative regardless of the type of alcoholic beverage consumed. All types of alcohol should be avoided during pregnancy.
D) This option is incorrect. Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can have far-reaching effects on fetal development, affecting both the heart and brain, among other organ systems.
QUESTIONS
A nurse is assessing a newborn with suspected congenital heart disease. Which clinical finding should the nurse prioritize as an early symptom of heart defects?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Difficulty swallowing and poor feeding may indicate other issues, such as gastrointestinal problems, but they are not early symptoms specific to congenital heart diseases.
B) Correct answer. Cyanosis (bluish skin or lips) during crying or feeding is an early clinical finding that may indicate inadequate oxygenation due to heart defects. This symptom is especially prominent in cyanotic congenital heart diseases.
C) This option is incorrect. Persistent cough and recurrent respiratory infections may be related to respiratory issues but are not specific early symptoms of congenital heart diseases.
D) This option is incorrect. Excessive weight gain and a rapid growth rate are not typical early symptoms of congenital heart diseases.
A client with a newborn diagnosed with congenital heart disease asks the nurse about the baby's feeding patterns. What should the nurse explain about feeding difficulties in infants with heart defects?
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Infants with congenital heart diseases may have feeding difficulties due to fatigue and inadequate oxygenation, which can affect their appetite and feeding patterns.
B) This option is incorrect. Feeding difficulties in infants with heart defects are common due to their increased energy expenditure and compromised cardiovascular function. These difficulties may require appropriate interventions and ongoing support.
C) Correct answer. Many infants with congenital heart diseases experience fatigue and increased energy expenditure due to their heart's extra workload. This can lead to feeding difficulties, inadequate weight gain, and slower growth.
D) This option is incorrect. Congenital heart diseases can significantly impact feeding patterns in infants, and special attention is required to support their nutritional needs.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Frequent sweating during feedings is not a normal response to the increased workload of the baby's heart. It can indicate an underlying issue related to heart function.
B) This option is incorrect. While gastrointestinal discomfort may cause sweating during feedings, it is not the most likely explanation, especially in the context of congenital heart diseases.
C) This option is incorrect. Inability to regulate body temperature is not a common reason for sweating during feedings in infants with congenital heart diseases.
D) Correct answer. Excessive sweating during feedings can be a sign of increased cardiac effort and inadequate oxygen supply in some congenital heart diseases. This symptom may be present in babies with cyanotic heart defects, where oxygen-rich blood is not adequately circulated to the body, leading to compensatory mechanisms like sweating to maintain oxygen balance.
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Decreased appetite and difficulty sleeping are common signs of heart failure in children with congenital heart diseases. Heart failure can lead to poor circulation, decreased cardiac output, and inadequate oxygenation, resulting in reduced appetite and difficulty sleeping due to increased effort in breathing.
B) This option is incorrect. Rapid growth and development milestones achieved ahead of schedule are not indicative of heart failure in children with congenital heart diseases.
C) This option is incorrect. Decreased heart rate and low blood pressure may be signs of cardiovascular compromise, but they are not specific to heart failure.
D) This option is incorrect. Frequent episodes of irritability and excessive crying may be present in infants with heart defects, but they are not specific to heart failure in toddlers.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. Clubbing of the fingers and toes is not a normal developmental finding in infants and young children. It can indicate an underlying health issue.
B) This option is incorrect. While chronic respiratory issues may cause clubbing, it is specifically related to congenital heart diseases and chronic low oxygen levels.
C) Correct answer. Clubbing of the fingers and toes can indicate chronic low oxygen levels and impaired cardiac function in children with congenital heart diseases. It is a result of changes in the blood vessels and tissues due to inadequate oxygenation.
D) This option is incorrect. Clubbing of the fingers and toes is not commonly observed during adolescence, and it is not temporary. It can persist if the underlying heart condition is not adequately managed.
Explanation
A) This option is incorrect. While heart murmurs can be common and innocent in children, a harsh, loud, and continuous heart murmur requires further evaluation.
B) This option is incorrect. A harsh, loud, and continuous heart murmur is not a normal finding and should be assessed for potential congenital heart diseases.
C) Correct answer. The presence of a harsh, loud, and continuous heart murmur in a child with recurrent respiratory infections is
concerning for potential congenital heart diseases. It may indicate an abnormal blood flow within the heart, which warrants further evaluation and diagnosis.
D) This option is incorrect. Heart murmurs that are harsh, loud, and continuous are not considered benign and require further evaluation and monitoring.
A nurse is assessing a school-age child with a congenital heart defect. Which symptom should the nurse recognize as a potential indicator of worsening heart failure?
Explanation
A) Correct answer. Weight gain and edema in the lower extremities can be signs of worsening heart failure in children with congenital heart defects. Fluid retention occurs due to the heart's inability to effectively pump blood, leading to fluid accumulation in the body.
B) This option is incorrect. While decreased heart rate and blood pressure within the normal range may be indicative of stable heart function, they are not specific indicators of worsening heart failure.
C) This option is incorrect. Improved appetite and increased physical activity level are positive indicators but do not specifically reflect the child's heart failure status.
D) This option is incorrect. Resolution of cyanosis and pink coloration of the lips and nail beds are positive signs of improved oxygenation and may indicate effective management of the heart defect but not the potential worsening of heart failure.
Explanation
A) The answer is A. The pallor and coolness of the skin may indicate poor cardiac output and impaired circulation commonly seen in congenital heart diseases. These signs are suggestive of reduced oxygen delivery to peripheral tissues.
B) Incorrect. The respiratory rate being within the normal range does not specifically point to a congenital heart disease. Other signs and symptoms should be assessed to confirm the diagnosis.
C) Incorrect. The closure and firmness of the fontanelle are related to the status of the infant's skull bones and do not directly indicate congenital heart disease.
D) Incorrect. Weight gain following the growth chart percentile for age is not directly associated with congenital heart diseases. There are more specific clinical indicators to consider in the assessment of this condition.
Explanation
A) The answer is A. Digoxin is commonly prescribed for clients with congenital heart diseases to improve cardiac contractility. It is essential to monitor the heart rate before administration since digoxin can cause bradycardia as a side effect.
B) Incorrect. The statement is not accurate. There is no need to avoid green, leafy vegetables while taking digoxin. However, the client should be informed about potential drug interactions and follow a balanced diet.
C) Incorrect. Clients taking digoxin should be cautious about consuming potassium-rich foods, as hypokalemia (low potassium levels) can potentiate the effects of digoxin and lead to toxicity.
D) Incorrect. Mild nausea can be a common side effect of digoxin, and the client should not discontinue the medication without consulting their healthcare provider. Instead, they should report any adverse effects for proper evaluation.
Explanation
A) The answer is A. Mild cyanosis during crying or feeding can indicate inadequate oxygenation and increased workload on the heart. This symptom requires immediate intervention to ensure proper oxygen supply to vital organs.
B) Incorrect. Occasional heart palpitations may not be a severe concern and may not require immediate intervention. However, the healthcare provider should still be notified for further evaluation.
C) Incorrect. Fatigue after physical activity is common in clients with congenital heart diseases due to compromised cardiac function. Although it needs attention, it does not require immediate intervention.
D) Incorrect. A heart murmur audible throughout systole and diastole can indicate structural heart abnormalities. While it requires medical follow-up, it may not need immediate intervention unless accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Explanation
A) The answer is A. Premedicating with an antipyretic before the dental procedure can help prevent bacterial endocarditis, a severe infection in clients with certain congenital heart diseases.
B) Incorrect. Antibiotic prophylaxis is recommended for some clients with congenital heart diseases to prevent bacterial endocarditis. The client should consult their healthcare provider for appropriate prophylactic measures.
C) Incorrect. The timing of the surgery in the afternoon does not significantly impact recovery. The appropriate timing should be determined by the healthcare provider and the client's medical condition.
D) Incorrect. Aspirin is an anticoagulant, and the client should consult their healthcare provider about the management of aspirin therapy before any surgical procedure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Prostaglandin E1 does not directly increase hemoglobin levels or oxygenation in the blood.
B) Incorrect. Prostaglandin E1 helps maintain the patency of the ductus arteriosus to ensure adequate blood flow to systemic circulation, especially in certain congenital heart diseases. It does not reduce pulmonary blood flow and pressure.
C) The answer is C. Prostaglandin E1 is used to keep the ductus arteriosus open, allowing blood to flow from the pulmonary artery to the aorta. In certain congenital heart diseases, such as critical congenital heart defects, this is necessary to ensure adequate blood circulation.
D) Incorrect. Prostaglandin E1 does not promote the growth of cardiac muscle tissue. Its primary therapeutic effect is related to the patency of the ductus arteriosus.
Explanation
A) The answer is A. Monitoring urine output closely is essential postoperatively to assess kidney perfusion and fluid balance, as infants are at risk of fluid shifts after cardiac surgery.
B) Incorrect. While administering prescribed analgesics is important for postoperative pain management, it is not the priority intervention among the options provided.
C) Incorrect. Encouraging deep breathing and coughing exercises is important to prevent respiratory complications, but it is not the priority intervention immediately after cardiac surgery.
D) Incorrect. Elevating the head of the bed can help with respiratory effort, but it is not the priority intervention. Monitoring urine output and fluid balance is more critical in the early postoperative period.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Encouraging high-intensity aerobic exercises daily is not appropriate for a client with a congenital heart disease, as it can put excessive strain on the heart and may not be safe.
B) The answer is B. Limiting physical activities to mild exercises and avoiding competitive sports is recommended for clients with congenital heart diseases to prevent overexertion and potential complications.
C) Incorrect. Complete restriction of physical activity for six months is not necessary for most clients with congenital heart diseases. It is essential to promote safe and appropriate physical activities.
D) Incorrect. Activities with prolonged standing may increase venous return and potentially worsen certain congenital heart conditions. The focus should be on low to moderate intensity exercises.
QUESTIONS
Explanation
A) The answer is A. Weight gain of 1 pound in a week can indicate fluid retention, which may be a sign of digoxin toxicity. The nurse should instruct the client to report this symptom immediately to prevent further complications.
B) Incorrect. A heart rate below 100 beats per minute is within the normal range for most clients. A lower heart rate is often expected in clients taking digoxin, and it does not require immediate reporting unless accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
C) Incorrect. Occasional episodes of diarrhea are common side effects of digoxin. The client should report persistent or severe diarrhea, but occasional episodes may not be a cause for immediate concern.
D) Incorrect. Mild swelling of the ankles after activity is not directly related to digoxin use. The nurse should monitor the client's ankles for any worsening swelling, but it does not require immediate reporting unless accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
The answer is A
Explanation
C) Incorrect. Dairy products rich in calcium are not contraindicated with enalapril use. Calcium and ACE inhibitors do not have direct interactions.
D) Incorrect. Foods high in vitamin B12 are not contraindicated with enalapril use. There is no specific dietary restriction regarding vitamin B12 intake for clients taking this medication.
Explanation
A) The answer is A. Prophylactic antibiotics are often given before surgical procedures to prevent infection, especially in clients with congenital heart diseases who may be at a higher risk of endocarditis.
B) Incorrect. While it's essential for the client to take precautions after surgery to reduce the risk of infection, avoiding contact with others for two weeks is not necessary or practical. Instead, following proper wound care and taking prescribed medications as instructed are more relevant measures.
C) Incorrect. Discharging the client early from the hospital does not necessarily reduce the risk of infection. Postoperative care and wound management are crucial to prevent infection, regardless of the length of the hospital stay.
D) Incorrect. All surgical procedures carry some risk of infection. While healthcare providers take measures to minimize this risk, it is not accurate to claim there is no risk at all.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Left-sided heart failure typically presents with symptoms such as pulmonary congestion, shortness of breath, and crackles in the lungs, rather than cyanosis and clubbing.
B) Incorrect. Right-sided heart failure can cause peripheral edema and jugular vein distention, but it does not usually lead to cyanosis and clubbing.
C) The answer is C. Cyanosis and clubbing of the fingers are signs of chronic hypoxia, which can occur in pulmonary hypertension. This condition increases pulmonary vascular resistance and impairs oxygenation, leading to these characteristic symptoms.
D) Incorrect. Peripheral vascular disease primarily affects the arteries and veins in the extremities and is not directly related to cyanosis and clubbing of the fingers.
Explanation
A) The answer is A. Before administering furosemide, it is essential to assess the child's respiratory rate because this medication is a loop diuretic that can lead to fluid and electrolyte imbalances, including hypokalemia. Respiratory rate assessment helps monitor for signs of respiratory distress, especially in clients with heart failure.
B) Incorrect. While monitoring the child's blood pressure is essential, it is not the priority action before administering furosemide. Blood pressure may be affected by the diuretic action of the medication, but respiratory status is more critical to assess initially.
C) Incorrect. Although monitoring electrolyte levels is important when administering furosemide, it is not the priority action. Assessing the child's respiratory rate takes precedence to identify any respiratory distress.
D) Incorrect. Determining the child's weight is relevant in assessing the effectiveness of furosemide therapy. However, it is not the priority action before administering the medication. Respiratory assessment is more critical for immediate intervention.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Not all congenital heart diseases resolve on their own. While some may improve over time, it is essential for the client to follow their healthcare provider's recommendations for monitoring and treatment.
B) Incorrect. While breastfeeding has many benefits for infants, it may not directly impact the congenital heart disease. The nurse should focus on educating the client about managing the specific heart condition.
C) Incorrect. Avoiding vaccinations and routine check-ups is not recommended. Regular check-ups and vaccinations are crucial for overall health, and the healthcare provider will guide the client regarding any specific precautions or modifications needed due to the heart condition.
D) The answer is D. Clients with congenital heart diseases are at increased risk of infections, so it is essential to educate the client about infection prevention measures, such as limiting contact with other children during times of increased risk.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Not all medications can be crushed, and mixing them with the infant's formula may affect their efficacy. Crushing medications should only be done when it is safe and appropriate, as determined by the healthcare provider.
B) Incorrect. Administering medications simultaneously may not be feasible or safe, as some medications require specific intervals between doses. The nurse should follow the prescribed administration schedule to ensure appropriate drug levels in the infant's system.
C) The answer is C. Using a medication organizer can help the nurse and the infant's parents keep track of the complex medication schedule. This helps prevent missed doses and ensures proper administration of each medication.
D) Incorrect. The nurse, along with the healthcare provider, should determine the medication dosing times based on the infant's condition and the prescribed schedule. Leaving the decision solely to the parents may lead to dosing errors or missed doses.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Taking an over-the-counter pain reliever may not address the underlying cause of the symptoms and is not the appropriate action in this situation.
B) Incorrect. Deep breathing exercises may not alleviate the symptoms of shortness of breath and chest pain. The client should seek medical attention for proper evaluation and management.
C) Incorrect. While resting quietly is generally advisable, it may not be sufficient to address the client's symptoms. Seeking medical attention is essential to identify and manage the cause of the symptoms.
D) The answer is D. Shortness of breath and chest pain can be signs of a cardiac event or worsening of the congenital heart disease. The client should seek medical attention immediately to receive appropriate evaluation and treatment.
Explanation
A) The answer is A. Before administering digoxin, the nurse should check the infant's apical heart rate for a full minute. Digoxin is a medication used to improve cardiac contractility, and knowing the heart rate helps ensure the medication is given safely and at the correct dose.
B) Incorrect. While measuring blood pressure is essential in some cases, it is not the priority action before administering digoxin.
C) Incorrect. Assessing capillary refill time is an important part of the overall assessment, but it is not the priority action before giving digoxin.
D) Incorrect. While observing for respiratory distress is crucial, it is not the priority action in this specific scenario of preparing to administer digoxin. Checking the heart rate takes precedence.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While solid foods are introduced around six months of age, the nurse should consider the specific condition of the infant's congenital heart disease before giving feeding recommendations.
B) The answer is B. Infants with congenital heart diseases may tire easily during feeding due to the increased effort required for sucking and swallowing. Feeding small, frequent meals can help prevent fatigue and ensure adequate nutrition.
C) Incorrect. Breastfeeding is generally encouraged, even for infants with congenital heart diseases. However, the nurse should consider any specific feeding challenges the infant may have due to their heart condition and provide appropriate support and guidance.
D) Incorrect. Limiting fluid intake may not be necessary unless specifically advised by the healthcare provider. Infants need sufficient hydration, and fluid intake should be managed based on the infant's overall health and condition.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While diagnostic testing may provide information that informs the choice of a surgical procedure, this is not the primary purpose of the tests.
B) Incorrect. While diagnostic testing may identify complications related to the heart disease, it is not the primary purpose of the tests.
C) The answer is C. Diagnostic testing in congenital heart diseases aims to evaluate heart function, blood flow patterns, and any structural abnormalities. These results guide the healthcare team in developing a comprehensive treatment plan for the client.
D) Incorrect. Most congenital heart diseases cannot be "cured" with diagnostic testing alone. However, the information obtained from the tests is crucial in determining the most appropriate management and treatment options.
Questions
A nurse is caring for an infant with a congenital heart disease who requires prostaglandin E1 therapy. What is the primary purpose of administering prostaglandin E1?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Prostaglandin E1 does not primarily aim to improve cardiac contractility. It is used for a different purpose in the management of congenital heart diseases.
B) Incorrect. Prostaglandin E1 is not used to reduce systemic blood pressure. In fact, it may have the opposite effect, causing vasodilation and potentially lowering blood pressure.
C) The answer is C. Prostaglandin E1 is used to promote and maintain the patency of the ductus arteriosus, especially in critical congenital heart defects. This ensures adequate blood flow to systemic circulation until corrective surgery can be performed.
D) Incorrect. Prostaglandin E1 does not decrease heart rate. It primarily affects the patency of the ductus arteriosus.
Blood transfusion
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Confirming the client's identity and blood type with the client's family member is not a reliable method for ensuring patient safety during a blood transfusion. The nurse should directly verify the client's identity and blood type with two unique identifiers, such as asking the client to state their full name and date of birth and comparing it to their identification band.
B) Correct: Obtaining informed consent from the client is a crucial step before initiating a blood transfusion. The nurse must ensure the client understands the risks and benefits of the transfusion and has willingly provided consent. A signed consent form is the formal documentation of this process.
C) Incorrect: Warming blood in a microwave oven is not an appropriate method for preventing hypothermia and can lead to hemolysis of the blood components. Blood should be warmed using an approved blood warmer designed for this purpose.
D) Incorrect: Administering a rapid bolus of normal saline is unnecessary and could lead to fluid overload in the client. The nurse should administer normal saline or another appropriate IV fluid at the prescribed rate if the client requires hydration before or after the transfusion, but not as a priming method.
A client who received a blood transfusion 2 hours ago is now experiencing symptoms of a transfusion reaction, including fever, chills, and shortness of breath. What is the nurse's priority action?
Explanation
A: Notifying the healthcare provider is an important step, but it is not the immediate priority. The nurse's first action should be to address the adverse reaction to prevent further harm to the client.
B: While administering antipyretics may help lower the client's fever, it does not address the underlying cause of the symptoms, which is the transfusion reaction. The priority is to stop the reaction from progressing.
C: Preparing to administer a diuretic would be appropriate if fluid overload was the primary concern. However, in the case of a transfusion reaction, the priority is to stop the transfusion to halt the reaction.
D: Discontinuing the blood transfusion immediately is the priority action because it stops the exposure to the blood product that is causing the reaction. Once the transfusion is stopped, further interventions can be assessed and implemented.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Slowing down the transfusion rate is not the appropriate action in this scenario. The client is experiencing signs of an allergic reaction, and the nurse must act promptly to address the situation.
B) Incorrect: Elevating the client's feet and lowering the head (Trendelenburg position) is not indicated for an allergic reaction. It may be used for clients in shock, but the priority is to manage the allergic reaction.
C) Correct: The nurse should immediately discontinue the transfusion and initiate the infusion of normal saline to maintain the client's intravascular volume. Discontinuing the blood transfusion helps prevent further exposure to the allergen (if an allergic reaction is confirmed) and addresses fluid volume needs.
D) Incorrect: While administering an antihistamine may be part of the treatment plan for an allergic reaction, it is not the immediate action. The nurse should first discontinue the transfusion and infuse normal saline as stated in option C.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Transfusing whole blood increases the risk of adverse reactions and is not commonly used in modern transfusion practices. Whole blood is usually separated into its individual components for transfusion.
B) Incorrect: Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) contains various clotting factors and is used primarily to treat bleeding disorders and coagulopathies, not to prevent transfusion reactions.
C) Correct: Packed red blood cells (PRBCs) contain primarily red blood cells without significant amounts of plasma, white blood cells, or platelets. For clients with a history of transfusion reactions, PRBCs are the most suitable blood component to minimize the risk of future reactions.
D) Incorrect: Platelets are used to treat thrombocytopenia and platelet dysfunction but do not provide the main benefit of minimizing the risk of future transfusion reactions as PRBCs do.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Placing the client in a supine position with legs elevated is not appropriate in this situation. The client is showing signs of a potential severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) or a transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), and the nurse should prioritize interventions accordingly.
B) Correct: Administering oxygen via a non-rebreather mask is the appropriate immediate action for a client experiencing respiratory distress and muffled heart sounds. This intervention helps improve oxygenation and respiratory function.
C) Incorrect: Checking the client's temperature and administering antipyretics is not indicated as the client's symptoms are not consistent with a fever. The focus should be on respiratory and cardiovascular support.
D) Incorrect: Stopping the blood transfusion is essential, but it is not the immediate action in this situation. The nurse's priority is to address the client's respiratory distress and ensure adequate oxygenation by administering oxygen, as stated in option B. Once the client is stable, the nurse should then notify the healthcare provider about the situation.
Questions
A nurse is caring for a client who has undergone major surgery and has a hemoglobin level of 8 g/dL. The client is experiencing symptoms of hypoxia, including tachycardia and shortness of breath. The nurse suspects the need for a blood transfusion. What action should the nurse take first?
Explanation
A: Notify the healthcare provider immediately to obtain a blood transfusion order – This is the priority action because the client’s hemoglobin level of 8 g/dL, along with symptoms of hypoxia, indicates a need for urgent medical intervention. Obtaining an order for a transfusion is crucial for addressing the underlying issue of low hemoglobin and associated hypoxia.
B: Administer supplemental oxygen to the client to improve oxygenation – While this action is important, it is not the first step. The low hemoglobin indicates a need for a transfusion, and notifying the provider can lead to quicker treatment.
C: Initiating IV access with a large-bore catheter is an important step in preparation for a possible blood transfusion, but it is not the first action. The client's current symptoms must be managed promptly.
D: Ambulation may be contraindicated post-major surgery, especially when the client is symptomatic. It could exacerbate the client's condition and is not the immediate priority in this scenario.
Explanation
A) Obtaining the client's informed consent is a critical step before any medical procedure, including blood transfusions. This ensures the client understands the risks and benefits of the transfusion and gives their consent willingly.
B) Confirming the client's blood type and Rh factor with the blood bank is essential to prevent transfusion reactions. Mismatching blood types can lead to severe transfusion reactions and is a crucial step in the transfusion process.
C) Administering pre-medication to prevent transfusion reactions is not a standard practice. However, the nurse should assess the client for any risk factors or history of previous transfusion reactions to take appropriate precautions.
D) Assessing the client's blood pressure and heart rate is an important part of the overall assessment before the blood transfusion.
Explanation
A) Stopping the blood transfusion immediately is the nurse's priority action if a transfusion reaction is suspected. This helps prevent further infusion of the potentially incompatible or problematic blood product.
B) Notifying the blood bank is essential to report the suspected transfusion reaction and to facilitate investigation and documentation. However, stopping the transfusion is the first step.
C) Administering antipyretics may help manage the client's fever, but it is not the nurse's priority action when a transfusion reaction is suspected.
D) Placing the client in a supine position with legs elevated is not a priority action when a transfusion reaction is suspected. The priority is to stop the transfusion and assess the client's vital signs and symptoms.
A nurse is preparing to administer a platelet transfusion to a client with severe thrombocytopenia. The nurse should:
Explanation
A. Platelets should be infused rapidly, typically over 30 to 60 minutes, to prevent clotting and ensure effectiveness.
B. A specialized platelet administration set with a filter should be used, not a standard IV infusion set.
C. Although ABO compatibility is less critical for platelets than for red blood cell transfusions, compatibility should still be verified to reduce the risk of reactions.
D. Platelets should not be warmed; they should be stored at room temperature and gently agitated to prevent clumping.
Explanation
A) Raising the head of the client's bed and administering oxygen is the immediate action to improve oxygenation and relieve respiratory distress in a client experiencing potential pulmonary edema, as evidenced by the pink, frothy sputum.
B) Obtaining a sputum sample for culture and sensitivity testing may be important to assess for infection, but it is not the nurse's immediate action in response to a severe transfusion reaction.
C) Administering a diuretic may help with pulmonary congestion, but it is not the nurse's immediate action in response to a severe transfusion reaction. The priority is to improve oxygenation.
D) Discontinuing the blood transfusion and removing the IV catheter is important, but the immediate action to address the client's respiratory distress is to raise the head of the bed and administer oxygen. Stopping the transfusion can follow after the client's respiratory status stabilizes.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP) contains clotting factors and is used to treat bleeding disorders, but it is not primarily responsible for promoting clot formation and controlling bleeding.
B) Correct: Platelets are responsible for promoting clot formation and controlling bleeding. They play a crucial role in hemostasis and are used to treat thrombocytopenia and platelet dysfunction.
C) Incorrect: Packed Red Blood Cells (PRBCs) primarily carry oxygen and are used to treat anemia and improve oxygenation, but they do not have a direct role in clot formation or controlling bleeding.
D) Incorrect: Albumin is a protein used to expand intravascular volume, especially in cases of hypoalbuminemia, but it does not have a significant role in clot formation or controlling bleeding.
Explanation
A) Correct: Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP) contains various clotting factors and is used to treat clotting factor deficiencies such as those found in coagulopathies or liver disease.
B) Incorrect: Platelets are used to treat thrombocytopenia and platelet dysfunction, not clotting factor deficiencies.
C) Incorrect: Cryoprecipitate is derived from FFP and contains concentrated fibrinogen and other clotting factors. It is used for specific clotting factor deficiencies but is not the primary treatment for clotting factor deficiencies in general.
D) Incorrect: Packed Red Blood Cells (PRBCs) are used to treat anemia and improve oxygenation but do not address clotting factor deficiencies.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP) is not the appropriate blood product for immediate volume replacement. It contains clotting factors and is used to manage bleeding disorders.
B) Incorrect: Platelets are used to treat thrombocytopenia and platelet dysfunction and do not provide volume replacement.
C) Correct: Packed Red Blood Cells (PRBCs) contain red blood cells and are used for volume replacement in clients with acute blood loss or anemia.
D) Incorrect: Albumin is used for volume expansion in cases of hypoalbuminemia and fluid resuscitation in certain situations, but PRBCs are more effective for rapid volume replacement.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP) contains clotting factors and is not the primary treatment for hypoalbuminemia.
B) Incorrect: Platelets are used to treat thrombocytopenia and platelet dysfunction, not hypoalbuminemia.
C) Incorrect: Packed Red Blood Cells (PRBCs) are primarily used to improve oxygenation in anemic clients and do not address hypoalbuminemia.
D) Correct: Albumin is the blood product of choice for addressing severe hypoalbuminemia. It is a protein that helps maintain oncotic pressure and regulates fluid balance within the blood vessels.
Explanation
A) Correct: Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP) contains various clotting factors and is used to manage clotting factor deficiencies, including those related to liver disease.
B) Incorrect: Platelets are used to treat thrombocytopenia and platelet dysfunction but do not primarily address clotting factor deficiencies caused by liver disease.
C) Incorrect: Cryoprecipitate is derived from FFP and contains concentrated fibrinogen and other clotting factors. It may be used in some cases of liver disease, but FFP is the more common choice for managing these conditions.
D) Incorrect: Packed Red Blood Cells (PRBCs) are used to improve oxygenation in anemic clients and are not the primary treatment for clotting factor deficiencies related to liver disease.
Questions
Explanation
A) Correct: The nurse should verify the client's identity and blood type with two unique identifiers, such as asking the client to state their full name and date of birth and comparing it to their identification band. This step ensures that the correct blood product is administered to the right client, promoting safety.
B) Incorrect: Confirming the expiration date of the blood product is important but not the first step in ensuring client safety during a blood transfusion. The nurse should first verify the client's identity and blood type.
C) Incorrect: Assessing the client's vital signs is essential, but it is not the first action to be taken. Verifying the client's identity and blood type is the priority before starting the transfusion.
D) Incorrect: Obtaining informed consent from the client is crucial but not the first action to be taken. The nurse should first verify the client's identity and blood type before seeking consent for the transfusion.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: A slight increase in blood pressure is not a significant vital sign alteration that requires immediate reporting before initiating the transfusion. It could be related to various factors, such as anxiety or pain.
B) Incorrect: A respiratory rate of 22 breaths per minute is within the normal range for an adult and does not require immediate reporting before starting the transfusion.
C) Incorrect: A decrease in heart rate from 88 to 72 beats per minute is not a critical vital sign alteration. As long as the heart rate remains within the client's baseline range, it does not need immediate reporting.
D) Correct: An elevated temperature of 38.5°C (101.3°F) may indicate a fever, which could be a sign of an infection or an adverse reaction to the transfusion. The nurse should report this vital sign alteration to the healthcare provider before proceeding with the transfusion to determine the appropriate course of action.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Warming the blood product in a microwave oven is not an appropriate action and could lead to hemolysis of the blood components. Blood should be warmed using an approved blood warmer designed for this purpose.
B) Incorrect: Administering a discolored blood product or one containing clots is unsafe and could cause harm to the client. The nurse should not proceed with the administration and should take appropriate actions.
C) Correct: If the nurse discovers that the blood product is discolored or contains clots, the nurse should discard the blood product appropriately and notify the blood bank immediately. This will ensure that the client receives a safe and suitable blood product for the transfusion.
D) Incorrect: Filtering the blood product through a standard IV filter is not sufficient to remove any clots present in the blood product. Using a blood product that appears abnormal could lead to adverse reactions in the client, so it is essential to obtain a replacement from the blood bank.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Iron-deficiency anemia is not a contraindication for a blood transfusion. In fact, it is one of the common indications for transfusion in clients with severe anemia.
B) Incorrect: Chronic kidney disease is not a contraindication for a blood transfusion. Transfusions may be necessary for clients with chronic kidney disease who develop anemia due to decreased erythropoietin production.
C) Correct: Hemolytic anemia is a contraindication for a blood transfusion. This condition involves the destruction of red blood cells, and a transfusion with incompatible blood can worsen the hemolysis and lead to a severe transfusion reaction.
D) Incorrect: Hypertension is not a contraindication for a blood transfusion. While the nurse should monitor blood pressure during the transfusion, hypertension alone does not preclude the need for a transfusion in a client with other indications for blood products.
A client expresses anxiety and fear about receiving a blood transfusion. What action should the nurse take to address the client's concerns?
Explanation
A) Incorrect: While explaining the blood transfusion procedure is essential, doing so in excessive detail may increase the client's anxiety. The nurse should provide information in a clear and concise manner, addressing the client's specific concerns.
B) Incorrect: Offering a warm blanket is a comfort measure but may not be sufficient to address the client's anxiety and fear about the transfusion. The nurse should engage in therapeutic communication and provide emotional support.
C) Incorrect: Requesting a sedative for the client may not be the best course of action unless specifically prescribed by the healthcare provider. It is essential to explore other interventions to address the client's anxiety before resorting to medication.
D) Correct: Providing the client with information about the benefits and risks of the transfusion can help alleviate their anxiety and fear. The nurse should engage in patient education, discuss the purpose of the transfusion, potential benefits, and possible risks involved. This empowers the client with knowledge and helps them make informed decisions.
Explanation
A) Correct: Red blood cells are the main blood component involved in the crossmatching process. Crossmatching ensures compatibility between the donor's red blood cells and the recipient's plasma, preventing adverse reactions during the transfusion.
B) Incorrect: White blood cells are not part of the crossmatching process. They play a role in the immune response but are not specifically assessed during crossmatching.
C) Incorrect: Platelets are not directly involved in the crossmatching process. Crossmatching primarily focuses on red blood cell compatibility.
D) Incorrect: Plasma is not directly involved in the crossmatching process. The focus is on ensuring compatibility between red blood cells and the recipient's plasma.
A client with blood type B-positive (B+) requires a blood transfusion. Which blood types are compatible with this client for a crossmatch?
Explanation
A. A-negative (A-) and AB-positive (AB+) are incompatible with B-positive (B+), as individuals with B+ blood can only receive blood from B or O types.
B. A-positive (A+) and AB-negative (AB-) are incompatible for the same reason.
C. AB-negative (AB-) and AB-positive (AB+) are not suitable donors for B-positive (B+) recipients.
D. O-negative (O-), B-positive (B+), and O-positive (O+) are all compatible with B-positive (B+), making this the correct choice.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Administering the blood transfusion when agglutination and incompatibility are detected is unsafe and may lead to severe transfusion reactions. The nurse should not proceed with the transfusion.
B) Correct: In the presence of agglutination and incompatibility between the donor's red blood cells and the client's plasma, the nurse must discontinue the blood transfusion immediately and return the blood to the blood bank. This ensures the client's safety and prevents further adverse reactions.
C) Incorrect: Increasing the infusion rate will not resolve the incompatibility issue and may worsen the client's condition. The nurse should stop the transfusion promptly.
D) Incorrect: Mixing the incompatible blood with normal saline will not resolve the incompatibility issue and is not a safe practice. The nurse should not proceed with the transfusion and should return the blood to the blood bank.
A nurse is preparing to crossmatch blood for a client with blood type O-positive(O+). Which blood type can safely receive blood from this client?
Explanation
A. AB-positive (AB+) individuals are universal recipients for red blood cells and can safely receive blood from an O-positive (O+) donor.
B. B-negative (B-) individuals require type B or O blood but must receive Rh-negative blood to avoid incompatibility.
C. A-negative (A-) individuals require type A or O blood and must receive Rh-negative blood.
D. AB-negative (AB-) individuals require type AB, A, B, or O blood but must receive Rh-negative blood to prevent a reaction.
A client with blood type AB-positive (AB+) requires a blood transfusion. Which blood types can safely donate to this client?
Explanation
A. A-negative (A-), B-negative (B-), AB-negative (AB-), and O-positive (O+) are all compatible with AB-positive (AB+) since AB+ individuals can receive any blood type.
B. A-positive (A+), O-negative (O-), AB-negative (AB-), and B-positive (B+) are also compatible for the same reason.
C. A-negative (A-), B-positive (B+), AB-negative (AB-), and O-positive (O+) are all suitable donor types.
D. AB-positive (AB+) is the universal recipient and can receive blood from any blood type.
A nurse is assessing a client who just received a blood transfusion. The client complains of back pain, fever, and chills. What action should the nurse take first?
Explanation
A. Notifying the healthcare provider is important but should be done after stopping the transfusion to prevent further reaction.
B. Administering acetaminophen does not address the underlying cause of the reaction and should not be the priority.
C. Stopping the transfusion and disconnecting the IV tubing is the first priority to prevent further exposure to the incompatible blood product, which could lead to a life-threatening hemolytic reaction.
D. Infusing normal saline is appropriate to maintain hydration, but it should be done after stopping the transfusion.
Explanation
A) Correct: The client's symptoms of respiratory distress and chest pain indicate a potential transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), a severe transfusion reaction. The nurse's priority intervention is to administer oxygen via a non-rebreather mask to improve oxygenation.
B) Incorrect: Discontinuing the blood transfusion immediately is necessary in suspected cases of TRALI, but it is not the priority intervention. First, the nurse should provide immediate respiratory support by administering oxygen.
C) Incorrect: Elevating the client's feet and lowering the head (Trendelenburg position) is not indicated for TRALI. It may be used for clients in shock, but the priority is to manage the client's respiratory distress and chest pain.
D) Incorrect: Administering diuretics is not the priority intervention for TRALI. TRALI is caused by a reaction to plasma components, not fluid overload, and diuretics may not address the underlying cause.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Administering antipyretics to reduce fever is not the appropriate intervention for an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. This type of reaction involves the destruction of red blood cells, not an elevation in body temperature.
B) Incorrect: Preparing to administer a diuretic is not the appropriate intervention for an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. Fluid overload is not a typical feature of this type of reaction.
C) Correct: Monitoring the client's vital signs frequently is a crucial intervention for an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. This type of reaction can cause rapid onset of severe symptoms, including fever, chills, hypotension, tachycardia, and potential shock.
D) Incorrect: Administering epinephrine is not the appropriate intervention for an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. Epinephrine is used to treat anaphylactic reactions, not hemolytic reactions.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Administering epinephrine is not the appropriate intervention for an allergic transfusion reaction characterized by urticaria and itching. Epinephrine is used to treat anaphylactic reactions.
B) Incorrect: Stopping the transfusion and disconnecting the IV tubing is appropriate in the event of an allergic transfusion reaction, but it should not be the first action. The nurse should first slow down or stop the transfusion if mild symptoms are present and notify the healthcare provider for further instructions.
C) Correct: Slowing down the transfusion rate may be appropriate for mild allergic reactions to reduce symptoms. However, if the reaction worsens, the nurse should stop the transfusion immediately.
D) Incorrect: Obtaining a blood sample for repeat crossmatching is not indicated in an allergic transfusion reaction. Allergic reactions are related to hypersensitivity to plasma proteins and do not involve compatibility issues between red blood cells and plasma.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Elevating the head of the bed may help promote lung expansion, but it is not the nurse's priority action when the client is experiencing severe symptoms like dyspnea, tachycardia, and chest pain during a transfusion.
B) Incorrect: Administering diuretics is not the appropriate action for the client's symptoms, which suggest a possible transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) or acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. Diuretics will not address the underlying cause.
C) Correct: The client's symptoms of dyspnea, tachycardia, and chest pain indicate a potential severe transfusion reaction. The nurse's priority action is to stop the transfusion immediately and notify the healthcare provider for further evaluation and intervention.
D) Incorrect: Continuing the transfusion at a slower rate is not appropriate when the client is experiencing severe symptoms. The nurse should first stop the transfusion and then notify the healthcare provider.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Mild itching on the client's forearms is a common and expected side effect of a blood transfusion and may not require immediate reporting to the healthcare provider.
B) Incorrect: Mild lower back pain that subsides is not a significant finding and may not require immediate reporting to the healthcare provider.
C) Correct: An increase in blood pressure by 10 mmHg from the client's baseline may indicate a potential transfusion reaction or fluid overload. The nurse should report this finding to the healthcare provider for further evaluation.
D) Incorrect: An increase in hemoglobin level by 2 g/dL after the transfusion is a positive outcome, indicating a successful transfusion. There is no need to report this finding to the healthcare provider.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: A mild headache is a common and expected side effect of a blood transfusion and may not require immediate reporting to the healthcare provider.
B) Correct: A slightly elevated temperature in a client who received a blood transfusion 2 hours ago could indicate a delayed transfusion reaction. The nurse should report this finding to the healthcare provider for further evaluation.
C) Incorrect: Pale and cool skin may be an expected finding in a client who received a blood transfusion, especially if they experienced a rapid transfusion or had a reaction. However, it is not the priority finding to report.
D) Incorrect: Generalized muscle weakness may occur for various reasons and may not be directly related to a delayed transfusion reaction. The nurse should prioritize reporting the slightly elevated temperature.
Explanation
A) Correct: The client's symptoms of hives, itching, and facial swelling indicate a potential allergic transfusion reaction (urticarial reaction). The nurse's immediate action is to stop the transfusion immediately and notify the healthcare provider for further evaluation and intervention.
B) Incorrect: While administering an antihistamine may be part of the treatment plan for an allergic transfusion reaction, it is not the immediate action. The nurse should first stop the transfusion and notify the healthcare provider.
C) Incorrect: Slowing down the transfusion rate is not appropriate in the presence of an allergic transfusion reaction. The nurse should stop the transfusion immediately.
D) Incorrect: Placing the client in a supine position with legs elevated is not indicated for an allergic transfusion reaction. It may be used for clients in shock, but the priority is to manage the allergic reaction.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Administering a bolus of normal saline may help increase intravascular volume, but it is not the first intervention to be implemented. The nurse should first identify the cause of the client's symptoms and take appropriate actions.
B) Correct: The client's symptoms of feeling lightheaded and dizzy, along with a drop in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate, suggest orthostatic hypotension. The nurse's first intervention should be to elevate the client's feet and lower the head to improve blood flow to the brain.
C) Incorrect: Checking the client's hemoglobin and hematocrit levels is essential but may not be the first intervention in this situation. The client's symptoms indicate an immediate need to address the orthostatic hypotension.
D) Incorrect: Notifying the healthcare provider for further evaluation is important, but it may not be the first intervention. The nurse should first take immediate actions to address the client's symptoms of orthostatic hypotension.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Obtaining a signed informed consent is an essential step before administering a blood transfusion, but it is not the priority action for preventing a potential complication related to blood compatibility. The nurse should first confirm the client's blood type and Rh factor.
B) Correct: The nurse's priority action is to confirm the client's blood type and Rh factor with two unique identifiers to ensure compatibility between the client and the blood product. This step is crucial for preventing transfusion reactions due to ABO and Rh incompatibility.
C) Incorrect: Ensuring that the blood product is properly labeled and has not expired is important for patient safety but is not the priority action before administering a blood transfusion. The nurse should first confirm the client's blood type and Rh factor.
D) Incorrect: Assessing the client's vital signs and baseline laboratory values is essential, but it is not the priority action for preventing a potential complication related to blood compatibility. The nurse should first confirm the client's blood type and Rh factor.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Fever and chills during a blood transfusion may be signs of a febrile transfusion reaction, not an allergic reaction. The nurse should provide information specific to preventing allergic reactions.
B) Correct: Itching, rash, and facial swelling are common signs of an allergic transfusion reaction. The nurse should instruct the client to notify the healthcare provider immediately if they experience these symptoms.
C) Incorrect: A brief period of increased heart rate after the transfusion may be normal, but it is not specific to preventing an allergic transfusion reaction. The nurse should focus on providing information about allergic reaction symptoms.
D) Incorrect: Lower back pain is not typically associated with allergic transfusion reactions. The nurse should provide information about symptoms that indicate an allergic reaction, such as itching, rash, and facial swelling.
Explanation
A) Correct: Pre-medicating the client with antihistamines before the transfusion can help prevent or minimize allergic transfusion reactions in clients with a history of severe allergies. Antihistamines block histamine release, reducing the risk of allergic symptoms.
B) Incorrect: Administering the blood transfusion rapidly is not a preventive measure for allergic transfusion reactions. In fact, rapid administration may increase the risk of adverse reactions.
C) Incorrect: Warming the blood product before administration is important to prevent hypothermia but is not directly related to preventing allergic transfusion reactions.
D) Incorrect: Monitoring the client's vital signs during the transfusion is a standard practice, but it is not the primary intervention for preventing allergic transfusion reactions. Pre-medication with antihistamines is a more targeted approach.
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Increasing the rate of the blood transfusion is not the appropriate action when the client is experiencing respiratory distress. Rapid transfusion may exacerbate the TRALI and lead to further complications.
B) Correct: Administering oxygen via a nasal cannula or face mask is a priority action for a client experiencing respiratory distress. Providing supplemental oxygen can help improve oxygenation and prevent further complications.
C) Incorrect: Placing the client in a supine position with legs elevated is not the appropriate action for a client with respiratory distress. This position may worsen the client's breathing difficulties.
D) Incorrect: Restarting the transfusion with a different blood product is not indicated in the presence of suspected TRALI. The nurse's priority is to manage the client's respiratory distress and discontinue the transfusion if necessary.
A nurse is caring for a client who experienced a mild allergic reaction during a blood transfusion. Which action should the nurse take to prevent future allergic reactions in this client?
Explanation
A) Incorrect: Discontinuing the blood transfusion may be necessary if the allergic reaction is severe, but it is not the appropriate action for a mild allergic reaction. The nurse should manage the current reaction and take preventive measures for future transfusions.
B) Incorrect: Administering an antihistamine is appropriate to manage the current allergic reaction,but it may not prevent future allergic reactions. The nurse should focus on preventing allergic reactions in future transfusions.
C) Incorrect: Notifying the healthcare provider is important for appropriate management, but it may not directly prevent future allergic reactions. The nurse should implement preventive measures.
D) Correct: Obtaining a sample for repeat crossmatching is essential to identify and select blood products that are less likely to cause an allergic reaction in the client. This step can help prevent future allergic transfusion reactions and ensure safer blood product selection.
Hemorrhage
Explanation
A) Correct. Dizziness and lightheadedness are common signs of decreased blood flow, indicating a potential worsening of internal bleeding. Immediate intervention is required to prevent further complications.
B) Incorrect. While a slightly decreased blood pressure could be a concern, it may not be an immediate priority. The nurse should closely monitor the blood pressure and respond promptly if it drops significantly or trends downward.
C) Incorrect. Pale and cool skin may indicate poor perfusion, but it doesn't necessarily require immediate intervention unless it worsens or is accompanied by other alarming signs.
D) Incorrect. Although heart rate can be affected by hemorrhage, being within the normal range doesn't necessarily warrant immediate intervention. Other signs and symptoms should be considered as well.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hemoglobin levels may initially be normal or slightly decreased, but they would decrease later due to the body's compensatory response to dilute the remaining blood.
B) Incorrect. Platelet count may not be significantly affected in the early stages of hemorrhage. It is mainly responsible for clot formation, which becomes more relevant in the later stages.
C) Incorrect. In the early stages of hemorrhage, the white blood cell count is not significantly affected. It plays a role in fighting infection and inflammation.
D) Correct. Hematocrit levels represent the proportion of red blood cells in the blood. During early stages of hemorrhage, there is a loss of red blood cells, leading to decreased hematocrit levels.
Explanation
A) Correct. Anticoagulant medication can interfere with the body's clotting mechanism, increasing the risk of bleeding.
B) Correct. A family history of bleeding disorders can be a risk factor for hemorrhage due to potential genetic predisposition.
C) Incorrect. Regular low-impact exercise is a positive lifestyle choice that helps maintain cardiovascular health and does not directly contribute to an increased risk of hemorrhage.
D) Correct. Recent major surgery can be a risk factor for hemorrhage due to potential surgical site bleeding or complications.
A nurse is monitoring a client for potential hemorrhage after a medical procedure. Which vital sign change is an early indicator of internal bleeding?
Explanation
A. Hypertension is not an early sign of hemorrhage; instead, hypotension occurs as blood loss progresses.
B. Bradycardia is not an expected response; tachycardia is more common due to compensatory mechanisms.
C. Tachypnea is an early indicator of internal bleeding as the body attempts to compensate for decreased oxygen delivery by increasing respiratory rate.
D. Hyperthermia is not associated with hemorrhage; instead, hypothermia can occur with significant blood loss.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Aspirin is an antiplatelet medication and can increase the risk of bleeding, so it should be avoided in clients at risk of hemorrhage.
B) Incorrect. Encouraging the client to participate in contact sports can increase the risk of trauma and bleeding, and it is not a preventive action.
C) Correct. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush for oral care can prevent gum and oral tissue injury, reducing the risk of bleeding in vulnerable clients.
D) Incorrect. Monitoring platelet levels daily is not a preventive action but a method of assessing the client's clotting status.
Questions
A nurse is providing education to a group of pregnant clients about the risk factors for postpartum hemorrhage. Which client statement indicates a need for further clarification?
Explanation
A. Having a previous C-section is a known risk factor for postpartum hemorrhage due to potential uterine scarring and complications during delivery.
B. A history of clotting disorders in the family can increase the risk of postpartum hemorrhage because it may indicate a predisposition to bleeding complications.
C. Expecting twins increases the risk of postpartum hemorrhage due to the larger uterine size and increased blood flow required to support multiple fetuses.
D. Planning to breastfeed exclusively does not increase the risk of postpartum hemorrhage. In fact, breastfeeding can help reduce the risk by promoting uterine contractions that help control bleeding after delivery. This statement indicates a need for further clarification.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While hypertension can be a risk factor for cardiovascular issues, it is not directly associated with an increased risk of hemorrhage.
B) Correct. Anticoagulant medication can interfere with the body's clotting mechanisms, making the client more susceptible to bleeding and hemorrhage.
C) Incorrect. Being a regular blood donor does not inherently increase the risk of hemorrhage unless the client donates too frequently, leading to anemia.
D) Incorrect. Having a balanced diet is essential for overall health, but it is not a specific risk factor for hemorrhage.
Explanation
A) Correct. In liver cirrhosis, the damaged liver may sequester platelets, leading to a decreased platelet count. However, an elevated platelet count (thrombocytosis) can occur as a compensatory response to decreased liver function and is a sign of an increased risk of hemorrhage due to poor clot formation.
B) Incorrect. Low prothrombin time (PT) indicates faster clotting and is not associated with an increased risk of hemorrhage.
C) Incorrect. Decreased ammonia levels are a positive finding in liver cirrhosis, as elevated ammonia levels are harmful to the brain.
D) Incorrect. Elevated liver enzymes are indicative of liver damage, but they do not directly impact the client's risk of hemorrhage.
Explanation
A) Correct. Chronic use of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and aspirin, can irritate the stomach lining and increase the risk of gastric ulcers, including duodenal ulcers.
B) Incorrect. A diet high in fiber and whole grains is generally beneficial and does not directly cause duodenal ulcers.
C) Incorrect. While acidic foods and beverages may aggravate existing ulcers, they are not the primary cause of the ulcer.
D) Incorrect. Excessive intake of vitamin K-rich foods can promote blood clotting and is not a cause of duodenal ulcers.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hemophilia does not increase the risk of forming blood clots. In fact, it causes difficulty in forming blood clots, leading to an increased risk of bleeding and hemorrhage.
B) Incorrect. Platelet count is not directly affected in hemophilia. It is primarily a disorder of clotting factors.
C) Correct. Hemophilia is a genetic disorder characterized by a deficiency or absence of specific clotting factors, which impairs the blood's ability to clot properly.
D) Incorrect. Hemophilia does not affect the number of red blood cells, which are responsible for oxygen transport.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. In DIC, platelet consumption and depletion occur due to widespread clot formation, leading to a decreased platelet count.
B) Incorrect. While inadequate production of clotting factors could lead to bleeding disorders, DIC is characterized by uncontrolled activation of the clotting cascade, leading to excessive clot formation initially, followed by consumption of clotting factors and increased bleeding.
C) Correct. DIC is a serious condition in which there is widespread activation of the clotting cascade, causing the formation of numerous small blood clots throughout the body. These clots can lead to organ dysfunction and excessive bleeding.
D) Incorrect. DIC is associated with decreased platelet count due to the consumption of platelets in the formation of multiple small clots.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Bradycardia is not typically an early clinical manifestation of hemorrhage. The body may initially compensate for the blood loss by increasing heart rate (tachycardia).
B) Incorrect. Hypotension may occur later in the course of hemorrhage as blood loss progresses, but it is not an early manifestation.
C) Incorrect. Pallor (pale skin) may occur later as a result of decreased blood volume, but it is not an early sign.
D) Correct. Restlessness and anxiety are early manifestations of hemorrhage, reflecting the body's compensatory response to maintain perfusion in the early stages of blood loss.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Swelling and bruising around the wound are common signs of external bleeding and do not directly indicate internal bleeding.
B) Correct. Cool and pale skin in the extremities may be indicative of vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow, which can occur in response to internal bleeding.
C) Incorrect. Blood oozing from the wound site is a typical sign of external bleeding and does not necessarily indicate internal bleeding.
D) Incorrect. Visible blood clot formation at the wound site is a normal part of the body's hemostatic response to control external bleeding and does not directly suggest internal bleeding.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Bright red blood in the stool typically indicates lower gastrointestinal bleeding, such as from hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
B) Correct. A tarry and sticky appearance of the stool, also known as melena, is characteristic of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. The dark color is due to the digestion of blood in the stomach.
C) Incorrect. A yellowish color of the stool is not associated with gastrointestinal bleeding. It can be related to other factors like diet or liver issues.
D) Incorrect. Clay-colored stools are pale and occur with problems in the biliary system, not with gastrointestinal bleeding.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A complete blood count (CBC) provides information about the client's red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, but it does not directly assess clotting function.
B) Incorrect. Serum electrolytes help assess the body's fluid balance and various organ functions, but they do not specifically indicate clotting function.
C) Correct. Prothrombin time (PT) is a measure of the time it takes for the blood to clot, primarily assessing the function of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. It is an essential test in evaluating clotting disorders.
D) Incorrect. Blood glucose level is not directly related to clotting function and is more indicative of a client's metabolic status.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While the respiratory rate is an important vital sign to monitor, it does not directly indicate the effectiveness of a blood transfusion.
B) Incorrect. Blood pressure is a critical vital sign, but it is not specific to assessing the effectiveness of a blood transfusion.
C) Incorrect. Urinary output is essential for assessing kidney function and fluid balance, but it does not directly reflect the impact of a blood transfusion.
D) Correct. Monitoring the hemoglobin level is crucial to determine if the blood transfusion has been effective in increasing the client's red blood cell count and improving oxygen-carrying capacity.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A neurological assessment is important to evaluate the client's central nervous system function, but it is not directly related to identifying bleeding sources.
B) Correct. A skin integrity assessment is essential to identify potential external bleeding sources, such as cuts, bruises, or petechiae, which may indicate underlying bleeding disorders.
C) Incorrect. While an abdominal assessment is crucial in identifying internal bleeding in the abdominal area, it is not the most essential assessment to identify bleeding sources overall.
D) Incorrect. A respiratory assessment is important for assessing oxygenation and respiratory status, but it is not the primary assessment to identify bleeding sources.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While a complete blood count (CBC) provides valuable information about the client's red blood cell count and hemoglobin levels, it does not directly confirm the presence of bleeding or assess the clotting function.
B) Incorrect. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a valuable tool for diagnosing various conditions but is not a primary test for confirming the presence of bleeding.
C) Correct. A coagulation panel, which includes prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (PTT), helps assess the clotting function and can aid in confirming the presence of bleeding and identifying coagulation disorders.
D) Incorrect. Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) is used to detect hidden blood in stool, which is indicative of lower gastrointestinal bleeding, but it does not confirm internal bleeding in other areas of the body.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Acute blood loss does not typically lead to a decreased platelet count. Platelet levels may remain within the normal range or slightly decrease due to hemodilution.
B) Correct. In acute blood loss, the concentration of red blood cells decreases, leading to hemoconcentration and elevated hemoglobin levels. This is the body's initial response to conserve oxygen-carrying capacity.
C) Incorrect. An increased white blood cell count is not a direct result of acute blood loss and may indicate other inflammatory or infectious processes.
D) Incorrect. Elevated liver enzymes are not a typical finding in acute blood loss. They are more indicative of liver injury or dysfunction.
Explanation
A) Correct. Arteriography is a radiographic procedure that uses contrast dye to visualize the blood vessels and can precisely identify the location and cause of bleeding, especially in cases of significant hemorrhage.
B) Incorrect. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to assess the heart's electrical activity and is not relevant to identifying the location of bleeding.
C) Incorrect. A chest X-ray may be performed for various respiratory or cardiovascular assessments, but it is not specific to identifying the cause of bleeding.
D) Incorrect. A complete blood count (CBC) provides valuable information about the client's red blood cells and hemoglobin levels but does not directly identify the exact location and cause of bleeding.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Gastric analysis is not commonly used to confirm the presence of blood in the stomach or identify the source of bleeding.
B) Incorrect. Abdominal ultrasound may be helpful in evaluating certain abdominal conditions but is not the primary test for diagnosing upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
C) Correct. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a direct visualization procedure that uses a flexible endoscope to examine the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. It allows for visualization of the source of bleeding and potential interventions like cauterization or sclerotherapy.
D) Incorrect. Stool culture is used to detect gastrointestinal infections but is not specific to diagnosing upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Explanation
A) Correct. Bone marrow aspiration involves the removal of a small sample of bone marrow from the hip bone to assess the production of blood cells and identify potential causes of bleeding disorders.
B) Incorrect. The statement describes an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), which is not the procedure scheduled for this client.
C) Incorrect. Monitoring blood pressure and heart rate is essential during any procedure, but it is not specific to bone marrow aspiration.
D) Incorrect. An ultrasound is not relevant to a bone marrow aspiration procedure and is not used to assess bleeding disorders. It is typically used for imaging soft tissues and organs.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While pain management is essential, it is not the priority when dealing with active bleeding that requires immediate intervention.
B) Incorrect. Positioning the client comfortably is important, but it is not the priority when there is active bleeding.
C) Correct. The priority intervention is to apply direct pressure to the bleeding site to control and reduce bleeding until further assessment and medical assistance can be obtained.
D) Incorrect. Obtaining a detailed health history is valuable for understanding the client's overall health, but it is not the priority when the client is actively bleeding and requires immediate intervention.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Checking the client's blood pressure is important but not the most critical action before starting a blood transfusion.
B) Correct. The most crucial step before administering any intervention, including a blood transfusion, is to verify the client's identification using two identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth or medical record number) to ensure the right blood is given to the right client.
C) Incorrect. While assessing the client's oxygen saturation is important, it is not the priority before starting a blood transfusion.
D) Incorrect. Obtaining consent for the blood transfusion is essential, but verifying the client's identification is more critical before administering the transfusion.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Administering oxygen is essential for a client experiencing difficulty breathing, but the nurse's immediate action should be to stop the blood transfusion and notify the healthcare provider.
B) Incorrect. While assessing the client's vital signs is important, the priority action is to stop the blood transfusion and seek immediate medical assistance.
C) Correct. Sudden difficulty breathing and chest pain after a blood transfusion may indicate an allergic reaction or transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI). The nurse should stop the transfusion immediately and inform the healthcare provider.
D) Incorrect. Elevating the head of the client's bed may be helpful in managing respiratory distress, but it is not the priority when there is a potential adverse reaction to the blood transfusion.
Explanation
A) Correct. Electric razors are safer than traditional razors because they reduce the risk of cuts and bleeding in clients with bleeding disorders.
B) Incorrect. Adequate hydration is essential for overall health, and limiting fluid intake is not recommended for clients with bleeding disorders.
C) Incorrect. High-impact exercises can increase the risk of injury and bleeding in clients with bleeding disorders. Low-impact exercises are preferable.
D) Incorrect. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can increase the risk of bleeding and should be avoided by clients with bleeding disorders.
Explanation
A) Correct. Anticoagulant therapy prevents blood from clotting effectively, which can lead to an increased risk of bleeding.
B) Incorrect. Anticoagulant therapy is not associated with elevated blood pressure readings.
C) Incorrect. Hyperactivity and restlessness are not typical adverse effects of anticoagulant therapy.
D) Incorrect. Anticoagulant therapy does not increase blood viscosity (thickness); instead, it reduces the blood's ability to form clots.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Applying a warm compress may promote vasodilation and increase bleeding in the joint. It is not recommended for managing joint bleeding in a client with hemophilia.
B) Correct. The priority intervention for managing joint bleeding in a client with hemophilia is to administer prescribed clotting factor replacement therapy to promote clot formation and stop the bleeding.
C) Incorrect. Elevating the affected joint can help reduce swelling, but it is not the priority intervention when the client is experiencing an acute joint bleed.
D) Incorrect. Encouraging active range of motion exercises can worsen joint bleeding and is contraindicated in a client with acute joint bleeding due to hemophilia.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While pain management is important, it is not the priority in the management of massive hemorrhage and hypovolemia.
B) Correct. The priority intervention for a client experiencing massive hemorrhage and hypovolemia is to initiate a blood transfusion to replace lost blood and improve oxygen-carrying capacity.
C) Incorrect. Emotional support is essential, but it is not the priority in the acute management of hemorrhage and hypovolemia.
D) Incorrect. Deep breathing exercises are not the priority when the client is experiencing massive hemorrhage and requires urgent interventions to stabilize their condition.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Topical antiseptics, such as hydrogen peroxide or alcohol, can help prevent infection but are safe to use on minor cuts when applied correctly.
B) Correct. Applying direct pressure to the bleeding site for at least 10 minutes helps control minor bleeding and allows the blood to clot, reducing the risk of excessive bleeding.
C) Incorrect. Aspirin is an antiplatelet medication and can increase the risk of bleeding. It should not be used to stop bleeding quickly without medical guidance.
D) Incorrect. Elevating the affected limb above the heart level is not typically necessary for minor bleeding episodes and may not be practical for all bleeding sites.
Explanation
A) Correct. The priority during the initial resuscitation phase of hypovolemic shock is to replace lost intravascular volume promptly. Administering IV fluids rapidly is crucial to improve tissue perfusion and blood pressure.
B) Incorrect. While administering supplemental oxygen is important for tissue oxygenation, it is not the primary intervention during the initial resuscitation phase.
C) Incorrect. Monitoring blood glucose levels is important for overall assessment but is not the priority during the initial resuscitation phase of hypovolemic shock.
D) Incorrect. Neurological assessments are essential but may not be the immediate priority during the initial resuscitation phase of hypovolemic shock.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Bradycardia is not typically an early sign of compensatory response to hypovolemia. The body often responds to hypovolemia with an increased heart rate (tachycardia).
B) Correct. In the early stages of hypovolemia, the body may attempt to compensate by increasing blood pressure to maintain perfusion to vital organs.
C) Incorrect. Warm, flushed skin may be present in the initial stages of hypovolemia, but it is not necessarily an early sign of compensatory response.
D) Incorrect. Decreased urine output is a later sign of hypovolemia when the body's compensatory mechanisms are no longer effective in maintaining blood flow to the kidneys.
Explanation
A) Correct. Before administering a blood transfusion, obtaining informed consent from the client is essential to ensure the client understands the procedure, its potential risks, and provides their voluntary agreement for the transfusion.
B) Incorrect. While pain assessment is important, it is not the most crucial action before starting a blood transfusion.
C) Incorrect. Prophylactic antibiotics are not typically administered before a blood transfusion unless specifically indicated for the client's condition.
D) Incorrect. While taking vital signs is important, obtaining consent is more critical before starting a blood transfusion.
Explanation
A) Correct. A CT scan is a valuable diagnostic tool to identify the cause and source of bleeding, especially in cases of significant hemorrhage.
B) Incorrect. While a complete blood count (CBC) provides valuable information about the client's red blood cells and hemoglobin levels, it does not directly identify the cause and source of bleeding.
C) Incorrect. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to assess the heart's electrical activity and is not relevant to identifying the cause and source of bleeding.
D) Incorrect. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is helpful in diagnosing various conditions but is not the primary test for identifying the cause and source of bleeding in a client with suspected hemorrhage.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While ambulation is important for overall health, it is not the priority action to prevent bleeding complications.
B) Incorrect. Prophylactic antibiotics may be prescribed for specific medical conditions but are not the primary intervention to prevent hemorrhage.
C) Correct. Applying pressure dressings to potential bleeding sites is the priority action to prevent or control bleeding. It helps promote hemostasis and reduces the risk of excessive bleeding.
D) Incorrect. Monitoring blood glucose levels is important for clients with diabetes but is not directly related to preventing hemorrhage.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While monitoring the client's pain level is important, it is not the priority when managing postpartum hemorrhage.
B) Incorrect. While breastfeeding can help stimulate uterine contractions, it is not the priority when actively managing postpartum hemorrhage.
C) Correct. Assessing the client's uterine contractions is the priority when managing postpartum hemorrhage. Weak or ineffective contractions can contribute to excessive bleeding after childbirth.
D) Incorrect. While educating the client about contraceptive methods is essential for family planning, it is not the immediate priority when managing postpartum hemorrhage.
Explanation
A) Correct. Increasing consumption of vitamin C-rich foods can enhance iron absorption, which is essential for replenishing iron stores in clients at risk of anemia due to hemorrhage.
B) Incorrect. Red meat and poultry products are good sources of heme iron, which is highly absorbable and beneficial for individuals at risk of anemia.
C) Incorrect. Leafy green vegetables are excellent sources of non-heme iron, which is also essential for iron intake in the diet.
D) Incorrect. Dairy products do not significantly impact iron intake and can be included in the diet unless the client has specific dietary restrictions.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While resuming normal activities is important, the client should also be cautious and monitor for any complications after a blood transfusion.
B) Correct. Monitoring for signs of infection at the transfusion site is crucial to identify any potential complications such as infection or infiltration.
C) Incorrect. Consuming citrus fruits and juices is not contraindicated after a blood transfusion and does not directly impact post-transfusion care.
D) Incorrect. Dark-colored stools are not an expected outcome after a blood transfusion. It is important for the client to be aware of any unusual changes in stool color or other potential side effects.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Avoiding contact sports is a relevant safety measure for some individuals with bleeding disorders, but it is not the priority in preventing cuts and bleeding at home.
B) Incorrect. While keeping the home environment cool may be helpful for some individuals with certain bleeding disorders, it is not the primary safety measure.
C) Correct. Using electric razors for shaving can prevent cuts and reduce the risk of bleeding in clients with bleeding disorders.
D) Incorrect. Taking aspirin daily is not recommended for clients with bleeding disorders as it can increase the risk of bleeding due to its antiplatelet effects.
Explanation
A) Correct. Avoiding herbal supplements is important as some herbs can interact with anticoagulant medications and affect their effectiveness.
B) Correct. Notifying the healthcare provider about unusual
bruising is essential, as it may indicate potential bleeding complications associated with anticoagulant therapy.
C) Incorrect. Taking aspirin while on anticoagulant therapy can increase the risk of bleeding and is not recommended without medical guidance.
D) Correct. Carrying a medical alert card indicating anticoagulant use is crucial to inform healthcare providers about the client's medication regimen in case of emergency.
Questions
Raynaud's Disease
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Raynaud's disease is not caused by an autoimmune response. It is a vasospastic disorder that affects the blood vessels in the fingers and toes.
B) Correct. Avoiding exposure to cold temperatures and taking measures to keep the extremities warm can help prevent Raynaud's attacks triggered by cold-induced vasospasm.
C) Incorrect. Raynaud's disease is not a bacterial infection. It is a vascular disorder characterized by episodes of vasospasm in the small arteries of the fingers and toes.
D) Incorrect. NSAIDs can help manage symptoms of pain and inflammation associated with Raynaud's attacks, but they do not cure the underlying condition.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Submerging the hands in hot water can lead to burns and is not recommended during a vasospastic attack.
B) Incorrect. Vigorous rubbing of the fingers can cause trauma and worsen the condition during an acute attack.
C) Incorrect. Placing the hands under running cold water may further exacerbate the vasospasm and is not recommended during an attack.
D) Correct. Moving to a warm area and gently wiggling the fingers can help increase blood flow and encourage vasodilation, potentially alleviating the symptoms of a vasospastic attack.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Skin redness and warmth are not characteristic symptoms of a vasospastic attack in Raynaud's disease. Instead, the affected areas become pale or cyanotic (blueish) due to decreased blood flow.
B) Correct. During a vasospastic attack in Raynaud's disease, the fingers or toes may appear cyanotic (blueish) and feel cold due to vasoconstriction of the blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the extremities.
C) Incorrect. Swelling and pitting edema are not typical symptoms of Raynaud's disease. They may occur in other conditions but are not associated with vasospastic attacks.
D) Incorrect. Thickening and hypertrophy of the nails are not specific to Raynaud's disease and may be seen in other nail disorders.
A client with Raynaud's disease is prescribed calcium channel blockers to manage vasospastic attacks. Which statement by the client indicates a correct understanding of the medication?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Calcium channel blockers are not prescribed to prevent infections during a vasospastic attack.
B) Incorrect. While some medications may require taking with food to avoid stomach upset, this is not a specific requirement for calcium channel blockers.
C) Correct. Calcium channel blockers work by dilating blood vessels and reducing vasospasms, thereby decreasing the frequency and severity of attacks in Raynaud's disease.
D) Incorrect. Calcium channel blockers do not affect platelet count and are not prescribed to improve blood flow through increased platelet production.
Explanation
A) Exposure to cold temperatures is a well-known trigger for Raynaud's disease. In this condition, blood vessels in the extremities (usually fingers and toes) constrict excessively in response to cold temperatures or emotional stress, causing reduced blood flow and discoloration of the affected areas.
B) Consuming a diet high in vitamin C is not a trigger for Raynaud's disease. While a balanced diet is important for overall health, vitamin C intake does not directly cause Raynaud's symptoms.
C) Physical activity and exercise do not trigger Raynaud's disease. In fact, regular exercise may improve circulation and is beneficial for overall cardiovascular health.
D) Emotional stress is another common trigger for Raynaud's disease, especially in individuals with the secondary form of the condition. Emotional stress can lead to vasoconstriction and exacerbate symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Explanation
A) Female gender is a risk factor for Raynaud's disease. Women are more likely to develop this condition compared to men. Smoking is also considered a risk factor as it can lead to vasoconstriction and exacerbate symptoms in susceptible individuals.
B) Low caffeine intake and a sedentary lifestyle are not established risk factors for Raynaud's disease. While a sedentary lifestyle may impact overall health, it is not specifically linked to Raynaud's.
C) Allergy to pollen and pet dander are unrelated to the development of Raynaud's disease. Raynaud's is primarily associated with vascular dysfunction, not allergic reactions.
D) Frequent handwashing and the use of hand sanitizer are not direct risk factors for Raynaud's disease. However, excessive exposure to cold water during handwashing may trigger symptoms in individuals with the condition.
Explanation
A) Hypertension and heart disease are not typically associated with Raynaud's disease. However, it's essential to monitor these conditions as they may have an impact on the overall management of the client's health.
B) Diabetes mellitus and obesity are not directly linked to Raynaud's disease. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is important for overall well-being, including managing Raynaud's symptoms.
C) Systemic lupus erythematosus and scleroderma are two autoimmune disorders that are often associated with secondary Raynaud's disease. In these conditions, the immune system attacks the body's tissues, leading to blood vessel abnormalities and an increased risk of Raynaud's symptoms.
D) Seasonal allergies and asthma are unrelated to the development or exacerbation of Raynaud's disease. These conditions primarily involve the respiratory system, not the vascular system.
Explanation
A) Avoiding stressful situations and practicing relaxation techniques can help manage Raynaud's disease. Stress is a trigger for the condition, and reducing stress can lead to a decrease in the frequency and severity of Raynaud's episodes.
B) Consuming spicy foods does not improve blood circulation and is not recommended as a management strategy for Raynaud's disease. Instead, it's important to focus on overall healthy eating habits.
C) Limiting fluid intake is unrelated to managing Raynaud's disease. Adequate hydration is essential for overall health but does not directly impact Raynaud's symptoms.
D) Decreasing physical activity is not advised for managing Raynaud's disease. Regular exercise is beneficial for overall circulation and cardiovascular health, but individuals with Raynaud's should be mindful of protecting their extremities from cold during outdoor activities.
Explanation
A) Beta-blockers are not commonly prescribed for Raynaud's disease. In fact, they may worsen the condition by causing vasoconstriction.
B) Antihistamines are not used to manage Raynaud's disease. They primarily target histamine receptors and are not effective in improving blood flow.
C) Oral corticosteroids are not typically used to manage Raynaud's disease. They have anti-inflammatory effects but are not effective in treating the underlying vascular dysfunction of Raynaud's.
D) Calcium channel blockers, such as nifedipine or amlodipine, are commonly prescribed for Raynaud's disease. These medications help relax and dilate blood vessels, improving blood flow to the extremities and reducing the frequency and severity of Raynaud's episodes.
Explanation
A) Wearing tight-fitting gloves and socks can restrict blood flow and worsen Raynaud's symptoms. It's essential to use loose-fitting clothing to ensure adequate circulation.
B) Using hand warmers and foot warmers directly against the skin can lead to burns or skin irritation. It's best to place these warmers in insulated pockets within loose-fitting gloves and socks.
C) Caffeine does not worsen Raynaud's symptoms in everyone, but it may trigger symptoms in
some individuals. However, complete avoidance of caffeine is not necessary for all clients with Raynaud's disease.
D) Layering clothing and using insulated, loose-fitting gloves and socks are recommended to protect against cold weather. This allows for better insulation and helps maintain blood flow to the extremities, reducing the risk of Raynaud's episodes.
Questions
Explanation
A) Warm and flushed skin is not a characteristic finding in Raynaud's disease. Instead, affected areas usually become pale or bluish due to reduced blood flow.
B) Swollen and tender joints in the fingers are not specific to Raynaud's disease. These symptoms may be indicative of other conditions, such as arthritis.
C) Ulcers or open sores on the fingertips are a common clinical feature of severe Raynaud's disease. Prolonged vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow can lead to tissue damage and the development of painful ulcers.
D) The hallmark of Raynaud's disease is color changes in response to cold or stress. The affected areas typically turn pale or bluish (cyanotic) due to decreased blood flow, followed by redness (rubor) when blood flow is restored. Absence of color changes is not characteristic of Raynaud's disease.
Explanation
A) Elevated blood pressure readings are not directly related to Raynaud's disease. While the condition can affect blood flow to the extremities, it does not cause consistently elevated blood pressure.
B) Hyperactive reflexes in the extremities are not typically associated with Raynaud's disease. These reflexes may be indicative of other neurological issues.
C) Skin thickening and tightening on the fingers are characteristic features of systemic sclerosis, which is a condition often associated with secondary Raynaud's disease. The combination of Raynaud's symptoms with skin changes may raise suspicion for an underlying autoimmune disorder.
D) Abnormal blood clotting tests are not specific to Raynaud's disease. Raynaud's primarily involves vasospasm and decreased blood flow, rather than abnormal clotting.
Explanation
A) A positive rheumatoid factor (RF) test is not specific to Raynaud's disease. It may be present in other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
B) Presence of autoimmune antibodies may indicate an underlying autoimmune disorder, but it is not the definitive diagnostic criteria for Raynaud's disease.
C) The definitive diagnosis of Raynaud's disease is based on the clinical history and physical examination findings. Characteristic symptoms, such as episodic color changes in response to cold or stress, along with a physical examination showing pallor, cyanosis, and rubor of the affected areas, help confirm the diagnosis.
D) Biopsy of affected skin tissue is not routinely performed to diagnose Raynaud's disease. The diagnosis is typically made based on clinical presentation and examination.
Explanation
A) Exposure to cold environments can worsen Raynaud's symptoms and should be avoided. Desensitization to cold is not a recommended strategy for managing the condition.
B) Avoiding stressors, such as exposure to cold temperatures and emotional stress, can help minimize Raynaud's episodes. Stress is a common trigger for Raynaud's disease, and reducing stress can lead to fewer and less severe episodes.
C) Wearing tight gloves and socks can restrict blood flow and worsen Raynaud's symptoms. Instead, loose-fitting, insulated gloves and socks are recommended.
D) Engaging in activities that cause vasoconstriction, such as smoking or using certain medications, can exacerbate Raynaud's symptoms. Clients should be advised to avoid such activities.
Explanation
A) Osteoarthritis and age-related joint changes are not directly associated with Raynaud's disease. Raynaud's is primarily related to vascular dysfunction.
B) Asthma and seasonal allergies do not typically cause or contribute to Raynaud's disease.
C) Gastrointestinal ulcers and reflux disease are not directly linked to Raynaud's disease. However, certain medications used to treat these conditions may trigger Raynaud's symptoms in some individuals.
D) Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and scleroderma are autoimmune disorders that can be associated with secondary Raynaud's disease. Autoimmune conditions may lead to vascular abnormalities and increase the risk of Raynaud's symptoms.
Explanation
A) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is not routinely used to diagnose Raynaud's disease. It may be used in certain cases to evaluate other possible underlying conditions.
B) Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic test commonly used to assess blood flow in the extremities. It helps visualize blood vessels, identify areas of constriction, and confirm the diagnosis of Raynaud's disease.
C) Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test used to assess heart function, and it is not directly related to the diagnosis of Raynaud's
disease.
D) Arteriography is an invasive procedure that involves injecting contrast dye into the arteries to visualize blood vessels. While it may be used in specific cases, it is not the primary diagnostic test for Raynaud's disease. Doppler ultrasound is preferred for initial evaluation due to its non-invasiveness.
Questions
Explanation
A) Exposure to cold temperatures is not recommended for clients with Raynaud's disease as it can trigger symptoms and worsen the condition.
B) Limiting fluid intake does not directly impact Raynaud's disease. Adequate hydration is essential for overall health, but it does not affect the frequency of Raynaud's episodes.
C) Engaging in regular physical exercise and activity is beneficial for individuals with Raynaud's disease. Exercise improves circulation and helps maintain vascular health, which may reduce the severity and frequency of Raynaud's symptoms.
D) Increasing caffeine consumption is not a recommended strategy for managing Raynaud's disease. While caffeine may have mild vasoconstrictive effects, it is not a significant factor in managing the condition.
Explanation
A) Antihistamines are not commonly used to manage Raynaud's disease. They primarily target histamine receptors and are not effective in dilating blood vessels.
B) Beta-blockers are not typically prescribed for Raynaud's disease. They may worsen the condition by causing vasoconstriction.
C) Calcium channel blockers, such as nifedipine or amlodipine, are commonly prescribed to manage Raynaud's disease. These medications help relax and dilate blood vessels, improving blood flow to the extremities and reducing the frequency and severity of Raynaud's episodes.
D) Oral corticosteroids are not used as a standard treatment for Raynaud's disease. They have anti-inflammatory effects but are not effective in treating the underlying vascular dysfunction of Raynaud's.
Explanation
A) While excessive caffeine intake may worsen Raynaud's symptoms in some individuals, complete avoidance of caffeine is not necessary. Moderate caffeine consumption is generally acceptable.
B) Keeping the affected areas warm with insulated gloves and socks is an essential measure to prevent episodes during cold weather. Proper insulation helps maintain blood flow and reduces the risk of Raynaud's symptoms.
C) Taking hot showers or baths is not recommended for individuals with Raynaud's disease. Sudden exposure to hot water may cause blood vessels to dilate rapidly, leading to potential complications.
D) Exposing the affected areas to cold water is not advised for clients with Raynaud's disease. It can trigger symptoms and worsen the condition.
Explanation
A) Vigorous rubbing of the affected areas during a Raynaud's episode may lead to further irritation and may not be effective in improving blood flow.
B) Applying direct heat, such as a heating pad, may cause burns or skin damage, especially if the client has reduced sensitivity due to vasoconstriction.
C) Elevating the affected extremities is not recommended during a Raynaud's episode, as it may further reduce blood flow to the extremities.
D) Placing the affected areas in warm (not hot) water can help dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow, relieving the symptoms of a Raynaud's episode.
Explanation
A) Avoiding stressors, both emotional and environmental (cold temperatures), is crucial for preventing Raynaud's episodes. Stress and cold are common triggers for the condition, and minimizing exposure to these factors can help reduce symptoms.
B) Regularly applying ice packs to the affected areas is not recommended for clients with Raynaud's disease. It may worsen symptoms and is not an effective preventive measure.
C) Consuming high doses of vitamin C is not a recommended preventive measure for Raynaud's disease. While a balanced diet is essential for overall health, vitamin C intake does not directly affect Raynaud's symptoms.
D) Smoking is not advised for individuals with Raynaud's disease. Smoking can exacerbate symptoms by causing vasoconstriction and reducing blood flow to the extremities.
Questions
Explanation
A) Exposure to cold temperatures is not recommended for clients with Raynaud's disease as it can trigger symptoms and worsen the condition.
B) Limiting fluid intake does not directly impact Raynaud's disease. Adequate hydration is essential for overall health, but it does not affect the frequency of Raynaud's episodes.
C) Engaging in regular physical exercise and activity is beneficial for individuals with Raynaud's disease. Exercise improves circulation and helps maintain vascular health, which may reduce the severity and frequency of Raynaud's symptoms.
D) Increasing caffeine consumption is not a recommended strategy for managing Raynaud's disease. While caffeine may have mild vasoconstrictive effects, it is not a significant factor in managing the condition.
Explanation
A) While excessive caffeine intake may worsen Raynaud's symptoms in some individuals, complete avoidance of caffeine is not necessary. Moderate caffeine consumption is generally acceptable.
B) Keeping the affected areas warm with insulated gloves and socks is an essential measure to prevent episodes during cold weather. Proper insulation helps maintain blood flow and reduces the risk of Raynaud's symptoms.
C) Taking hot showers or baths is not recommended for individuals with Raynaud's disease. Sudden exposure to hot water may cause blood vessels to dilate rapidly, leading to potential complications.
D) Exposing the affected areas to cold water is not advised for clients with Raynaud's disease. It can trigger symptoms and worsen the condition.
Explanation
A) Vigorous rubbing of the affected areas during a Raynaud's episode may lead to further irritation and may not be effective in improving blood flow.
B) Applying direct heat, such as a heating pad, may cause burns or skin damage, especially if the client has reduced sensitivity due to vasoconstriction.
C) Elevating the affected extremities is not recommended during a Raynaud's episode, as it may further reduce blood flow to the extremities.
D) Placing the affected areas in warm (not hot) water can help dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow, relieving the symptoms of a Raynaud's episode.
Explanation
A) Avoiding stressors, both emotional and environmental (cold temperatures), is crucial for preventing Raynaud's episodes. Stress and cold are common triggers for the condition, and minimizing exposure to these factors can help reduce symptoms.
B) Regularly applying ice packs to the affected areas is not recommended for clients with Raynaud's disease. It may worsen symptoms and is not an effective preventive measure.
C) Consuming high doses of vitamin C is not a recommended preventive measure for Raynaud's disease. While a balanced diet is essential for overall health, vitamin C intake does not directly affect Raynaud's symptoms.
D) Smoking is not advised for individuals with Raynaud's disease. Smoking can exacerbate symptoms by causing vasoconstriction and reducing blood flow to the extremities.
Explanation
A) Raynaud's disease is not directly affected by sun exposure, so avoiding going outdoors during peak sun hours is not necessary for managing Raynaud's symptoms.
B) Wearing heavy winter clothing in warm weather is not recommended as it may lead to discomfort and overheating. Instead, the focus should be on protecting the extremities from sudden temperature changes.
C) Keeping the air conditioning at a very low temperature is not necessary for managing Raynaud's symptoms during the summer months. However, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature is important to prevent extreme temperature fluctuations.
D) Using sunscreen with high SPF on the affected areas is important, especially if the client's Raynaud's symptoms are triggered by exposure to sunlight. Sunscreen helps protect the skin from harmful UV rays and may reduce the risk of exacerbating symptoms during the summer.
Questions
Explanation
A) Regularly soaking hands in cold water is not recommended for clients with Raynaud's disease as it can trigger symptoms and worsen the condition.
B) Stopping all physical activities is not advised for clients with Raynaud's disease. Regular exercise is beneficial for overall cardiovascular health and can help improve circulation.
C) Avoiding wearing gloves can worsen Raynaud's symptoms as proper insulation is essential to maintain blood flow and prevent triggers.
D) Stress and emotional factors are common triggers for Raynaud's disease. Recommending stress-reduction techniques and relaxation exercises can help the client manage stress, reduce the frequency of episodes, and improve their overall well-being.
Explanation
A) Elevating the affected extremities above the heart level is not recommended during a Raynaud's episode, as it may further reduce blood flow to the extremities.
B) Applying direct heat, such as a heating pad, may cause burns or skin damage, especially if the client has reduced sensitivity due to vasoconstriction.
C) Providing warm blankets and insulated clothing is appropriate during a Raynaud's episode to help keep the client warm and minimize the effects of vasoconstriction. Proper insulation can improve blood flow and alleviate symptoms.
D) Encouraging the client to engage in physical activity during an episode may exacerbate symptoms. It is best to provide a comfortable, warm environment for the client to help them relax and recover.
Explanation
A) Avoiding caffeine is recommended for some clients with Raynaud's disease as excessive caffeine intake can worsen symptoms in certain individuals.
B) Applying ice packs to the affected areas during hot weather is not recommended for clients with Raynaud's disease. It may not be effective in preventing episodes, and it can be uncomfortable.
C) Consuming high doses of vitamin C is not a recommended preventive measure for Raynaud's disease. While a balanced diet is essential for overall health, vitamin C intake does not directly affect Raynaud's symptoms.
D) Smoking is not advised for individuals with Raynaud's disease. Smoking can exacerbate symptoms by causing vasoconstriction and reducing blood flow to the extremities.
Explanation
A) Wearing tight-fitting gloves and socks can restrict blood flow and worsen Raynaud's symptoms. Instead, loose-fitting, insulated gloves and socks are recommended.
B) Hand warmers and foot warmers can be helpful in managing Raynaud's symptoms during the winter season. Using them appropriately does not lead to dependency.
C) Avoiding handwashing is not recommended for hygiene reasons. Proper handwashing is essential, but it is advisable to use warm water and dry hands thoroughly afterward to minimize cold exposure.
D) Layering clothing and using insulated, loose-fitting gloves and socks are recommended for protection during the winter season. These measures provide better insulation and help maintain blood flow to the extremities.
Explanation
A) Raynaud's disease is not directly affected by sun exposure, so avoiding going outdoors during peak sun hours is not necessary for managing Raynaud's symptoms.
B) Wearing heavy winter clothing in warm weather is not recommended as it may lead to discomfort and overheating. Instead, the focus should be on protecting the extremities from sudden temperature changes.
C) Keeping the air conditioning at a very low temperature is not necessary for managing Raynaud's symptoms during the summer months. However, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature is important to prevent extreme temperature fluctuations.
D) Using sunscreen with high SPF on the affected areas is important, especially if the client's Raynaud's symptoms are triggered by exposure to sunlight. Sunscreen helps protect the skin from harmful UV rays and may reduce the risk of exacerbating symptoms during the summer.
Explanation
A) Drinking caffeinated beverages is not a recommended stress-reduction technique for individuals with Raynaud's disease. Excessive caffeine intake may worsen symptoms.
B) Engaging in vigorous physical exercise may be beneficial for overall health, but during stressful periods, it may exacerbate Raynaud's symptoms. Moderate exercise is a better option.
C) Practicing deep breathing exercises and meditation can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Stress reduction is important for individuals with Raynaud's disease, as stress is a common trigger for episodes.
D) Watching stimulating movies or TV shows may not be the most effective stress-reduction technique for managing Raynaud's disease. It is essential to find calming and soothing activities to help manage stress and reduce symptoms.
Questions
A nurse is providing education to a client newly diagnosed with Raynaud's disease. Which statement made by the client indicates a correct understanding of the condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Raynaud's disease is not caused by an autoimmune response. It is a vasospastic disorder that affects the blood vessels in the fingers and toes.
B) Correct. Avoiding exposure to cold temperatures and taking measures to keep the extremities warm can help prevent Raynaud's attacks triggered by cold-induced vasospasm.
C) Incorrect. Raynaud's disease is not a bacterial infection. It is a vascular disorder characterized by episodes of vasospasm in the small arteries of the fingers and toes.
D) Incorrect. NSAIDs can help manage symptoms of pain and inflammation associated with Raynaud's attacks, but they do not cure the underlying condition.
Aneurysm and peripheral vascular disorder
Explanation
A) Correct - Pain level assessment is essential in monitoring for aneurysm rupture because sudden, severe, and persistent pain is a common manifestation. It could indicate that the aneurysm is leaking or has ruptured, requiring immediate medical attention.
B) Incorrect - While blood pressure measurement is important in managing aneurysm, it may not be the best indicator of an imminent rupture. Some aneurysms are asymptomatic until they rupture.
C) Incorrect - Respiratory rate evaluation is not a primary assessment for aneurysm rupture. Although respiratory distress may occur due to pain or compromised blood flow after rupture, it is not the initial priority.
D) Incorrect - While monitoring urinary output is important in various clinical settings, it is not a priority assessment for aneurysm rupture. There are more specific symptoms related to aneurysm rupture that the nurse should focus on.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - While resting and elevating the legs can provide relief for some vascular conditions, it may not effectively manage intermittent claudication. Resting during pain may help temporarily, but it does not address the underlying cause.
B) Incorrect - Applying direct heat to the affected area is not recommended for managing intermittent claudication. Heat may worsen the condition and should be avoided.
C) Correct - Regular physical exercise is the most appropriate intervention for managing intermittent claudication. Engaging in supervised exercise programs, such as walking, can improve peripheral circulation and reduce symptoms.
D) Incorrect - Over-the-counter painkillers may provide temporary relief but do not address the underlying cause of intermittent claudication. Relying solely on painkillers may lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment of PVD.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Avoiding all physical activities is unnecessary and may lead to deconditioning and other health issues. Moderate physical activity is generally encouraged for clients with aneurysms to maintain cardiovascular health.
B) Incorrect - While reducing sodium intake can be beneficial for managing hypertension, it is not a direct preventive measure for aneurysm progression. The primary focus should be on reducing risk factors like smoking and hypertension.
C) Correct - Smoking cessation is crucial in preventing the progression of thoracic aortic aneurysms. Smoking is a significant risk factor for aneurysm development and growth, and quitting can help reduce the risk of rupture.
D) Incorrect - Limiting fluid intake is not a preventive measure for thoracic aortic aneurysm progression. Adequate hydration is important for overall health and should not be restricted unless specifically recommended by a healthcare provider for other reasons.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - While monitoring urine output is essential, it is not the priority for a client post-abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Other assessments take precedence to detect immediate complications.
B) Incorrect - Assisting with early ambulation is important for postoperative recovery, but it is not the priority when there might be a risk of complications from the surgery.
C) Correct - Assessing pedal pulses bilaterally is the priority nursing action post-abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Diminished or absent pedal pulses could indicate compromised blood flow to the lower extremities, possibly due to a clot or embolism.
D) Incorrect - Monitoring blood glucose levels is relevant for some clients, but it is not the priority in this situation, unless the client has a specific history of diabetes or altered glucose levels that could impact their recovery.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Regular physical exercise is not a risk factor for aneurysms. In fact, it is associated with a reduced risk of various cardiovascular diseases, including some peripheral vascular disorders.
B) Correct - Hypertension is a significant risk factor for the development of aneurysms. Elevated blood pressure can weaken arterial walls, increasing the risk of aneurysm formation and rupture.
C) Incorrect - A low LDL level below 100 mg/dL is generally considered a healthy lipid profile and is not a risk factor for aneurysms. However, high LDL levels are associated with atherosclerosis and peripheral vascular disorders.
D) Incorrect - A vegetarian diet is not a risk factor for aneurysms. In fact, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including aneurysms.
Explanation
A) Correct - Encouraging the client to decrease tobacco and alcohol consumption can significantly reduce their risk of peripheral vascular disorders. Smoking and excessive alcohol intake are known risk factors for various vascular conditions.
B) Incorrect - Increasing caffeine intake does not have a significant impact on the risk of peripheral vascular disorders. It is not a primary factor contributing to the development of such conditions.
C) Incorrect - Daily fiber intake, if adequate, can be beneficial for cardiovascular health. A high-fiber diet can help reduce cholesterol levels and improve overall vascular health.
D) Incorrect - Reducing physical activity is not recommended as a way to reduce the risk of peripheral vascular disorders. Regular physical exercise is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of many vascular conditions.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - A high-stress lifestyle can contribute to various health issues, but it is not a genetic risk factor for aneurysms. Stress may exacerbate hypertension, which is a known risk factor.
B) Incorrect - Smoking history is a behavioral risk factor rather than a genetic one. Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of aneurysms through direct and indirect mechanisms.
C) Correct - A positive family history of aneurysms is a genetic risk factor. Having a first-degree relative with a history of an aneurysm increases an individual's risk of developing one.
D) Incorrect - A sedentary lifestyle is a behavioral risk factor for aneurysms, not a genetic one. Lack of physical activity can contribute to hypertension and other risk factors.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - A history of migraines is not a risk factor for peripheral artery disease. PAD is primarily associated with atherosclerosis and arterial occlusion.
B) Incorrect - Exposure to cold temperatures can exacerbate symptoms in individuals with PAD, but it is not a primary risk factor for the development of the condition.
C) Correct - Hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol levels) is a significant risk factor for PAD. Elevated cholesterol can contribute to atherosclerosis and the narrowing of peripheral arteries.
D) Incorrect - While family history can be important in assessing an individual's overall risk for various diseases, it is not a direct risk factor for PAD. Diabetes itself is a risk factor for PAD, not its family history.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Limiting daily water intake is not a lifestyle modification that directly impacts aneurysm prevention. Adequate hydration is generally encouraged for overall health.
B) Correct - Engaging in regular aerobic exercise is a lifestyle modification that can help prevent aneurysms and promote cardiovascular health. Exercise improves blood circulation and reduces the risk of various vascular disorders.
C) Incorrect - Consuming a high-fat diet is not recommended for aneurysm prevention. High-fat diets can contribute to atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular issues.
D) Incorrect - Smoking, even in small amounts, is a significant risk factor for aneurysms. Any amount of smoking should be strongly discouraged for individuals interested in preventing aneurysms and peripheral vascular disorders.
Questions
A nurse is assessing a client suspected of having an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). Which of the following physical assessment findings should the nurse prioritize?
Explanation
A) Correct - The presence of a bruit (a turbulent blood flow sound) over the abdominal area is a priority finding when assessing for an AAA. It indicates possible turbulence caused by blood flow through the dilated artery and should be promptly reported for further evaluation.
B) Incorrect - Clubbing of the fingers is not a specific finding associated with AAA or peripheral vascular disorders. It may be related to respiratory or cardiac issues but is not relevant to this assessment.
C) Incorrect - Decreased urinary output may indicate kidney dysfunction or renal artery involvement in aneurysms, but it is not a priority finding compared to the presence of a bruit, which directly points to the aneurysm.
D) Incorrect - Cyanosis of the extremities may suggest compromised peripheral circulation, but it is not directly related to an AAA assessment. The presence of a bruit is more specific to aneurysm evaluation.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Angiography is a diagnostic test used to visualize blood vessels after the injection of a contrast medium. While it can assess blood flow, it is not the most common test for PVD.
B) Incorrect - An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to assess the electrical activity of the heart and is not specific to PVD or lower extremity blood flow.
C) Correct - The ankle-brachial index (ABI) is the most commonly used test to assess blood flow in the lower extremities for PVD. It compares blood pressure measurements at the ankle and arm to determine peripheral artery occlusive disease.
D) Incorrect - A lumbar puncture is not used to assess blood flow in the lower extremities. It is a procedure for obtaining cerebrospinal fluid for diagnostic purposes in certain neurological conditions.
Explanation
A) Correct - Fasting for at least 8 hours before cerebral angiography is essential to reduce the risk of aspiration during the procedure, as it involves the injection of contrast dye.
B) Incorrect - Chest pain is not a normal sensation during cerebral angiography. If chest pain occurs during the test, the client should inform the healthcare team immediately.
C) Incorrect - While some procedures, like angioplasty, require lying flat for several hours to prevent bleeding, cerebral angiography does not typically require this position after the test.
D) Incorrect - It is essential to stay hydrated after cerebral angiography to help flush out the contrast dye from the system. The client should be encouraged to drink fluids, unless contraindicated for another reason.
Explanation
A) Correct - During a venous Doppler ultrasound, the transducer emits sound waves that create a warm sensation as it moves across the skin. This is a normal and common experience during the test.
B) Incorrect - Unlike some procedures that require fasting, a venous Doppler ultrasound does not require the client to be NPO.
C) Incorrect - While removing metal jewelry is necessary for certain imaging tests like an MRI, it is not typically required for a venous Doppler ultrasound.
D) Incorrect - Bending the knees during a venous Doppler ultrasound does not interfere with the procedure. The client can usually lie in a comfortable position during the test.
Explanation
A) Correct - Checking for allergies to iodine or shellfish is a priority assessment after a peripheral arteriography because contrast dye containing iodine is used during the procedure. An allergic reaction to the dye can be life-threatening and requires immediate intervention.
B) Incorrect - Assessing for pedal pulses bilaterally is important in general, but it is not the priority assessment immediately after a peripheral arteriography.
C) Incorrect - Monitoring blood glucose levels may be relevant for clients with diabetes, but it is not the priority assessment after a peripheral arteriography.
D) Incorrect - Evaluating respiratory rate and oxygen saturation is essential in many post-procedure assessments, but it is not the priority immediately after a peripheral arteriography. The focus is on assessing for any immediate allergic reactions to the contrast dye.
Questions
A client with a history of peripheral artery disease (PAD) reports sudden severe pain, numbness, and coolness in their right leg. What is the most appropriate action for the client to take?
Explanation
A. Applying a heating pad is not appropriate because clients with PAD have reduced circulation, increasing the risk of burns due to impaired sensation.
B. Elevating the leg above heart level can further reduce arterial blood flow, worsening ischemia.
C. Resting and avoiding movement is the best action, as sudden severe pain, numbness, and coolness suggest acute arterial occlusion, a medical emergency requiring immediate evaluation to prevent limb loss.
D. Performing gentle leg exercises is not advisable, as movement could further compromise circulation in an acutely ischemic limb.
Explanation
A) Correct - Monitoring for hypertension is essential in the postoperative period after an endovascular repair of an AAA. Hypertension can increase stress on the repaired vessel and may lead to complications.
B) Incorrect - Hypoglycemia is not a common complication after AAA repair. It is not directly related to the procedure or the aneurysm itself.
C) Incorrect - Peripheral edema may occur for various reasons, but it is not a specific complication of AAA repair unless there are other underlying factors.
D) Incorrect - Hemorrhage is a significant concern during and immediately after the procedure, but in the postoperative period, it would be an immediate complication rather than one to monitor for.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Deep breathing exercises are not appropriate for sudden, severe, tearing chest pain in a client with a known TAA. This type of pain may indicate aortic dissection, a medical emergency.
B) Incorrect - Taking an over-the-counter painkiller may temporarily relieve the pain, but it will not address the underlying issue. The priority action is to seek medical attention immediately.
C) Incorrect - Lying down and resting is not appropriate for sudden, severe, tearing chest pain associated with a TAA. This type of pain requires urgent evaluation by healthcare professionals.
D) Correct - Seeking immediate medical attention is crucial for a client experiencing sudden, severe, tearing chest pain associated with a TAA. This presentation may indicate aortic dissection, a life-threatening complication.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Hypoglycemia is not a common complication of femoral artery catheterization. It is not directly related to the procedure or the femoral artery itself.
B) Incorrect - Hypothermia is not a typical complication of femoral artery catheterization. The procedure is typically performed under controlled environmental conditions.
C) Correct - Bleeding and hematoma at the insertion site are common complications of femoral artery catheterization. The nurse should closely monitor the insertion site for any signs of bleeding or swelling.
D) Incorrect - While elevated blood pressure can be a concern after some procedures, it is not a specific complication of femoral artery catheterization. The primary focus after the procedure is on monitoring the insertion site.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Thrombosis (formation of a blood clot within the vessel) is a potential complication of various peripheral vascular aneurysms, including popliteal artery aneurysms.
B) Incorrect - Embolization (dislodgment of a blood clot or debris) is a potential complication of various peripheral vascular aneurysms, including popliteal artery aneurysms.
C) Correct - Venous stasis (poor venous blood flow) is a unique complication of popliteal artery aneurysms. The aneurysm can compress surrounding veins, leading to venous stasis and its consequences.
D) Incorrect - Atherosclerosis (build-up of plaque within the artery) is a general complication of many peripheral vascular disorders, not unique to popliteal artery aneurysms.
Questions
A client has been diagnosed with a small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). The client asks the nurse about treatment options. What is the most appropriate response by the nurse?
Explanation
A) Incorrect - While surgical repair is an option for larger or symptomatic AAAs, it is not the only treatment option for small, asymptomatic AAAs.
B) Correct - For small asymptomatic AAAs, close monitoring of the aneurysm size and growth is a common approach. The size and rate of growth will determine the appropriate treatment plan.
C) Incorrect - Blood-thinning medications are not the standard treatment for small asymptomatic AAAs. These medications are generally used for other cardiovascular conditions.
D) Incorrect - Endovascular repair may be an option for some AAAs, but it is not the best treatment for all cases, especially small, asymptomatic ones. The appropriate treatment plan will depend on the client's specific circumstances.
Explanation
A) Correct - Monitoring for signs of stroke is the priority during the immediate postoperative period for a client who underwent carotid artery endarterectomy. The procedure involves removing plaque buildup from the carotid artery, which can potentially dislodge and cause a stroke.
B) Incorrect - Assessing the surgical incision for bleeding is important, but it is not the priority when compared to monitoring for signs of stroke after a carotid endarterectomy.
C) Incorrect - Administering pain medications is essential for the client's comfort, but it is not the priority during the immediate postoperative period when there is a higher risk of stroke.
D) Incorrect - Encouraging coughing and deep breathing is a standard postoperative nursing intervention, but it is not the priority in this situation. The focus should be on monitoring for stroke symptoms.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - While angioplasty may be effective for some cases of PAD, it is not always the best treatment option and may not be suitable for everyone.
B) Incorrect - Surgical bypass grafting is an option for severe cases of PAD, but it may not be the most effective treatment for all clients.
C) Incorrect - Amputation is considered a last resort for PAD and is only considered when all other treatment options have been exhausted and the limb is at risk for gangrene or life-threatening complications.
D) Correct - Medical management with lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and regular exercise, is often the first-line treatment for PAD. This approach aims to improve blood flow and manage symptoms before considering more invasive interventions.
Explanation
A) Correct - After an endovascular stent graft placement for an AAA, clients should avoid heavy lifting for at least 2 weeks to prevent stress on the graft site and minimize the risk of complications.
B) Incorrect - Stopping all blood-thinning medications is not advisable after an endovascular stent graft placement. These medications may be prescribed to prevent blood clots around the graft site.
C) Incorrect - While follow-up CT scans are essential to monitor the success of the procedure and assess the aneurysm's stability, they are not expected to be frequent. The frequency of follow-up scans will be determined by the healthcare provider based on the client's progress.
D) Incorrect - Beginning a rigorous exercise routine immediately after the procedure is not recommended. Clients should gradually resume physical activity as guided by their healthcare provider to avoid complications and promote proper healing.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Mild bruising at the injection site is a common side effect of anticoagulant therapy and does not require immediate reporting unless it worsens or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
B) Incorrect - Occasional fatigue and weakness are general symptoms and may not be directly related to anticoagulant therapy. They may require monitoring but do not require immediate reporting.
C) Correct - Blood in the urine or stools can indicate bleeding, which is a potential complication of anticoagulant therapy. This symptom should be reported promptly to the healthcare provider.
D) Incorrect - Occasional dizziness upon standing may not be directly related to anticoagulant therapy. While dizziness should be monitored, it does not require immediate reporting unless it worsens or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Arterial blood gas levels are important for assessing respiratory status but are not specifically related to monitoring the success of peripheral artery bypass surgery.
B) Incorrect - Central venous pressure (CVP) monitoring is typically not necessary for clients who have undergone peripheral artery bypass surgery. It is used to assess fluid volume status in critical care settings.
C) Correct - Assessing peripheral pulses distal to the surgical site is crucial in monitoring the success of peripheral artery bypass surgery. Improved blood flow should result in stronger and more palpable pulses in the affected limb.
D) Incorrect - Monitoring abdominal girth is not directly related to peripheral artery bypass surgery. It may be relevant for assessing other conditions, but it does not specifically monitor the success of the procedure.
A client with a diagnosed popliteal artery aneurysm asks the nurse about treatment options. Whattreatment is considered the definitive therapy for popliteal artery aneurysms?
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Endovascular stent graft placement is a treatment option for popliteal artery aneurysms, but it is not considered the definitive therapy for all cases.
B) Incorrect - Medication management with anticoagulants is not the definitive therapy for popliteal artery aneurysms. Anticoagulants may be prescribed to prevent clot formation, but they do not address the aneurysm itself.
C) Correct - Surgical excision and graft placement are considered the definitive therapy for popliteal artery aneurysms. This procedure involves removing the aneurysm and replacing it with a graft to restore proper blood flow.
D) Incorrect - Conservative management with lifestyle changes may be recommended in certain cases, but it is not the definitive therapy for popliteal artery aneurysms, especially when the aneurysm poses a significant risk of rupture.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - While regular aerobic exercise is beneficial for overall vascular health, it may not specifically alleviate Raynaud's disease symptoms during cold weather.
B) Incorrect - Applying a heating pad to the affected areas is not the most effective intervention for managing Raynaud's disease symptoms. It may not fully address the underlying vascular constriction.
C) Correct - Avoiding exposure to cold temperatures is essential for managing Raynaud's disease symptoms. Cold temperatures can trigger vasospasm in affected areas, leading to color changes and discomfort.
D) Incorrect - Over-the-counter antihistamines are not a standard treatment for Raynaud's disease and may not directly alleviate symptoms related to cold weather exposure.
A client underwent open surgical repair for an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). What should the client be instructed to report to the healthcare provider during the postoperative period?
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Mild incisional pain is expected after open surgical repair and can be managed with prescribed pain medications. It does not require immediate reporting.
B) Incorrect - Some incisional drainage with slight redness may be normal in the early postoperative period. However, increasing drainage or significant redness may indicate infection and should be reported to the healthcare provider.
C) Correct - Mild swelling of the legs may indicate a fluid retention issue or impaired circulation, which can be a concern after AAA repair. It should be reported for further evaluation.
D) Incorrect - Sudden onset of chest pain is not directly related to the AAA repair and may indicate a different medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Encouraging early ambulation and leg exercises is essential after peripheral artery bypass surgery to promote blood circulation and prevent complications like deep vein thrombosis.
B) Correct - Elevating the affected leg above heart level while resting can help reduce swelling and promote blood flow, aiding in the healing process after peripheral artery bypass surgery.
C) Incorrect - Applying direct pressure to the surgical incision if it starts bleeding may worsen the bleeding. Instead, the client should apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth and seek immediate medical attention if bleeding does not stop.
D) Incorrect - Taking hot baths is not recommended after peripheral artery bypass surgery. Heat may dilate blood vessels and increase blood flow, potentially causing complications at the surgical site.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Avoiding showering or bathing for 24 hours after the procedure is unnecessary. Clients can usually shower the day after the angioplasty, but should avoid soaking the insertion site in water.
B) Correct - Keeping the insertion site dry and covered with a dressing is the appropriate wound care for the first 24 hours after peripheral angioplasty. This helps prevent infection and protect the site.
C) Incorrect - Cleaning the insertion site with hydrogen peroxide daily is not recommended, as it may delay wound healing. Instead, clients should follow the healthcare provider's instructions on wound care.
D) Incorrect - Rubbing the insertion site with a washcloth during showers is not advisable, as it may irritate the area and interfere with proper wound healing. The insertion site should be gently washed without scrubbing.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Assessing pain level at the insertion site is important but not the priority assessment when evaluating the immediate complications of femoral artery cannulation.
B) Correct - Assessing peripheral pulses distal to the insertion site is the priority when evaluating the adequacy of blood flow after femoral artery cannulation. Diminished or absent pulses may indicate vascular compromise.
C) Incorrect - The client's ability to ambulate independently is a relevant assessment but not the priority when immediately assessing the complications of femoral artery cannulation.
D) Incorrect - Capillary refill of the fingers is important but is not the priority assessment in the immediate post-procedure period following femoral artery cannulation.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Avoiding physical activity for the first 6 weeks is unnecessary and may hinder the client's recovery. Gradual activity resumption is generally recommended after peripheral artery bypass surgery.
B) Correct - Light walking is a suitable form of physical activity to begin the day after peripheral artery bypass surgery. Gradual and controlled walking helps improve blood circulation and promotes healing.
C) Incorrect - Participating in strenuous exercises immediately after peripheral artery bypass surgery is not recommended. Strenuous activities can put stress on the surgical site and increase the risk of complications.
D) Incorrect - Waiting until fully recovered before engaging in any physical activity is unnecessary and may delay the client's recovery process. Controlled and gradual activity resumption is usually preferred.
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Administering intravenous pain medication is important for the client's comfort but is not the priority in the immediate postoperative period after EVAR.
B) Correct - Monitoring for signs of graft occlusion is the priority in the immediate postoperative period after EVAR. Graft occlusion can lead to severe complications and requires prompt intervention.
C) Incorrect - Encouraging the client to cough and deep breathe is important for postoperative lung expansion, but it is not the priority when compared to monitoring for graft occlusion after EVAR.
D) Incorrect - Checking vital signs every 4 hours is a standard nursing intervention, but it is not the priority in the immediate postoperative period after EVAR, especially when graft occlusion may pose a more immediate threat.
Questions
A client with peripheral artery disease (PAD) is scheduled for an angioplasty. What information should the nurse provide to the client about the procedure?
Explanation
A) Incorrect - Complete fasting is typically not required for an angioplasty procedure. The client may receive specific instructions about food and drink restrictions, but a 24-hour fasting period is unnecessary.
B) Incorrect - Angioplasty is not associated with chest pain. It is primarily performed to improve blood flow in narrowed or blocked arteries, such as those in the legs in PAD.
C) Incorrect - Angioplasty is usually performed with local anesthesia, not general anesthesia. The client will be awake but may receive sedation to help them relax during the procedure.
D) Correct - After the procedure, the client is typically advised to lie flat and keep the leg straight for several hours to prevent bleeding and promote vessel healing. This position helps to apply pressure at the site of the angioplasty.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Explanation
A) Correct. CPR is a life-saving technique used to restore circulation and maintain oxygenation in individuals who have experienced cardiac arrest or have stopped breathing. It involves chest compressions to manually pump blood and provide oxygen to vital organs.
B) Incorrect. CPR is not intended to stop all heart rhythms; rather, it aims to keep blood flowing to vital organs until more advanced medical assistance can be provided.
C) Incorrect. CPR is a critical intervention for severe emergencies like cardiac arrest and is not limited to treating minor heart conditions.
D) Incorrect. While CPR is crucial in the immediate response to cardiac arrest, it is not a substitute for professional medical care. Timely activation of emergency medical services is essential to ensure the best possible outcome.
Explanation
A) Correct. The recommended compression-to-ventilation ratio for adult CPR is 30:2. This means 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths.
B) Incorrect. Continuous compressions without providing ventilations can lead to inadequate oxygenation, which is essential for the survival of the individual.
C) Incorrect. The ratio of 15:2 is not the current guideline for adult CPR. The correct ratio is 30:2.
D) Incorrect. The compression-to-ventilation ratio in adult CPR is not based on the individual's weight but follows the standard 30:2 guideline.
Explanation
A) Correct. In the event of an unresponsive individual with no breathing and no pulse, the nurse's immediate action is to activate the emergency response system and retrieve the AED. Early access to the AED can significantly improve the chances of survival for the client in case they are experiencing a shockable rhythm.
B) Incorrect. Chest compressions should be started immediately after identifying an unresponsive individual with no pulse. The rate of compressions should be 100 to 120 compressions per minute, not 60.
C) Incorrect. The current guidelines recommend starting with chest compressions, not rescue breaths, when assessing an unresponsive individual without a pulse.
D) Incorrect. Time is critical during a cardiac arrest, and the nurse should not wait for additional healthcare providers before initiating CPR and activating the emergency response system.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While it's natural for the family member to be concerned, it's essential to empower them to act in case of an emergency. Waiting for healthcare professionals to arrive may delay life-saving interventions.
B) Incorrect. While CPR should ideally be performed by trained individuals, untrained bystanders can still make a significant difference in saving a life by providing chest compressions.
C) Correct. Encouraging the family member that attempting CPR, even if they are not perfect, is better than doing nothing at all. Hands-only CPR (chest compressions) can be effective and is better than no intervention.
D) Incorrect. While formal training in advanced life support is ideal, bystanders without formal training can still perform hands-only CPR, which involves chest compressions, until professional help arrives.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Defibrillation is used to stop abnormal heart rhythms, but it is not intended to restore a pulse directly. Effective CPR and defibrillation work together to improve the chances of restoring circulation.
B) Incorrect. While defibrillation can stop certain abnormal heart rhythms, it does not address all cardiac arrest situations.
C) Incorrect. Defibrillation is not used to relieve pain or discomfort. Its primary purpose is to restore a normal heart rhythm.
D) Correct. Early defibrillation is crucial because it helps to reset the heart's electrical activity, allowing the heart to resume an effective rhythm. The sooner defibrillation is performed, the better the chances of restoring a normal heart rhythm and improving the chances of survival.
Questions
Explanation
A) Correct. The first step in BLS for adult cardiac arrest is to check for responsiveness and call for help. It is crucial to quickly assess whether the victim is conscious and breathing before proceeding with CPR.
B) Incorrect. In adult cardiac arrest, the first step is not to deliver rescue breaths. Rescue breaths are part of the BLS sequence, but they come after chest compressions have been initiated.
C) Incorrect. While assessing the victim's pulse is important, it is not the first step in adult cardiac arrest management. The first step is to check for responsiveness and call for help.
D) Incorrect. Administering an opioid antagonist is not part of the BLS guidelines. The focus of BLS is on providing immediate chest compressions and rescue breaths to support circulation and oxygenation.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The correct compression rate for BLS chest compressions is higher than 80 compressions per minute. This rate may not be sufficient to maintain adequate circulation.
B) Correct. The correct compression rate for BLS chest compressions in an unresponsive client without a pulse is 100-120 compressions per minute. This rate ensures adequate blood flow to vital organs during CPR.
C) Incorrect. 30 compressions per minute is too low for effective chest compressions during BLS. The recommended rate is higher, as mentioned in option B.
D) Incorrect. 60 compressions per minute is lower than the recommended rate for BLS chest compressions. The correct rate, as mentioned in option B, is 100-120 compressions per minute.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. For children in cardiac arrest, the standard CPR technique involves both chest compressions and rescue breaths. Hands-Only CPR is most appropriate for adults in cardiac arrest.
B) Incorrect. Near-drowning incidents may involve respiratory issues and potential water aspiration, making the delivery of rescue breaths essential. Hands-Only CPR is not the most appropriate technique in this situation.
C) Correct. Hands-Only CPR is most appropriate when the client is unresponsive and not breathing after sudden cardiac arrest, especially in adult victims. In such cases, bystanders can provide continuous chest compressions until professional help arrives.
D) Incorrect. For severe allergic reactions, the primary intervention is to administer epinephrine and seek emergency medical assistance. Hands-Only CPR is not indicated for anaphylactic reactions.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Placing the hands on the lower half of the breastbone is not the correct hand placement for adult CPR chest compressions. The hands should be positioned higher on the sternum.
B) Incorrect. Placing one hand on the chest and the other on the forehead is not the correct hand placement for adult CPR. Both hands should be positioned on the sternum.
C) Incorrect. Placing the hands on the upper abdomen is not the correct hand placement for adult CPR. The hands should be positioned on the sternum.
D) Correct. The correct hand placement for adult CPR chest compressions is to center the hands on the sternum, between the nipples. Proper hand placement ensures effective compression depth and allows for adequate blood flow during CPR.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Compressing the chest to a depth of 1 inch (2.5 cm) is too shallow for effective adult CPR. Deeper compressions are required.
B) Correct. The correct compression depth for adult CPR is at least 2 inches (5 cm). This depth allows for sufficient blood flow to vital organs and is consistent with current BLS guidelines.
C) Incorrect. Compressing the chest to a depth of 3 inches (7.5 cm) is deeper than necessary for adult CPR. Excessive compression depth may cause harm.
D) Incorrect. Compressing the chest to a depth of 4 inches (10 cm) is much deeper than the recommended depth for adult CPR. Excessive depth can lead to rib fractures and other injuries.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The compression-to-ventilation ratio of 5:1 is not the current guideline for adult CPR. The correct ratio involves more frequent compressions.
B) Correct. The recommended compression-to-ventilation ratio for adult CPR is 30:2. This means 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths.
C) Incorrect. Continuous compressions without providing ventilations can lead to inadequate oxygenation, which is essential for the survival of the individual.
D) Incorrect. The compression-to-ventilation ratio of 10:1 is not the current guideline for adult CPR. The correct ratio involves more frequent compressions and periodic rescue breaths.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Defibrillation is not used to relieve pain and discomfort during cardiac arrest. Its primary purpose is to restore a normal heart rhythm.
B) Correct. Early defibrillation is crucial in BLS because it is the most effective intervention to restore a normal heart rhythm during cardiac arrest. It involves delivering an electric shock to the heart to stop chaotic rhythms like ventricular fibrillation and allow the heart's natural pacemaker to regain control.
C) Incorrect. Early defibrillation is not used to assess the client's response to BLS interventions. It is a time-sensitive intervention aimed at restoring a viable heart rhythm.
D) Incorrect. Defibrillation is appropriate for specific cardiac rhythms, especially ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. In these cases, early defibrillation is vital. Delaying defibrillation can significantly decrease the chances of successful resuscitation.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While emotional comfort is important, high-quality CPR is not primarily aimed at ensuring the client's emotional comfort during resuscitation efforts.
B) Incorrect. High-quality CPR focuses on providing effective chest compressions and ventilations to the client, rather than conserving the energy of healthcare providers.
C) Incorrect. High-quality CPR emphasizes proper technique and compression depth to minimize the risk of injury to both the client and the healthcare provider.
D) Correct. High-quality CPR is critical because it improves the likelihood of restoring blood circulation and oxygenation to vital organs during resuscitation efforts. Effective chest compressions maintain blood flow, while rescue breaths provide oxygen to the lungs, enhancing the chances of a successful resuscitation outcome.
Questions
Explanation
A) Correct. The first link in the Chain of Survival is early recognition and activation of the emergency response system. Recognizing a cardiac arrest or life-threatening emergency and calling for help immediately is crucial to initiating a timely and effective resuscitation response.
B) Incorrect. While the rapid delivery of advanced life support is essential, it is not the first link in the Chain of Survival. Before advanced life support, there are other critical components that need to be activated.
C) Incorrect. Initiating chest compressions and rescue breaths is a vital part of the Chain of Survival, but it is not the first link. Early recognition and activation of the emergency response system take precedence.
D) Incorrect. While medications play a role in advanced cardiac life support, they are not part of the initial links in the Chain of Survival. The first link focuses on early recognition and activation of the emergency response system.
Explanation
A) Correct. The second link in the Chain of Survival is the immediate initiation of bystander CPR. When a cardiac arrest occurs, bystanders who can perform high-quality CPR increase the chances of survival for the victim until professional medical help arrives.
B) Incorrect. While the early arrival of advanced medical personnel is vital, it is not the second link in the Chain of Survival. Bystander CPR comes before advanced medical personnel in the sequence.
C) Incorrect. While the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) is essential, it is not the second link in the Chain of Survival. Bystander CPR is the immediate response after early recognition and activation of the emergency response system.
D) Incorrect. Administration of intravenous medications is part of advanced life support, which comes later in the Chain of Survival. The second link is focused on bystander CPR.
Explanation
A) Correct. The third link in the Chain of Survival is the prompt arrival of emergency medical services (EMS). After early recognition, bystander CPR, and the use of AEDs, the next crucial step is for trained medical professionals to arrive quickly to continue advanced care.
B) Incorrect. Advanced airway management techniques are important in advanced life support, but they do not represent the third link in the Chain of Survival. Prompt arrival of EMS is the focus at this stage.
C) Incorrect. Administration of antiarrhythmic medications is part of advanced cardiac life support, which occurs later in the Chain of Survival. The third link pertains to EMS arrival.
D) Incorrect. Immediate initiation of advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) is part of the overall resuscitation effort, but it is not the specific third link in the Chain of Survival. Prompt arrival of EMS takes precedence.
Explanation
A) Correct. The fourth link in the Chain of Survival is the early use of therapeutic hypothermia after resuscitation. Therapeutic hypothermia is a post-resuscitation intervention used to improve neurological outcomes and survival in certain cardiac arrest cases.
B) Incorrect. The administration of antiplatelet medications is not part of the Chain of Survival. It may be used in the management of certain cardiac conditions but is not specific to the resuscitation process.
C) Incorrect. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a respiratory intervention and is not part of the Chain of Survival. The fourth link focuses on therapeutic hypothermia.
D) Incorrect. Transfer to a specialized cardiac care facility may be necessary for further management, but it is not the fourth link in the Chain of Survival. The fourth link pertains to the use of therapeutic hypothermia after resuscitation.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The administration of thrombolytic therapy is not the fifth and final link in the Chain of Survival. Thrombolytic therapy may be used for certain cardiac conditions but is not specific to the resuscitation process.
B) Incorrect. While returning to normal daily activities is an important goal, it is not the fifth and final link in the Chain of Survival. The Chain of Survival primarily focuses on the immediate response to cardiac arrest and resuscitation efforts.
C) Correct. The fifth and final link in the Chain of Survival is the continuation of advanced cardiac life support (ACLS). After successful resuscitation, ongoing advanced medical care is provided to stabilize the patient and manage any underlying cardiac issues.
D) Incorrect. Long-term cardiac rehabilitation may be beneficial after a cardiac event, but it is not the fifth and final link in the Chain of Survival. The focus of the Chain of Survival is on the immediate response and resuscitation efforts.
Questions
Explanation
A) Correct. The absence of a pulse is the most reliable indicator of cardiac arrest. In cardiac arrest, the heart is no longer pumping effectively, leading to the absence of a palpable pulse.
B) Incorrect. An irregular breathing pattern may be observed in various medical conditions, including respiratory distress, but it is not as definitive as the absence of a pulse in indicating cardiac arrest.
C) Incorrect. Cyanosis of the lips and fingertips can occur in various situations, such as respiratory failure or decreased oxygenation, but it is not specific to cardiac arrest.
D) Incorrect. Sudden loss of consciousness can occur due to various reasons, including seizures or fainting, and is not solely indicative of cardiac arrest.
Explanation
A) Correct. The first step in recognizing cardiac arrest is to assess the client's level of responsiveness. If the client is unresponsive, the nurse should proceed with assessing for the absence of breathing and a pulse.
B) Incorrect. While cyanosis may be a sign of decreased oxygenation, it is not the first step in recognizing cardiac arrest. Assessing responsiveness is the primary step.
C) Incorrect. Asking about chest pain may be important in assessing other cardiac conditions, but it is not the first step in recognizing cardiac arrest.
D) Incorrect. Determining the client's blood pressure reading is not the first step in recognizing cardiac arrest. Assessing responsiveness is the initial priority.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. This client's statement demonstrates an understanding of the importance of calling for emergency medical assistance immediately in a cardiac arrest situation.
B) Incorrect. This client's statement indicates knowledge of the need to initiate chest compressions promptly if a person is unresponsive and not breathing.
C) Correct. Performing a thorough physical examination is not recommended in cardiac arrest situations, as it may delay life-saving interventions like chest compressions and rescue breaths.
D) Incorrect. This client's statement reflects an understanding of the significance of early recognition in improving survival rates during cardiac arrest.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While prompt action is important, performing CPR on someone who does not require it can be harmful. CPR should only be initiated in confirmed cases of cardiac arrest.
B) Correct. Performing CPR on someone who is not in cardiac arrest can cause harm and is not indicated. It is crucial to ensure the person is unresponsive and not breathing before initiating CPR.
C) Incorrect. Bystanders can play a vital role in initiating CPR in cardiac arrest situations. CPR training is not limited to healthcare professionals.
D) Incorrect. In cardiac arrest situations, time is of the essence. Waiting for emergency medical services to arrive without initiating CPR can significantly reduce the chances of survival for the individual experiencing cardiac arrest.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While medications are important in advanced cardiac life support, the primary goal of early recognition and response is not the immediate administration of medications.
B) Incorrect. While transporting the client to a specialized cardiac care facility is necessary for some patients, it is not the primary goal of early recognition and response.
C) Incorrect. Advanced airway management and oxygen support are important in the resuscitation process, but the primary goal at the early stage is not advanced airway management.
D) Correct. The primary goal of early recognition and response in cardiac arrest situations is to start immediate chest compressions and deliver rescue breaths to support circulation and oxygenation. These interventions are essential to maintaining blood flow and oxygen delivery to vital organs until advanced medical support is available.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Compressing the chest to a depth of 1 inch (2.5 cm) is too shallow for effective adult CPR. Deeper compressions are required.
B) Correct. The recommended compression depth for adult CPR is 2 inches (5 cm). This depth allows for sufficient blood flow to vital organs and is consistent with current CPR guidelines.
C) Incorrect. Compressing the chest to a depth of 3 inches (7.5 cm) is deeper than necessary for adult CPR. Excessive compression depth may cause harm.
D) Incorrect. Compressing the chest to a depth of 4 inches (10 cm) is much deeper than the recommended depth for adult CPR. Excessive depth can lead to rib fractures and other injuries.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. For children in cardiac arrest, the standard CPR technique involves both chest compressions and rescue breaths. Hands-Only CPR is most appropriate for adults in cardiac arrest.
B) Incorrect. Near-drowning incidents may involve respiratory issues and potential water aspiration, making the delivery of rescue breaths essential. Hands-Only CPR is not the most appropriate technique in this situation.
C) Correct. Hands-Only CPR is most appropriate when the client is unresponsive and not breathing after sudden cardiac arrest, especially in adult victims. In such cases, bystanders can provide continuous chest compressions until professional help arrives.
D) Incorrect. For severe allergic reactions, the primary intervention is to administer epinephrine and seek emergency medical assistance. Hands-Only CPR is not indicated for anaphylactic reactions.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Placing the hands on the lower half of the breastbone is not the correct hand placement for adult CPR chest compressions. The hands should be positioned higher on the sternum.
B) Incorrect. Placing one hand on the chest and the other on the forehead is not the correct hand placement for adult CPR. Both hands should be positioned on the sternum.
C) Incorrect. Placing the hands on the upper abdomen is not the correct hand placement for adult CPR. The hands should be positioned on the sternum.
D) Correct. The correct hand placement for adult CPR chest compressions is to center the hands on the sternum, between the nipples. Proper hand placement ensures effective compression depth and allows for adequate blood flow during CPR.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The compression-to-ventilation ratio of 5:1 is not the current guideline for adult CPR. The correct ratio involves more frequent compressions.
B) Correct. The recommended compression-to-ventilation ratio for adult CPR is 30:2. This means 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths.
C) Incorrect. The compression-to-ventilation ratio of 15:2 is not the current guideline for adult CPR. The correct ratio involves more frequent compressions, as mentioned in option B.
D) Incorrect. The compression-to-ventilation ratio of 10:1 is not the current guideline for adult CPR. The correct ratio involves more frequent compressions and periodic rescue breaths, as mentioned in option B.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While emotional comfort is important, high-quality CPR is not primarily aimed at ensuring the client's emotional comfort during resuscitation efforts.
B) Incorrect. High-quality CPR focuses on providing effective chest compressions and ventilations to the client, rather than conserving the energy of healthcare providers.
C) Incorrect. High-quality CPR emphasizes proper technique and compression depth to minimize the risk of injury to both the client and the healthcare provider.
D) Correct. High-quality CPR is critical because it improves the likelihood of restoring blood circulation and oxygenation to vital organs during resuscitation efforts. Effective chest compressions maintain blood flow, while rescue breaths provide oxygen to the lungs, enhancing the chances of a successful resuscitation outcome.
Questions
Explanation
A) Correct. The first step when using an AED is to turn on the device and check for responsiveness. Ensuring the AED is powered on and ready for use is critical before starting any other steps.
B) Incorrect. After turning on the AED, the provider should place the pads on the victim's chest and connect the AED. However, this is not the first step in the process.
C) Incorrect. After connecting the AED to the victim, the device will automatically analyze the victim's heart rhythm to determine if a shock is needed. However, analyzing the rhythm is not the first step.
D) Incorrect. Performing a quick physical examination is not the first step when using an AED. The immediate priority is to check for responsiveness and turn on the AED.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. An AED is not used to relieve pain and discomfort during cardiac arrest. Its primary purpose is to restore a normal heart rhythm.
B) Correct. The primary purpose of an AED is to restart the heart and restore a normal heart rhythm during cardiac arrest. It delivers a controlled electric shock to the heart to stop abnormal rhythms and allow the heart's natural pacemaker to regain control.
C) Incorrect. While medications may be used in advanced cardiac life support, an AED is not designed to administer medications. Its focus is on delivering defibrillation shocks.
D) Incorrect. While an AED may have basic monitoring capabilities, its primary purpose is not to monitor vital signs during resuscitation efforts. The AED is used for defibrillation to treat cardiac arrest.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Placing the pads on the right side of the chest is not the correct position for defibrillation. The pads should be positioned differently.
B) Correct. The proper placement of AED pads involves placing one pad on the center of the chest and the other pad on the left side of the chest. This placement allows the electrical current to flow effectively through the heart and is consistent with current guidelines.
C) Incorrect. Placing one pad on the back and the other on the front of the chest is not the recommended position for AED pads. The pads should be placed on the chest.
D) Incorrect. Placing the pads on the lower abdomen is not the correct position for defibrillation. The pads should be positioned on the chest to deliver the electric shock to the heart.
Explanation
A) Correct. Ensuring that the AED is turned on before placing the pads on the victim's chest is a safety measure. This ensures the AED is ready for use and can begin the analysis process immediately.
B) Incorrect. While it is essential to stand clear and avoid touching the victim during defibrillation, this is not the response to the client's question about general safety measures.
C) Incorrect. It is crucial to stand clear and avoid touching the victim while the AED is analyzing and delivering a shock. Performing CPR during defibrillation can interfere with the accuracy of the analysis and the delivery of the shock.
D) Incorrect. The AED is specifically designed for use during cardiac arrest when the victim is unresponsive and not conscious. Using the AED is not appropriate for conscious individuals who can follow instructions.
Questions
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While providing regular breaks for team members is important, it is not the primary purpose of closed-loop communication during CPR.
B) Correct. The primary purpose of closed-loop communication in a CPR team is to ensure that team members understand their roles and responsibilities clearly. It involves repeating back and confirming instructions to promote effective teamwork and prevent errors.
C) Incorrect. Closed-loop communication primarily focuses on intra-team communication to coordinate resuscitation efforts efficiently. Informing bystanders is important, but it is not the primary purpose of closed-loop communication.
D) Incorrect. Reporting resuscitation outcomes to the hospital administration is not the primary purpose of closed-loop communication during CPR. Its focus is on effective communication within the resuscitation team.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While the team leader plays a crucial role in providing direction, making all decisions independently can hinder effective team dynamics. Collaboration and input from team members are essential for optimal outcomes.
B) Incorrect. While delegation is important, expecting the team leader to delegate all tasks without involvement from other team members does not promote effective team dynamics. Communication and coordination are essential.
C) Correct. Encouraging open communication and input from all team members fosters effective team dynamics during CPR. Each team member brings valuable insights and skills to contribute to the resuscitation efforts.
D) Incorrect. While maintaining a calm demeanor is important, the team leader should involve other team members in decision-making and communication. Effective team dynamics rely on collaborative efforts.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While verbal communication is crucial during CPR, relying solely on verbal communication may not be sufficient for accurate information exchange, especially in high-stress situations.
B) Correct. CPR teams use both verbal and written communication for a comprehensive understanding of the resuscitation plan. Verbal communication allows for real-time updates, while written communication, such as documentation and checklists, helps ensure critical information is conveyed and understood.
C) Incorrect. Hand signals and nonverbal cues can be valuable additions to communication during CPR, especially in noisy environments or when verbal communication is challenging.
D) Incorrect. While electronic devices can be used for communication, they may not be practical or necessary during CPR. Verbal and written communication are the primary modes of communication in such situations.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While task assignment is an essential aspect of leadership, this example does not demonstrate closed-loop communication, which involves feedback and confirmation from the team member.
B) Correct. In closed-loop communication, the team leader gives instructions, and the team member provides confirmation once the task is completed. This process ensures clear communication and understanding between the team leader and team member.
C) Incorrect. Closed-loop communication involves two-way communication with feedback. In this example, the team leader is not seeking input or feedback from team members.
D) Incorrect. Closed-loop communication involves active engagement and acknowledgment between the team leader and team members. In this example, the team leader expects acknowledgment or response from team members.
Questions
Leukemia
A client asks the nurse, "What is leukemia?" How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia does not primarily affect the lymph nodes. It is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow, where abnormal white blood cells are produced.
B) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not characterized by the overproduction of platelets. Platelets are involved in blood clotting, and their overproduction is not a feature of leukemia.
C) This choice is correct. Leukemia is a type of cancer characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal white blood cells in the bone marrow. These abnormal cells then enter the bloodstream, crowding out healthy blood cells and impairing normal blood cell function.
D) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not an autoimmune disorder. It is a cancerous condition involving abnormal white blood cell growth.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because chronic leukemia can affect both children and adults, not just children and young adults.
B) This choice is incorrect because chronic leukemia progresses more slowly than acute leukemia and does not typically require immediate treatment.
C) This choice is correct. Chronic leukemia is characterized by the overproduction of mature and functional white blood cells. Unlike acute leukemia, the abnormal cells in chronic leukemia are more developed and functional, but they may not function correctly, leading to an accumulation of these cells in the blood.
D) This choice is incorrect because chronic leukemia usually presents with milder symptoms compared to acute leukemia. Hospitalization is not typically required unless complications arise.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not always caused by inherited genetic mutations. While genetic factors can contribute to the development of some types of leukemia, it is not the only cause.
B) This choice is incorrect because there are known genetic links to certain types of leukemia. For example, some forms of leukemia, such as chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), are associated with specific genetic mutations.
C) This choice is incorrect because genetic factors and environmental factors can both play a role in the development of leukemia. Some cases may be influenced more by genetic factors, while others may be influenced more by environmental factors.
D) This choice is correct. Leukemia can have various causes, including genetic mutations, exposure to certain environmental factors (e.g., radiation, certain chemicals), and viral infections. While some cases may have a genetic basis, others may be triggered by environmental factors or have an unknown cause.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not a contagious disease. It cannot spread from person to person through direct contact.
B) This choice is correct. Leukemia is not contagious. It is a type of cancer caused by abnormal white blood cells in the bone marrow and blood. It cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
C) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not contagious, even if the person has a weakened immune system. It is not a communicable disease.
D) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not transmitted through blood transfusions. Blood transfusions involve screened and tested blood products, and leukemia cannot be passed on through this process.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because unexplained weight gain is not a common symptom of leukemia. Weight loss may be more typical in some cases.
B) This choice is correct. Easy bruising and bleeding are common manifestations of leukemia due to a decreased number of healthy blood cells and platelets, which are responsible for clotting.
C) This choice is correct. Persistent fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of leukemia. Leukemia can lead to a decrease in normal blood cells, causing anemia and leading to fatigue and weakness.
D) This choice is correct. Leukemia can weaken the immune system, making the person more susceptible to infections, leading to frequent infections and fever.
E) This choice is correct. Leukemia can cause the enlargement of lymph nodes, leading to painful and swollen lymph nodes.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while a complete blood count (CBC) is an important initial screening test for leukemia, it alone is not definitive for diagnosis. A CBC may show abnormal levels of blood cells, prompting further investigation, including a bone marrow biopsy.
B) This choice is incorrect because a urinalysis is not used to diagnose leukemia. It is a test used to evaluate kidney function and detect urinary abnormalities.
C) This choice is incorrect because a chest X-ray is not a definitive diagnostic tool for leukemia. It is primarily used to assess the lungs and chest organs for conditions such as pneumonia or tumors.
D) This choice is correct. A bone marrow biopsy is a definitive diagnostic tool to confirm leukemia. In this procedure, a small sample of bone marrow is taken from the hipbone or breastbone and examined under a microscope to determine if leukemia cells are present. It allows for the identification of abnormal cells in the bone marrow, helping to establish the diagnosis and type of leukemia.
A nurse is providing care for a client undergoing treatment for leukemia. The client develops neutropenia. What is the nurse's priority intervention?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because administering pain medication for bone pain is important for the client's comfort, but it is not the priority in this situation. Neutropenia is characterized by a low neutrophil count, which can lead to an increased risk of infection.
B) This choice is incorrect because while monitoring for signs of bleeding or bruising is essential for a client with thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), it is not the priority in this scenario. Neutropenia increases the risk of infection, which is the primary concern.
C) This choice is correct. Implementing strict isolation precautions is the priority for a client with neutropenia. Neutropenia results in a decreased ability to fight off infections, so measures to prevent exposure to potential pathogens are crucial in reducing the risk of infection.
D) This choice is incorrect because avoiding invasive procedures and injections is a precaution for clients with thrombocytopenia, not specifically neutropenia. While both conditions involve low blood cell counts, the risk of infection is the primary concern in neutropenia.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia does not primarily affect the lymph nodes. It is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow, where abnormal white blood cells are produced.
B) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not characterized by the overproduction of platelets. Platelets are involved in blood clotting, and their overproduction is not a feature of leukemia.
C) This choice is correct. Leukemia is a type of cancer characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal white blood cells in the bone marrow. These abnormal cells then enter the bloodstream, crowding out healthy blood cells and impairing normal blood cell function.
D) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not an autoimmune disorder. It is a cancerous condition involving abnormal white blood cell growth.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not limited to just one type. There are different subtypes of leukemia, including acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), among others.
B) This choice is correct. Leukemia can be broadly classified into two main types: acute leukemia, which progresses rapidly and requires immediate treatment, and chronic leukemia, which progresses more slowly.
C) This choice is incorrect because the classification of leukemia is not solely based on age. Leukemia can occur in both children and adults.
D) This choice is incorrect because the classification of leukemia does not involve solid tumors. Leukemia is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow, characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal white blood cells.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because acute leukemia is characterized by a rapid onset and fast progression of symptoms. It requires immediate treatment due to its aggressive nature.
B) This choice is correct. Acute leukemia is characterized by the uncontrolled and rapid proliferation of abnormal white blood cells in the bone marrow, which leads to a high accumulation of these immature cells in the bloodstream.
C) This choice is incorrect because, in general, acute leukemia has a lower survival rate compared to chronic leukemia. Acute leukemia requires immediate and aggressive treatment, and the prognosis depends on various factors, including the subtype and individual response to therapy.
D) This choice is incorrect because acute leukemia is not indolent or slow-growing. It progresses rapidly and can have a significant impact on blood cell counts and overall health.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because chronic leukemia can affect both children and adults, not just children and young adults.
B) This choice is incorrect because chronic leukemia progresses more slowly than acute leukemia and does not typically require immediate treatment.
C) This choice is correct. Chronic leukemia is characterized by the overproduction of mature and functional white blood cells. Unlike acute leukemia, the abnormal cells in chronic leukemia are more developed and functional, but they may not function correctly, leading to an accumulation of these cells in the blood.
D) This choice is incorrect because chronic leukemia usually presents with milder symptoms compared to acute leukemia. Hospitalization is not typically required unless complications arise.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a bone marrow biopsy is not performed to remove a tumor mass. The purpose of the procedure is to obtain a sample of bone marrow tissue for diagnostic evaluation.
B) This choice is incorrect because assessing the presence of circulating cancer cells in the bloodstream is typically done through a blood test, not a bone marrow biopsy. The biopsy provides direct information about the condition of the bone marrow.
C) This choice is incorrect because evaluating the overall blood cell count and differential is typically done through a complete blood count (CBC) test, not a bone marrow biopsy. The biopsy provides more detailed information about the bone marrow and its cellular composition.
D) This choice is correct. The primary purpose of a bone marrow biopsy is to obtain a sample of bone marrow tissue for examination under a microscope. This allows healthcare professionals to assess the presence of abnormal cells, determine the type and extent of leukemia, and guide treatment decisions.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because stem cell transplantation is not the primary treatment for all cases of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It may be considered in certain cases, but targeted therapy is the standard first-line treatment for most patients with CML.
B) This choice is incorrect because while chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used in some leukemia treatments, they are not the main treatments for CML. Targeted therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors is the standard approach for CML management.
C) This choice is correct. The mainstay of treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is targeted therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). TKIs are oral medications that specifically target the abnormal protein produced by the BCR-ABL gene, which drives the overproduction of white blood cells in CML. These medications are highly effective and have revolutionized the treatment of CML, leading to improved outcomes for many patients.
D) This choice is incorrect because watchful waiting and supportive care may be considered for certain low-risk or asymptomatic cases of CML, but it is not the primary treatment approach. Targeted therapy with TKIs is the standard treatment for most patients with CML.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because chemotherapy for acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) usually lasts much longer than a few weeks. ALL treatment consists of several phases, and the overall duration can extend over several years.
B) This choice is correct. Treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) typically involves multiple phases, including induction, consolidation, and maintenance therapy. The induction phase aims to achieve remission, the consolidation phase aims to eliminate any remaining cancer cells, and the maintenance phase aims to prevent relapse and keep the leukemia in remission. Overall, the treatment can extend over several years, depending on the client's response to therapy and risk factors.
C) This choice is incorrect because it does not accurately reflect the standard treatment approach for ALL. Clients with ALL do not typically switch from chemotherapy to radiation therapy after a few days.
D) This choice is incorrect because ALL treatment typically involves multiple rounds of chemotherapy, not just a single round. The goal is to achieve long-term remission and prevent relapse, which requires a more comprehensive treatment approach over an extended period.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a family history of diabetes is not a known risk factor for leukemia. While genetics can play a role in some leukemia cases, diabetes is not associated with leukemia development.
B) This choice is incorrect because exposure to asbestos is a risk factor for certain types of cancer, such as lung cancer and mesothelioma, but it is not a primary risk factor for leukemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because while autoimmune disorders can affect the immune system, they are not a known risk factor for leukemia.
D) This choice is correct. A previous diagnosis of lymphoma is a significant risk factor for developing leukemia. Lymphoma and leukemia are both types of blood cancers, and individuals with a history of lymphoma have an increased risk of developing leukemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because there is no strong evidence to support smoking as a major risk factor for leukemia. Smoking is primarily associated with lung cancer and other respiratory conditions.
B) This choice is incorrect because while smoking is associated with other types of cancer, such as lung, throat, and mouth cancers, it is not definitively linked to leukemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because while smoking can increase the risk of certain cancers, its link to leukemia remains uncertain. Research on this topic has not provided conclusive evidence of a significant association between smoking and leukemia development.
D) This choice is correct. The link between smoking and leukemia is still uncertain and not well-established. While smoking is a known risk factor for several types of cancer, its specific role in leukemia development requires further study.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a history of frequent dental cavities is not a known risk factor for leukemia.
B) This choice is incorrect because allergies to pollen and pet dander are not associated with an increased risk of leukemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because recurrent urinary tract infections are not known to be a risk factor for leukemia.
D) This choice is correct. Previous treatment with chemotherapy and radiation is a significant risk factor for developing leukemia. Certain chemotherapeutic agents and radiation therapy can damage healthy blood-forming cells in the bone marrow, potentially leading to the development of leukemia later on. This type of leukemia is often referred to as secondary or treatment-related leukemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a sedentary lifestyle is not a known risk factor for leukemia. Physical inactivity is associated with other health conditions but not leukemia.
B) This choice is incorrect because having a vegetarian diet is not a risk factor for developing leukemia.
C) This choice is correct. A history of tobacco use is a potential risk factor for leukemia. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of various cancers, and while the link to leukemia is not as clear as with other cancers, it is still considered a possible risk factor.
D) This choice is incorrect because a family history of diabetes is not a known risk factor for leukemia.
Explanation
A) This statement is correct. Having a family history of leukemia is considered a risk factor for developing the disease, particularly in cases of familial or hereditary leukemia.
B) This statement is correct. Exposure to high levels of ionizing radiation, such as during radiation therapy or nuclear accidents, is a well-known risk factor for leukemia.
C) This statement is correct. Individuals with Down syndrome have an increased risk of developing leukemia, particularly acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
D) This statement is incorrect. While physical activity is beneficial for overall health and may reduce the risk of various cancers, there is no evidence to suggest that being physically active specifically reduces the risk of developing leukemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because exposure to benzene is indeed a known risk factor for developing leukemia. Benzene is a chemical compound found in certain industrial settings and can increase the risk of developing leukemia, particularly acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
B) This choice is correct. Exposure to benzene is associated with an increased risk of leukemia. Benzene is a known carcinogen and can cause damage to blood-forming cells in the bone marrow, leading to the development of leukemia in some individuals.
C) This choice is incorrect because while benzene exposure is associated with an increased risk of leukemia, it is not primarily linked to skin cancer.
D) This choice is incorrect because benzene exposure can affect individuals of all ages, not just children. It is a risk factor for leukemia development in adults as well as children.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia does not result from an overproduction of platelets. Leukemia involves an overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
B) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not caused by the body's immune system attacking healthy white blood cells. Instead, it involves the uncontrolled growth of abnormal white blood cells.
C) This choice is correct. Leukemia is characterized by genetic mutations in the bone marrow cells, particularly in the stem cells that produce white blood cells. These mutations lead to uncontrolled growth and proliferation of abnormal white blood cells, interfering with the normal production of other blood cells.
D) This choice is incorrect because an imbalance of red blood cells would not trigger the overproduction of white blood cells. Leukemia is specifically a disorder of white blood cell proliferation.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because AML is not characterized by the overproduction of immature lymphocytes. It involves the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal myeloid cells in the bone marrow.
B) This choice is incorrect because AML does not cause abnormal proliferation of red blood cells. Anemia may occur as a result of AML due to the displacement of normal blood-forming cells in the bone marrow.
C) This choice is correct. AML is a type of leukemia that arises from genetic mutations in the myeloid stem cells. These mutations lead to uncontrolled growth and accumulation of abnormal myeloid cells, including granulocytes, monocytes, and platelets.
D) This choice is incorrect because the abnormal growth of plasma cells leading to the production of abnormal antibodies is characteristic of multiple myeloma, not AML.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because CLL specifically involves the overproduction of abnormal lymphocytes, not myeloid cells. Myeloid cells are affected in other types of leukemia, such as AML.
B) This choice is incorrect because CLL is a chronic and indolent type of leukemia. It has a slow onset and progresses slowly over time, unlike some other leukemias that may have a more rapid course.
C) This choice is correct. In CLL, abnormal lymphocytes, mainly B-lymphocytes, accumulate in the bone marrow and interfere with the production of other blood cells, including red blood cells, platelets, and other white blood cells.
D) This choice is incorrect because CLL does not involve a genetic mutation leading to uncontrolled growth of red blood cells. That description is more characteristic of polycythemia vera, a different type of blood disorder.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because ALL does not result in the overproduction of red blood cells. It primarily affects lymphocytes, not red blood cells.
B) This choice is incorrect because ALL involves the overproduction of abnormal lymphocytes, not normal white blood cells. These abnormal lymphocytes crowd out normal cells.
C) This choice is correct. In ALL, the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal lymphocytes leads to the overcrowding of the bone marrow. As a result, normal bone marrow cells, including red blood cells, platelets, and other white blood cells, are suppressed, leading to various cytopenias.
D) This choice is incorrect because ALL does not cause the bone marrow to become fibrous and unable to produce any blood cells. That description is more characteristic of myelofibrosis, a different bone marrow disorder.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia arises from the uncontrolled growth and division of abnormal blood cells, not normal blood cells. These abnormal cells disrupt the normal functioning of the blood and bone marrow.
B) This choice is incorrect because while cancerous cells may infiltrate and replace healthy tissues in other types of cancer, leukemia primarily affects the bone marrow and blood, not other organs like the liver and lungs.
C) This choice is incorrect because while leukemia does involve genetic mutations, the formation of abnormal blood cells primarily occurs within the bone marrow, not in the lymph nodes.
D) This choice is correct. The pathophysiology of leukemia involves the abnormal proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow stem cells. These cells undergo genetic mutations, leading to the development of leukemia and the production of abnormal blood cells.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia does not lead to the increased production of normal red blood cells. Instead, it causes the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
B) This choice is incorrect because leukemia does not lead to the accumulation of normal platelets in the blood. Thrombocytopenia, or low platelet count, is common in leukemia due to the suppression of normal platelet production in the bone marrow.
C) This choice is correct. In leukemia, the proliferation of abnormal white blood cells crowds out and suppresses the normal bone marrow stem cells responsible for producing red blood cells, platelets, and other white blood cells. This suppression leads to anemia and thrombocytopenia.
D) This choice is incorrect because while cancerous cells may infiltrate healthy tissues in other types of cancer, leukemia primarily affects the bone marrow and blood, not other organs or tissues.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because the lymphatic system does not filter and remove abnormal blood cells in leukemia. The role of the lymphatic system is primarily related to the circulation of lymph fluid and the immune response, not the removal of abnormal blood cells.
B) This choice is incorrect because the lymphatic system is not responsible for producing and releasing abnormal white blood cells in leukemia. Leukemia originates from the bone marrow, not the lymphatic system.
C) This choice is correct. Leukemia is primarily a disorder of the bone marrow and blood. It does not directly involve the lymphatic system, which is responsible for carrying lymph fluid and supporting the body's immune function.
D) This choice is incorrect because while cancerous cells may infiltrate other organs and tissues in other types of cancer, leukemia primarily affects the bone marrow and blood, not the lymphatic system.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because fatigue and weakness are common symptoms in leukemia, but they are not specific enough to confirm the diagnosis on their own.
B) This choice is correct. Night sweats and fever are classic symptoms of leukemia, especially in cases of acute leukemia. These symptoms are related to the presence of abnormal white blood cells in the bloodstream and their impact on the body's immune response.
C) This choice is incorrect because unexplained weight gain is not a typical symptom of leukemia. Weight loss is more commonly associated with this condition due to decreased appetite and increased energy expenditure.
D) This choice is incorrect because persistent headaches are not specific to leukemia and may indicate other underlying health issues.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because swollen lymph nodes are more characteristic of chronic leukemia, not acute leukemia like AML.
B) This choice is correct. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is commonly associated with enlarged lymph nodes due to the accumulation of abnormal lymphocytes in these areas. It is a slow-progressing leukemia and often presents with lymphadenopathy.
C) This choice is incorrect because while ALL may involve enlarged lymph nodes, it is more commonly associated with symptoms like fatigue, bleeding, and bone pain.
D) This choice is incorrect because while CML may present with enlarged spleen and liver, it is less likely to cause significant lymphadenopathy compared to CLL.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because increased platelet production would not lead to easy bruising and petechiae. It would, in fact, improve clotting abilities.
B) This choice is incorrect because overproduction of red blood cells would not directly cause easy bruising and petechiae. It may lead to symptoms like fatigue and pallor.
C) This choice is correct. Easy bruising and petechiae are common in leukemia due to a deficiency of platelets and impaired clotting factors in the blood. Leukemia can lead to decreased platelet production and clotting abnormalities, resulting in easy bleeding and bruising.
D) This choice is incorrect because a deficiency of white blood cells would not directly cause easy bruising and petechiae. It might lead to an increased risk of infections.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because bone marrow suppression would lead to decreased production of blood cells but may not directly cause bone pain and tenderness.
B) This choice is incorrect because excessive calcium levels in the blood would not be a common cause of bone pain and tenderness in leukemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because rapid growth of bone tissue would not be a typical cause of bone pain and tenderness in leukemia.
D) This choice is correct. Bone pain and tenderness in leukemia are often caused by the accumulation of leukemic cells in the bones. These abnormal cells infiltrate the bone marrow and bone tissue, leading to pain and tenderness.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because red blood cells are not directly involved in the body's immune response. Decreased red blood cells may cause anemia, but they are not responsible for frequent infections and recurrent fevers.
B) This choice is incorrect because platelets are involved in clotting and do not directly impact the body's immune response.
C) This choice is correct. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell responsible for fighting infections. In leukemia, particularly when neutrophils are affected, the body's ability to fight infections becomes compromised, leading to frequent infections and recurrent fevers.
D) This choice is incorrect because lymphocytes, specifically B-lymphocytes, are affected in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). While CLL can lead to increased susceptibility to infections, neutrophil dysfunction is more commonly associated with recurrent infections in leukemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because impaired bone density would not directly cause ecchymoses on the skin. It might lead to an increased risk of fractures, but not bruising.
B) This choice is correct. Ecchymoses (bruises) of varying sizes with minimal trauma are common in leukemia due to a deficiency of platelets and impaired clotting factors in the blood. Leukemia can lead to decreased platelet production and clotting abnormalities, resulting in easy bleeding and bruising.
C) This choice is incorrect because increased production of platelets would improve clotting abilities and reduce the risk of ecchymoses.
D) This choice is incorrect because elevated levels of red blood cells would not directly cause ecchymoses on the skin. It may lead to other symptoms like increased blood viscosity.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because impaired wound healing is not a typical cause of enlarged gums and bleeding in leukemia.
B) This choice is incorrect because a hyperactive immune response is not directly related to oral symptoms in leukemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because overproduction of saliva is not a typical cause of enlarged gums and bleeding in leukemia.
D) This choice is correct. Enlarged gums (gingival hypertrophy) and bleeding from the gums are characteristic oral symptoms of acute leukemia. Leukemic cells can infiltrate the gums and oral tissues, leading to inflammation, bleeding, and gum enlargement.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a complete blood count (CBC) provides information about the number of blood cells, but it does not directly assess the bone marrow for leukemia.
B) This choice is correct. Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy involve the collection of bone marrow samples from the sternum or hip bone. These samples are then analyzed to determine the presence of leukemia cells, assess cell morphology, and determine the type of leukemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because flow cytometry analysis is used to identify specific markers on the surface of cells and can aid in diagnosing and classifying leukemia. However, it is not the primary test used to assess the bone marrow directly.
D) This choice is incorrect because magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is not commonly used to assess bone marrow in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. A lumbar puncture is performed to assess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for the presence of leukemic cells in cases where leukemia may have spread to the central nervous system. This procedure helps determine if the client requires specific treatment to target leukemia in the CNS.
B) This choice is incorrect because a lumbar puncture is not primarily used to evaluate liver and kidney function.
C) This choice is incorrect because measuring blood glucose levels is not the primary purpose of a lumbar puncture.
D) This choice is incorrect because determining the client's platelet count is not the primary purpose of a lumbar puncture. Platelet counts are typically obtained through a blood test.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because an elevated red blood cell count is not a typical finding in leukemia. Leukemia is characterized by the overproduction of white blood cells, not red blood cells.
B) This choice is correct. Leukemia is associated with an elevated white blood cell count, particularly an abnormal increase in blast cells, which are immature cells indicative of leukemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because an elevated platelet count is not a typical finding in leukemia. Leukemia is more commonly associated with thrombocytopenia, which is a decreased platelet count.
D) This choice is incorrect because the laboratory report indicating elevated levels of blast cells in the peripheral blood supports the suspicion of leukemia, not the blast cells' presence in the bone marrow.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because assessing bone density and strength is not the primary purpose of a CT scan in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia.
B) This choice is correct. A CT scan is commonly used to identify enlarged lymph nodes and organs, which can occur in leukemia as a result of cancerous cell proliferation and infiltration into the lymphatic system and other organs.
C) This choice is incorrect because measuring lung capacity is not the primary purpose of a CT scan in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because monitoring cardiac function is not the primary goal of a CT scan in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because flow cytometry analysis is not primarily used to assess the client's heart function.
B) This choice is incorrect because determining the client's blood type is not the primary purpose of flow cytometry analysis in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia.
C) This choice is correct. Flow cytometry analysis is a specialized laboratory technique used to classify the type of leukemia and its subtype based on specific cell markers present on the surface of leukemic cells. This information helps guide the appropriate treatment plan.
D) This choice is incorrect because evaluating the client's kidney function is not the primary purpose of flow cytometry analysis in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a bone marrow biopsy is not primarily performed to assess the client's platelet count. Platelet counts are typically obtained through a blood test.
B) This choice is incorrect because evaluating the effectiveness of chemotherapy is not the primary reason for performing a bone marrow biopsy in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia. The biopsy is performed to determine the presence of cancerous cells in the bone marrow and aid in diagnosing leukemia.
C) This choice is correct. A bone marrow biopsy involves the collection of bone marrow samples to determine the presence of cancerous cells and assess cell morphology in the bone marrow. This information is crucial in diagnosing leukemia and determining the appropriate treatment plan.
D) This choice is incorrect because measuring the client's bone density is not the primary reason for performing a bone marrow biopsy.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a cytogenetic analysis is not primarily used to assess the client's immune response.
B) This choice is incorrect because determining the client's blood type is not the primary goal of a cytogenetic analysis in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia.
C) This choice is correct. Cytogenetic analysis is a laboratory test that identifies specific genetic abnormalities, such as chromosomal rearrangements, deletions, or mutations, in the leukemic cells. These genetic findings are essential for diagnosing specific types of leukemia, determining prognosis, and guiding treatment decisions.
D) This choice is incorrect because evaluating the client's liver function is not the primary goal of a cytogenetic analysis in the diagnostic evaluation of leukemia.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because chemotherapy is not a surgical procedure and does not involve the removal of tumor masses.
B) This choice is incorrect because while immunotherapy may be used as a treatment approach in some cases, the primary goal of chemotherapy is to directly destroy leukemia cells.
C) This choice is correct. The primary goal of chemotherapy in leukemia treatment is to use powerful medications to kill or inhibit the growth of leukemia cells, leading to remission.
D) This choice is incorrect because pain relief and symptom management are not the primary goals of chemotherapy in leukemia treatment.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because stem cells used in transplantation are typically not extracted from the client's cancerous tissues.
B) This choice is correct. In a stem cell transplant, stem cells are collected from the bone marrow of a matched donor (allogeneic transplant) or the client themselves (autologous transplant). These stem cells are then infused into the client's bloodstream to replace the damaged bone marrow and produce healthy blood cells.
C) This choice is incorrect because stem cells used in transplantation are not taken from a tumor.
D) This choice is incorrect because stem cells used in transplantation are not harvested from the client's peripheral blood.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because chemotherapy may cause a decreased platelet count, leading to a risk of bleeding, rather than increased blood clotting and thrombosis.
B) This choice is incorrect because chemotherapy does not typically cause elevated blood pressure and hypertension.
C) This choice is correct. Nausea, vomiting, and hair loss are common side effects of chemotherapy due to its effect on rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles and cells lining the digestive tract.
D) This choice is incorrect because excessive bleeding and hemorrhage are not common side effects of chemotherapy in leukemia treatment.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because the distinction between targeted therapy and chemotherapy is not based on whether the medications are derived from natural or synthetic sources.
B) This choice is correct. Targeted therapy is designed to selectively target leukemia cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells and reducing side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy, which affects both cancerous and healthy cells.
C) This choice is incorrect because the method of administration (hospitalization or outpatient) can vary for both targeted therapy and chemotherapy, depending on the specific drug and treatment plan.
D) This choice is incorrect because targeted therapy and chemotherapy are used in various stages of leukemia treatment, depending on the type and stage of the disease.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a stem cell transplant is primarily used to replace the damaged bone marrow and restore normal blood cell production, but it is not a specific treatment for anemia.
B) This choice is correct. A blood transfusion involves infusing healthy red blood cells into the client's bloodstream to address anemia and improve oxygen-carrying capacity.
C) This choice is incorrect because radiation therapy is primarily used to target and destroy cancer cells, not to address anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because immune checkpoint inhibitors are a type of immunotherapy used to enhance the body's immune response against cancer cells, but they are not a specific treatment for anemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because replacing damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells is the primary goal of a stem cell transplant, not radiation therapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because while radiation therapy may be used to reduce the size of leukemia masses and induce remission in some cases, it is not typically used to eliminate all leukemia cells throughout the body.
C) This choice is correct. Radiation therapy is used to target and destroy cancer cells in specific areas where leukemia is localized, such as in the brain or other parts of the body. It can be used in combination with other treatment modalities.
D) This choice is incorrect because enhancing the body's immune response against leukemia is the goal of immunotherapy, not radiation therapy.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because stimulating the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow is not the primary purpose of immunotherapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because suppressing the immune system is not the primary purpose of immunotherapy in leukemia treatment. In fact, immunotherapy aims to enhance the immune system's ability to recognize and target cancer cells.
C) This choice is correct. Immunotherapy is used to boost the body's natural defense mechanisms, particularly the immune system, to better recognize and attack leukemia cells.
D) This choice is incorrect because inhibiting the growth of cancerous tumors is not the primary purpose of immunotherapy. Other treatment approaches, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapy, may be used for this purpose.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because mild fatigue and weakness are common symptoms in leukemia and may be expected in the client's condition.
B) This choice is correct. Bruising and petechiae are signs of decreased platelet count and potential clotting abnormalities, which can lead to bleeding complications. Immediate intervention is necessary to prevent serious bleeding.
C) This choice is incorrect because a weight loss of 2 pounds in a month is not alarming and can be caused by various factors unrelated to leukemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because occasional headaches and dizziness are not immediate concerns in leukemia and may have other causes.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while aerobic exercise is beneficial for overall health, it may not directly protect the client from infection in the context of low WBC count during chemotherapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because during chemotherapy, live vaccines should be avoided as they can pose a risk to immunocompromised clients with low WBC counts.
C) This choice is correct. Placing the client in a private room with negative pressure helps reduce the risk of exposure to infectious agents, especially in immunocompromised clients with low WBC counts who are at higher risk of infection.
D) This choice is incorrect because limiting the number of healthcare providers entering the client's room may be beneficial to reduce the risk of exposure to potential infections, but placing the client in a private room with negative pressure is a more comprehensive measure.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush helps prevent gum bleeding and trauma to the oral mucosa, reducing the risk of infection in clients with low platelet counts.
B) This choice is incorrect because during leukemia treatment, outdoor activities may expose the client to potential sources of infection. It is better to avoid crowded places and maintain good hand hygiene.
C) This choice is correct. Raw fruits and vegetables may carry bacteria and pathogens, and the client with leukemia, particularly those undergoing chemotherapy, is at a higher risk of infection. It is advised to thoroughly wash and cook fruits and vegetables before consumption.
D) This choice is incorrect because although emotional support from friends and family is essential, it is crucial to limit the number of visitors to reduce the risk of exposure to potential infections.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because peripheral neuropathy is more commonly associated with certain chemotherapy drugs, not radiation therapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because nausea and vomiting are common side effects of chemotherapy, not radiation therapy.
C) This choice is incorrect because alopecia (hair loss) is more commonly associated with chemotherapy, not radiation therapy.
D) This choice is correct. Neutropenia, which is a decrease in the number of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell), is a potential side effect of radiation therapy. This can increase the client's risk of infection, and regular monitoring of blood counts is necessary during treatment.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because alcohol-based mouthwash can further irritate the mucosal lining and worsen mucositis. It should be avoided.
B) This choice is incorrect because ice chips and cold beverages may provide temporary relief, but pain medication is the priority intervention to manage severe mucositis and alleviate discomfort.
C) This choice is correct. Administering prescribed pain medications, such as topical analgesics or systemic pain relief, is essential in managing the severe pain associated with mucositis.
D) This choice is incorrect because spicy foods can aggravate mucositis and should be avoided to prevent further irritation of the mucosal lining.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because gentle stretching exercises are generally safe and do not significantly increase the risk of bleeding in clients with low platelet counts.
B) This choice is incorrect because deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis, such as leg exercises and anti-embolism stockings, is essential to prevent blood clots but is not directly related to bleeding risk.
C) This choice is incorrect because using a soft-bristled toothbrush helps prevent gum bleeding and trauma to the oral mucosa but does not address the risk of bleeding from other areas.
D) This choice is correct. Vigorous nose blowing can lead to trauma to the nasal mucosa and increase the risk of bleeding, especially in clients with low platelet counts who are prone to bleeding episodes.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because mild redness and tenderness at the IV site are common findings and may indicate a local inflammatory response to the IV infusion.
B) This choice is incorrect because a temperature of 99.8°F (37.7°C) is slightly elevated but not a critical finding. The client's healthcare provider should be notified if the temperature is significantly elevated or if other symptoms are present.
C) This choice is incorrect because a small amount of blood in the IV tubing may be due to a minor infiltration or a common occurrence during IV administration. However, the nurse should monitor the IV site and flow rate closely.
D) This choice is correct. Crackles and decreased breath sounds on auscultation may indicate fluid overload or pulmonary edema, which could be a severe complication of IV chemotherapy. The healthcare provider should be notified immediately to assess the client's respiratory status and provide appropriate intervention.
Questions
A nurse is providing education to a client diagnosed with leukemia who asks, "What causes leukemia?" How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because leukemia is not primarily caused by exposure to infectious agents. While some viral infections may increase the risk of certain types of leukemia, infectious agents are not the main cause.
B) This choice is correct. The exact cause of leukemia is not fully understood, and it can vary among individuals. It is believed to result from a combination of genetic mutations and environmental factors, but no single cause has been identified for all cases.
C) This choice is incorrect because while genetic mutations can play a role in the development of some types of leukemia, they are not the only cause. Environmental factors and other unknown factors also contribute to leukemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because while environmental toxins and pollution may be risk factors for some individuals, they are not the leading factors in all cases of leukemia.
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Avoiding sitting for long periods during long flights is a recommended preventive measure for individuals at risk of DVT. Prolonged immobility can increase the risk of blood clot formation in the legs during travel.
B) This choice is incorrect. Stopping prescribed anticoagulant medication increases the risk of blood clot formation and should never be done without the guidance of a healthcare provider. Anticoagulants are often prescribed to prevent or treat DVT and reduce the risk of clot progression or recurrence.
C) This choice is correct. Wearing compression stockings, as directed by a healthcare provider, can help prevent DVT by improving blood flow in the legs and reducing the risk of clot formation.
D) This choice is correct. Staying hydrated and drinking plenty of water can help prevent DVT by maintaining adequate blood volume and circulation. Dehydration can increase the risk of blood clot formation.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because auscultating the lungs for crackles is not directly related to confirming the presence of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Lung auscultation may be performed to assess for potential complications of DVT, such as pulmonary embolism.
B) This choice is correct. Homans' sign is a clinical test used to assess for the presence of DVT. The nurse flexes the client's knee and gently dorsiflexes the foot. A positive Homans' sign is indicated by calf pain or discomfort during dorsiflexion and may suggest the presence of a blood clot in the deep veins of the leg.
C) This choice is incorrect because measuring blood pressure in both arms is not a specific assessment for deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It may be done as part of a routine assessment but does not confirm the presence of DVT.
D) This choice is incorrect because performing a capillary refill test is not specific to DVT assessment. Capillary refill is a measure of peripheral perfusion and may be useful in assessing overall circulatory status, but it does not directly confirm the presence of DVT.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while relieving leg pain and swelling is an important aspect of DVT treatment, the primary goal is to prevent the clot from dislodging and causing a pulmonary embolism or other complications.
B) This choice is correct. The primary goal of DVT treatment is to prevent the clot from dislodging and traveling to the lungs, where it can cause a potentially life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulant therapy and other interventions are used to stabilize the clot and prevent its migration.
C) This choice is incorrect because eliminating the risk factors for DVT is not the primary goal of treatment for a client who already has DVT. Preventing clot progression and complications take precedence over addressing risk factors at this stage.
D) This choice is incorrect because while administering anticoagulant therapy is a common treatment for DVT, it is a specific intervention rather than the primary goal. Anticoagulants help prevent the clot from growing and reduce the risk of embolism.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Encouraging active range of motion exercises helps prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) by promoting blood flow and reducing stasis in the veins. Moving the legs and ankles regularly helps prevent clot formation in immobilized clients.
B) This choice is incorrect because low-dose aspirin is not specifically indicated for preventing DVT. While aspirin may have some antiplatelet effects, it is not the primary preventive measure for DVT in high-risk clients.
C) This choice is incorrect because applying a heating pad to the affected leg is not a preventive measure for DVT. Heat application is not recommended for DVT prevention and could cause burns or injury.
D) This choice is incorrect because providing a soft mattress for the client's bed does not directly prevent DVT. The focus should be on encouraging movement and mobility to prevent DVT in clients at risk.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Warfarin is an anticoagulant that works by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. Clients on warfarin should be advised to avoid significant fluctuations in vitamin K intake, as found in foods like leafy greens and other green vegetables, to maintain consistent anticoagulation levels.
B) This choice is incorrect because discontinuing warfarin suddenly can increase the risk of blood clot formation and other complications. Clients should follow their healthcare provider's instructions for warfarin dosing and management.
C) This choice is incorrect because taking warfarin with grapefruit juice is not recommended and may not improve medication absorption. Grapefruit juice can interfere with the metabolism of some medications, but it is not a recommended method for enhancing warfarin absorption.
D) This choice is incorrect because clients on warfarin should be cautious about taking over-the-counter pain medications, especially nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can increase the risk of bleeding. Clients should consult their healthcare provider before taking any new medications while on warfarin.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because age and family history are non-modifiable risk factors for DVT. While they may increase the risk, they cannot be changed or controlled by the client.
B) This choice is incorrect because stopping prescribed anticoagulant medication is not recommended and may increase the risk of DVT. Anticoagulants are often prescribed to prevent or treat DVT and should not be discontinued without healthcare provider guidance.
C) This choice is correct. Smoking is a modifiable risk factor for DVT, and quitting smoking can reduce the risk of blood clot formation and other cardiovascular complications.
D) This choice is incorrect because while the client may have difficulty controlling a sedentary lifestyle, it is still considered a modifiable risk factor for DVT. Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce the risk of blood clot formation.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a family history of high cholesterol is not directly related to DVT risk. While high cholesterol may contribute to other cardiovascular conditions, it is not a primary risk factor for DVT.
B) This choice is incorrect because a history of asthma is not a direct risk factor for DVT. Asthma is a respiratory condition and is not significantly associated with blood clot formation.
C) This choice is correct. Prolonged immobility during long flights, especially in cramped spaces, is a known risk factor for DVT. This condition is often referred to as "economy class syndrome" due to its association with long-haul flights in tight seating.
D) This choice is incorrect because the use of medications for diabetes does not directly relate to DVT risk. While some medications may influence blood clotting, diabetes itself is not a primary risk factor for DVT.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Gender is a non-modifiable risk factor for DVT, with women generally having a higher risk than men. Hormonal changes, such as those associated with pregnancy, oral contraceptives, and hormone replacement therapy, can contribute to the increased risk in women.
B) This choice is incorrect because obesity is a modifiable risk factor for DVT, not a non-modifiable one. Clients can work to achieve and maintain a healthy weight to reduce their risk.
C) This choice is incorrect because smoking history is a modifiable risk factor for DVT. Clients can quit smoking to decrease their risk of blood clot formation.
D) This choice is incorrect because a sedentary lifestyle is a modifiable risk factor for DVT. Clients can engage in regular physical activity to reduce their risk.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because DVT is not caused by a bacterial infection in the blood vessels. It is primarily related to the formation of blood clots within the veins due to various risk factors.
B) This choice is incorrect because while injuries may be associated with DVT in some cases, they are not the primary cause. The formation of blood clots in the veins remains the underlying cause.
C) This choice is incorrect because atherosclerosis in the arteries is not the main cause of DVT. Atherosclerosis is a condition that involves the buildup of plaque in the arteries, not the veins.
D) This choice is correct. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is primarily caused by the formation of blood clots within the veins, typically in the lower extremities. These clots can obstruct blood flow and may lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because advanced age is a non-modifiable risk factor for DVT. While age is associated with increased risk, it is not directly related to the client's use of hormonal therapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because male gender is not a risk factor for DVT. Women, particularly those on estrogen-based therapies like hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives, are at higher risk.
C) This choice is incorrect because smoking history is a modifiable risk factor for DVT, not directly related to hormonal therapy. Smoking increases the risk of clot formation and is not specific to the client's use of hormonal therapy.
D) This choice is correct. Estrogen-based hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptives can increase the risk of DVT due to their effect on blood coagulation. Estrogen can increase the production of certain clotting factors, raising the risk of blood clot formation in the veins. It is essential for healthcare providers to weigh the benefits and risks when prescribing hormonal therapy to clients.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because chest pain and shortness of breath are more indicative of a potential pulmonary embolism, a serious complication of DVT. While DVT can lead to a pulmonary embolism, the primary manifestation of DVT is related to the affected limb.
B) This choice is correct. Warmth and redness over the affected area, typically the calf or thigh, are common clinical manifestations of DVT. The warmth is due to the inflammatory response caused by the blood clot formation.
C) This choice is incorrect because pedal edema and bilateral leg pain are non-specific findings and can be caused by various conditions, not just DVT. They are not specific enough to diagnose DVT on their own.
D) This choice is incorrect because weak pedal pulses and cool extremities are not typically associated with DVT. These findings suggest potential arterial insufficiency rather than venous thrombosis.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because palpating the pulses in the extremities primarily assesses arterial blood flow, not venous thrombosis. While pulse assessment is essential, it is not the priority for identifying DVT-related manifestations.
B) This choice is correct. Measuring calf and thigh circumference can help identify possible DVT by comparing the affected leg's size to the unaffected one. DVT can cause localized swelling in the affected limb.
C) This choice is incorrect because auscultating the lungs for crackles is not a specific assessment for DVT. Crackles may be present in pulmonary edema, which can be a complication of DVT, but they do not directly assess the presence of a blood clot in the veins.
D) This choice is incorrect because performing a capillary refill test is primarily used to assess peripheral perfusion and is not specific to DVT assessment.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because swelling and redness in the affected leg are common clinical manifestations of DVT but are not specific to detecting potential complications like a pulmonary embolism. The nurse should focus on respiratory and cardiovascular assessments for this purpose.
B) This choice is incorrect because elevated body temperature and chills may indicate an infection but are not specific to detecting potential complications of DVT, such as a pulmonary embolism.
C) This choice is correct. Pleuritic chest pain (sharp chest pain worsened by deep breathing or coughing) and hemoptysis (coughing up blood) are classic clinical manifestations of a pulmonary embolism, a potentially life-threatening complication of DVT.
D) This choice is incorrect because abdominal pain and distension are not typical signs of a pulmonary embolism. Abdominal pain may be related to other causes, such as gastrointestinal issues.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis assesses oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood, primarily used for respiratory and acid-base evaluations, not for confirming DVT.
B) This choice is correct. The D-dimer blood test is a screening test used to detect the presence of blood clot breakdown products in the blood. Elevated levels of D-dimer may suggest the presence of a blood clot, prompting further diagnostic testing for DVT.
C) This choice is incorrect because an electrocardiogram (ECG) primarily assesses the electrical activity of the heart and is not specific to confirming DVT. It may be useful to assess cardiac function in individuals with suspected pulmonary embolism.
D) This choice is incorrect because a chest X-ray is not used to confirm DVT. It is helpful in assessing the lungs and heart, particularly for detecting potential complications of DVT like a pulmonary embolism, but it does not directly diagnose DVT.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while monitoring blood pressure is essential, it is not the priority action for clients on anticoagulant therapy. The primary concern is assessing the client's response to the medication and their risk of bleeding.
B) This choice is correct. Monitoring the client's prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) is crucial in assessing the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy. The PT and INR measure how long it takes the blood to clot and help determine the appropriate dosage of anticoagulants to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.
C) This choice is incorrect because checking the client's blood glucose levels is not directly related to monitoring the response to anticoagulant therapy. Blood glucose monitoring is essential for clients with diabetes but not a priority in this context.
D) This choice is incorrect because evaluating the client's respiratory rate and pattern is not the priority action for monitoring the response to anticoagulant therapy. Respiratory assessment is vital in detecting potential complications like a pulmonary embolism but does not directly assess the client's anticoagulation status.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because venous Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test commonly used to diagnose DVT. However, it is not considered the gold standard due to potential limitations in visualizing small clots and deep veins.
B) This choice is incorrect because the D-dimer blood test is a screening test used to detect the presence of blood clot breakdown products. While it can help rule out DVT when negative, it is not the definitive diagnostic test.
C) This choice is incorrect because magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a sensitive imaging modality but is not considered the gold standard for diagnosing DVT. MRI may be used in specific cases, but contrast venography remains the gold standard.
D) This choice is correct. Contrast venography involves injecting contrast dye into the veins and taking X-ray images to visualize the blood flow and detect any clots. It is considered the gold standard for diagnosing DVT, as it provides direct visualization of the clot and the extent of its involvement.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while the D-dimer blood test is used to rule out DVT in low-risk individuals, the Wells score assessment is typically performed first to assess the client's pretest probability of DVT.
B) This choice is incorrect because magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is not typically used as an initial diagnostic test for DVT. It may be employed in specific cases but is not the first-line test.
C) This choice is incorrect because a complete blood count (CBC) is a general blood test that does not directly assess the risk of DVT. It may provide information about overall health but is not specific to DVT assessment.
D) This choice is correct. The Wells score assessment is a validated tool used to estimate the likelihood of DVT based on clinical criteria and risk factors. It is commonly used as the first step in the diagnostic workup to determine if further testing, such as venous Doppler ultrasound or D-dimer blood test, is necessary.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. The D-dimer blood test is a rapid and sensitive screening test that can help rule out DVT in low-risk individuals. A negative D-dimer result can be useful in excluding DVT, avoiding unnecessary imaging or invasive tests.
B) This choice is incorrect because contrast venography is not a rapid test and involves invasive procedures. It is not used as a first-line screening test due to its complexity and potential risks.
C) This choice is incorrect because magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may provide valuable information, but it is not the first choice for rapid rule-out of DVT. MRI may be employed in specific cases when initial screening tests are inconclusive.
D) This choice is incorrect because the Wells score assessment is not a diagnostic test but a scoring system to estimate the likelihood of DVT. It does not provide rapid results to rule out DVT directly.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because fasting is not necessary before a venous Doppler ultrasound. The client can eat and drink normally before the test.
B) This choice is incorrect because the client should continue to take prescribed medications as usual unless otherwise instructed by the healthcare provider. Medications that thin the blood, such as anticoagulants, may not be stopped before the test.
C) This choice is correct. The client should wear loose-fitting clothing that can be easily removed to allow access to the affected area during the ultrasound. This facilitates the ultrasound technician's ability to perform the test accurately.
D) This choice is incorrect because contrast dye is not typically used in a venous Doppler ultrasound. Contrast venography may involve the use of contrast dye, but not Doppler ultrasound.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because anticoagulants do not dissolve existing blood clots in the veins. They prevent further clot formation and allow the body's natural mechanisms to dissolve the clot over time.
B) This choice is correct. Anticoagulants work by inhibiting the clotting factors in the blood, which prevents the formation of new blood clots and reduces the risk of the existing clot enlarging or causing additional complications.
C) This choice is incorrect because while anticoagulants may indirectly reduce pain and inflammation by preventing further clot formation, their primary action is to prevent clotting, not directly reduce pain and inflammation associated with DVT.
D) This choice is incorrect because while anticoagulants can improve blood flow by preventing clot formation, they do not directly "improve" blood flow to the affected limb.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because compression stockings do not dissolve existing blood clots. Their primary purpose is to prevent new blood clots from forming by aiding blood flow and preventing stasis in the veins.
B) This choice is incorrect because while compression stockings may help reduce swelling in the affected leg by supporting venous return, their primary function is to prevent DVT and not specifically address swelling.
C) This choice is incorrect because compression stockings primarily target venous circulation in the legs and do not directly improve blood circulation throughout the entire body.
D) This choice is correct. Compression stockings exert pressure on the legs, assisting in venous return and preventing blood from pooling and clot formation. They are used as a preventive measure for individuals at risk of DVT or those diagnosed with DVT to reduce the risk of complications and recurrence.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because monitoring prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) is more relevant to monitoring oral anticoagulant therapy (e.g., warfarin) and not intravenous heparin therapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because while liver function tests may be important for some medications, they are not the priority for clients on intravenous heparin therapy. Heparin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys.
C) This choice is incorrect because while administering heparin via a central venous catheter is possible, it is not the priority action for safe administration. Monitoring the client's response to heparin therapy is more important.
D) This choice is correct. Monitoring the client's activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is the priority action when administering intravenous heparin. The aPTT reflects the client's response to heparin and helps adjust the dosage to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of bleeding.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Warfarin works by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors in the liver. Consistent vitamin K intake can impact the effectiveness of warfarin, so it is important for clients to maintain a stable vitamin K intake and avoid sudden changes in their diet.
B) This choice is incorrect because warfarin does not directly dissolve the blood clot in the leg. It prevents the formation of new clots and allows the body's natural mechanisms to dissolve the existing clot over time.
C) This choice is incorrect because while taking warfarin at the same time each day can help with adherence, the priority teaching point is about vitamin K intake and not the exact timing of the medication.
D) This choice is incorrect because discontinuing warfarin without medical guidance can be dangerous. Warfarin is typically prescribed for a specific duration, and its cessation should be guided by the healthcare provider based on the client's individual condition and risk factors.
A client with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is prescribed enoxaparin, a low molecular weight heparin (LMWH). What is the nurse's priority action before administering the medication?
Explanation
A. Measuring the client's blood pressure is an important assessment but is not the immediate priority when preparing to administer enoxaparin.
B. Assessing the client's platelet count is critical before administering enoxaparin, especially because low molecular weight heparins can lead to heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). Monitoring platelet levels helps to ensure the client's safety and prevent complications.
C. Ensuring the client has an indwelling urinary catheter is not necessary for the administration of enoxaparin and does not relate to its safety or efficacy.
D. Obtaining the client's weight is relevant for dosing but is secondary to assessing the platelet count, particularly in light of the risk of HIT.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while isometric exercises can promote blood flow, the recommended preventive measure for DVT is wearing graduated compression stockings. Exercises alone may not be sufficient to prevent clot formation.
B) This choice is correct. Graduated compression stockings apply pressure to the lower extremities, improving blood flow and reducing the risk of stasis and clot formation. They are commonly used as a preventive measure for clients at risk of DVT, particularly after surgery or during prolonged immobility.
C) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake is not a preventive measure for DVT and may not be safe or appropriate for all clients. Adequate hydration is essential to maintain blood volume and circulation.
D) This choice is incorrect because elevating the legs while resting is a recommended measure to improve blood flow and reduce edema, which can be beneficial. However, wearing graduated compression stockings is a more specific preventive measure for DVT.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Prolonged sitting or standing in one position can lead to reduced blood flow and stasis, increasing the risk of DVT. Encouraging regular movement and changing positions can help prevent clot formation.
B) This choice is incorrect because massaging the legs may not be suitable for everyone and is not a primary preventive measure for DVT. While it can aid in improving blood circulation, it should be done cautiously and not as a standalone preventive action.
C) This choice is incorrect because increasing the intake of vitamin K-rich foods is not a preventive measure for DVT. Vitamin K is involved in the clotting process, but it does not directly impact the risk of DVT.
D) This choice is incorrect because taking over-the-counter pain medications for leg discomfort does not prevent DVT. While pain management may be necessary for symptomatic relief, it does not address the underlying risk factors for DVT.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Performing calf-stretching exercises in the aisle can help improve blood circulation in the legs during a long flight and reduce the risk of stasis and clot formation.
B) This choice is incorrect because using a heating pad on the legs during a flight may not be feasible or safe. It is not a recommended preventive measure for DVT.
C) This choice is incorrect because wearing compression stockings during the flight is a recommended preventive measure for DVT. Compression stockings help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of clot formation during prolonged immobility.
D) This choice is incorrect because taking prescribed anticoagulant medication before boarding a flight is not a recommended preventive measure for all clients. The decision to take anticoagulant medication before a flight should be based on the client's individual risk factors and medical history.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because regular physical activity is an essential preventive measure for DVT. Encouraging the client to engage in physical activity is vital for maintaining good circulation and reducing the risk of clot formation.
B) This choice is incorrect because a diet high in saturated fats and cholesterol is not a recommended preventive measure for DVT. A healthy, balanced diet is important for overall health, but it does not specifically prevent DVT.
C) This choice is incorrect because elevating the legs above heart level while resting is beneficial for reducing edema and improving blood flow but is not the primary preventive measure for DVT.
D) This choice is correct. The client should continue taking prescribed anticoagulant medication as directed by their healthcare provider. Anticoagulant therapy is often prescribed for a specific duration to prevent clot formation and reduce the risk of complications in clients with DVT.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because mild leg swelling after prolonged standing may be expected, especially in clients with a history of DVT. It is not a critical symptom to report immediately.
B) This choice is correct. Redness and warmth at the site of the affected leg could indicate an inflammatory response or progression of the clot. These signs may be indicative of a potential complication, such as an infection or extension of the clot, and should be reported immediately for further evaluation and intervention.
C) This choice is incorrect because occasional cramping in the unaffected leg may not be directly related to the DVT. While any changes in leg symptoms should be reported to the healthcare provider, this symptom is less urgent than redness and warmth in the affected leg.
D) This choice is incorrect because mild fatigue and generalized body aches are non-specific symptoms and may not be directly related to DVT. While it is essential to report any new or concerning symptoms, redness and warmth in the affected leg are more indicative of potential complications related to DVT.
Questions
A nurse is caring for a client with suspected deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Which diagnostic test is used to assess blood flow and detect clots in the deep veins of the legs non-invasively?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because the D-dimer blood test is a screening test for DVT but does not directly assess blood flow or detect clots non-invasively.
B) This choice is incorrect because magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a sensitive imaging modality, but it may not be readily available or suitable for all clients. It is not the primary choice for non-invasive assessment of blood flow and clots in suspected DVT.
C) This choice is incorrect because contrast venography is an invasive procedure involving the injection of contrast dye and X-ray imaging. It is not non-invasive, and venous Doppler ultrasound is a preferred first-line test.
D) This choice is correct. Venous Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to assess blood flow in the veins and detect clots in the deep veins of the legs. It is readily available, safe, and does not involve the use of contrast dye or radiation.
Peripheral vascular disease
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. DVT is characterized by swelling, warmth, and redness in the affected leg, but it does not cause leg pain that improves with rest.
B) This choice is correct. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a condition where there is a narrowing or blockage of the arteries in the extremities, leading to reduced blood flow. The hallmark symptom of PAD is intermittent claudication, which is leg pain that occurs during walking or physical activity and improves with rest.
C) This choice is incorrect because Raynaud's disease is a disorder that affects the blood vessels in the fingers and toes, causing them to spasm and turn white, then blue, and finally red. It is not characterized by leg pain while walking.
D) This choice is incorrect because varicose veins are enlarged and twisted veins, usually in the legs, that can cause discomfort and cosmetic concerns. However, they do not typically cause leg pain that improves with rest.
Explanation
A) This choice is concerning and may indicate deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Swelling and tenderness in the calf can be a sign of a blood clot, and immediate evaluation is required to prevent potential complications such as a pulmonary embolism. However, it is not as critical as the finding in option D.
B) This choice is concerning and may indicate peripheral artery disease (PAD). Intermittent claudication during physical activity suggests reduced blood flow to the extremities, but it does not require immediate intervention.
C) This choice is concerning and may indicate Raynaud's disease. Raynaud's disease involves the fingers or toes turning white, then blue, and finally red due to blood vessel spasms, but it is not as urgent as the finding in option D.
D) This choice is correct. Ulceration on the lower leg with foul-smelling discharge indicates a severe complication of peripheral vascular disease, possibly related to peripheral artery disease (PAD) or venous insufficiency. Ulcers that have an unpleasant odor and are not healing require immediate intervention to prevent infection and further tissue damage.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while smoking can be a risk factor for deep vein thrombosis (DVT), diabetes and hypertension are not significant risk factors for this condition. DVT is more commonly associated with prolonged immobility, surgery, or trauma.
B) This choice is incorrect because Raynaud's disease is not directly related to smoking, diabetes, or hypertension. Raynaud's disease involves blood vessel spasms and is more commonly associated with exposure to cold temperatures or stress.
C) This choice is correct. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) involves the narrowing or blockage of arteries in the extremities, leading to reduced blood flow. Smoking, diabetes, and hypertension are significant risk factors for the development of PAD. Smoking damages blood vessels, diabetes increases the risk of atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries), and hypertension can lead to arterial damage and narrowing.
D) This choice is incorrect because varicose veins are typically caused by weakened or damaged valves in the veins, leading to the pooling of blood and the development of enlarged and twisted veins. Smoking, diabetes, and hypertension are not primary risk factors for varicose veins.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Elevating the legs above heart level while sitting can improve venous return, reducing swelling and promoting blood circulation in the legs. This position helps counteract the effects of gravity on blood flow.
B) This choice is incorrect because applying direct heat to the affected extremities is not a recommended method for improving blood circulation in peripheral vascular disease. Heat can cause vasodilation, which may exacerbate symptoms such as swelling and pain.
C) This choice is incorrect because crossing the legs while seated can impede venous return and contribute to blood pooling in the legs. It is not a recommended activity for individuals with peripheral vascular disease.
D) This choice is incorrect because limiting physical activity is not recommended for individuals with peripheral vascular disease. Regular physical activity, such as walking, can actually improve blood circulation and overall vascular health. However, individuals with peripheral vascular disease should be cautious not to overexert themselves and should consult with their healthcare provider regarding appropriate levels of physical activity.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Smoking is the most significant risk factor for peripheral artery disease (PAD). Smoking damages blood vessels, promotes atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries), and narrows blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow to the extremities.
B) This choice is incorrect because while a sedentary lifestyle can be a contributing factor to peripheral vascular diseases, it is not the most common cause of PAD.
C) This choice is incorrect because while family history can play a role in the development of PAD, it is not the most common cause. Other modifiable risk factors, such as smoking and diabetes, have a more significant impact on PAD.
D) This choice is incorrect because high dietary sodium intake is not a direct cause of PAD. However, reducing sodium intake can benefit overall cardiovascular health, especially for individuals with hypertension.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because decreased blood glucose levels are not associated with an increased risk of peripheral vascular disease (PAD) in diabetes. In fact, hypoglycemia (low blood glucose levels) can lead to acute complications but is not a significant factor in the development of PAD.
B) This choice is incorrect because increased insulin production is not a primary factor contributing to PAD in diabetes. Insulin is essential for glucose metabolism but does not directly impact blood vessel function.
C) This choice is correct. Diabetes can lead to impaired blood vessel function, primarily through the process of atherosclerosis. High blood glucose levels can damage blood vessel walls, leading to plaque buildup and narrowing of the arteries, reducing blood flow to the extremities and contributing to PAD.
D) This choice is incorrect because an elevated white blood cell count is not directly related to the increased risk of PAD in diabetes. While chronic inflammation and white blood cell count can play a role in atherosclerosis, it is not the primary factor contributing to PAD in diabetes.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because hypertension (high blood pressure) is not a significant risk factor for venous insufficiency. Venous insufficiency involves the impairment of venous valves and blood flow in the veins, not arterial hypertension.
B) This choice is incorrect because atherosclerosis is associated with peripheral artery disease (PAD), not venous insufficiency. Atherosclerosis involves the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow in the extremities.
C) This choice is correct. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs. DVT can lead to damage to the venous valves and veins, causing venous insufficiency and complications such as chronic venous insufficiency and venous ulcers.
D) This choice is incorrect because Raynaud's disease primarily affects the fingers and toes, causing them to spasm and change color in response to cold or stress. It is not directly related to the development of venous insufficiency.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because increased blood viscosity (thickness) is not primarily associated with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or obesity. It is more commonly associated with conditions such as polycythemia or dehydration.
B) This choice is incorrect because hypercoagulability of the blood is not a direct risk factor associated with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or obesity. Hypercoagulability is more commonly associated with conditions such as certain clotting disorders.
C) This choice is incorrect because impaired cardiac function is not a direct risk factor for the development of PAD in the context of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or obesity. However, impaired cardiac function can contribute to heart-related peripheral vascular diseases, such as congestive heart failure.
D) This choice is correct. Hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and obesity are significant risk factors for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries. Atherosclerosis involves the buildup of plaque, including cholesterol and other substances, on the arterial walls, leading to narrowed and hardened arteries, reducing blood flow to the extremities and contributing to PAD.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. As individuals age, the risk of peripheral vascular diseases increases due to several factors, including the weakening of arterial walls and the accumulation of plaque in the arteries (atherosclerosis). Aging is associated with changes in blood vessels, such as decreased elasticity and increased stiffness, which can contribute to the development of peripheral vascular diseases.
B) This choice is incorrect because while physical fitness can influence the risk of cardiovascular diseases, age-related changes in blood vessels can still increase the risk of peripheral vascular diseases, even in physically fit individuals.
C) This choice is incorrect because the risk of peripheral vascular diseases does not remain stable with no significant changes. Aging is associated with various physiological changes that can impact cardiovascular health and increase the risk of peripheral vascular diseases.
D) This choice is incorrect because while gender and ethnicity can influence the risk of certain conditions, age is a significant independent risk factor for the development of peripheral vascular diseases. The age-related changes in blood vessels apply to individuals of all genders and ethnicities.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Intermittent claudication is a hallmark symptom of peripheral arterial disease (PAD). It refers to pain, cramping, or weakness in the legs that occurs during physical activity and is relieved by rest. This symptom is due to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to the muscles during exercise.
B) This choice is incorrect because deep vein thrombosis (DVT) typically presents with symptoms such as swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected leg, but it does not cause pain that is relieved by rest.
C) This choice is incorrect because Raynaud's phenomenon primarily affects the fingers and toes, causing them to turn white, then blue, and finally red due to blood vessel spasms in response to cold or stress. It is not associated with pain in the legs during walking.
D) This choice is incorrect because chronic venous insufficiency involves symptoms such as leg swelling, skin changes, and the development of venous ulcers, but it is not characterized by pain that occurs with walking and is relieved by rest.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. A non-healing ulcer on the lower leg is a significant concern and requires immediate intervention. Non-healing ulcers can be a complication of peripheral vascular disease and may indicate impaired blood flow and tissue damage. Prompt assessment and treatment are necessary to prevent infection and promote wound healing.
B) This choice is incorrect because occasional leg cramps at night can be a common symptom, especially in older adults, and are not typically indicative of an acute medical emergency.
C) This choice is incorrect because mild coolness of the feet bilaterally can be a sign of reduced blood flow, but it is not an immediate concern requiring urgent intervention. However, it should be further assessed to determine the severity of the vascular condition.
D) This choice is incorrect because visible varicose veins on the calves, while often a cosmetic concern, are not typically associated with immediate risks. Varicose veins are dilated and twisted veins that result from venous insufficiency but are not an urgent medical condition.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because using heating pads to warm cold feet can cause burns or injuries, especially in clients with impaired sensation due to peripheral vascular disease. Clients with PAD may experience cold feet due to reduced blood flow, but external heating sources should be used with caution.
B) This choice is incorrect because moisturizing the skin is essential for individuals with peripheral vascular disease to prevent dryness and cracking, which can lead to skin breakdown and infections. Proper skin care is important to maintain skin integrity and prevent complications.
C) This choice is correct. Clients with peripheral vascular disease should inspect their feet daily for any changes, such as cuts, sores, blisters, or signs of infection. Reduced blood flow can slow down wound healing, and prompt identification and treatment of foot problems are crucial to prevent infections and potential complications.
D) This choice is incorrect because while elevating the legs above heart level can temporarily improve blood flow and reduce swelling, prolonged elevation can impede blood flow and is not recommended for extended periods. Clients with PAD should be encouraged to perform regular, moderate physical activity to improve blood circulation.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Numbness and tingling in the feet are symptoms associated with arterial insufficiency in peripheral vascular disease (PAD). Reduced blood flow to the extremities can lead to sensory changes and discomfort, including numbness and tingling.
B) This choice is incorrect because venous insufficiency is more commonly associated with symptoms such as leg swelling, skin changes, and the development of venous ulcers, but it does not typically cause numbness and tingling in the feet.
C) This choice is incorrect because peripheral nerve compression can cause localized numbness and tingling, but it is not a primary symptom of peripheral vascular disease. Peripheral nerve compression may occur due to various factors, such as nerve impingement or entrapment.
D) This choice is incorrect because systemic inflammation is not a direct cause of numbness and tingling in the feet in peripheral vascular disease. Systemic inflammation can contribute to other conditions, but it is not the primary cause of sensory changes associated with PAD.
A client with peripheral vascular disease (PAD) is prescribed cilostazol, a medication that improves blood flow in the legs. The nurse should instruct the client to:
Explanation
For a client with peripheral vascular disease (PAD) who is prescribed cilostazol, the nurse should provide the following instruction:
C) Avoid grapefruit juice while on cilostazol.
Grapefruit juice can interact with certain medications, including cilostazol, and may lead to increased levels of the medication in the bloodstream. This can potentially cause adverse effects or interfere with the intended therapeutic effects of cilostazol. Therefore, clients taking cilostazol should be advised to avoid grapefruit juice.
The other options are not appropriate:
A) Increasing the dosage of cilostazol without consulting a healthcare provider is not recommended and can be dangerous.
B) Cilostazol can be taken with or without food, so taking it on an empty stomach is not necessary.
D) While compression stockings can be used for some individuals with PAD, their use should be discussed with the healthcare provider and is not specific to cilostazol instructions.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because angiography is an invasive procedure that involves the injection of contrast dye into the blood vessels to visualize their structure and blood flow. It is not a non-invasive test.
B) This choice is incorrect because venography is an imaging test that involves the injection of contrast dye into a vein to visualize its flow. It is not commonly used to assess blood flow and blood pressure in the legs.
C) This choice is correct. Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to assess blood flow and blood pressure in the legs. It helps identify areas of reduced blood flow, blockages, and abnormalities in the blood vessels.
D) This choice is incorrect because magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic imaging technique that provides detailed images of the body's internal structures using a magnetic field and radio waves. While it can be used to assess blood vessels, it is not the primary test for evaluating blood flow in peripheral vascular diseases.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. The ankle-brachial index (ABI) is a non-invasive test that compares the blood pressure in the arms and legs. The test involves using a blood pressure cuff and Doppler ultrasound to measure blood pressure in the ankles and arms. The ratio of ankle to brachial pressure helps assess the severity of peripheral vascular disease and determine if there is reduced blood flow to the legs.
B) This choice is incorrect because oxygen saturation in the extremities is not directly measured with an ankle-brachial index (ABI) test. Oxygen saturation is commonly measured using pulse oximetry, which assesses the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is saturated with oxygen.
C) This choice is incorrect because an ankle-brachial index (ABI) test is not used to measure blood glucose levels before and after meals. Blood glucose levels are typically assessed using a blood test or fingerstick glucose monitoring in clients with diabetes.
D) This choice is incorrect because an ankle-brachial index (ABI) test does not evaluate blood flow through the heart's chambers. It focuses on assessing blood pressure and blood flow in the arms and legs to diagnose peripheral vascular disease.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because asthma is not directly associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis or peripheral vascular disease. Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects the airways, not the blood vessels.
B) This choice is incorrect because osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease and is not directly linked to an increased risk of atherosclerosis or peripheral vascular disease.
C) This choice is incorrect because while hypothyroidism can impact cardiovascular health, it is not a primary risk factor for atherosclerosis or peripheral vascular disease. Hypothyroidism can lead to elevated cholesterol levels, but hypercholesterolemia is the specific condition related to increased cholesterol levels and atherosclerosis.
D) This choice is correct. Hypercholesterolemia, characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood, is a significant risk factor for atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arterial walls. Atherosclerosis is a common cause of peripheral vascular disease, leading to reduced blood flow to the extremities and various cardiovascular complications.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because arteriography is an invasive procedure that involves the insertion of a catheter through a blood vessel, typically in the groin or arm, to inject contrast dye directly into the arteries. It is not performed using a small incision in the leg.
B) This choice is incorrect because keeping the leg immobile after an arteriography is not necessary. However, the client will be asked to rest and avoid strenuous activities for a few hours following the procedure.
C) This choice is incorrect because the procedure that uses sound waves to visualize blood flow is a Doppler ultrasound, not an arteriography. Arteriography involves the use of contrast dye and X-rays to visualize the arterial blood vessels.
D) This choice is correct. Arteriography requires the use of contrast dye to enhance the visualization of blood vessels during X-ray imaging. There is a risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast dye, and clients should be informed about this potential complication before the procedure. Precautions may be taken, and the client's medical history should be reviewed to identify any contraindications to the use of contrast dye.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because cardiac catheterization is an invasive procedure that involves the insertion of a catheter into the heart chambers or coronary arteries. It is used to assess the heart's structure and function, not blood flow in the legs.
B) This choice is incorrect because an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart to assess heart rate and rhythm. It is not used to assess blood flow in the legs.
C) This choice is correct. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of blood vessels. It can assess blood flow in the legs, identify blockages, and provide valuable information about the vascular status of the extremities.
D) This choice is incorrect because a pulmonary function test (PFT) is a test used to assess lung function and diagnose respiratory conditions. It is not used to assess blood flow in the legs or detect peripheral vascular disease.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because headache is a common side effect of cilostazol but is generally not a severe adverse reaction that requires immediate reporting. Headaches can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers if needed.
B) This choice is incorrect because diarrhea is a known side effect of cilostazol but is not typically severe or life-threatening. Clients should be encouraged to stay hydrated and notify their healthcare provider if it becomes bothersome.
C) This choice is incorrect because muscle cramps can occur as a side effect of cilostazol, but they are not considered an urgent adverse reaction. Mild muscle cramps can often be managed with stretching and hydration.
D) This choice is correct. Dizziness is a significant adverse effect of cilostazol and should be reported immediately. Cilostazol can cause a drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness, lightheadedness, and a risk of falls. If a client experiences severe dizziness or fainting, they should seek medical attention promptly.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because encouraging prolonged standing can worsen symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Prolonged standing increases venous pressure in the legs and can lead to further swelling and discomfort.
B) This choice is correct. Elevating the legs above heart level when resting is a beneficial intervention for individuals with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Elevating the legs helps improve venous return and reduces swelling in the legs.
C) This choice is incorrect because applying warm compresses to the legs may provide temporary relief for some individuals, but it is not a primary intervention for managing chronic venous insufficiency (CVI).
D) This choice is incorrect because tight-fitting compression stockings are commonly used to manage chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), but they should be fitted appropriately by a healthcare professional. Wearing overly tight compression stockings can impede blood flow and cause discomfort.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while administering analgesics for pain relief is important for the client's comfort, it is not the priority in this situation. The non-healing ulcer may require further assessment and interventions beyond pain relief.
B) This choice is correct. In a client with peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and a non-healing foot ulcer, there is a risk of infection due to reduced blood flow and compromised tissue healing. Initiating prophylactic antibiotics is a priority to prevent or manage infection and promote wound healing.
C) This choice is incorrect because elevating the affected foot can be beneficial to improve blood flow in individuals with venous insufficiency or edema but may not be as effective for individuals with peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
D) This choice is incorrect because promoting regular foot inspections is essential for clients with peripheral vascular diseases, but in this case, the non-healing ulcer requires immediate attention. Proper wound care, including assessment, cleaning, and dressing, should be part of the client's plan of care, but antibiotic therapy is the priority in this situation.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake is not a standard post-procedure instruction following angioplasty with stent placement. Adequate hydration is important for recovery and overall health.
B) This choice is incorrect because walking is generally encouraged following angioplasty with stent placement. Early mobilization helps prevent complications such as blood clots and promotes blood flow through the treated vessel.
C) This choice is correct. After angioplasty with stent placement, clients are often prescribed dual antiplatelet therapy, which typically includes aspirin and another antiplatelet medication such as clopidogrel. Dual antiplatelet therapy helps prevent blood clots from forming around the stent and reduces the risk of stent re-narrowing (restenosis).
D) This choice is incorrect because applying ice packs to the incision site is not a standard post-procedure instruction after angioplasty with stent placement. Ice packs are not typically used for this type of procedure, and the incision site is usually managed with sterile dressings and wound care.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because increasing sodium intake can lead to fluid retention and exacerbate swelling, which is counterproductive for clients with peripheral vascular disease (PAD).
B) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake can lead to dehydration and is not typically recommended for individuals with PAD. Adequate hydration is important for overall health and vascular function.
C) This choice is correct. A low-fat and low-cholesterol diet is essential for individuals with peripheral vascular disease (PAD) to reduce the buildup of plaque in the arteries (atherosclerosis) and improve blood flow. Lowering dietary intake of saturated fats and cholesterol helps manage cardiovascular risk factors.
D) This choice is incorrect because consuming high amounts of caffeine can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, which may be detrimental for clients with PAD. Moderate caffeine intake is generally recommended.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because avoiding all physical activity can lead to deconditioning and worsen exercise tolerance over time. Regular exercise is beneficial for individuals with peripheral vascular disease (PAD) to improve blood flow and manage symptoms.
B) This choice is incorrect because waiting until the pain becomes severe and then stopping (known as the "stop-and-rest" method) is not recommended for individuals with PAD. This approach can lead to inadequate exercise and may not provide the benefits of regular walking.
C) This choice is incorrect because engaging in a daily high-intensity exercise regimen is not appropriate for individuals with PAD, especially if they experience intermittent claudication. High-intensity exercise can exacerbate leg pain and may not be well-tolerated.
D) This choice is correct. Gradually increasing walking distance over time is a recommended approach for individuals with PAD to improve exercise tolerance and manage intermittent claudication. The goal is to push the limits of walking distance without causing severe pain, allowing the individual to gradually build endurance and improve blood flow.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because crossing the legs while sitting can impede blood flow and worsen symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Clients with CVI should avoid crossing their legs and keep them uncrossed to promote blood flow.
B) This choice is correct. Elevating the legs above heart level when resting is a beneficial self-care strategy for individuals with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Elevating the legs helps improve venous return, reduce swelling, and alleviate discomfort.
C) This choice is incorrect because while applying warm compresses may provide temporary relief for some individuals with CVI, it is not a primary self-care strategy for promoting venous return. Warm compresses may be more suitable for acute injuries or inflammation.
D) This choice is incorrect because while wearing compression stockings is a recommended intervention for individuals with CVI, tight-fitting compression stockings can impede blood flow and cause discomfort. Compression stockings should be fitted appropriately by a healthcare professional to ensure optimal efficacy.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because soaking the feet in hot water is not recommended for individuals with peripheral vascular disease (PAD) or cold feet. Hot water can cause burns or injuries, especially in clients with reduced sensation due to PAD.
B) This choice is incorrect because while wearing thick socks can provide some insulation, it is not a comprehensive solution for managing cold feet caused by reduced blood flow.
C) This choice is incorrect because using an electric blanket may not be specific to the feet and may not effectively address the issue of cold feet due to PAD.
D) This choice is correct. Avoiding exposure to cold temperatures is a recommended self-care measure for individuals with peripheral vascular disease (PAD) experiencing cold feet. Cold temperatures can further constrict blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the extremities. Clients should keep their feet warm and protect them from cold weather using appropriate footwear and clothing.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while nicotine replacement therapy can be helpful for individuals trying to quit smoking, it is not the priority intervention. The primary goal is to promote smoking cessation itself, as it provides the most significant health benefits.
B) This choice is incorrect because smokeless tobacco is not a safe alternative to smoking and is not recommended for promoting vascular health. Smokeless tobacco still contains harmful substances that can damage blood vessels and increase cardiovascular risks.
C) This choice is correct. Providing education on the benefits of smoking cessation is a priority intervention for a client with peripheral vascular disease (PAD) who has a history of smoking. Smoking is a significant risk factor for PAD and other cardiovascular diseases. Quitting smoking can lead to immediate and long-term health improvements, including improved blood flow and reduced risk of complications.
D) This choice is incorrect because advising the client to smoke fewer cigarettes per day is not sufficient to address the adverse effects of smoking on vascular health . Smoking cessation is the most effective approach to improve vascular health and reduce the risk of PAD-related complications.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because lying down and elevating the legs during episodes of intermittent claudication may provide temporary relief, but it does not address the underlying issue. Encouraging the client to stop and rest perpetuates the pain cycle and may hinder progress in managing PAD symptoms.
B) This choice is incorrect because deep breathing exercises are not directly related to managing intermittent claudication. While deep breathing exercises can be beneficial for relaxation and stress reduction, they do not specifically address the leg pain experienced during walking.
C) This choice is correct. Encouraging the client to continue walking during episodes of intermittent claudication helps build endurance and improves blood flow to the legs. Gradual increases in walking distance and duration can help the client tolerate longer periods of activity before experiencing pain.
D) This choice is incorrect because using a heating pad on the affected area is not recommended for managing intermittent claudication. Heat may not provide significant pain relief, and it does not address the underlying vascular issues causing the pain.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because elevating the legs above heart level for only 15 minutes daily may not provide sufficient benefit for managing edema and skin changes in clients with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Continuous and prolonged elevation, along with compression therapy, is more effective in reducing swelling.
B) This choice is correct. Applying compression bandages or stockings is a standard intervention for managing edema and skin changes in clients with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Compression helps improve venous return and reduce swelling in the lower legs.
C) This choice is incorrect because soaking the legs in hot water is not recommended for clients with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Hot water may cause skin irritation and worsen skin changes associated with CVI.
D) This choice is incorrect because encouraging long periods of standing can worsen symptoms in clients with CVI. Prolonged standing increases venous pressure in the legs and can lead to further swelling and discomfort.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because mild incisional pain is common after peripheral artery bypass surgery and may be managed with prescribed pain medications. However, severe or worsening pain should be reported to the healthcare provider.
B) This choice is incorrect because mild swelling in the feet is a common post-operative finding after peripheral artery bypass surgery and may resolve with time. However, excessive or sudden swelling should be reported to the healthcare provider.
C) This choice is correct. Pallor (pale color) and coolness of the affected foot may indicate reduced blood flow to the extremity, which could be a sign of a complication such as graft occlusion or clot formation. These signs should be reported immediately for prompt evaluation and intervention.
D) This choice is incorrect because tingling sensation in the legs is common after surgery and may be related to changes in blood flow or nerve irritation. It is not typically a sign that requires immediate reporting unless it is severe or accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
A client with peripheral vascular disease (PAD) is scheduled for a percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PT with stent placement. What pre-procedure information should the nurse provide to the client?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because avoiding eating or drinking for 24 hours before the procedure is not typically required for a percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) with stent placement. The client may be instructed to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the procedure to prevent aspiration during sedation, but a 24-hour fast is not necessary.
B) This choice is incorrect because percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) with stent placement is typically performed under local anesthesia or conscious sedation, not general anesthesia. General anesthesia is not required for this procedure.
C) This choice is incorrect because percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) with stent placement is a minimally invasive procedure that does not involve making a large incision in the abdomen. It is usually performed using small punctures or incisions in the groin or arm to insert a catheter.
D) This choice is correct. A percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) with stent placement involves the insertion of a catheter through a blood vessel, typically in the groin or arm, to reach the narrowed or blocked artery. The catheter is used to inflate a small balloon and place a stent to open the artery and improve blood flow. Providing information about the catheter insertion is essential for the client's understanding of the procedure.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because encouraging the client to massage the legs daily may not be appropriate for individuals with peripheral vascular disease (PAD). Vigorous massage can damage fragile blood vessels and exacerbate skin breakdown or injury.
B) This choice is incorrect because applying adhesive tape directly to the skin can cause skin trauma and increase the risk of skin breakdown. Dressings should be secured using appropriate medical tapes or dressings that are designed for skin protection.
C) This choice is correct. Regularly inspecting the skin for redness, discoloration, or signs of breakdown is crucial for early detection of impaired skin integrity in clients with peripheral vascular disease (PAD). Prompt identification and intervention can help prevent the development of pressure ulcers or wounds.
D) This choice is incorrect because using a donut-shaped cushion for sitting is generally not recommended for preventing skin breakdown. Donut cushions can increase pressure on the area around the coccyx and may cause more harm than good. Clients at risk of skin breakdown should be repositioned regularly and encouraged to shift their weight to relieve pressure on vulnerable areas.
Questions
A nurse is providing education to a client about peripheral vascular diseases. The nurse explains that these diseases primarily affect which body system?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because peripheral vascular diseases primarily affect the cardiovascular system, not the respiratory system. The respiratory system involves the lungs and the exchange of gases, while the cardiovascular system involves the heart and blood vessels.
B) This choice is correct. Peripheral vascular diseases are conditions that affect the blood vessels outside the heart and brain, including the arteries and veins in the extremities (arms and legs). These diseases can lead to reduced blood flow, pain, and various complications.
C) This choice is incorrect because peripheral vascular diseases do not primarily affect the nervous system. While some peripheral vascular diseases may have neurological implications, they are not primarily neurological disorders.
D) This choice is incorrect because peripheral vascular diseases do not primarily affect the gastrointestinal system. The gastrointestinal system involves the digestion and absorption of nutrients, which is not directly related to peripheral vascular diseases.
A nurse is providing education to a client with peripheral vascular disease (PAD). The nurse should instruct the client to perform which exercise to improve blood flow in the legs?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because weightlifting is not typically recommended for individuals with peripheral vascular disease (PAD). High-intensity weightlifting can increase blood pressure and may not be suitable for clients with cardiovascular conditions.
B) This choice is incorrect because running, especially high-impact running, may be too strenuous for individuals with PAD and could lead to discomfort or injury. Low-impact exercises are generally preferred.
C) This choice is incorrect because high-impact aerobics can be too intense for individuals with PAD and may not be well-tolerated, especially if they experience leg pain during exercise.
D) This choice is correct. Walking is a low-impact exercise that can be beneficial for individuals with peripheral vascular disease. It promotes blood flow in the legs, increases circulation, and helps manage intermittent claudication (pain during walking) associated with PAD. Gradually increasing walking distance and duration can improve cardiovascular fitness and overall health.
Congestive Cardiac Failure
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because sudden weight gain, shortness of breath, and ankle swelling are not normal with CHF and may indicate worsening of the condition. The nurse should not reassure the client but rather take appropriate action to address the symptoms.
B) This choice is incorrect because the client's symptoms suggest fluid retention, and increasing fluid intake would exacerbate the condition. The nurse should not encourage the client to increase fluid intake without consulting the healthcare provider.
C) This choice is correct. The client's sudden weight gain, shortness of breath, and ankle swelling are signs of worsening congestive heart failure. The nurse's priority action is to notify the healthcare provider immediately to address the client's worsening condition and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
D) This choice is incorrect because administering a diuretic is not within the nurse's scope of practice without a healthcare provider's order. The nurse should first notify the healthcare provider to evaluate the client's condition and determine the appropriate intervention.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a significant risk factor for congestive heart failure (CHF). Prolonged hypertension can lead to the heart's increased workload, causing it to weaken over time and eventually leading to CHF. The client's symptoms of fatigue, difficulty breathing, and nocturia (frequent urination at night) are common manifestations of CHF resulting from uncontrolled hypertension.
B) This choice is incorrect because diabetes mellitus, while a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, is not directly associated with the symptoms described by the client. However, diabetes can exacerbate CHF if the client's blood glucose levels are not well-controlled.
C) This choice is incorrect because smoking history is a risk factor for various cardiovascular diseases, but it is not specifically linked to the symptoms reported by the client in this case.
D) This choice is incorrect because a family history of heart disease may increase the client's risk of developing CHF, but it does not directly contribute to the current symptoms the client is experiencing.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because ascites (abdominal swelling due to fluid accumulation) is a sign of right-sided heart failure, not left-sided heart failure.
B) This choice is incorrect because dependent edema (swelling in the legs and ankles) is also a sign of right-sided heart failure, not left-sided heart failure.
C) This choice is correct. Crackles in the lungs, also known as rales, are the classic hallmark of left-sided heart failure. They occur when fluid accumulates in the lungs, leading to abnormal lung sounds on auscultation.
D) This choice is incorrect because jugular vein distention is associated with right-sided heart failure, not left-sided heart failure.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because restricting all physical activity is not recommended for clients with congestive heart failure. Regular, moderate exercise can be beneficial for heart health when appropriately prescribed by the healthcare provider.
B) This choice is correct. Regularly weighing themselves, ideally daily, and reporting sudden weight gain to the healthcare provider is essential for clients with congestive heart failure. Sudden weight gain may indicate fluid retention, a worsening of heart failure, or medication non-compliance.
C) This choice is incorrect because a high-sodium diet can worsen fluid retention and exacerbate congestive heart failure symptoms. The client should follow a low-sodium diet to manage fluid balance.
D) This choice is incorrect because taking prescribed medications only when symptoms worsen is not appropriate for congestive heart failure management. The client should take prescribed medications as directed by the healthcare provider, even when feeling well, to prevent symptom exacerbation and improve heart function.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because hypertension is not a common side effect of digoxin. Digoxin is used to treat heart failure and can help control blood pressure in some cases.
B) This choice is incorrect because hyperkalemia (elevated potassium levels) is not a common side effect of digoxin. In fact, digoxin can sometimes cause hypokalemia (low potassium levels) as a side effect.
C) This choice is correct. Bradycardia (slow heart rate) is a common side effect of digoxin. Digoxin works by increasing the force of the heart's contractions and can slow down the heart rate. Clients taking digoxin should have their heart rate monitored regularly, and the healthcare provider should be notified if the heart rate is below the prescribed parameters.
D) This choice is incorrect because respiratory alkalosis is not a common side effect of digoxin. Digoxin does not directly affect the respiratory system.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while infections and viral illnesses can contribute to heart failure in some cases, they are not the leading causes of CHF. Hypertension and coronary artery disease are more common risk factors.
B) This choice is correct. Hypertension (high blood pressure) and coronary artery disease (narrowing or blockage of the heart's blood vessels) are the leading causes of CHF. Both conditions place increased stress on the heart and can lead to heart muscle damage and failure.
C) This choice is incorrect because while excessive physical exertion and overworking the heart can contribute to heart failure, they are not the primary causes of CHF. Underlying conditions like hypertension and coronary artery disease are more significant risk factors.
D) This choice is incorrect because anemia and low red blood cell count can impact heart function, but they are not the main causes of CHF. Hypertension and coronary artery disease are more commonly associated with the development of CHF.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Alcohol abuse can lead to dilated cardiomyopathy, a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and weakened, contributing to congestive heart failure. Chronic alcohol consumption can cause toxic effects on the heart muscle, leading to impaired pumping function.
B) This choice is incorrect because malnutrition, while it can impact overall health, is not a direct precipitating cause of congestive heart failure. However, malnutrition can exacerbate heart failure symptoms and weaken the heart further.
C) This choice is incorrect because a sedentary lifestyle can be a risk factor for heart disease, including congestive heart failure, but it is not a direct precipitating cause of the client's condition in this scenario.
D) This choice is incorrect because occupational exposure to toxins can have health implications, but it is not directly related to the client's signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure in this case.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a body mass index (BMI) of 22 kg/m² is within the normal range and is not directly associated with the development of congestive heart failure in this scenario.
B) This choice is incorrect because a blood pressure of 120/80 mmHg is within the normal range and does not indicate a direct precipitating factor for congestive heart failure in this case.
C) This choice is incorrect because a fasting blood glucose level of 90 mg/dL is within the normal range and is not directly associated with the development of congestive heart failure in this scenario.
D) This choice is correct. A serum cholesterol level of 240 mg/dL indicates high cholesterol, which is a risk factor for coronary artery disease. Coronary artery disease is a leading cause of congestive heart failure and may have contributed to the client's condition.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because age is a non-modifiable risk factor for congestive heart failure. While age increases the risk of heart disease, including CHF, it cannot be changed or modified.
B) This choice is incorrect because family history of heart disease is a non-modifiable risk factor. While individuals with a family history of heart disease may have an increased risk of developing CHF, it is not something that can be changed or modified.
C) This choice is correct. Smoking is a modifiable risk factor for congestive heart failure. Smoking damages blood vessels, increases blood pressure, and can lead to atherosclerosis, all of which contribute to heart failure.
D) This choice is incorrect because gender is a non-modifiable risk factor for congestive heart failure. While men may have a slightly higher risk of heart failure compared to women, gender is not something that can be changed or modified.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while electrolyte imbalances can have cardiovascular implications, they are not directly associated with diabetes mellitus or congestive heart failure.
B) This choice is incorrect because left-sided heart failure is not directly related to uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. However, diabetes can exacerbate heart failure if not well-controlled due to its impact on blood vessels and the heart.
C) This choice is incorrect because decreased afterload is not directly related to uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Afterload refers to the resistance the heart has to overcome to eject blood into the circulation.
D) This choice is correct. Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus can lead to microvascular damage, particularly in the small blood vessels of the heart. This damage can contribute to heart muscle dysfunction and congestive heart failure. Diabetes is a significant risk factor for developing heart failure.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because orthopnea is a different symptom where the client experiences difficulty breathing while lying flat and finds relief by sitting upright or standing.
B) This choice is correct. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea is characterized by sudden breathlessness that awakens the client from sleep, usually 1-2 hours after falling asleep. The client may feel the need to sit upright or dangle the legs to breathe comfortably.
C) This choice is incorrect because peripheral edema refers to swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, which is a common symptom of congestive heart failure but does not match the client's reported symptom.
D) This choice is incorrect because tachypnea is rapid breathing and is not specifically related to the client's nighttime symptom of sudden breathlessness.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because palpitations refer to an abnormal awareness of the heart's beating, which is not described by the client.
B) This choice is incorrect because angina pectoris is chest pain or discomfort due to inadequate blood flow to the heart muscle. The client's complaint is related to physical activity causing fatigue and weakness, not chest pain.
C) This choice is correct. Dyspnea on exertion refers to shortness of breath or difficulty breathing that occurs with physical activity or exertion. The client's symptoms of feeling fatigued and weak after mild activity suggest exertional dyspnea, which is common in congestive heart failure.
D) This choice is incorrect because peripheral cyanosis is bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to reduced blood flow, which is not described by the client.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because clubbing refers to the enlargement of the fingertips and nails due to chronic hypoxia, which is not related to the client's reported symptoms.
B) This choice is correct. Peripheral edema refers to swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, which is a common symptom of congestive heart failure. The client's symptoms of swollen ankles, legs, and abdomen indicate peripheral edema.
C) This choice is incorrect because pitting edema is a specific type of edema where pressure on the skin leaves an indentation or "pit." While the client's edema may indeed be pitting, the question does not provide enough information to confirm this.
D) This choice is incorrect because ascites is the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity and is not specific to the client's reported symptoms of swollen ankles and legs.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because wheezing on auscultation is a characteristic finding in respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), not congestive heart failure.
B) This choice is incorrect because hyperactive bowel sounds are not specific to congestive heart failure and are more indicative of gastrointestinal activity.
C) This choice is incorrect because the absence of jugular vein distention is not directly related to fluid accumulation in the lungs. Jugular vein distention is associated with right-sided heart failure.
D) This choice is correct. Crackles, also known as rales, are abnormal lung sounds heard on auscultation and may indicate fluid accumulation in the lungs, a common symptom of congestive heart failure. The presence of crackles suggests pulmonary congestion due to fluid leaking into the alveoli.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because hemoptysis refers to coughing up blood from the respiratory tract, which is not described by the client.
B) This choice is incorrect because dyspnea refers to difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, not a dry, persistent cough.
C) This choice is incorrect because paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea is characterized by sudden breathlessness that awakens the client from sleep, not a dry cough.
D) This choice is correct. Cardiac asthma is a form of wheezing or coughing that occurs as a result of fluid accumulation in the lungs due to congestive heart failure. It is not caused by asthma but is a manifestation of heart failure impacting the respiratory system.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because an electrocardiogram (ECG) is a valuable diagnostic tool for assessing the heart's electrical activity and rhythm, but it is not the gold standard for diagnosing CHF. It can provide information about possible cardiac hypertrophy or rhythm disturbances associated with heart failure.
B) This choice is incorrect because a chest X-ray is helpful in evaluating heart size and the presence of pulmonary congestion, but it is not the gold standard for diagnosing CHF.
C) This choice is correct. An echocardiogram is the gold standard for diagnosing CHF. It uses ultrasound waves to assess the heart's structure and function, including ejection fraction and valve function, providing critical information to confirm the diagnosis of heart failure.
D) This choice is incorrect because a brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) level is a blood test that can aid in the diagnosis of CHF. Elevated BNP levels indicate heart strain, but it is not the gold standard for diagnosing CHF.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a narrowed mediastinum is not a characteristic finding in congestive heart failure. The mediastinum is the central region of the chest, and its width is not specifically related to CHF.
B) This choice is incorrect because hyperinflated lungs are a characteristic finding in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), not congestive heart failure.
C) This choice is correct. Cardiomegaly, an enlarged heart, is a common finding in congestive heart failure. The heart may appear enlarged on a chest X-ray due to fluid accumulation and strain on the heart muscle.
D) This choice is incorrect because a normal cardiac silhouette on a chest X-ray would not be indicative of congestive heart failure. The presence of cardiomegaly is more suggestive of heart failure.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a complete blood count (CBC) is a general blood test that measures different components of the blood, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It is not specifically used to measure heart strain or diagnose CHF.
B) This choice is incorrect because a basic metabolic panel (BMP) is a blood test that measures electrolytes, kidney function, and glucose levels. It is not specific to diagnosing CHF.
C) This choice is correct. A brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) level is a blood test specifically used to measure heart strain. Elevated BNP levels can indicate heart failure, making it a valuable diagnostic tool in assessing suspected CHF.
D) This choice is incorrect because a C-reactive protein (CRP) level is a marker of inflammation and is not specific to diagnosing CHF.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a high-pitched, scratchy sound heard during inhalation is called a pleural friction rub and is associated with pleuritis or inflammation of the pleura, not congestive heart failure.
B) This choice is correct. An S3 heart sound is an extra heart sound heard immediately after S1 and S2, often described as a "ventricular gallop." It is associated with congestive heart failure and indicates increased fluid volume and strain on the ventricles.
C) This choice is incorrect because a prolonged, whooshing sound heard during systole is a heart murmur, which can be caused by various conditions, but it is not specific to the presence of an S3 sound.
D) This choice is incorrect because an irregular heart rhythm with varying intensity is characteristic of cardiac arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats and is not specific to the presence of an S3 sound.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because serum electrolyte levels are not directly measured during an echocardiogram. They are typically assessed through a blood test and are not specific to evaluating heart function using ultrasound.
B) This choice is incorrect because blood pressure readings are not directly measured during an echocardiogram. Blood pressure is typically assessed using a sphygmomanometer and is not specific to evaluating heart function using ultrasound.
C) This choice is incorrect because oxygen saturation levels are not directly measured during an echocardiogram. Oxygen saturation is typically assessed using a pulse oximeter and is not specific to evaluating heart function using ultrasound.
D) This choice is correct. Ejection fraction (EF) is a parameter measured during an echocardiogram to assess the client's heart function. It represents the percentage of blood pumped out of the heart's left ventricle with each heartbeat and is an essential indicator of heart muscle efficiency and potential heart failure.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because ACE inhibitors should not be taken with grapefruit juice. Grapefruit juice can interfere with the metabolism of the medication, leading to increased levels and potential side effects.
B) This choice is incorrect because the client should not adjust the dose of the ACE inhibitor without consulting their healthcare provider. Blood pressure should be monitored, but any dosage adjustments should be made by the healthcare provider based on the client's response to the medication.
C) This choice is correct. ACE inhibitors can cause a side effect of a persistent dry cough, and in some cases, difficulty breathing. The client should promptly report these symptoms to their healthcare provider for evaluation and possible adjustment of the medication regimen.
D) This choice is incorrect because while ACE inhibitors can increase potassium levels, avoiding foods high in potassium is not necessary unless specifically directed by the healthcare provider. The client should follow a balanced diet and inform the healthcare provider of any changes in their dietary habits.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because loop diuretics can lead to increased sodium excretion, potentially causing hypernatremia (high sodium levels) rather than hyponatremia (low sodium levels).
B) This choice is incorrect because loop diuretics do not typically cause hypocalcemia (low calcium levels). They primarily affect sodium, potassium, and water excretion.
C) This choice is incorrect because loop diuretics are more likely to cause hypokalemia (low potassium levels) rather than hyperkalemia (high potassium levels). Loop diuretics can increase potassium excretion, leading to a potential deficiency.
D) This choice is correct. Loop diuretics are potent potassium-wasting diuretics, meaning they increase potassium excretion in the urine, potentially causing hypokalemia. The nurse should closely monitor the client's potassium levels and provide potassium supplementation if necessary.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Beta-blockers should not be abruptly discontinued, as sudden discontinuation can lead to rebound effects and worsen the client's condition. Gradual tapering of the medication is necessary under the guidance of the healthcare provider.
B) This choice is incorrect because taking a beta-blocker with a high-fat meal is not necessary. Beta-blockers can be taken with or without food, but consistent administration is essential for optimal therapeutic effects.
C) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake is not specific to the administration of beta-blockers. Fluid intake may need to be adjusted based on the client's overall fluid balance and congestive heart failure status, but it is not a direct instruction related to the medication.
D) This choice is incorrect because the timing of beta-blocker administration varies depending on the specific beta-blocker prescribed and the client's individual response. Some beta-blockers may be taken in the morning, while others may be taken in the evening. The client should follow the prescribed schedule given by the healthcare provider.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because bradycardia (slow heart rate) is not a common adverse effect of furosemide, a loop diuretic.
B) This choice is incorrect because hyperglycemia (high blood glucose levels) is not a common adverse effect of furosemide. In fact, furosemide can sometimes cause transient hypoglycemia.
C) This choice is correct. Hypotension (low blood pressure) is a potential adverse effect of furosemide due to its diuretic action. Furosemide causes the excretion of excess fluid, leading to a decrease in blood volume, which can result in hypotension.
D) This choice is incorrect because a dry, nonproductive cough is associated with ACE inhibitors, not furosemide.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while digoxin can impact liver function, it is not the primary parameter to be monitored. Liver function tests may be performed periodically to assess liver health during digoxin therapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because serum sodium levels are not directly impacted by digoxin. However, electrolyte imbalances, including hypokalemia, can potentiate digoxin toxicity, so potassium levels should be monitored.
C) This choice is correct. Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside that can impact renal function. Monitoring urine output is essential to assess kidney function and the client's response to the medication.
D) This choice is incorrect because blood glucose levels are not specifically impacted by digoxin. However, hypokalemia resulting from digoxin therapy can cause alterations in glucose metabolism, so blood glucose levels should be monitored in clients taking digoxin.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. ACE inhibitors are used to lower blood pressure and reduce the workload on the heart. The client should monitor their blood pressure regularly and report any significant changes to their healthcare provider. Adjustments to the medication dosage should only be made under the guidance of the healthcare provider.
B) This choice is incorrect because while ACE inhibitors can increase potassium levels, avoiding foods high in potassium is not necessary unless specifically directed by the healthcare provider. The client should follow a balanced diet and inform the healthcare provider of any changes in their dietary habits.
C) This choice is incorrect because ACE inhibitors should not be taken with grapefruit juice. Grapefruit juice can interfere with the metabolism of the medication, leading to increased levels and potential side effects.
D) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake is not specific to the administration of ACE inhibitors. Fluid intake may need to be adjusted based on the client's overall fluid balance and congestive heart failure status, but it is not a direct instruction related to the medication.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because hypokalemia (low potassium levels) is more commonly associated with loop diuretics rather than beta-blockers.
B) This choice is incorrect because while hypotension (low blood pressure) can be a potential adverse effect of beta-blockers, it is not the primary adverse effect to be monitored for.
C) This choice is correct. Bradycardia (slow heart rate) is a common adverse effect of beta-blockers, which work by slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of the heart's contractions. The nurse should monitor the client's heart rate and report any significant changes or symptoms of bradycardia to the healthcare provider.
D) This choice is incorrect because hyperglycemia (high blood glucose levels) is not a common adverse effect of beta-blockers. In fact, beta-blockers can sometimes cause transient hypoglycemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because hypernatremia (high sodium levels) is not a common adverse effect of loop diuretics. Loop diuretics primarily impact sodium and water excretion.
B) This choice is incorrect because hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) is not typically associated with loop diuretics. In fact, loop diuretics can lead to increased potassium excretion, potentially causing hypokalemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) is not a common adverse effect of loop diuretics. Loop diuretics primarily affect sodium, potassium, and water excretion.
D) This choice is correct. Loop diuretics are potent potassium-wasting diuretics, meaning they increase potassium excretion in the urine, potentially causing hypokalemia. The nurse should closely monitor the client's potassium levels and provide potassium supplementation if necessary.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because serum sodium levels are not directly impacted by digoxin. However, electrolyte imbalances, including hypokalemia, can potentiate digoxin toxicity, so potassium levels should be monitored.
B) This choice is incorrect because while digoxin can impact liver function, it is not the primary parameter to be monitored. Liver function tests may be performed periodically to assess liver health during digoxin therapy.
C) This choice is correct. Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside that can impact renal function. Monitoring urine output is essential to assess kidney function and the client's response to the medication.
D) This choice is incorrect because blood glucose levels are not specifically impacted by digoxin. However, hypokalemia resulting from digoxin therapy can cause alterations in glucose metabolism, so blood glucose levels should be monitored in clients taking digoxin.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake is not specific to the administration of spironolactone. Fluid intake may need to be adjusted based on the client's overall fluid balance and congestive heart failure status, but it is not a direct instruction related to the medication.
B) This choice is correct. Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic that can cause hyperkalemia (high potassium levels). The client should avoid foods high in potassium to help prevent potassium overload and potential adverse effects.
C) This choice is incorrect because the timing of spironolactone administration may vary depending on the client's individual response and the presence of other medications. The client should follow the prescribed schedule given by the healthcare provider.
D) This choice is incorrect because monitoring blood pressure daily and adjusting the dose accordingly is not specific to the administration of spironolactone. While blood pressure may need to be monitored regularly, dosage adjustments should only be made under the guidance of the healthcare provider.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because consuming a diet high in sodium would exacerbate fluid retention in congestive heart failure. Clients with CHF should follow a low-sodium diet to reduce fluid overload and manage edema.
B) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake to 1 liter per day is too restrictive and may lead to dehydration. Fluid restriction is essential for some clients with CHF, but the specific limit should be determined by the healthcare provider based on the client's individual needs.
C) This choice is incorrect because while potassium intake may need to be monitored, restricting potassium-rich foods is not a universal instruction for clients with CHF. It depends on the client's overall potassium levels and specific medication regimen.
D) This choice is correct. Following a low-sodium diet is essential for clients with congestive heart failure to reduce fluid retention and manage symptoms of fluid overload.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because taking digoxin with a high-fat meal is not necessary. Digoxin can be taken with or without food, but consistent administration is essential for optimal therapeutic effects.
B) This choice is incorrect because skipping a dose of digoxin can lead to suboptimal medication levels and reduced effectiveness. If the client experiences nausea or vomiting, they should contact their healthcare provider for guidance.
C) This choice is correct. Digoxin is used to treat congestive heart failure and other cardiac conditions. It is crucial for clients to monitor their blood pressure regularly, especially if their healthcare provider has instructed them to adjust the medication dose based on their blood pressure readings.
D) This choice is incorrect because while avoiding certain over-the-counter medications is essential while on digoxin due to potential drug interactions, it is not the primary instruction for the client. The client should discuss any new medications, including over-the-counter drugs, with their healthcare provider to ensure they are safe to take with digoxin.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because bradycardia (slow heart rate) is not a common adverse effect of furosemide, a loop diuretic.
B) This choice is correct. Furosemide is a loop diuretic that can lead to increased potassium excretion in the urine, potentially causing hypokalemia (low potassium levels). The nurse should closely monitor the client's potassium levels and provide potassium supplementation if necessary.
C) This choice is incorrect because hypertension (high blood pressure) is not typically associated with loop diuretics like furosemide. In fact, furosemide is used to treat hypertension and congestive heart failure by promoting the excretion of excess fluid and reducing blood pressure.
D) This choice is incorrect because hyperglycemia (high blood glucose levels) is not a common adverse effect of furosemide. In fact, furosemide can sometimes cause transient hypoglycemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake to 1 liter per day is too restrictive and may lead to dehydration. Fluid restriction is essential for some clients with CHF, but the specific limit should be determined by the healthcare provider based on the client's individual needs.
B) This choice is incorrect because fluid restriction should not be limited to the evening only. Clients with CHF should monitor their fluid intake throughout the day to prevent fluid overload.
C) This choice is incorrect because drinking fluids primarily with meals may not be sufficient for managing fluid intake. Fluid intake should be balanced throughout the day to avoid excessive fluid retention.
D) This choice is correct. Monitoring daily weights is an essential strategy for clients with congestive heart failure to manage fluid balance. Sudden weight gain can indicate fluid retention, a common symptom of CHF. Clients should be instructed to report any significant weight changes to their healthcare provider promptly.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because taking the nitrate medication with food is not necessary. Nitrate medications are usually taken sublingually or by mouth and are not associated with significant stomach upset.
B) This choice is correct. Nitrate medications, such as nitroglycerin, can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure when used concurrently with erectile dysfunction medications, specifically phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5 inhibitors) like sildenafil (Viagra) or tadalafil (Cialis). Clients should be warned against using these medications together to prevent hypotension and potential cardiovascular complications.
C) This choice is incorrect because grapefruit juice is not typically associated with nitrate medications. Grapefruit juice can interact with certain medications, but it is not a known interaction with nitrates.
D) This choice is incorrect because increasing the nitrate dose without healthcare provider guidance can be dangerous. Clients should be instructed to take nitrate medications as prescribed and seek immediate medical attention if chest pain is not relieved within a specific timeframe, as directed by their healthcare provider.
Questions
Myocardial Infarction (MI) and Angina Pectoris
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because obtaining a detailed health history is important, but administering aspirin is the priority action in a suspected MI. Aspirin helps to prevent further clot formation and reduces the risk of complications during a myocardial infarction.
B) This choice is correct. Administering aspirin as prescribed is the priority action in a suspected MI. Aspirin acts as an antiplatelet agent and can help to prevent the formation of blood clots that could exacerbate the blockage in the coronary artery.
C) This choice is incorrect because while performing a complete physical examination is important, administering aspirin takes precedence in a suspected MI to address the potential clot formation.
D) This choice is incorrect because placing the client in a supine position is not the priority action in a suspected MI. The client's position should be adjusted based on their comfort and ability to breathe effectively.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Stable angina is typically predictable and occurs with exertion or emotional stress. It subsides with rest and nitroglycerin use. The pain is usually relieved within a few minutes after rest or medication administration.
B) This choice is incorrect because unstable angina is characterized by chest pain that occurs at rest or with minimal exertion and is more severe and prolonged than stable angina. It may indicate an impending myocardial infarction and requires immediate medical attention.
C) This choice is incorrect because variant (Prinzmetal) angina is caused by coronary artery vasospasm, which leads to chest pain even at rest. It is not typically relieved by rest and nitroglycerin, but rather by calcium channel blockers or nitrate medications.
D) This choice is incorrect because microvascular angina is characterized by chest pain caused by abnormalities in the small blood vessels in the heart. It may not always be relieved by nitroglycerin, and it is not the most likely diagnosis in this presentation.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while aspirin is important for clients with angina, the priority teaching point is the use of nitroglycerin for chest pain relief during angina episodes.
B) This choice is incorrect because keeping a log of triggers can be helpful for managing angina, but it is not the priority teaching point regarding the immediate relief of chest pain.
C) This choice is incorrect because limiting physical activity to avoid exertion is not the primary management strategy for angina. Moderate exercise, as tolerated, is beneficial for clients with stable angina.
D) This choice is correct. Nitroglycerin is a vasodilator that helps to relax and widen blood vessels, improving blood flow and relieving chest pain during an angina episode. Teaching the client to use nitroglycerin as needed for chest pain relief is a priority in angina management.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because sharp, stabbing chest pain is not the typical presentation of an acute MI. It is more common in conditions like pleuritis or pneumothorax.
B) This choice is incorrect because chest pain relieved by rest and nitroglycerin is more characteristic of stable angina, not an acute MI. Acute MI pain is typically not relieved by these measures.
C) This choice is correct. Sudden, severe chest pain that radiates to the back is a classic presentation of an acute myocardial infarction. The pain is often described as crushing or pressure-like and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath, diaphoresis, and nausea.
D) This choice is incorrect because mild, intermittent chest discomfort during activity is more typical of stable angina, not an acute MI. Acute MI pain is usually more severe, prolonged, and occurs at rest or with minimal exertion.
A client with angina pectoris is prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin tablets. What instructions should the nurse provide about taking nitroglycerin?
Explanation
A: This choice is incorrect because nitroglycerin tablets should not be swallowed immediately; they are designed to dissolve under the tongue to provide rapid relief from chest pain.
B: This choice is incorrect as nitroglycerin tablets do not need to be taken with water; they should dissolve sublingually and taking them with water could dilute the medication, reducing its effectiveness.
C: This choice is incorrect because crushing the tablet and mixing it with food would delay and potentially reduce the absorption of the medication, which is critical during an episode of angina.
D: This is the correct instruction because nitroglycerin tablets are very sensitive to light and moisture, which can reduce their effectiveness. Keeping them in their original bottle ensures they are protected from environmental factors that could degrade the medication.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because vasospasm of the coronary arteries, known as variant (Prinzmetal) angina, is a type of angina pectoris but not the primary cause of MI. Vasospasms may contribute to the development of unstable angina but are not the primary mechanism leading to MI.
B) This choice is correct. The formation of atherosclerotic plaques within the coronary arteries is the primary cause of MI. Atherosclerosis is a gradual process of plaque buildup, narrowing the coronary arteries, and reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. If a plaque ruptures, it can lead to the formation of a blood clot that completely obstructs the artery, causing MI.
C) This choice is incorrect because inflammation of the heart muscle, known as myocarditis, is a separate condition and not the primary cause of MI.
D) This choice is incorrect because increased heart rate and contractility can be associated with certain conditions but are not the primary cause of MI. MI is primarily caused by atherosclerotic plaque formation and subsequent thrombus formation in the coronary arteries.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a family history of coronary artery disease is a non-modifiable risk factor for angina pectoris. It increases the client's risk but cannot be altered through lifestyle changes.
B) This choice is incorrect because age over 65 years old is a non-modifiable risk factor for angina pectoris. While the risk of angina increases with age, it cannot be changed through lifestyle modifications.
C) This choice is correct. Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a modifiable risk factor for angina. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes, medications, and other interventions can help reduce the risk of developing angina and other cardiovascular diseases.
D) This choice is incorrect because gender (male) is a non-modifiable risk factor for angina pectoris. While men are generally at higher risk for angina than premenopausal women, gender cannot be changed to alter the risk.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because smoking is a modifiable risk factor for MI. Cessation of smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing MI and other cardiovascular diseases.
B) This choice is incorrect because a sedentary lifestyle is a modifiable risk factor for MI. Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce the risk of MI.
C) This choice is incorrect because diabetes mellitus is a modifiable risk factor for MI. Managing diabetes through lifestyle changes, medications, and blood sugar control can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications, including MI.
D) This choice is correct. A family history of MI is a non-modifiable risk factor because it is based on genetic factors that cannot be changed through lifestyle modifications. Having a close relative with a history of MI increases an individual's risk of developing MI, but it cannot be altered or eliminated through lifestyle changes.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because chest pain caused by an irregular heart rhythm is more characteristic of arrhythmias, not angina pectoris.
B) This choice is correct. Angina pectoris is caused by the narrowing of the coronary arteries due to atherosclerotic plaques, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle during periods of increased demand (e.g., physical exertion, stress).
C) This choice is incorrect because inflammation in the lining of the heart is associated with conditions like pericarditis or myocarditis, not angina pectoris.
D) This choice is incorrect because chest pain caused by the heart muscle overworking is more typical of conditions like heart failure, not angina pectoris.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Engaging in regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight are effective strategies for reducing the risk of MI. Physical activity helps improve cardiovascular health, manage weight, and reduce other risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.
B) This choice is incorrect because while limiting saturated fat intake is important for heart health, it is not the most effective approach to lower the risk of MI when compared to engaging in physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight.
C) This choice is incorrect because quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption are essential for reducing the risk of MI, but they may not be as effective as regular physical activity and weight management.
D) This choice is incorrect because controlling stress through relaxation techniques and counseling is beneficial for overall well-being, but it may not be the most effective approach to reduce the risk of MI when compared to regular physical activity and weight management. Stress management is still an important aspect of cardiovascular health, but it should be combined with other lifestyle changes for optimal risk reduction.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because sharp, stabbing pain is not typically associated with angina pectoris. It may be more characteristic of conditions like pleuritis or musculoskeletal pain.
B) This choice is incorrect because constant, burning pain is not typical of angina pectoris. It may be associated with conditions like heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
C) This choice is correct. Angina pectoris is often described as a crushing or pressure-like pain in the chest, which can be triggered by exertion or emotional stress. The pain may also radiate to the neck, jaw, or left arm.
D) This choice is incorrect because radiating pain to the left arm is associated with both angina pectoris and myocardial infarction (MI), but it is not specific enough to differentiate between the two conditions.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Diaphoresis (profuse sweating) is an early sign of myocardial infarction (MI) and is caused by the activation of the sympathetic nervous system in response to the heart muscle's decreased oxygen supply. Diaphoresis is often accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea.
B) This choice is incorrect because elevated blood pressure can occur during an acute MI, but it is not an early sign of the condition.
C) This choice is incorrect because elevated body temperature is not typically associated with an MI. It may be indicative of an infection or other inflammatory conditions.
D) This choice is incorrect because bradycardia (slow heart rate) is not an early sign of an MI. Tachycardia (rapid heart rate) is more commonly associated with an acute MI as the body attempts to compensate for the decreased cardiac output.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Administering sublingual nitroglycerin is the priority action during an angina episode. Nitroglycerin acts as a vasodilator and helps relax and widen blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart and reducing chest pain during an angina attack.
B) This choice is incorrect because assisting the client to lie flat in bed is not the priority during an angina episode. The client should be positioned in a comfortable position that allows them to breathe easily.
C) This choice is incorrect because obtaining an electrocardiogram (ECG) is important for assessing the client's cardiac status, but it is not the priority during an ongoing angina episode.
D) This choice is incorrect because providing oxygen therapy may be beneficial if the client is hypoxic, but it is not the priority during an angina episode. The priority is to administer nitroglycerin to relieve chest pain.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because chest pain relieved by rest and nitroglycerin is characteristic of stable angina, not an MI. Stable angina is triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress and is usually relieved by rest and nitroglycerin use.
B) This choice is correct. Diaphoresis (profuse sweating) and nausea are clinical manifestations commonly associated with an MI but not usually seen in stable angina. These symptoms are a result of the sympathetic nervous system's response to the heart muscle's decreased oxygen supply during an MI.
C) This choice is incorrect because chest pain triggered by emotional stress is characteristic of stable angina, not an MI. Emotional stress can cause vasospasms in the coronary arteries, leading to angina episodes.
D) This choice is incorrect because shortness of breath and wheezing may occur in both stable angina and MI, especially if the heart's pumping ability is compromised. These symptoms are not specific to MI and can also be seen in other cardiac and respiratory conditions.
Explanation
A) This choice is not the most concerning finding among the options presented. A blood pressure of 130/80 mmHg is within a normal range and does not indicate an immediate risk to the client.
B) This choice is not the most concerning finding among the options presented. A heart rate of 90 beats per minute is within a normal range and does not indicate an immediate risk to the client.
C) This choice is not the most concerning finding among the options presented. An oxygen saturation of 95% on room air is within a normal range and does not indicate an immediate risk to the client.
D) This choice is correct. An elevated ST segment on the electrocardiogram (ECG) is an important sign of an acute myocardial infarction (MI). It indicates myocardial ischemia and injury. The nurse should take immediate action, such as notifying the healthcare provider and implementing appropriate interventions for the client's acute coronary syndrome. Prompt medical intervention is crucial to minimize cardiac damage and improve the client's prognosis.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the primary diagnostic tests used to confirm the diagnosis of a myocardial infarction (MI). An ECG can show characteristic changes, such as ST-segment elevation or Q waves, indicative of myocardial ischemia and injury.
B) This choice is incorrect because an echocardiogram is a useful imaging test to assess the heart's structure and function, but it is not the primary diagnostic test for confirming an MI.
C) This choice is incorrect because a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable tool for assessing heart function and detecting certain cardiac abnormalities, but it is not typically the initial diagnostic test for MI.
D) This choice is incorrect because a chest X-ray can help identify other conditions like pulmonary edema or lung disorders, but it is not the primary diagnostic test for MI.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Measuring troponin levels in the blood is a common initial diagnostic test for evaluating suspected angina pectoris or myocardial infarction (MI). Troponins are specific markers released into the bloodstream when there is cardiac muscle damage, and elevated troponin levels indicate myocardial injury.
B) This choice is incorrect because a stress test is used to assess the heart's response to increased demand and is typically performed after the initial evaluation, such as measuring troponin levels, to confirm the presence of angina or MI.
C) This choice is incorrect because coronary angiography is an invasive procedure used to visualize the coronary arteries and assess for blockages. It is not typically the initial diagnostic test for angina pectoris or MI.
D) This choice is incorrect because cardiac catheterization is an invasive procedure used to measure pressures within the heart and evaluate coronary artery blockages. It is not typically the initial diagnostic test for angina pectoris or MI.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because a stress test is not primarily used to assess for the presence of atherosclerotic plaques. It is used to evaluate the heart's response to increased demand and identify exercise-induced changes in the ECG, which may indicate myocardial ischemia.
B) This choice is incorrect because a stress test does not measure cardiac biomarker levels in the blood. Cardiac biomarkers like troponin are typically measured through blood tests to diagnose myocardial infarction (MI).
C) This choice is correct. The primary purpose of a stress test is to evaluate the heart's response to increased demand, such as physical exercise or the administration of medication that simulates exercise. During the test, the client's heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG are monitored for signs of ischemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because a stress test is not used to visualize the coronary arteries for blockages. It is a non-invasive test primarily used to assess the heart's functional capacity.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because measuring the levels of cardiac biomarkers in the blood is not the purpose of coronary angiography. Cardiac biomarkers are measured through blood tests to diagnose conditions like myocardial infarction (MI).
B) This choice is incorrect because a stress test evaluates the heart's response to increased demand and is different from coronary angiography.
C) This choice is correct. Coronary angiography is an invasive procedure that involves injecting a contrast dye into the coronary arteries. The dye allows visualization of the coronary arteries and identifies any blockages or narrowing that may be causing angina or other cardiac symptoms.
D) This choice is incorrect because assessing the heart's function using sound waves is characteristic of an echocardiogram, not coronary angiography.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because administering sublingual nitroglycerin is an important intervention to relieve chest pain in clients with angina pectoris, but obtaining a 12-lead ECG is the priority in a client suspected of experiencing an MI. The ECG helps in diagnosing MI and determining the appropriate treatment plan.
B) This choice is correct. The priority nursing intervention during the initial assessment of a client with suspected MI is to obtain a 12-lead ECG. The ECG provides crucial information about cardiac electrical activity and helps identify ST-segment elevation, indicating myocardial ischemia or injury.
C) This choice is incorrect because initiating intravenous (IV) access is an essential step in the management of an MI, but it is not the priority over obtaining a 12-lead ECG.
D) This choice is incorrect because administering aspirin is an essential intervention during an MI to help reduce platelet aggregation and prevent further clot formation. However, obtaining a 12-lead ECG takes precedence in the initial assessment to confirm the diagnosis and guide further interventions.
A client with angina pectoris reports chest pain and is receiving oxygen therapy. The client asks the nurse about the purpose of oxygen administration. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A: Oxygen does not directly dilate coronary arteries; medications such as nitrates are responsible for this effect.
B: While oxygen aids in metabolic processes, it does not directly affect the heart's pumping efficiency in the context of angina pectoris.
C: Oxygen therapy increases the oxygen saturation of the blood, which can help alleviate symptoms like shortness of breath and chest pain associated with angina by ensuring that the heart muscle receives sufficient oxygen to function properly.
D: Oxygen therapy is not a treatment for preventing clot formation; this is typically managed with anticoagulant medications.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while rest is essential during an angina episode, lying down in bed for an extended period is not necessary after administering nitroglycerin.
B) This choice is incorrect because monitoring blood pressure and heart rate every 15 minutes is not a standard nursing intervention after nitroglycerin administration. Monitoring vital signs as needed for the client's condition is appropriate.
C) This choice is incorrect because there is no need for the client to avoid drinking water or fluids after taking sublingual nitroglycerin.
D) This choice is correct. After taking sublingual nitroglycerin for chest pain relief, the client should sit or lie down and avoid sudden position changes. Nitroglycerin can cause systemic vasodilation and may lead to orthostatic hypotension, increasing the risk of dizziness or falls if the client stands up abruptly. Taking a seated or lying position reduces this risk and allows the medication to work effectively to relieve chest pain.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat fluid retention and edema in clients with congestive heart failure (CHF), but it does not directly reduce myocardial oxygen demand.
B) This choice is correct. Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that reduces heart rate and blood pressure, resulting in decreased myocardial oxygen demand. It is often prescribed to clients with an MI and a history of CHF to improve cardiac function and reduce the workload on the heart.
C) This choice is incorrect because aspirin is an antiplatelet medication that prevents further clot formation and is commonly prescribed in clients with acute coronary syndrome, including MI. While it is beneficial in the context of MI management, it does not directly reduce myocardial oxygen demand.
D) This choice is incorrect because nitroglycerin is a vasodilator used to relieve chest pain (angina) by dilating blood vessels and increasing blood flow to the heart muscle. While it helps reduce anginal symptoms, it does not directly reduce myocardial oxygen demand as metoprolol does.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because sublingual nitroglycerin should not be swallowed with water. It is intended to dissolve under the tongue for rapid absorption into the bloodstream to provide quick relief from chest pain.
B) This choice is incorrect because the timing of nitroglycerin administration is not dependent on meals. Sublingual nitroglycerin should be taken as needed when chest pain occurs.
C) This choice is correct. Sublingual nitroglycerin is administered by placing the tablet under the tongue, where it dissolves and is absorbed directly into the bloodstream. This method allows for rapid onset of action and is used to relieve acute chest pain.
D) This choice is incorrect because sublingual nitroglycerin is not meant for daily or preventive use. It is specifically used to treat acute episodes of chest pain (angina) and should be taken only when needed. Clients with angina may be prescribed long-acting nitroglycerin preparations for prophylactic use, but sublingual nitroglycerin is intended for immediate relief of anginal symptoms.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because aspirin does not directly dilate coronary arteries. Aspirin's primary action in MI management is its antiplatelet effect, which prevents platelets from clumping together and forming blood clots in coronary arteries, reducing the risk of further blockages.
B) This choice is correct. Aspirin is commonly prescribed during an acute MI to prevent blood clot formation and reduce the risk of further blockages in the coronary arteries. It is a crucial medication in the management of acute coronary syndrome.
C) This choice is incorrect because aspirin's primary action is not to lower blood pressure or improve cardiac pumping efficiency. These actions are typically achieved through other medications, such as beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors, in the management of MI.
D) This choice is incorrect because while aspirin is used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, its primary role in MI management is its antiplatelet effect, as mentioned earlier.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Clopidogrel (Plavix) is an antiplatelet medication commonly prescribed for clients with unstable angina to prevent platelet aggregation and reduce the risk of blood clot formation in coronary arteries.
B) This choice is incorrect because nitroglycerin is a vasodilator used to relieve angina symptoms, but it does not have the antiplatelet effect necessary for managing unstable angina.
C) This choice is incorrect because atorvastatin is a statin medication used to lower cholesterol levels and prevent cardiovascular events, but it does not have the antiplatelet effect required for managing unstable angina.
D) This choice is incorrect because metoprolol is a beta-blocker used to reduce heart rate and blood pressure, but it is not an antiplatelet agent like clopidogrel.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while PCI can indirectly relieve chest pain by restoring blood flow to the heart, its primary purpose is not to reduce inflammation in the heart muscle.
B) This choice is correct. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) involves the insertion of a catheter with a balloon at the tip into the blocked coronary artery. The balloon is inflated to compress the plaque and open the artery, and then a stent is placed to keep the artery open and improve blood flow to the heart.
C) This choice is incorrect because PCI's primary purpose is not to lower blood pressure but to restore blood flow to the heart by treating coronary artery blockages.
D) This choice is incorrect because the description provided is more characteristic of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, not PCI.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because heparin does not directly dissolve existing blood clots in coronary arteries. It is used to prevent further clot formation and growth.
B) This choice is incorrect because heparin's primary action is not to relax blood vessels. It is an anticoagulant that inhibits clot formation.
C) This choice is correct. Heparin is an anticoagulant medication used to prevent further clot formation in coronary arteries and reduce the risk of complications in clients with unstable angina.
D) This choice is incorrect because heparin is not a pain reliever. It does not directly address chest discomfort during angina episodes; its role is in preventing and managing thrombosis.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because fibrinolytic therapy is not used to reduce heart rate and blood pressure. Its primary purpose is to dissolve blood clots that are causing the myocardial infarction.
B) This choice is correct. Fibrinolytic therapy, also known as thrombolytic therapy, is used to break down existing blood clots in coronary arteries during an ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). By dissolving the clot, blood flow to the heart muscle can be restored and prevent further damage.
C) This choice is incorrect because stabilizing the heart's electrical activity is not the primary purpose of fibrinolytic therapy. It is used to address the mechanical obstruction caused by the clot in coronary arteries.
D) This choice is incorrect because although fibrinolytic therapy does improve blood flow to the heart muscle by dissolving clots, its primary purpose is not to improve oxygen supply directly. Rather, it aims to restore blood flow by eliminating the clot causing the infarction.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because inserting a stent is a part of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and not coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). CABG involves using blood vessels (grafts) to bypass blocked coronary arteries and restore blood flow to the heart.
B) This choice is incorrect because removing plaque from coronary arteries is not the primary purpose of CABG. CABG involves bypassing blocked arteries rather than removing the plaque.
C) This choice is incorrect because repairing damaged heart valves and improving cardiac function is a different surgical procedure, such as valve repair or replacement surgery. CABG does not address heart valve issues.
D) This choice is correct. Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure that involves taking a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body and grafting it to the blocked coronary artery. The graft bypasses the blockage, restoring blood flow to the heart and improving myocardial oxygen supply. CABG is used to treat significant coronary artery disease and improve cardiac function in clients with unstable angina or myocardial infarction.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because ranolazine does not increase heart rate and cardiac output. Instead, it has a neutral effect on heart rate.
B) This choice is incorrect because ranolazine does not directly dilate coronary arteries. Its primary action is to reduce myocardial oxygen demand and improve oxygen utilization in the heart.
C) This choice is correct. Ranolazine is an anti-anginal medication that primarily works by reducing myocardial oxygen demand. It achieves this by inhibiting the late sodium current in cardiac cells, which helps decrease intracellular calcium levels, thereby reducing the energy required for the heart's contraction and relaxation. This results in improved oxygen utilization in the heart muscle and decreased anginal symptoms.
D) This choice is incorrect because ranolazine is not an antiplatelet medication. Its mechanism of action is related to its effects on myocardial oxygen demand and utilization, not its impact on platelet aggregation and clot formation.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while cardiac rehabilitation may have cardiovascular benefits, its primary focus is on promoting overall heart health and reducing the risk of future heart attacks through lifestyle changes and education.
B) This choice is correct. Cardiac rehabilitation is a comprehensive program that aims to improve the overall cardiovascular health of individuals who have experienced a myocardial infarction or other heart conditions. It involves a combination of exercise, education, and counseling to support lifestyle changes that promote heart health and prevent future cardiovascular events.
C) This choice is incorrect because while psychological counseling may be a part of the cardiac rehabilitation program, it is not the primary purpose. The main focus is on physical and lifestyle aspects to improve cardiovascular health.
D) This choice is incorrect because cardiac rehabilitation does involve physical exercise, but the primary goal is not to improve lung function and oxygenation. Instead, it aims to improve cardiovascular endurance, strength, and overall heart health.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while exercise can contribute to weight loss and reduce the risk of diabetes, its primary benefit in cardiac rehabilitation is related to cardiovascular health, specifically improving blood flow to the heart and lowering blood pressure.
B) This choice is correct. Regular exercise in cardiac rehabilitation has significant benefits for the cardiovascular system. It improves blood flow to the heart muscle, enhances collateral circulation, and can help lower blood pressure, all of which are crucial in managing and preventing further complications after an MI.
C) This choice is incorrect because although exercise can help build muscle strength and improve bone health, these are not the primary benefits sought in cardiac rehabilitation. The focus is on cardiovascular health and recovery.
D) This choice is incorrect because while exercise can have positive effects on mental health, such as reducing stress and anxiety, its primary benefit in cardiac rehabilitation is related to cardiovascular health.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because nuts and seeds are sources of healthy fats and can be beneficial for heart health when consumed in moderation.
B) This choice is incorrect because avocado and olive oil are sources of monounsaturated fats, which are considered heart-healthy fats. They can be included in a heart-healthy diet.
C) This choice is correct. Saturated fats, commonly found in fatty cuts of red meat and butter, are known to increase LDL cholesterol levels and should be limited in a heart-healthy diet to reduce the risk of future cardiovascular events.
D) This choice is incorrect because whole grains and legumes are sources of complex carbohydrates and plant-based proteins that can be part of a heart-healthy diet. They provide essential nutrients and fiber that are beneficial for heart health.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because e-cigarettes and vaping are not considered safe alternatives to smoking and are not recommended as a way to quit smoking. They can also pose health risks to the cardiovascular system.
B) This choice is incorrect because gradually decreasing cigarette intake may not be as effective as setting a quit date and quitting smoking altogether.
C) This choice is incorrect because while nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) can be helpful for some individuals in managing cravings during the quitting process, it is not the primary recommendation. Avoiding triggers and setting a quit date are essential strategies for successful smoking cessation.
D) This choice is correct. Setting a quit date is an effective approach to quitting smoking. It allows individuals to mentally prepare for the change and commit to the process. Avoiding situations or triggers that may lead to smoking is also crucial for breaking the habit and preventing relapse.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because stress does not cause the heart to pump faster. While stress can activate the sympathetic nervous system and increase heart rate, the primary impact on the heart is related to hormonal responses.
B) This choice is incorrect because stress-induced vasodilation of coronary arteries is not a typical response. Instead, stress can lead to vasoconstriction, potentially reducing blood flow to the heart.
C) This choice is correct. During stress, the body releases adrenaline (epinephrine) and other stress hormones, which can lead to vasoconstriction of coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. Additionally, the release of adrenaline can increase heart rate, resulting in increased myocardial oxygen demand.
D) This choice is incorrect because stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure rather than suppressing these responses.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because beta-blockers do not directly dilate blood vessels. They primarily work by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart and blood vessels, leading to decreased heart rate and reduced blood pressure.
B) This choice is incorrect because beta-blockers do not directly affect cholesterol levels or prevent the formation of plaques in arteries. Their primary action is on the cardiovascular system, particularly the heart and blood pressure.
C) This choice is correct. Beta-blockers are commonly prescribed after an MI to reduce the workload of the heart and lower blood pressure. By blocking the effects of adrenaline, they help slow down the heart rate and reduce the force of contraction, thereby decreasing myocardial oxygen demand and improving the heart's efficiency.
D) This choice is incorrect because beta-blockers do not directly prevent blood clot formation in coronary arteries. Anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications are used to reduce the risk of clot formation in individuals at high risk for recurrent heart attacks.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because encouraging the client to stop taking medications without consulting the healthcare provider can be dangerous, especially after an MI. Medications prescribed after an MI are essential for managing cardiovascular risks and should not be discontinued without medical advice.
B) This choice is incorrect because it is not appropriate to downplay the potential side effects of medications. While side effects may be uncommon, it is essential to provide accurate information and address the client's concerns.
C) This choice is correct. Providing information about possible side effects and instructing the client to report any adverse reactions to the healthcare provider is essential. It empowers the client to recognize and manage potential side effects appropriately, ensuring that any concerns are addressed promptly by the healthcare team.
D) This choice is incorrect because suggesting over-the-counter medications without consulting the healthcare provider can be unsafe and may interact with prescribed medications. It is essential to address side effects with the healthcare team for appropriate management and adjustments to the medication regimen if needed.
Questions
A nurse is caring for a client admitted with chest pain, and the healthcare provider orders a cardiac biomarker test. Which biomarker is most specific for diagnosing a myocardial infarction (MI)?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because myoglobin is a cardiac biomarker that may be elevated in MI, but it lacks specificity and can also be elevated in other conditions like skeletal muscle injury.
B) This choice is incorrect because C-reactive protein (CRP) is an inflammatory marker and is not specific to MI. It may be elevated in various inflammatory conditions.
C) This choice is incorrect because brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a biomarker associated with heart failure and is not specific to diagnosing MI.
D) This choice is correct. Troponin is the most specific biomarker for diagnosing MI. Elevated troponin levels in the blood indicate cardiac muscle damage, making it a reliable marker for myocardial infarction. Troponin levels rise shortly after the onset of MI and remain elevated for several days, making it valuable in both early and delayed MI detection.
A client with suspected myocardial infarction (MI) is admitted to the emergency department. The nurse asks the client about the onset and duration of chest pain. Which response should the nurse consider as indicative of an MI?
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. The sudden onset of chest pain lasting for 30 minutes is a typical clinical manifestation of myocardial infarction (MI). The duration and intensity of chest pain are important indicators that suggest an acute cardiac event.
B) This choice is incorrect because chest discomfort lasting for a few days may be more characteristic of unstable angina, not an MI. Unstable angina is also a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention, but it is not synonymous with MI.
C) This choice is incorrect because chest pain that comes and goes, lasting only a few seconds at a time, is not typical of an MI. Such symptoms may indicate other non-cardiac conditions or stable angina.
D) This choice is incorrect because a similar episode of chest pain a few months ago is not indicative of the current acute event. The nurse should focus on the client's current symptoms and their acute presentation to determine the appropriate interventions.
A nurse is caring for a client admitted with myocardial infarction (MI). The client's blood pressure drops, and the client becomes restless and anxious. What intervention should the nurse initiate first?
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Administering oxygen therapy is the priority intervention when a client with MI experiences a drop in blood pressure and becomes restless and anxious. Oxygen can improve tissue oxygenation and help stabilize the client's condition.
B) This choice is incorrect because elevating the client's legs may be beneficial in certain situations, but it is not the priority when the client is experiencing a drop in blood pressure and restlessness due to MI.
C) This choice is incorrect because obtaining a 12-lead ECG is important for assessing and diagnosing MI, but it is not the priority when the client's condition is deteriorating rapidly.
D) This choice is incorrect because initiating cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is not indicated in this scenario. The client is still conscious and experiencing symptoms, indicating a need for prompt oxygen administration and further assessment.
Anemia
Explanation
A) This statement is incorrect because anemia is characterized by a decrease in red blood cell production or an abnormal decrease in hemoglobin levels, not an increase in red blood cell production.
B) This statement is incorrect because anemia is caused by a deficiency in iron, not an excess of iron.
C) This statement is correct. Anemia is characterized by a reduced number of red blood cells or a decreased hemoglobin concentration, which leads to a diminished ability of the blood to carry oxygen throughout the body.
D) This statement is incorrect. Anemia is not caused by a viral infection affecting the bone marrow; rather, it is typically caused by nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, or blood loss.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because oranges are a good source of vitamin C, which enhances iron absorption, but they do not provide significant iron content.
B) This choice is correct because spinach is a good source of iron, which is essential for clients with iron-deficiency anemia.
C) This choice is correct because red meat contains heme iron, a highly absorbable form of iron that can help improve iron levels in clients with anemia.
D) This choice is correct because nuts and seeds, such as pumpkin seeds and almonds, are good sources of iron.
A client with anemia is prescribed ferrous sulfate supplements. A nurse should instruct the client to take the supplement:
Explanation
A. With meals
Taking ferrous sulfate with meals may reduce its absorption because food, particularly dairy products and certain medications, can interfere with iron absorption.
B. On an empty stomach
Ferrous sulfate is best absorbed on an empty stomach, as food can inhibit iron absorption. However, if gastrointestinal irritation occurs, it may be taken with a small amount of food.
C. At bedtime
Taking iron supplements at bedtime is not ideal because it can cause gastrointestinal discomfort, which may interfere with sleep.
D. Simultaneously with calcium supplements
Calcium supplements can interfere with the absorption of iron, so they should not be taken at the same time as ferrous sulfate. It is recommended to space them out by at least 2 hours.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because vitamin A deficiency does not cause megaloblastic anemia.
B) This choice is correct because megaloblastic anemia is typically caused by a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid, which are essential for normal red blood cell production.
C) This choice is incorrect because vitamin C deficiency leads to scurvy, a condition unrelated to megaloblastic anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because vitamin D deficiency can lead to conditions like rickets, but it does not cause megaloblastic anemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct because the client is showing signs of decreased oxygen-carrying capacity due to anemia, and providing oxygen can help improve oxygen saturation levels and alleviate symptoms.
B) This choice is incorrect because pain medication does not address the underlying issue of anemia and the client's symptoms.
C) This choice is incorrect because assessing pain levels is not the priority when the client is presenting with symptoms of anemia and potential oxygen deficiency.
D) This choice is incorrect because although rest and activity balance are essential for overall well-being, they do not directly address the client's acute symptoms related to anemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because administering pain medication addresses the pain associated with the vaso-occlusive crisis, but the priority is to improve oxygenation first.
B) This choice is incorrect because warm compresses may provide comfort, but they do not directly address the underlying issue of vaso-occlusion and oxygen deficiency.
C) This choice is incorrect because although increasing fluid intake can help improve blood flow, it does not take precedence over addressing the oxygen deficiency.
D) This choice is correct because initiating oxygen therapy is the first priority in managing a vaso-occlusive crisis in a client with sickle cell anemia. It helps improve oxygenation and tissue perfusion, which are crucial during this crisis.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia is characterized by an increased destruction of red blood cells, which would typically result in a high reticulocyte count.
B) This choice is incorrect because iron-deficiency anemia is characterized by a low level of iron, which leads to decreased hemoglobin production but does not necessarily affect reticulocyte count.
C) This choice is correct. Aplastic anemia is characterized by the failure of the bone marrow to produce an adequate number of red blood cells, leading to a low reticulocyte count.
D) This choice is incorrect because pernicious anemia is caused by a deficiency in vitamin B12, which affects red blood cell maturation but does not directly influence reticulocyte count.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia typically presents with normocytic and normochromic red blood cells, as the bone marrow compensates by releasing immature red blood cells.
B) This choice is incorrect because sickle cell anemia is characterized by the presence of sickle-shaped red blood cells and is not associated with microcytic and hypochromic cells.
C) This choice is correct. Thalassemia is a type of anemia in which the synthesis of globin chains is impaired, leading to microcytic and hypochromic red blood cells.
D) This choice is incorrect because pernicious anemia is associated with macrocytic and normochromic red blood cells due to vitamin B12 deficiency.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Folate-deficiency anemia can present with fatigue, weakness, and glossitis (inflammation of the tongue), leading to a red, sore tongue.
B) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia is characterized by the destruction of red blood cells, and it does not specifically cause a red, sore tongue.
C) This choice is incorrect because sickle cell anemia primarily causes vaso-occlusive crises and pain, not symptoms related to the tongue.
D) This choice is incorrect because iron-deficiency anemia does not cause glossitis; however, it may present with fatigue and weakness.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because iron deficiency is one of the causes of anemia, but in chronic kidney disease, impaired erythropoietin production is the primary reason.
B) This choice is correct. Anemia in chronic kidney disease is primarily caused by decreased production of erythropoietin, a hormone produced by the kidneys that stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
C) This choice is incorrect because hemolysis of red blood cells is not the main cause of anemia in chronic kidney disease.
D) This choice is incorrect because vitamin B12 deficiency is not typically associated with anemia in chronic kidney disease.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Iron-deficiency anemia may present with an increased number of target cells on the peripheral blood smear, which are red blood cells with a central area of pallor and a surrounding ring of hemoglobin. This appearance is due to a reduced hemoglobin content in relation to cell size.
B) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia is characterized by the destruction of red blood cells and typically presents with different morphological changes on the peripheral blood smear.
C) This choice is incorrect because sickle cell anemia is associated with the presence of sickle-shaped cells, not target cells.
D) This choice is incorrect because aplastic anemia is characterized by a decrease in the number of all formed elements of the blood (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets), and it does not typically cause target cells.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because iron-deficiency anemia is associated with microcytic and hypochromic red blood cells, not macrocytic and normochromic cells.
B) This choice is incorrect because aplastic anemia typically presents with normocytic and normochromic red blood cells.
C) This choice is incorrect because sickle cell anemia does not cause macrocytic and normochromic red blood cells.
D) This choice is correct. Megaloblastic anemia is characterized by macrocytic (large) and normochromic (normal color) red blood cells, which are the result of impaired DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. This condition is often caused by vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. A vegetarian diet, especially if not well-balanced and lacking in iron-rich foods, can lead to iron-deficiency anemia.
B) This choice is incorrect. Chronic kidney disease is more likely to cause anemia due to impaired erythropoietin production rather than directly causing iron deficiency.
C) This choice is incorrect. Excessive red blood cell destruction is associated with hemolytic anemia, not iron-deficiency anemia.
D) This choice is correct. Gastrointestinal bleeding, such as from peptic ulcers or inflammatory bowel disease, can lead to chronic blood loss and iron-deficiency anemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because pernicious anemia is not related to iron deficiency, so increasing iron-rich foods will not address the underlying cause.
B) This choice is incorrect because vitamin C actually enhances the absorption of vitamin B12, which is essential in pernicious anemia.
C) This choice is correct. Pernicious anemia is caused by the lack of intrinsic factor, a protein necessary for vitamin B12 absorption. Clients with pernicious anemia will require lifelong vitamin B12 supplementation, often through intramuscular injections.
D) This choice is incorrect. Leafy green vegetables are good sources of folate, which is not directly related to pernicious anemia.
A nurse is assessing a client with anemia, and the client reports a history of chronic alcoholism. Which type of anemia is most likely to be associated with alcoholism?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because folate-deficiency anemia is associated with a deficiency of folic acid, often caused by poor dietary intake or malabsorption, but not specifically linked to alcoholism.
B) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia is characterized by the destruction of red blood cells and is not directly related to alcoholism.
C) This choice is incorrect because sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder and is not caused by alcohol consumption.
D) This choice is correct. Macrocytic anemia is commonly associated with alcoholism due to the direct toxic effects of alcohol on bone marrow, resulting in the production of larger-than-normal red blood cells (macrocytes).
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because iron-deficiency anemia is not typically associated with hemolysis or elevated bilirubin levels.
B) This choice is correct. Hemolytic anemia is characterized by the destruction of red blood cells, leading to the release of bilirubin, which causes jaundice and elevated bilirubin levels.
C) This choice is incorrect because pernicious anemia is caused by a deficiency in vitamin B12 and does not directly involve hemolysis.
D) This choice is incorrect because aplastic anemia is characterized by bone marrow suppression, resulting in decreased production of all blood cells, not hemolysis.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because iron-deficiency anemia is not directly related to chronic inflammatory diseases; it is more commonly associated with blood loss or inadequate iron intake.
B) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia is not specifically linked to chronic inflammatory diseases.
C) This choice is incorrect because aplastic anemia is characterized by bone marrow suppression and is not primarily associated with chronic inflammatory conditions.
D) This choice is correct. Anemia of chronic disease (ACD), also known as anemia of inflammation, is a type of anemia that occurs in the setting of chronic inflammatory diseases. It is typically caused by the body's response to the inflammation, leading to impaired red blood cell production and a shortened red blood cell lifespan.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because iron-deficiency anemia is more likely in clients with gastric bypass surgery due to reduced iron absorption, but it is not specific to this surgery.
B) This choice is correct. Pernicious anemia is associated with gastric bypass surgery because the procedure can lead to the loss of intrinsic factor-producing cells in the stomach, which is essential for vitamin B12 absorption.
C) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia is not directly linked to gastric bypass surgery.
D) This choice is incorrect because sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder and is not related to gastric bypass surgery.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because polyuria, or increased urination, is not a common symptom of anemia. It may be associated with other conditions like diabetes.
B) This choice is incorrect because increased appetite is not typically associated with anemia. In fact, some clients with anemia may have a reduced appetite due to fatigue and weakness.
C) This choice is correct. Anemia leads to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, which can result in shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion.
D) This choice is incorrect because anemia causes fatigue and decreased energy levels, not increased energy levels.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because petechiae, which are tiny red or purple spots on the skin, are associated with platelet disorders and not directly related to anemia.
B) This choice is correct. Pallor (pale skin) and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes) are related clinical manifestations of anemia. Jaundice can occur in hemolytic anemias when the breakdown of red blood cells leads to an accumulation of bilirubin.
C) This choice is incorrect because cyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the skin, is not directly related to anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because diaphoresis, or excessive sweating, is not a typical clinical manifestation of anemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because tingling sensation and difficulty maintaining balance are not typical symptoms of iron-deficiency anemia.
B) This choice is incorrect because aplastic anemia primarily affects the bone marrow and results in decreased production of all blood cells, not specifically causing tingling sensation or balance issues.
C) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia is characterized by the destruction of red blood cells and is not directly related to neurological symptoms like tingling and balance difficulties.
D) This choice is correct. Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia can cause neurological symptoms, including tingling in the hands and feet (paresthesia) and difficulty maintaining balance due to nerve damage.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because anemia is not directly associated with elevated blood pressure. In fact, low blood pressure may be observed in some individuals with anemia due to decreased blood volume.
B) This choice is correct. Anemia leads to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood, and the body compensates by increasing the heart rate to supply more oxygen to vital organs and tissues.
C) This choice is incorrect because excessive thirst is not a typical symptom of anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because anemia is more likely to cause a decreased appetite rather than an increased appetite.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because increased blood pressure is not typically observed during a vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell anemia.
B) This choice is incorrect because pale skin and mucous membranes are more likely to be seen in clients with anemia due to decreased red blood cell count, but it is not specific to a vaso-occlusive crisis.
C) This choice is correct. A vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell anemia is characterized by the blockage of small blood vessels, leading to severe pain, particularly in the joints and bones.
D) This choice is incorrect because clients experiencing a vaso-occlusive crisis are more likely to feel fatigued and weak due to the lack of oxygen delivery, rather than having high energy levels.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Headaches and dizziness are common symptoms of iron-deficiency anemia due to decreased oxygen delivery to the brain.
B) This choice is incorrect because headaches and dizziness are not specific to hemolytic anemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because pernicious anemia is primarily associated with neurological symptoms such as tingling and difficulty maintaining balance, but not specifically headaches and dizziness.
D) This choice is incorrect because headaches and dizziness are not directly related to aplastic anemia. Aplastic anemia primarily affects the bone marrow and leads to decreased production of all blood cells, rather than causing symptoms specific to the brain.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because an electrocardiogram (ECG) is not a diagnostic test for anemia. It is used to assess heart function.
B) This choice is correct. A complete blood count (CBC) is the primary diagnostic test used to confirm the presence of anemia. It provides information about red blood cell count, hemoglobin levels, hematocrit, and other parameters related to blood cell characteristics.
C) This choice is incorrect because serum creatinine is used to assess kidney function, not to diagnose anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because a urinalysis is not a diagnostic test for anemia. It is used to assess kidney function and urinary tract health.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. A low mean corpuscular volume (MCV) indicates microcytic red blood cells, which are characteristic of iron-deficiency anemia.
B) This choice is incorrect because hemolytic anemia typically presents with a normal or elevated MCV, not a low MCV.
C) This choice is incorrect because megaloblastic anemia is associated with an elevated MCV due to the presence of larger-than-normal red blood cells (macrocytic).
D) This choice is incorrect because pernicious anemia is associated with a macrocytic MCV, not a microcytic MCV.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Vitamin C enhances the absorption of non-heme iron (the type of iron found in plant-based foods and supplements), so increasing vitamin C intake can help improve iron absorption. This can help differentiate between iron-deficiency anemia (improved iron absorption with increased vitamin C) and anemia of chronic disease (improved iron absorption with decreased vitamin C intake).
B) This choice is incorrect because increasing folate intake may help with megaloblastic anemia caused by folate deficiency, but it does not directly differentiate between iron-deficiency anemia and other types of anemia.
C) This choice is incorrect because increasing vitamin B12 intake does not help differentiate between iron-deficiency anemia and other types of anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because increasing protein intake is important for overall health but does not directly help differentiate between iron-deficiency anemia and other types of anemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because hemoglobin electrophoresis is used to identify abnormal hemoglobin types, not to assess the size and shape of red blood cells.
B) This choice is incorrect because a reticulocyte count measures the number of immature red blood cells in the blood and helps determine if the bone marrow is responding appropriately to anemia, but it does not assess the size and shape of red blood cells.
C) This choice is correct. A peripheral blood smear is used to examine the morphology of red blood cells, including their size, shape, and appearance. It can help identify different types of anemia and determine the cause of anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because serum iron levels provide information about iron status but do not directly assess the size and shape of red blood cells.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Serum ferritin levels are used to assess the body's iron stores. Ferritin is a protein that stores iron in the body, and low levels of serum ferritin indicate iron deficiency.
B) This choice is incorrect because the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a nonspecific indicator of inflammation and is not directly related to iron stores.
C) This choice is incorrect because total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) measures the amount of iron that can be bound to transferrin, a protein that transports iron in the blood, but it does not directly assess iron stores.
D) This choice is incorrect because the white blood cell count (WBC) is not directly related to iron stores or the evaluation of anemia.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because the Schilling test is not used to diagnose iron-deficiency anemia. It is primarily used to diagnose pernicious anemia, a type of megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency.
B) This choice is correct. The Schilling test is used to diagnose pernicious anemia by assessing the body's ability to absorb vitamin B12 from the digestive system.
C) This choice is incorrect because the Schilling test is not used to diagnose aplastic anemia. Aplastic anemia is diagnosed through other means, such as bone marrow biopsy and blood tests.
D) This choice is incorrect because the Schilling test is not used to diagnose hemolytic anemia. Hemolytic anemia is diagnosed through blood tests and other assessments to determine red blood cell destruction.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because oranges are rich in vitamin C, which enhances iron absorption, but they do not contain significant amounts of iron.
B) This choice is incorrect because milk is not a good source of iron and may even hinder iron absorption when consumed in large quantities.
C) This choice is correct. Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are excellent sources of iron and can help improve iron levels in clients with iron-deficiency anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because white bread is not a significant source of iron and does not help in increasing iron levels.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because coffee contains substances that can inhibit iron absorption.
B) This choice is incorrect because tea, especially black tea, contains tannins that can hinder iron absorption.
C) This choice is incorrect because water does not enhance iron absorption.
D) This choice is correct. Orange juice, or any other vitamin C-rich beverage, enhances the absorption of non-heme iron found in supplements and plant-based foods.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Epoetin alfa is a synthetic form of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. One of the potential side effects of this medication is an increase in blood pressure (hypertension).
B) This choice is incorrect because hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) is not a common side effect of epoetin alfa therapy.
C) This choice is incorrect because hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is not a common side effect of epoetin alfa therapy.
D) This choice is incorrect because hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) is not a common side effect of epoetin alfa therapy.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because taking ferrous sulfate with water is generally acceptable and does not significantly affect iron absorption.
B) This choice is incorrect because taking ferrous sulfate with orange juice, which is rich in vitamin C, can enhance iron absorption and is often recommended.
C) This choice is incorrect because taking ferrous sulfate with milk can reduce iron absorption, but it is not as significant as with tea or coffee.
D) This choice is correct. Tea, especially black tea, contains tannins that can inhibit iron absorption when taken with ferrous sulfate or other iron supplements.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while antibiotics may be necessary if there is an infection, they are not the priority intervention during a vaso-occlusive crisis.
B) This choice is incorrect because blood transfusions may be needed if there is severe anemia or complications, but they are not the priority intervention during a vaso-occlusive crisis.
C) This choice is correct. Initiating oxygen therapy is a priority in managing a vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell anemia. Providing supplemental oxygen can help improve tissue oxygenation and reduce the severity of the crisis.
D) This choice is incorrect because although encouraging fluid intake is important in managing sickle cell anemia, it is not the priority intervention during a vaso-occlusive crisis.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while blood pressure monitoring is essential for clients with chronic kidney disease, it is not specifically related to ESA therapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because serum potassium levels are important in chronic kidney disease, but they are not directly related to ESA therapy.
C) This choice is incorrect because dietary sodium intake is important in managing fluid balance in chronic kidney disease, but it is not directly related to ESA therapy.
D) This choice is correct. ESA therapy stimulates the production of red blood cells, and adequate iron levels are necessary for this process. Clients with chronic kidney disease often have decreased iron levels due to various factors, and iron supplementation is crucial for the success of ESA therapy.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Taking iron supplements with orange juice or other vitamin C-rich beverages enhances iron absorption due to the presence of vitamin C, which facilitates the absorption of non-heme iron.
B) This choice is incorrect because milk can inhibit iron absorption when taken with iron supplements.
C) This choice is incorrect because tea, especially black tea, contains tannins that can hinder iron absorption.
D) This choice is incorrect because carbonated water does not enhance iron absorption.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Taking the iron supplement with meals may reduce gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea and stomach upset, which are common with iron supplementation.
B) This choice is incorrect because taking iron supplements with meals may reduce iron absorption due to interference with other dietary components.
C) This choice is incorrect because taking the supplement with meals does not directly improve its effectiveness in treating anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because interactions with other medications are not specifically related to the timing of iron supplementation with meals.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because ESA therapy is not typically associated with hypotension. In fact, an increase in blood pressure is a potential side effect of ESAs.
B) This choice is incorrect because hypokalemia (low potassium levels) is not a common adverse effect of ESA therapy.
C) This choice is incorrect because hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is not a typical side effect of ESA therapy.
D) This choice is correct. ESA therapy can increase the risk of thrombosis (blood clot formation) due to the stimulation of red blood cell production. Clients receiving ESAs should be monitored for signs of thrombosis, such as swelling, pain, and redness in the extremities.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because whole-grain bread contains phytates that can inhibit iron absorption, and although eggs enhance non-heme iron absorption, the combination with whole-grain bread may not be as effective as other options.
B) This choice is correct. Red meat is a rich source of heme iron, which is well-absorbed, and dairy products are sources of calcium that do not significantly inhibit heme iron absorption. Combining heme iron with calcium-rich foods can help optimize iron uptake.
C) This choice is incorrect because although spinach is a source of non-heme iron, it also contains substances such as oxalates that can hinder iron absorption. Nuts, while being nutritious, do not specifically enhance iron absorption.
D) This choice is incorrect because both lentils and beans are sources of non-heme iron, and the combination does not provide a significant enhancer of iron absorption.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because monitoring the client's temperature is important, but it is not the priority during the PRBC transfusion process.
B) This choice is incorrect because administering pain medication may be necessary if the client is experiencing discomfort during or after the transfusion, but it is not the priority action.
C) This choice is incorrect because obtaining informed consent is an essential step before any medical intervention, including transfusions, but it is not the priority during the transfusion process.
D) This choice is correct. Checking the client's blood type is a priority before administering a PRBC transfusion to ensure compatibility and prevent adverse reactions. Transfusion reactions can be life-threatening, so verifying the blood type is crucial for client safety.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because while regular aerobic exercises can be beneficial for overall health, they may be too strenuous for a client experiencing fatigue and weakness due to anemia.
B) This choice is incorrect because resistance training may require a significant amount of energy and effort, which may not be suitable for a client with anemia and symptoms of fatigue and weakness.
C) This choice is correct. Taking frequent naps throughout the day can help the client conserve energy and manage the symptoms of fatigue and weakness associated with anemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because limiting fluid intake is not a recommended strategy for managing fatigue and weakness in clients with anemia. Adequate hydration is important for overall health, and clients should be encouraged to drink enough fluids.
Questions
Complications of Intravenous therapy
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of swelling, redness, and warmth around the insertion site are indicative of phlebitis, which is inflammation of the vein caused by irritants in the IV solution or mechanical trauma from the catheter.
B) This choice is incorrect because infiltration refers to the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues, causing swelling and coolness around the insertion site.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is characterized by symptoms such as shortness of breath, elevated blood pressure, and bounding pulse, not local symptoms around the IV site.
D) This choice is incorrect because air embolism occurs when air enters the vascular system, leading to symptoms such as dyspnea, cyanosis, and chest pain, rather than localized symptoms at the insertion site.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis and infiltration typically do not cause chest pain, dyspnea, and tachycardia.
B) This choice is incorrect because infiltration is associated with localized symptoms around the IV site, not systemic symptoms like chest pain and dyspnea.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload may cause respiratory distress and tachycardia, but it is not typically associated with sudden chest pain.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of sudden chest pain, dyspnea, and tachycardia are potential signs of an air embolism, which occurs when air enters the vascular system through the IV catheter and can lead to serious respiratory and cardiac complications.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis is characterized by redness, warmth, and swelling around the insertion site, not blanching of the skin.
B) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of a cool sensation, swelling, and blanching of the skin are indicative of infiltration, which occurs when IV fluid leaks into the surrounding tissues.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with local symptoms around the insertion site.
D) This choice is incorrect because catheter occlusion may affect the IV flow rate, but it does not typically cause the symptoms described by the client.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis and infiltration are not associated with symptoms of shortness of breath, crackles in the lungs, and jugular vein distention.
B) This choice is incorrect because infiltration typically does not cause respiratory symptoms like shortness of breath and crackles in the lungs.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of shortness of breath, crackles in the lungs (rales), and jugular vein distention are potential signs of fluid overload, which occurs when there is an excessive volume of IV fluids administered.
D) This choice is incorrect because catheter occlusion does not cause respiratory symptoms like those described by the client.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. Changing the IV tubing every 24 hours is a recommended intervention to reduce the risk of catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs) by minimizing the accumulation of microorganisms in the tubing.
B) This choice is incorrect because administering antibiotics prophylactically is not a standard practice for preventing CRBSIs, and it can contribute to antibiotic resistance.
C) This choice is incorrect because keeping the IV bag above the level of the heart is a technique used to regulate IV flow rate, but it is not specifically related to preventing CRBSIs.
D) This choice is incorrect because using a large-gauge catheter is not a preventive measure for CRBSIs. The appropriate catheter size should be based on the client's clinical condition and the prescribed therapy.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with redness and warmth around the insertion site, but it does not cause a painful, red streak along the arm.
B) This choice is incorrect because infiltration is characterized by swelling and blanching of the skin near the IV site, not a painful, red streak.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of a painful, warm, and red streak along the arm near the IV site are indicative of thrombophlebitis, which is the inflammation of a vein associated with the formation of a blood clot.
D) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with a painful, warm, and red streak along the arm.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because the client's preference for IV therapy over oral fluids is not a valid indication for initiating IV therapy. Clinical indications should guide the decision, not personal preferences.
B) This choice is incorrect because a history of IV drug use does not automatically indicate a need for IV therapy for dehydration. The client's current condition and clinical status should determine the need for IV fluids.
C) This choice is correct. In cases of severe dehydration where the client is unable to tolerate oral intake, IV therapy is essential to provide rapid rehydration and restore fluid and electrolyte balance.
D) This choice is incorrect because the family's request alone is not a sufficient indication for initiating IV therapy. The decision should be based on the client's clinical condition and medical needs.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration is not directly related to the client's history of heart failure.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis is not specifically associated with heart failure but rather with irritants in the IV solution or mechanical trauma.
C) This choice is correct. Clients with a history of heart failure are at an increased risk of fluid overload due to their compromised cardiac function. Monitoring for signs of fluid overload, such as dyspnea, jugular vein distention, and peripheral edema, is essential during IV therapy.
D) This choice is incorrect because an air embolism is not directly related to the client's history of heart failure.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis does not present with symptoms of dyspnea, chest pain, and cyanosis.
B) This choice is incorrect because infiltration does not cause sudden onset dyspnea, chest pain, and cyanosis. Infiltration involves localized symptoms around the insertion site.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload does not typically cause sudden onset dyspnea, chest pain, and cyanosis.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of sudden onset dyspnea, chest pain, and cyanosis are indicative of a pulmonary embolism, which occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs. This can be a life-threatening complication of IV therapy, especially in clients receiving antibiotics who are at higher risk for clot formation.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because administering the medication rapidly is not necessarily essential and can increase the risk of complications. Medications should be administered at the appropriate rate to prevent adverse effects.
B) This choice is incorrect because diluting the medication with a large volume of IV fluid may be unnecessary and may slow down the administration without specific indications.
C) This choice is correct. Checking the client's allergies and medication compatibility is essential to prevent adverse reactions and complications. Ensuring that the prescribed medication is appropriate for the client and does not interact negatively with other medications or allergies is crucial.
D) This choice is incorrect because the choice of IV catheter size depends on the medication's compatibility and viscosity, not just using a smaller gauge catheter for all medication infusions.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration is not typically associated with chills, fever, and an elevated heart rate.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis may cause local symptoms at the IV site but is not generally associated with systemic symptoms like fever and chills.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload does not cause fever and chills but rather manifests as symptoms like dyspnea, edema, and increased blood pressure.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of chills, fever, and elevated heart rate are indicative of sepsis, a serious infection that can occur as a complication of IV therapy. Sepsis can develop if bacteria enter the bloodstream through the IV catheter and lead to a systemic inflammatory response.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration is not typically associated with symptoms of chest pain, difficulty breathing, decreased blood pressure, and weak pulse.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis does not cause sudden onset chest pain, difficulty breathing, decreased blood pressure, and weak pulse.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with symptoms like chest pain and decreased blood pressure. It may cause elevated blood pressure due to increased fluid volume.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of sudden chest pain, difficulty breathing, decreased blood pressure, and weak pulse are indicative of anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction. Anaphylaxis can occur in response to an allergen in the IV fluid or medication and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because receiving a potassium-containing solution is not associated with hypokalemia, but rather with the risk of hyperkalemia due to the increased potassium intake.
B) This choice is correct. Clients with chronic kidney disease are at risk of hyperkalemia, and receiving a potassium-containing solution through IV therapy can further elevate potassium levels.
C) This choice is incorrect because IV therapy with a potassium-containing solution is not related to hypocalcemia.
D) This choice is incorrect because IV therapy with a potassium-containing solution is not associated with hyponatremia.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with redness, warmth, and swelling around the insertion site, not coolness and pallor.
B) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of swelling, coolness, and pallor around the insertion site, along with a slowed infusion and discomfort, are indicative of infiltration, which occurs when IV fluid leaks into the surrounding tissues.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with localized symptoms like those described by the client.
D) This choice is incorrect because an air embolism is not associated with symptoms of infiltration, such as swelling and coolness around the IV site.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues, not puncturing the vein. Burning pain is not typically associated with infiltration.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis is characterized by redness, warmth, and swelling around the insertion site, not fluid leakage and burning pain.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not related to the puncture of the vein and leakage of IV fluid. Symptoms of fluid overload include dyspnea, elevated blood pressure, and jugular vein distention.
D) This choice is correct. The nurse should suspect extravasation, which occurs when IV fluid or medication leaks into the surrounding tissues due to catheter puncture. Burning pain and discomfort at the insertion site are common symptoms of extravasation.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with redness, warmth, and swelling around the insertion site but does not cause blistering of the skin.
B) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves swelling and coolness around the IV site, not blistering and redness.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with pain, burning, swelling, or blistering around the IV site.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of pain, burning, swelling, redness, and blistering around the IV site are indicative of extravasation, which occurs when chemotherapy or other vesicant medications leak into the surrounding tissues, causing tissue damage and skin breakdown.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis is characterized by redness, warmth, and swelling around the insertion site, not edema and coolness.
B) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of edema, coolness, sluggish infusion, and discomfort at the site are indicative of infiltration, which occurs when IV fluid leaks into the surrounding tissues.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with localized symptoms like those described by the client.
D) This choice is incorrect because an air embolism is not associated with symptoms of infiltration, such as edema and coolness around the IV site.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of pain, burning, redness, and tenderness at the insertion site are indicative of a potential complication, such as phlebitis or infiltration. The nurse should stop the IV infusion immediately to prevent further damage.
B) This choice is incorrect because elevating the arm may not address the underlying complication of phlebitis or infiltration.
C) This choice is incorrect because applying a warm compress is not the priority. The nurse should first stop the infusion to prevent complications.
D) This choice is incorrect because administering an analgesic may provide temporary relief, but it does not address the potential complication causing the client's symptoms. The nurse should first stop the IV infusion to assess the site and determine appropriate interventions.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues, not redness, warmth, and tenderness around the insertion site.
B) This choice is incorrect because extravasation occurs when IV fluid or medication leaks into the surrounding tissues due to catheter puncture, but it does not present with redness and swelling.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness, and pain around the insertion site are indicative of phlebitis, which is the inflammation of the vein caused by irritants in the IV solution or mechanical trauma from the catheter.
D) This choice is incorrect because an air embolism is not associated with symptoms of phlebitis, such as redness and swelling around the IV site.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because applying a warm compress is not necessarily essential to prevent thrombophlebitis. It may provide comfort but does not directly prevent its development.
B) This choice is incorrect because limiting the use of the affected arm for IV insertion may not be necessary. The choice of insertion site should be based on the client's clinical condition and the nurse's assessment.
C) This choice is correct. The nurse should avoid using a tourniquet during IV insertion in a client with a history of DVT to minimize trauma to the vein and reduce the risk of thrombophlebitis formation.
D) This choice is incorrect because selecting a small-gauge catheter is not the primary intervention to prevent thrombophlebitis in a client with a history of DVT. The choice of catheter size should be based on the client's clinical needs and vein condition.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues and is not associated with chest pain, dyspnea, and tachycardia.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with localized symptoms around the insertion site and is not associated with chest pain, dyspnea, and tachycardia.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload does not typically cause chest pain, dyspnea, and tachycardia but rather manifests as symptoms such as elevated blood pressure, jugular vein distention, and edema.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of chest pain, dyspnea, and tachycardia are potential signs of thrombophlebitis, which is the inflammation of a vein associated with the formation of a blood clot. The clot can become dislodged and travel to the lungs, leading to a pulmonary embolism, which presents with chest pain and dyspnea.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration is characterized by swelling, coolness, and pallor around the insertion site, not a palpable, cord-like structure along the vein.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with redness, warmth, and swelling around the insertion site, not a palpable, cord-like structure.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with a palpable, cord-like structure along the vein . It may cause generalized edema and increased blood pressure.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of tenderness and a palpable, cord-like structure along the vein are indicative of thrombophlebitis, which is the inflammation of a vein associated with the formation of a blood clot. The palpable cord-like structure is likely a thrombus within the vein.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues and is not associated with fever, chills, and malaise.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with localized symptoms around the insertion site, not red streaks along the vein path.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of fever, chills, malaise, and red streaks along the vein path are indicative of sepsis, which is a severe infection that can occur as a complication of IV therapy. Red streaks along the vein path may indicate the spread of infection along the vein.
D) This choice is incorrect because thrombophlebitis does not typically present with symptoms of fever, chills, and malaise. It is associated with tenderness and a palpable, cord-like structure along the vein.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues and is not associated with purulent drainage and redness.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with redness, warmth, and swelling around the insertion site, but it does not cause purulent drainage.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of tenderness, redness, warmth, and purulent drainage around the insertion site are indicative of an infection, which can occur as a complication of IV therapy if bacteria enter the bloodstream through the catheter.
D) This choice is incorrect because thrombophlebitis does not typically cause purulent drainage at the insertion site.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues and is not typically associated with systemic symptoms like fever, tachycardia, and hypotension.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with localized symptoms around the insertion site and is not associated with systemic symptoms like fever, tachycardia, and hypotension.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with symptoms of fever, tachycardia, and hypotension. It is characterized by symptoms such as dyspnea and edema.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of fever, tachycardia, and hypotension are potential signs of sepsis, a severe infection that can occur as a complication of IV therapy. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues and is not associated with purulent drainage and redness.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with localized symptoms around the insertion site, such as redness, warmth, and swelling, but it does not cause purulent drainage.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of pain, redness, and purulent drainage at the IV site are indicative of an infection, which can occur as a complication of IV therapy, especially in clients with diabetes who may have compromised immune systems.
D) This choice is incorrect because thrombophlebitis does not typically cause purulent drainage at the insertion site.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues and is not typically associated with systemic symptoms like fever, confusion, and low blood pressure.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with localized symptoms around the insertion site and is not associated with systemic symptoms like fever, confusion, and low blood pressure.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with symptoms of fever, chills, and confusion. It may cause elevated blood pressure and edema.
D) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of fever, chills, confusion, low blood pressure, and mottled skin are potential signs of sepsis, a severe infection that can occur as a complication of IV therapy. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues and is not associated with warmth and swelling along the vein path.
B) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with localized symptoms around the insertion site, such as redness, warmth, and swelling, but it does not cause tenderness, warmth, and swelling along the vein path.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of tenderness, warmth, and swelling along the vein path are indicative of thrombophlebitis, which is the inflammation of a vein associated with the formation of a blood clot. The clot can cause obstruction along the vein path, leading to the symptoms described by the client.
D) This choice is incorrect because sepsis typically presents with systemic symptoms like fever, chills, and confusion, not localized symptoms along the vein path.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because administering the medication as prescribed may exacerbate the allergic reaction and is not safe without further assessment and medical guidance.
B) This choice is correct. The client's statement about being allergic to penicillin and experiencing itchiness in the throat suggests a potential allergic reaction. The nurse should withhold the medication and promptly notify the healthcare provider to assess the client's allergic response and determine an alternative course of action.
C) This choice is not the priority action. While assessing the severity of the itchiness is important, the nurse's priority is to withhold the medication and notify the healthcare provider about the potential allergic reaction.
D) This choice is incorrect because administering an antihistamine before notifying the healthcare provider may mask the symptoms of the allergic reaction and delay appropriate management.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. The client's sudden onset of hives, facial swelling, and difficulty breathing suggests a Type I (Immediate) hypersensitivity reaction, also known as anaphylaxis. Type I hypersensitivity reactions occur within minutes to hours after exposure to an allergen, leading to the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
B) This choice is incorrect because Type II (Cytotoxic) hypersensitivity reactions involve antibodies attacking specific cells or tissues, leading to cell destruction. They are not associated with the symptoms described by the client.
C) This choice is incorrect because Type III (Immune Complex-Mediated) hypersensitivity reactions involve the formation of immune complexes that deposit in tissues and trigger inflammation, but they do not typically present with generalized hives and facial swelling.
D) This choice is incorrect because Type IV (Delayed) hypersensitivity reactions occur 24 to 72 hours after exposure to an allergen and are mediated by T cells, leading to localized skin reactions like contact dermatitis. They are not associated with the rapid onset of symptoms described by the client.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because administering IV medications rapidly may increase the risk of an allergic reaction, especially in a client with a history of multiple drug allergies.
B) This choice is incorrect because switching to oral medications may not be appropriate or feasible for all IV medications. The nurse should consider alternative medications only after performing a thorough allergy assessment and consulting with the healthcare provider.
C) This choice is incorrect because the choice of IV catheter gauge is not directly related to preventing allergic reactions. It should be based on the medication's compatibility and viscosity.
D) This choice is correct. A thorough allergy assessment is essential in a client with a history of multiple drug allergies to identify potential allergens and prevent exposure to allergenic medications. The nurse should communicate allergies to the healthcare team and document them in the client's medical record, using allergy alerts or wristbands, to ensure safe medication administration.
Explanation
A) This choice is correct. The client's localized symptoms of swelling, erythema, and pain at the IV site may indicate a local allergic reaction or chemical irritation. The nurse should discontinue the IV medication immediately to prevent the progression of the reaction and assess the client further for any systemic signs of an allergic reaction.
B) This choice is not the priority action. While administering an antihistamine may relieve symptoms of an allergic reaction, the nurse's priority is to discontinue the IV medication and assess the client's condition.
C) This choice is not the priority action. While notifying the healthcare provider is important, the nurse's immediate priority is to discontinue the IV medication and assess the client's condition.
D) This choice is not the priority action. Elevating the arm may provide comfort, but the nurse's priority is to discontinue the IV medication and assess the client's condition for any signs of a systemic allergic reaction.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because Type I (Immediate) hypersensitivity reactions typically involve immediate symptoms like hives, facial swelling, and difficulty breathing, not fever, rash, and elevated liver enzymes.
B) This choice is incorrect because Type II (Cytotoxic) hypersensitivity reactions involve antibodies attacking specific cells or tissues, leading to cell destruction. Elevated liver enzymes may occur in some drug-induced cytotoxic reactions, but they are not commonly associated with fever and rash.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of fever, rash, and elevated liver enzymes are potential signs of a Type III (Immune Complex-Mediated) hypersensitivity reaction. In this type of hypersensitivity, immune complexes formed by antibodies and antigens deposit in tissues and trigger inflammation, which can affect multiple organs, including the liver.
D) This choice is incorrect because Type IV (Delayed) hypersensitivity reactions occur 24 to 72 hours after exposure to an allergen and are mediated by T cells, leading to localized skin reactions like contact dermatitis. They are not associated with fever and elevated liver enzymes.
Questions
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because using the same insertion site for all IV catheter changes can lead to complications such as phlebitis and infiltration due to repetitive trauma to the vein.
B) This choice is incorrect because changing the IV catheter every 72 hours as per policy may not be necessary unless the catheter is no longer functioning properly or the site shows signs of complications. Changing the catheter prematurely can increase the risk of complications.
C) This choice is correct. Rotating the IV insertion site with each catheter change helps to distribute the risk of complications across multiple sites and allows previously used sites time to heal and recover.
D) This choice is incorrect because administering medications in large volumes to minimize insertion frequency is not a safe practice. Medication volumes should be appropriate for the client's needs, and insertion frequency should follow evidence-based guidelines.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with localized symptoms around the insertion site, such as redness and warmth, not shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heart rate.
B) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heart rate suggest an air embolism, which occurs when air enters the bloodstream through the IV catheter. This is a medical emergency, and the nurse should take immediate action to protect the client's airway, administer oxygen, and notify the healthcare provider.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with symptoms of shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heart rate. It is characterized by symptoms such as edema and elevated blood pressure.
D) This choice is incorrect because infiltration involves the inadvertent administration of IV fluid into the surrounding tissues and is not associated with symptoms of shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heart rate.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because elevating the client's arm may not address the underlying complication of infiltration. The nurse's priority is to discontinue the IV infusion to prevent further complications.
B) This choice is incorrect because applying a warm compress is not the priority action. The nurse should first discontinue the IV infusion to assess the site and determine appropriate interventions.
C) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of pain, burning, redness, swelling, and coolness around the insertion site are indicative of infiltration, which occurs when IV fluid leaks into the surrounding tissues. The nurse's priority is to discontinue the IV infusion to prevent further complications and assess the site for potential tissue damage.
D) This choice is incorrect because administering an analgesic may provide temporary pain relief, but it does not address the underlying complication of infiltration. The nurse should first discontinue the IV infusion and assess the site for potential complications.
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because mixing all the medications in one syringe is not recommended, as it may lead to medication incompatibilities or chemical reactions between medications.
B) This choice is incorrect because flushing the IV line with a large amount of normal saline does not prevent medication incompatibilities. It is essential to consult with the pharmacist to verify compatibility before administration.
C) This choice is correct. The nurse should consult with the pharmacist to verify the compatibility of the IV medications before administration. Certain medications may interact with each other or with the IV solution, leading to potential incompatibilities or adverse reactions.
D) This choice is incorrect because increasing the IV flow rate to hasten medication infusion does not prevent medication incompatibilities. It is essential to confirm compatibility before administering the medications.
A nurse is caring for a client receiving IV therapy. Which action is essential to prevent catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs)?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because administering IV fluids through the largest available catheter is not necessary for preventing CRBSIs. The appropriate catheter size should be based on the client's clinical needs and the prescribed therapy.
B) This choice is incorrect because changing the IV catheter dressing daily is not necessarily recommended unless the dressing is soiled or loose. Frequent dressing changes can increase the risk of contamination and infection. The nurse should follow evidence-based guidelines for catheter care and dressing changes.
C) This choice is correct. Using sterile technique during IV insertion and care is essential for preventing CRBSIs. Sterile technique helps to reduce the risk of introducing pathogens into the bloodstream, which can lead to infection.
D) This choice is incorrect because frequently accessing the IV catheter for blood draws can increase the risk of CRBSIs. The nurse should minimize unnecessary catheter access and follow aseptic technique when drawing blood or administering medications through the catheter.
A nurse is caring for a client with an IV catheter in place for medication administration. The nurse notes swelling and coolness around the insertion site. Which complication of IV therapy should the nurse suspect?
Explanation
A) This choice is incorrect because phlebitis typically presents with redness, warmth, and swelling around the insertion site, not coolness.
B) This choice is correct. The client's symptoms of swelling and coolness around the insertion site are indicative of infiltration, which occurs when IV fluid leaks into the surrounding tissues.
C) This choice is incorrect because fluid overload is not associated with localized symptoms like swelling and coolness at the IV site.
D) This choice is incorrect because an air embolism is not associated with symptoms of swelling and coolness at the IV site.
Exams on Blood and Cardiovascular Disorders
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginLessons
 Naxlex
Just Now
Naxlex
Just Now
- Hypertension
- Congenital Heart Disease
- Blood transfusion
- Hemorrhage
- Raynaud's Disease
- Aneurysm and peripheral vascular disorder
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
- Leukemia
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Congestive Cardiac Failure
- Myocardial Infarction (MI) and Angina Pectoris
- Anemia
- Complications of Intravenous therapy
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
Hypertension
Introduction
- Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a chronic condition that affects the cardiovascular system and increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other complications.
- Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and expressed as two numbers: systolic pressure (the pressure when the heart contracts) and diastolic pressure (the pressure when the heart relaxes).
- Normal blood pressure is less than 120/80 mmHg. Hypertension is defined as blood pressure that is consistently higher than 140/90 mmHg or 130/80 mmHg for people with diabetes or chronic kidney disease.
- Hypertension can be classified as primary (essential) or secondary. Primary hypertension has no identifiable cause and develops gradually over many years. Secondary hypertension is caused by an underlying condition or medication and can occur suddenly and be more severe.
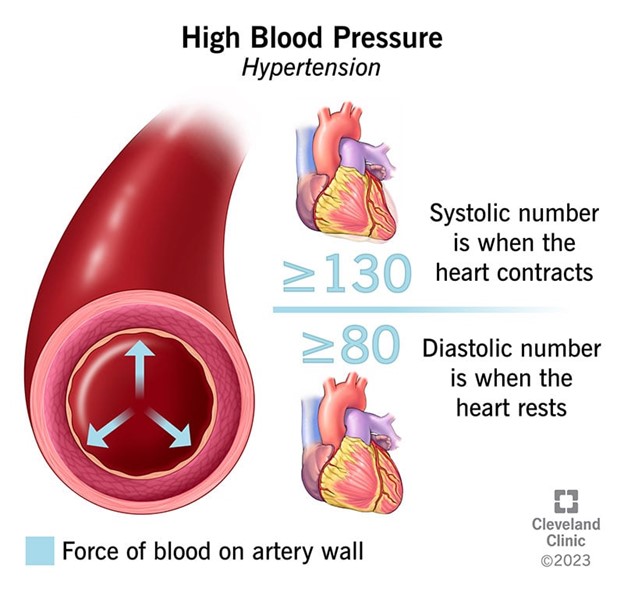
Risk Factors and Causes
- The exact cause of primary hypertension is unknown, but several factors can increase the risk of developing it, such as:
- Age: Blood pressure tends to rise with age as the arteries become stiffer and narrower.
- Family history: Hypertension tends to run in families and may have a genetic component.
- Race: African Americans are more likely to develop hypertension than other races and may have more severe complications.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts more strain on the heart and increases the volume of blood that circulates.
- Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise can lead to obesity, high cholesterol, diabetes, and other conditions that affect blood pressure.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the lining of the arteries, reduces the oxygen in the blood, and increases the heart rate and blood pressure.
- Alcohol: Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure and damage the liver and kidneys.
- Salt: Eating too much salt can cause the body to retain fluid and increase blood pressure.
- Stress: Chronic stress can trigger the release of hormones that constrict the blood vessels and increase blood pressure.
- Secondary hypertension can be caused by various conditions or medications that affect the kidneys, adrenal glands, thyroid, heart, blood vessels, or nervous system. Some examples are:
- Kidney disease: Impaired kidney function can affect the balance of fluid and electrolytes in the body and increase the production of renin, a hormone that raises blood pressure.
- Adrenal disorders: Conditions such as Cushing's syndrome, pheochromocytoma, or hyperaldosteronism can cause excess production of cortisol, adrenaline, or aldosterone, hormones that affect blood pressure.
- Thyroid disorders: Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can alter the metabolism and cardiac output and affect blood pressure.
- Heart defects: Congenital or acquired defects such as coarctation of the aorta, aortic valve stenosis, or patent ductus arteriosus can increase the resistance to blood flow and raise blood pressure.
- Blood vessel disorders: Conditions such as vasculitis (inflammation of the blood vessels), arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), or fibromuscular dysplasia (abnormal growth of cells in the artery walls) can narrow or damage the arteries and increase blood pressure.
- Nervous system disorders: Conditions such as brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, or autonomic dysreflexia can affect the regulation of blood pressure by the nervous system.
- Medications: Certain drugs such as oral contraceptives, steroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), decongestants, antidepressants, or stimulants can raise blood pressure as a side effect.

Clinical Manifestations
- Hypertension is often asymptomatic until it reaches a severe level or causes organ damage. However, some people may experience some signs and symptoms of hypertension, such as:
- Headaches, especially in the morning
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Blurred vision or eye problems
- Nosebleeds
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Fatigue or weakness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Confusion or altered mental status
- These symptoms may indicate a hypertensive crisis, which is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. A hypertensive crisis is defined as a systolic blood pressure of ≥180 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure of ≥120 mmHg, with or without signs of organ damage. Signs of organ damage may include:
- Stroke (a sudden loss of brain function due to reduced blood flow or bleeding in the brain)
- Heart attack (a sudden blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle)
- Heart failure (a condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs)
- Aortic dissection (a tear in the inner layer of the large artery that carries blood from the heart)
- Kidney failure (a condition in which the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste and fluid from the blood)
- Retinopathy (damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer of the eye)
- Encephalopathy (brain dysfunction due to high blood pressure
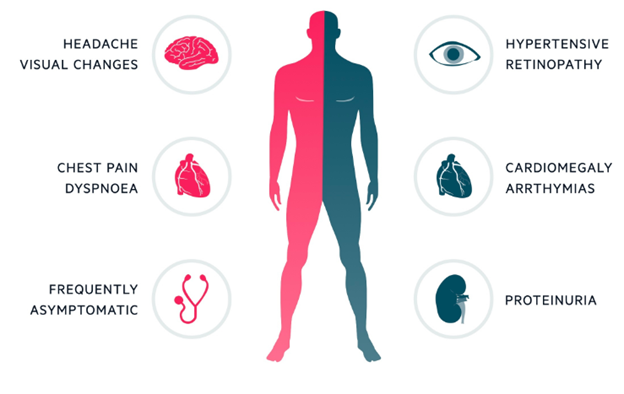
Diagnostic Tests
- The diagnosis of hypertension is based on the average of two or more accurate blood pressure measurements taken on two or more visits to the healthcare provider. Blood pressure can be measured using a sphygmomanometer (a device that consists of a cuff, a gauge, and a stethoscope) or an electronic device. Blood pressure can also be measured at home using a home blood pressure monitor or at a public place using a kiosk blood pressure machine. However, these methods may not be as accurate as those performed by a healthcare provider.
- In addition to blood pressure measurement, other tests may be ordered to evaluate the cause and severity of hypertension, as well as the presence and extent of organ damage. These tests may include:
- Blood tests, such as complete blood count (CBC), electrolytes, glucose, creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), uric acid, cholesterol, triglycerides, and others, to assess kidney function, blood sugar levels, lipid profile, and other factors that may affect blood pressure.
- Urine tests, such as urinalysis and microalbuminuria, to check for protein, blood, glucose, and other substances in the urine that may indicate kidney damage or infection.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG), a test that records the electrical activity of the heart and can detect abnormal rhythms, enlarged chambers, ischemia (reduced blood flow), or previous damage.
- Echocardiogram, an ultrasound test that uses sound waves to create images of the heart and can measure its size, shape, function, and valve structure.
- Chest X-ray, a test that uses radiation to produce images of the chest and can show signs of heart enlargement, fluid accumulation in the lungs, or other lung problems.
- Renal ultrasound, is an ultrasound test that uses sound waves to create images of the kidneys and can detect abnormalities such as cysts, stones, tumors, or blockages.
- Renal arteriography, an invasive test that involves injecting a contrast dye into the renal arteries (the blood vessels that supply the kidneys) and taking Xray images to visualize any narrowing or blockage that may cause renal artery stenosis (a condition in which one or both renal arteries are narrowed).
- Other tests may be performed depending on the suspected cause or complication of hypertension.
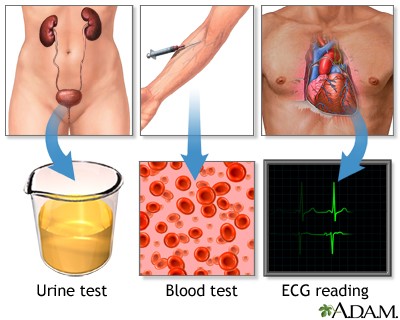
Complications and Target Organ Damage
- Hypertension can lead to serious complications and target organ damage if left untreated or poorly controlled. Target organs are those that are most affected by high blood pressure and include the heart, brain, kidneys, eyes, and arteries. Some of the common complications and target organ damage caused by hypertension are:
- Stroke: Hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke, which occurs when there is reduced blood flow or bleeding in the brain. Stroke can cause permanent disability or death depending on the location and extent of brain damage. Symptoms of stroke include sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, face drooping, slurred speech, confusion, difficulty seeing, severe headache, dizziness, loss of balance, or loss of consciousness.
- Heart attack: Hypertension can increase the risk of heart attack by causing coronary artery disease (CAD), which is a condition in which plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. Plaque can narrow or block the arteries and reduce blood flow to the heart. If a plaque ruptures and forms a clot, it can completely block an artery and cause a heart attack
- Management and Treatment Options
- Pharmacologic therapy: antihypertensive drugs such as diuretics, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, etc.
- Lifestyle modifications: weight reduction, dietary sodium restriction, regular physical activity, moderation of alcohol intake, smoking cessation, stress management, etc.
- Patient education: the importance of adherence to medication regimen, self-monitoring of blood pressure, recognition of signs and symptoms of complications, follow-up care, etc.
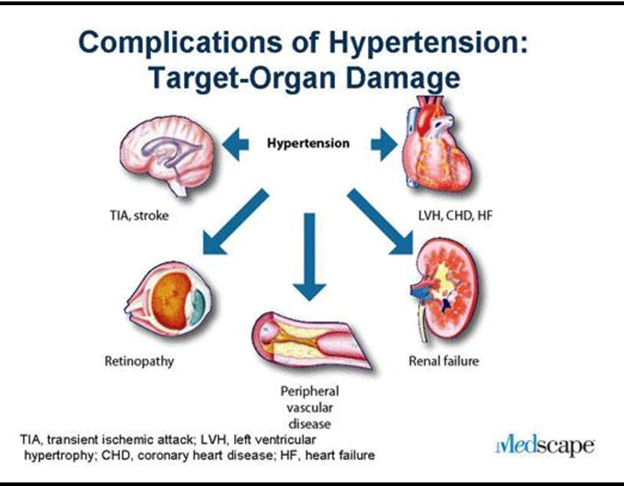
Nursing Interventions
- Assess blood pressure regularly using appropriate cuff size and technique
- Monitor for adverse effects of antihypertensive drugs such as hypotension, bradycardia, dizziness, fatigue, headache, cough, etc.
- Administer antihypertensive drugs as prescribed and teach patients how to take them correctly
- Encourage the patient to follow lifestyle modifications and provide resources and support
- Teach patient how to measure blood pressure at home and when to report abnormal readings
- Provide emotional support and reassurance to patient and family
Summary
- Hypertension is a common condition that increases the risk of cardiovascular complications such as stroke, heart attack, heart failure, kidney disease, etc.
- Hypertension is defined as a systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of more than 90 mmHg based on the average of two or more accurate blood pressure measurements during two or more consultations with the healthcare provider
- Hypertension is classified into four categories: normal, elevated, stage 1 hypertension, and stage 2 hypertension based on the blood pressure readings
- Hypertension is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors that affect the balance between cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance
- Hypertension is asymptomatic in most cases but may cause headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, chest pain, dyspnea, etc. in severe or uncontrolled cases
Conclusion
- Hypertension is a prevalent and serious medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels in the arteries.
- It is often referred to as the "silent killer" due to its asymptomatic nature in the early stages, emphasizing the need for routine screenings and awareness.
- Understanding the risk factors, causes, and pathophysiology of hypertension is essential for effective management and prevention of complications.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction, are key components of hypertension management.
- Medications, when prescribed, can significantly help in controlling blood pressure and reducing the risk of complications.
- Nurses play a vital role in educating patients about hypertension, monitoring their condition, and providing support for adherence to treatment plans.
- By addressing modifiable risk factors and promoting healthy behaviors, nurses contribute to reducing the burden of hypertension-related complications and improving overall patient outcomes.
- Hypertension management requires a collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals, patients, and their families to achieve better control and enhance quality of life.
Congenital Heart Disease
Introduction
- CHD is a term that refers to any structural abnormality of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth.
- CHD can affect the blood flow, oxygenation, and function of the heart and other organs.
- CHD can be classified into two main categories: defects that increase pulmonary blood flow (left-to-right shunts) and defects that decrease pulmonary blood flow (right-to-left shunts or obstructions).
- CHD can also be classified by the presence or absence of cyanosis, which is a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to low oxygen levels in the blood.
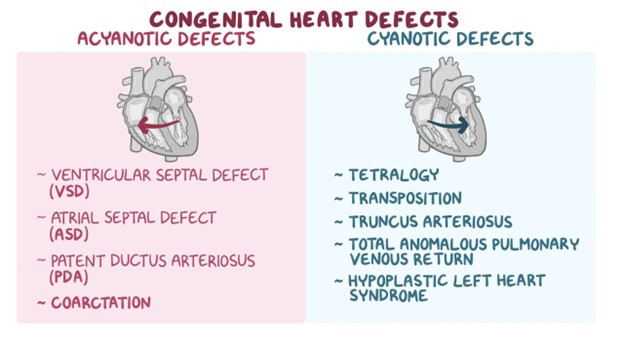
Etiology and Risk Factors
- The exact cause of most CHDs is unknown, but they are likely multifactorial, involving genetic, environmental, and maternal factors.
- Some genetic syndromes that are associated with CHD include Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Marfan syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome, and Noonan syndrome.
- Some environmental factors that can increase the risk of CHD include maternal infections (rubella, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis), maternal diabetes, maternal alcohol use, maternal smoking, maternal exposure to certain drugs (anticonvulsants, lithium, retinoic acid), and maternal exposure to radiation or chemicals.
- Some maternal factors that can increase the risk of CHD include advanced maternal age (>35 years), multiple gestation, preexisting cardiac disease, and history of a previous child with CHD.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
- CHD is a term that refers to abnormalities in the structure or function of the heart that are present at birth
- The causes of CHD are not fully understood, but some risk factors include genetic syndromes, maternal infections, maternal diabetes, maternal substance abuse, and environmental exposures
- CHD can result in heart failure, which is a condition where the heart is not able to pump blood effectively to meet the body's needs
- Heart failure can cause symptoms such as tachycardia, hypotension, weak pulses, fatigue, cardiomegaly, pulmonary congestion, and systemic congestion
- CHD can also result in hypoxia, which is a condition where there is insufficient oxygen in the body
- Hypoxia can cause symptoms such as cyanosis, tachypnea, dyspnea, clubbing of nails, and polycythemia
- The type and severity of symptoms depend on the type and size of the defect, the presence of other defects, and the degree of shunting between the chambers or vessels
Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnosis of CHD is based on a combination of history, physical examination, chest Xray, electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram (ECHO), cardiac catheterization, and other tests as indicated
- History: The nurse should obtain information about the prenatal history, family history of CHD or genetic syndromes, maternal infections or illnesses during pregnancy, exposure to drugs or toxins during pregnancy, onset, and duration of symptoms, feeding difficulties, growth patterns, activity tolerance, and medications
- Physical examination: The nurse should assess for signs of heart failure and hypoxia, such as heart rate and rhythm, blood pressure and pulses in all extremities, respiratory rate and effort, oxygen saturation, skin color and temperature, edema, liver size, weight and height percentiles, and developmental milestones
- Chest Xray: This test can show the size and shape of the heart and lungs, and detect any abnormalities such as cardiomegaly or pulmonary edema
- ECG: This test can measure the electrical activity of the heart and detect any arrhythmias or conduction problems
- ECHO: This test uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart and its structures. It can show the size and function of the chambers and valves, the direction and magnitude of blood flow, and the presence and location of any defects
- Cardiac catheterization: This is an invasive procedure where a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel (usually in the groin) and advanced to the heart. It can measure pressures and oxygen levels in different parts of the heart and vessels, inject contrast dye to visualize any defects or obstructions and perform interventions such as closing defects or dilating stenotic valves
Treatment Options
- The treatment of CHD depends on the type and severity of the defect, the age and condition of the child, and the availability of resources
- Some general goals of treatment are to improve cardiac function, reduce pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), prevent infection or complications, promote growth and development, and provide emotional support to the child and family
- Some common treatment options include:
-
- Medications: These can include diuretics (to reduce fluid retention), inotropes (to increase contractility), vasodilators (to decrease afterload), beta-blockers (to decrease heart rate
- and oxygen demand), digoxin (to improve cardiac output), anticoagulants (to prevent thrombosis), antibiotics (to prevent infection), indomethacin (to close patent ductus arteriosus [PDA]), prostaglandins (to keep PDA open), or antiarrhythmics (to treat arrhythmias)
- Non-surgical interventions: These can include cardiac catheterization procedures such as balloon angioplasty (to widen stenotic valves or vessels), stent placement (to keep vessels open), coil embolization (to occlude PDA or collateral vessels), device closure (to seal atrial septal defect [ASD] or ventricular septal defect [VSD]), or radiofrequency ablation (to destroy abnormal electrical pathways)
- Surgical interventions: These can include palliative or corrective procedures such as shunt placement (to increase or decrease pulmonary blood flow), banding (to restrict pulmonary blood flow), patch closure (to repair ASD or VSD), valve repair or replacement, arterial switch (to correct transposition of the great arteries), Fontan procedure (to divert systemic venous blood to the pulmonary artery), or heart transplant
Nursing Considerations and Patient Education
- The nursing care of a child with CHD involves monitoring vital signs, oxygen saturation, fluid balance, weight and growth, nutritional status, developmental status, and signs of infection or complications
- The nurse should also provide interventions such as administering medications, oxygen therapy, chest physiotherapy, suctioning, feeding assistance, positioning, activity restriction or promotion, pain management, wound care, and infection prevention
- The nurse should educate the child and family about the diagnosis, treatment plan, medications, signs and symptoms of worsening condition, follow-up care, home care, and community resources
- The nurse should also provide emotional support and counseling to the child and family, and refer them to appropriate services such as social work, psychology, genetics, cardiology, or palliative care
Summary
- CHD is a common and complex condition that affects the structure and function of the heart
- CHD can cause heart failure and hypoxia, which can affect the child's growth and development
- CHD can be diagnosed by history, physical examination, and various tests such as chest Xray, ECG, ECHO, and cardiac catheterization
- CHD can be treated by medications, nonsurgical interventions, surgical interventions, or a combination of these options
- The nursing care of a child with CHD involves monitoring, interventions, education, and support
Conclusion
- Congenital heart diseases are a diverse group of conditions that affect the structure and function of the heart from birth.
- These conditions may involve abnormalities in the heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, or the way blood flows through the heart.
- Congenital heart diseases can range from mild and asymptomatic to severe, requiring immediate medical intervention.
- Early diagnosis and timely medical management play a crucial role in improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals with congenital heart diseases.
- Advancements in medical technology and surgical procedures have significantly improved the prognosis and treatment options for those with congenital heart diseases.
- Long-term follow-up and ongoing care are essential to monitor and manage potential complications associated with these conditions throughout the individual's life.
- Support and education for individuals with congenital heart diseases and their families are vital in promoting understanding, adherence to treatment plans, and overall wellbeing.
Blood transfusion
Introduction
- Blood transfusion is the administration of whole blood or its components to a client who has a deficiency or loss of blood volume or components
- Blood transfusion can be lifesaving, but it also carries risks of adverse reactions, infections, and immunologic complications
- Nurses play a vital role in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of blood transfusion by following evidence-based guidelines, policies, and procedures
Indications for Blood Transfusion
- The decision to transfuse blood or its components depends on several factors, such as:
- The client's clinical condition and symptoms
- The cause and severity of blood loss or deficiency
- The availability and suitability of alternative therapies
- The risks and benefits of transfusion
- The client's preferences and values
- Some common indications for blood transfusion are:
- Acute or chronic anemia due to blood loss, hemolysis, or decreased production of red blood cells (RBCs)
- Bleeding disorders due to deficiency or dysfunction of clotting factors or platelets
- Hemorrhagic shock due to massive blood loss from trauma, surgery, or obstetric complications
- Thrombocytopenia or platelet dysfunction due to bone marrow suppression, autoimmune disorders, or medications
- Hematologic malignancies or bone marrow transplantation that require stem cell support or immunosuppression
Blood Components and Products
- Whole blood is rarely used for transfusion, except in cases of massive hemorrhage or exchange transfusion
- Blood components are derived from whole blood by separation processes such as centrifugation, filtration, or freezing
- Blood products are manufactured from plasma by fractionation or recombinant technology
- The main types of blood components and products are:
- Packed red blood cells (PRBCs): contain concentrated RBCs with minimal plasma; used to increase oxygen-carrying capacity and treat anemia
- Platelets: contain concentrated platelets with some plasma; used to prevent or treat bleeding due to thrombocytopenia or platelet dysfunction
- Fresh frozen plasma (FFP): contains liquid plasma with all clotting factors; used to replace clotting factors in bleeding disorders or massive transfusion
- Cryoprecipitate: contains concentrated fibrinogen, factor VIII, von Willebrand factor, and factor XIII; used to treat bleeding due to fibrinogen deficiency or von Willebrand disease
- Albumin: contains purified albumin protein; used to expand plasma volume in hypovolemic shock or hypoalbuminemia
- Immunoglobulins: contain antibodies against specific antigens; used to provide passive immunity in immunodeficiency or exposure to infections
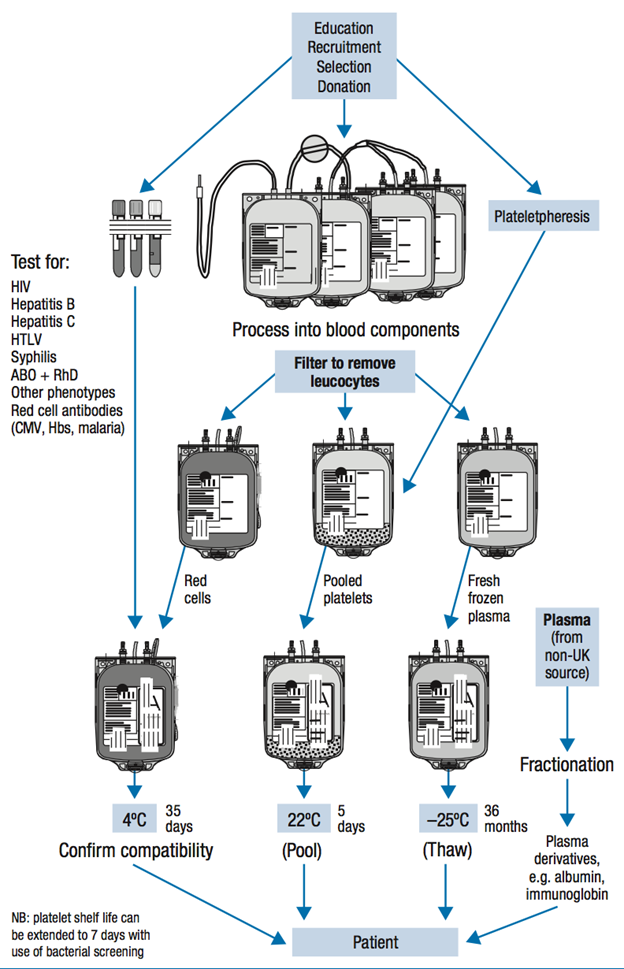
Pre-transfusion Assessment and Preparation
- Before administering a blood transfusion, the nurse should perform the following steps :
- Obtain a written prescription from the provider that specifies the type, amount, rate, and duration of the transfusion
- Verify the client's identity using two identifiers (e.g., name, date of birth) and check the armband for accuracy
- Review the client's medical history, allergies, vital signs, laboratory results, medications, and previous transfusion reactions
- Educate the client about the purpose, procedure, risks, benefits, and alternatives of the transfusion; obtain informed consent if required by the facility policy
- Assess the client's baseline physical condition, especially the cardiovascular, respiratory, renal, and neurologic systems; report any abnormal findings to the provider
- Ensure that a current blood sample is available for typing and crossmatching; label the sample with the client's name, identification number, date, and time of collection
- Obtain the blood component or product from the blood bank as close to the transfusion time as possible; inspect the blood bag for leaks, clots, discoloration, or expiration date
- Compare the information on the blood bag label with the transfusion record and the client's armband; check the blood type, Rh factor, unit number, and donor number; involve another licensed nurse in the verification process
- Select the appropriate intravenous (IV) access device, tubing, and solution for the transfusion; use a large-bore (18- to 20-gauge) catheter for PRBCs and a smaller-bore (22- to 24-gauge) catheter for other components; use a Y-type blood administration set with an in-line filter and a 0.9% sodium chloride solution as the compatible IV fluid
- Perform hand hygiene and don gloves; prime the tubing with the IV solution and flush the IV site; connect the blood component or product to the tubing and hang it on an infusion pump or a gravity drip
Blood Compatibility and Crossmatching
- Blood compatibility is determined by the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of RBCs and antibodies in the plasma
- The most important antigens are the ABO group (A, B, AB, or O) and the Rh factor (positive or negative)
- The most common antibodies are antiA, anti-B, anti-D (Rh), and irregular antibodies that react with other antigens
- Blood compatibility is based on the principle of avoiding agglutination (clumping) or hemolysis (destruction) of RBCs due to antigen-antibody reactions
- The ideal blood transfusion is autologous (from the client's own blood), followed by allogeneic (from a compatible donor)
- The universal donor is O negative, meaning that it can be given to any recipient regardless of their blood type
- The universal recipient is AB positive, meaning that it can receive any blood type without adverse reactions
- Crossmatching is a laboratory test that confirms the compatibility of the donor's blood with the recipient's blood
- Crossmatching involves mixing a sample of the donor's RBCs with a sample of the recipient's plasma and observing for agglutination or hemolysis
- A compatible crossmatch indicates that there is no reaction between the donor's RBCs and the recipient's plasma
- An incompatible crossmatch indicates that there is a reaction between the donor's RBCs and the recipient's plasma; this can lead to a transfusion reaction if transfused
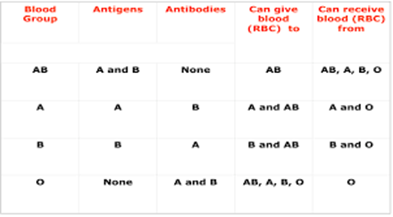
Transfusion Reactions and Management
- A transfusion reaction is an adverse response to a blood transfusion that can range from mild to severe or fatal
- Transfusion reactions can be classified into four categories: immunologic, nonimmunologic, infectious, and delayed
- Immunologic reactions are caused by antigen-antibody reactions between the donor's blood and the recipient's immune system
- Examples of immunologic reactions are:
- Acute hemolytic reaction: occurs when the recipient's antibodies destroy the donor's RBCs; symptoms include fever, chills, back pain, chest pain, dyspnea, hypotension, tachycardia, hemoglobinuria, jaundice, and renal failure; treatment involves stopping the transfusion, maintaining IV access with normal saline, monitoring vital signs and urine output, administering oxygen and fluids as ordered, collecting blood and urine samples for testing, and reporting to the provider and blood bank
- Febrile nonhemolytic reaction: occurs when the recipient's antibodies react with the donor's leukocytes; symptoms include fever, chills, headache, flushing, and anxiety; treatment involves stopping or slowing down the transfusion, administering antipyretics as ordered, monitoring vital signs and symptoms, collecting blood samples for testing, and reporting to the provider and blood bank
- Allergic reaction: occurs when the recipient's antibodies react with plasma proteins in the donor's blood; symptoms include urticaria (hives), pruritus (itching), rash, angioedema (swelling), bronchospasm (wheezing), anaphylaxis (shock); treatment involves stopping or slowing down the transfusion, administering antihistamines or corticosteroids as ordered, monitoring vital signs and symptoms, administering epinephrine and oxygen as ordered for severe reactions, collecting blood samples for testing, and reporting to the lab.
- The management of transfusion reactions depends on the type and severity of the reaction. - The general steps are:
-
- Stop the transfusion immediately and disconnect the tubing from the catheter.
- Maintain IV access with normal saline using new tubing and a new bag.
- Notify the provider and the blood bank.
- Monitor vital signs, urine output, and hemodynamic status.
- Administer oxygen, antihistamines, corticosteroids, vasopressors, fluids, or epinephrine as ordered.
- Collect blood samples from the recipient and send them to the lab for typing and crossmatching, direct antiglobulin test (DAT), and hemolysis studies.
- Collect urine samples from the recipient and send them to the lab for hemoglobinuria testing.
- Return the blood bag and tubing to the blood bank for culture and analysis.
- Document the incident and report it to the appropriate authorities.
Monitoring and Post-transfusion Care
- Monitoring during blood transfusion is essential to detect any signs of transfusion reactions or complications. The nurse should:
- Verify the identity of the recipient and the blood product using two identifiers and check for compatibility before starting the transfusion.
- Use a filter needle or a blood administration set with a filter to prevent clots or debris from entering the IV line.
- Use normal saline as the only compatible solution to infuse with blood products.
- Start the transfusion slowly (2 mL/min) for the first 15 minutes and monitor vital signs closely. If no reaction occurs, increase the rate as ordered but do not exceed 4 hours for each unit of packed red blood cells (PRBCs).
- Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes for the first hour and then every hour until the end of the transfusion. Compare with baseline values and report any changes.
- Monitor for signs and symptoms of transfusion reactions or complications such as fever, chills, rash, itching, dyspnea, chest pain, back pain, hemoglobinuria, hypotension, tachycardia, shock, or DIC.
- Stay with the recipient for at least the first 15 minutes of the transfusion or until stable.
- Educate the recipient about potential adverse effects and instruct them to report any discomfort or unusual sensations immediately.
- Posttransfusion care involves evaluating the outcome of the transfusion and documenting relevant information. The nurse should:
- Assess vital signs at least once after completing the transfusion and compare with baseline values.
- Assess hemoglobin and hematocrit levels before and after the transfusion to evaluate its effectiveness.
- Assess fluid balance and electrolyte levels to monitor for fluid overload or hypocalcemia.
- Dispose of used blood bags and tubing according to infection control policies.
- Document the type and amount of blood product transfused, infusion time, vital signs
Potential Complications and Prevention
- Hemolytic reaction: caused by ABO or Rh incompatibility; symptoms include fever, chills, back pain, chest pain, dyspnea, hypotension, tachycardia, hemoglobinuria, and renal failure. Prevention: verify blood type and crossmatch; stop transfusion immediately if suspected; send blood bag and tubing to the lab; maintain IV access with normal saline; monitor vital signs and urine output; administer diuretics, fluids, and vasopressors as ordered; collect blood and urine samples for testing.
- Febrile reaction: caused by antibodies to donor leukocytes or platelets; symptoms include fever, chills, headache, flushing, and anxiety. Prevention: use leukocyte-reduced or washed blood products; stop transfusion if suspected; administer antipyretics as ordered; restart transfusion slowly if no other symptoms are present.
- Allergic reaction: caused by sensitivity to plasma proteins or other components of the blood product; symptoms include urticaria, pruritus, wheezes, angioedema, and anaphylaxis. Prevention: use plasma-reduced or washed blood products; premedicate with antihistamines or corticosteroids as ordered; stop transfusion if suspected; administer epinephrine, antihistamines, or corticosteroids as ordered; maintain airway and oxygenation.
- Circulatory overload: caused by transfusing too much or too fast for the client's cardiac status; symptoms include dyspnea, crackles, cough, tachycardia, hypertension, distended neck veins, and pulmonary edema. Prevention: use appropriate blood product and rate for the client's condition; monitor vital signs and lung sounds; elevate the head of the bed; administer diuretics, oxygen, and morphine as ordered.
- Bacterial contamination: caused by transfusing blood products that are contaminated with microorganisms; symptoms include fever, chills, hypotension, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and septic shock. Prevention: follow strict aseptic technique when handling blood products; inspect blood products for discoloration, gas bubbles, or cloudiness; report any signs of contamination to the blood bank; stop transfusion if suspected; send blood bag and tubing to the lab; maintain IV access with normal saline; monitor vital signs and urine output; administer antibiotics, fluids, and vasopressors as ordered; collect blood cultures.
Summary
- Blood transfusion is a lifesaving procedure that involves administering whole blood or blood components to a client who needs them.
- Blood transfusion requires careful monitoring and post-transfusion care to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- Blood transfusion can cause various complications such as hemolytic reaction, febrile reaction, allergic reaction, circulatory overload, and bacterial contamination.
- Blood transfusion complications can be prevented by verifying blood type and crossmatch, using appropriate blood product and rate, following strict aseptic technique, inspecting blood products for contamination, and stopping transfusion immediately if any adverse reaction is suspected.
Conclusion
- Blood transfusion is a complex process that requires knowledge of the indications, contraindications, types of blood products, administration techniques, potential complications, prevention strategies, and nursing interventions.
- Nurses play a vital role in ensuring safe and effective blood transfusion for their clients by following evidence-based guidelines and protocols.
- Nurses should also educate their clients about the benefits and risks of blood transfusion and provide emotional support throughout the procedure.
Hemorrhage
Introduction
- Hemorrhage is the loss of blood from a damaged blood vessel, either internally or externally
- Hemorrhage can be classified as arterial, venous, or capillary, depending on the source of bleeding
- Hemorrhage can also be categorized as primary, secondary, or tertiary, depending on the timing of bleeding after an injury or surgery
- Hemorrhage can lead to hypovolemia, shock, organ failure, and death if not treated promptly and effectively
Causes and Risk Factors
- The causes of hemorrhage vary depending on the type and location of bleeding, but some common causes include:
- Trauma, such as blunt force, penetrating, or blast injuries
- Surgery, especially involving major blood vessels or organs
- Coagulation disorders, such as hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, or anticoagulant therapy
- Vascular anomalies, such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, or varices
- Inflammation or infection, such as gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, diverticulitis, or appendicitis
- Malignancy, such as tumors, metastases, or leukemia
- Pregnancy and childbirth complications, such as placenta previa, placental abruption, or uterine rupture
- The risk factors of hemorrhage depend on the underlying cause and the individual's health status, but some general risk factors include:
- Age, as older adults have more fragile blood vessels and less compensatory mechanisms
- Gender, as females have a higher risk of bleeding due to menstruation, pregnancy, and childbirth
- Medications, such as anticoagulants, antiplatelets, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or corticosteroids
- Comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, liver disease, kidney disease, or anemia

Assessment and Clinical Manifestations
- The assessment of hemorrhage involves obtaining a detailed history of the onset, duration, frequency, amount, color, and source of bleeding; any associated symptoms or factors; any previous episodes or treatments; and any relevant medical history or medications
- The clinical manifestations of hemorrhage depend on the type and severity of bleeding, but some common signs and symptoms include:
- Pallor, cyanosis, jaundice, or petechiae on the skin and mucous membranes
- Tachycardia, hypotension, thready pulse, or weak peripheral pulses
- Tachypnea, dyspnea, orthopnea, or crackles in the lungs
- Oliguria or anuria in the urine output
- Altered mental status, confusion, drowsiness, or coma in the neurological function
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distension, or guarding in the gastrointestinal system
- Hematemesis, melena, hematochezia, or occult blood in the stool in the gastrointestinal bleeding
- Hemoptysis, epistaxis, hematuria, menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, or postmenopausal bleeding in the respiratory, nasal, urinary, or reproductive bleeding

Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnostic evaluation of hemorrhage involves various laboratory tests and imaging studies to confirm the presence, source, extent, and effects of bleeding. Some common tests include:
- Complete blood count (CBC), including hemoglobin, hematocrit, red blood cell (RBC) count, white blood cell (WBC) count, and platelet count. These tests measure the amount and quality of blood cells and indicate the degree of blood loss and anemia.
- Coagulation studies, including prothrombin time (PT), international normalized ratio (INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), fibrinogen level, D-dimer test, and thrombin time (TT). These tests measure the ability of blood to clot and indicate the presence of coagulation disorders or anticoagulant therapy.
- Blood type and crossmatch. This test determines the compatibility of blood for transfusion and prevents transfusion reactions.
- Serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and liver function tests (LFTs). These tests measure the levels of electrolytes and metabolic waste products in the blood and indicate the effects of bleeding on the kidney and liver function.
- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. This test measures the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in the blood and indicates the effects of bleeding on the acid-base balance and tissue perfusion.
- Urinalysis. This test detects the presence of blood, protein, glucose, ketones, or bacteria in the urine and indicates the effects of bleeding on the urinary system.
- Endoscopy. This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera and light into the gastrointestinal tract to visualize the source and extent of bleeding and perform interventions such as cauterization, clipping, or banding.
- Colonoscopy. This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera and light into the colon to visualize the source and extent of bleeding and perform interventions such as polypectomy, cauterization, or injection.
- Angiography. This procedure involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels and taking X-rays to visualize the source and extent of bleeding and perform interventions such as embolization or stenting.
- Ultrasound. This procedure involves using sound waves to create images of the internal organs and structures and detect the presence of fluid, masses, or abnormalities.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan. This procedure involves using X-rays and a computer to create cross-sectional images of the body and detect the presence of fluid, masses, or abnormalities.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. This procedure involves using a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the body and detect the presence of fluid, masses, or abnormalities.
Management and Interventions
- The management and interventions for hemorrhage aim to stop the bleeding, restore the blood volume, correct the coagulation disorders, prevent the complications, and treat the underlying cause. Some common interventions include:
- Hemostasis. This involves applying direct pressure, elevation, tourniquet, or dressing to the bleeding site; suturing or stapling the wound; cauterizing or clipping the vessel; embolizing or stenting the artery; or performing surgery to repair or remove the damaged tissue or organ.
- Fluid resuscitation. This involves administering intravenous fluids, such as normal saline, lactated Ringer's solution, or colloids,
- Blood transfusion. This involves administering blood products, such as
- packed red blood cells (PRBCs),
- fresh frozen plasma (FFP),
- platelets,
- or cryoprecipitate,
- Medications. This involves administering medications, such as :
- antifibrinolytics,
- hemostatic agents,
- vasopressors,
- analgesics,
- antibiotics,
- or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs),
- to enhance
- the clot formation,
- constrict
- the blood vessels,
- relieve
- the pain,
- prevent
- or treat
- the infection,
- or reduce
- the gastric acid secretion.
- Oxygen therapy. This involves administering supplemental oxygen via nasal cannula, mask, or mechanical ventilation to improve the oxygen delivery to the tissues.
Emergency Care and Resuscitation
- Emergency care and resuscitation for hemorrhage involve rapid assessment, stabilization, monitoring, and transport of the patient to a higher level of care. Some key steps include:
- Assessing the airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs) and initiating cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if needed.
- Apply direct pressure, elevation, tourniquet, or dressing to control the external bleeding.
- Inserting an intravenous line and administering fluids and medications as ordered.
- Monitoring vital signs, hemoglobin level, urine output, and mental status.
- Administering oxygen therapy as needed.
- Preparing for blood transfusion as ordered.
- Identifying and treating the underlying cause of bleeding.
- Transporting the patient to a trauma center or intensive care unit (ICU) as soon as possible.
Nursing Priorities and Patient Education
- Assess the patient for signs and symptoms of hemorrhage, such as hypotension, tachycardia, pallor, diaphoresis, decreased urine output, altered mental status, and bleeding from wounds or body orifices.
- Monitor the patient's vital signs, hemoglobin, hematocrit, coagulation profile, and fluid balance frequently.
- Identify and control the source of bleeding as soon as possible. Apply direct pressure, elevate the affected area, or use hemostatic agents if indicated.
- Administer fluids, blood products, and medications as prescribed to restore circulating volume and hemostasis. Monitor for transfusion reactions and fluid overload.
- Provide oxygen therapy and maintain a patent airway to ensure adequate tissue oxygenation.
- Maintain a warm environment and prevent hypothermia, which can worsen coagulopathy and bleeding.
- Educate the patient and family about the causes, risk factors, prevention, and treatment of hemorrhage. Teach them to recognize and report signs of bleeding or infection promptly.
- Instruct the patient to avoid activities that can increase the risk of bleeding, such as using NSAIDs, aspirin, or herbal remedies that affect clotting; brushing teeth vigorously; blowing nose forcefully; straining during bowel movements; or inserting anything into body cavities without medical advice.
- Encourage the patient to eat a well-balanced diet rich in iron, vitamin K, and protein to promote blood formation and healing.
Summary
- Hemorrhage is the medical term for excessive bleeding from blood vessels.
- It can occur internally (inside the body) or externally (outside the body).
- Causes of hemorrhage may include trauma, surgery, ulcers, ruptured blood vessels, or medical conditions affecting blood clotting.
- Symptoms of hemorrhage depend on the location and severity but may include rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, weakness, dizziness, and pale skin.
- Hemorrhage can be life-threatening, especially if not promptly controlled or treated.
- Treatment may involve applying pressure to the bleeding site, using hemostatic agents, transfusing blood products, or performing surgical interventions.
- Prevention strategies include safety measures to avoid injuries and managing medical conditions that increase the risk of bleeding.
Conclusion
- Hemorrhage is a significant medical condition characterized by excessive bleeding from blood vessels.
- It can occur internally or externally and may result from various factors, such as trauma, surgery, or underlying medical conditions.
- Prompt recognition and management of hemorrhage are crucial to prevent severe complications and potentially life-threatening situations.
- Common signs and symptoms of hemorrhage include hypotension, tachycardia, pallor, and weakness.
- Treatment strategies for hemorrhage include direct pressure to control bleeding, fluid resuscitation, and blood transfusions when necessary.
- Preventive measures, such as safety precautions, regular medical checkups, and appropriate use of anticoagulant medications, can help reduce the risk of hemorrhage.
- Timely intervention and collaboration among healthcare professionals are vital in ensuring positive outcomes for patients experiencing hemorrhage.
Raynaud's Disease
Introduction
- Raynaud's Disease is a condition that affects the blood circulation in some areas of the body, such as fingers and toes, causing them to feel cold, numb, and change color when exposed to cold temperatures or stress
- There are two types of Raynaud's Disease: primary and secondary
- Primary Raynaud's Disease is the most common form and has no known cause or underlying condition
- Secondary Raynaud's Disease is less common and is caused by another medical condition, such as autoimmune diseases, vascular diseases, or occupational factors
- Raynaud's Disease can affect the quality of life of people who have it, but it is not usually disabling or life-threatening
Triggers and Risk Factors
- The main trigger of Raynaud's Disease is cold exposure, which causes the blood vessels in the affected areas to narrow and limit blood flow
- Other triggers include emotional stress, smoking, caffeine, certain medications, and vibrating tools
- The risk factors for developing Raynaud's Disease include:
-
- Being female
- Having a family history of the condition
- Living in a cold climate
- Having an underlying condition that affects blood vessels or connective tissues, such as lupus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, or atherosclerosis
- Working in occupations that involve exposure to cold or vibration, such as construction, agriculture, or food processing
Clinical Features and Diagnosis
- The main feature of Raynaud's Disease is the color change of the affected areas during an attack, which usually follows a pattern of white-blue-red
- White: The skin turns pale or white as blood flow is reduced
- Blue: The skin turns blue or purple as blood vessels react to low oxygen levels
- Red: The skin turns red or pink as blood flow returns and causes warmth, tingling, or pain
- Other features include:
- Coldness and numbness of the affected areas
- Pins and needles sensation or stinging pain upon warming or stress relief
- Difficulty moving the affected areas
- Swelling or ulcers in severe cases
- The diagnosis of Raynaud's Disease is based on:
-
- The history and physical examination of the patient
- The observation of an attack or its simulation with cold exposure or stress test
- The exclusion of other conditions that can cause similar symptoms
- The identification of any underlying condition that can cause secondary Raynaud's Disease
- The blood tests to check for inflammation, antibodies, or other markers of vascular or connective tissue diseases
Management and Treatment
- The management and treatment of Raynaud's Disease aim to:
- Reduce the frequency and severity of attacks
- Prevent complications such as tissue damage or infection
- Treat any underlying condition that causes secondary Raynaud's Disease
- The management and treatment options include:
- Lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies
- Medications to improve blood circulation, such as calcium channel blockers (e.g. nifedipine), alpha-blockers (e.g. prazosin), vasodilators (e.g. nitroglycerin), or neurotoxins (e.g. botulinum toxin)
- Surgery to cut or block the sympathetic nerves that control blood vessel constriction in severe cases that do not respond to medications

Lifestyle Modifications and Self-Care
- The lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies for managing Raynaud's Disease include:
- Keeping the body warm by wearing layers of clothing, gloves, socks, hats, scarves, etc.
- Avoiding exposure to cold temperatures or sudden changes in temperature
- Warming the affected areas by rubbing them, placing them in warm water, or using heating pads
- Avoiding emotional stress or practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises
- Quitting smoking and limiting caffeine intake, as they can constrict blood vessels and worsen symptoms
- Avoiding medications or substances that can trigger or worsen attacks, such as beta-blockers, decongestants, estrogen, or cocaine
- Exercising regularly to improve blood circulation and overall health
- Eating a healthy and balanced diet that includes foods rich in vitamin B, omega3 fatty acids, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin E
- Taking care of the skin and nails of the affected areas by moisturizing them, avoiding injuries or infections, and treating any wounds promptly
Nursing Interventions and Patient Support
- The nursing interventions and patient support for people with Raynaud's Disease include:
- Educating the patient and family about the condition, its causes, triggers, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention
- Assessing the patient's risk factors, medical history, current medications, and underlying conditions
- Monitoring the patient's vital signs, blood flow, skin color, temperature, sensation, and pain level
- Administering medications as prescribed and monitoring their effectiveness and side effects
- Providing warmth and comfort to the patient during an attack and assisting with warming measures
- Encouraging the patient to follow the lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies as mentioned above
- Referring the patient to other health care professionals or support groups as needed
- Providing emotional support and counseling to the patient and family
Summary
- Raynaud's Disease is a condition that affects the blood circulation in some areas of the body, such as fingers and toes, causing them to feel cold, numb, and change color when exposed to cold temperatures or stress
- There are two types of Raynaud's Disease: primary and secondary
- The main trigger of Raynaud's Disease is cold exposure, but other factors such as emotional stress, smoking, caffeine, certain medications, and vibrating tools can also trigger or worsen attacks
- The main feature of Raynaud's Disease is the color change of the affected areas during an attack, which usually follows a pattern of white-blue-red
- The diagnosis of Raynaud's Disease is based on the history and physical examination of the patient, the observation of an attack or its simulation with cold exposure or stress test, the exclusion of other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, the identification of any underlying condition that can cause secondary Raynaud's Disease, and the blood tests to check for inflammation, antibodies, or other markers of vascular or connective tissue diseases
- The management and treatment of Raynaud's Disease aim to reduce the frequency and severity of attacks, prevent complications such as tissue damage or infection, treat any underlying condition that causes secondary Raynaud's Disease, and improve the quality of life of people who have it
- The management and treatment options include lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies (such as keeping warm, avoiding stress, and quitting smoking), medications to improve blood circulation (such as calcium channel blockers), and surgery to cut or block the sympathetic nerves in severe cases
- The nursing interventions and patient support for people with Raynaud's Disease include educating the patient and family about the condition, assessing the patient's risk factors and underlying conditions, monitoring the patient's blood flow and pain level, administering medications as prescribed, providing warmth and comfort to the patient during an attack, encouraging the patient to follow the lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies, referring the patient to other health care professionals or support groups as needed, and providing emotional support and counseling to the patient and family
Conclusion
- Raynaud's Disease is a common condition that can affect anyone but is more prevalent in women, people who live in cold climates, and people who have certain medical conditions that affect blood vessels or connective tissues
- Raynaud's Disease can cause discomfort, pain, and reduced quality of life for people who have it, but it is not usually disabling or life-threatening
- Raynaud's Disease can be managed effectively with lifestyle modifications, self-care strategies, medications, and surgery in severe cases
- People with Raynaud's Disease can benefit from education, monitoring, treatment, and support from healthcare professionals, especially nurses
Aneurysm and peripheral vascular disorder
Introduction
- An aneurysm is an abnormal dilation of an artery caused by weakening of the arterial wall
- A peripheral vascular disorder is any condition that affects the blood vessels outside the heart and brain
- These conditions can cause pain, swelling, numbness, ischemia, embolism, rupture, bleeding, infection, or stroke
- These conditions are more common in men, older adults, smokers, and people with a family history of aneurysms
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes and Risk Factors of Aneurysms:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of fatty deposits and plaque in the arteries can weaken the arterial walls and increase the risk of aneurysm formation.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of aneurysms can predispose individuals to develop aneurysms, suggesting a genetic component to the condition.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Chronic hypertension can put extra stress on arterial walls, making them more susceptible to developing aneurysms.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for aneurysms, as it contributes to arterial wall damage and inflammation.
- Age: Aneurysms are more common in older individuals, as arterial walls tend to weaken with age.
- Gender: Men are at a higher risk of developing aneurysms compared to women.
- Trauma: Physical injury or trauma to blood vessels can lead to the formation of an aneurysm.
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Certain inherited connective tissue disorders, such as Marfan syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, can increase the risk of aneurysm development.
Causes and Risk Factors of Peripheral Vascular Disorders:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in the arteries, which narrows and hardens the blood vessels, is a common cause of peripheral vascular disorders.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to peripheral vascular complications like peripheral artery disease (PAD) and peripheral neuropathy.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can strain and damage blood vessels, contributing to peripheral vascular diseases.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for peripheral vascular disorders, as it damages blood vessels and increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to poor circulation and increase the risk of peripheral vascular diseases.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on the circulatory system, increasing the likelihood of developing vascular problems.
- Family History: A family history of peripheral vascular disorders can indicate a genetic predisposition to these conditions.
- Age: Peripheral vascular disorders become more common with advancing age, as blood vessels naturally lose some elasticity and become more prone to damage.
- Hyperlipidemia: Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can contribute to the formation of plaque and atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of peripheral vascular diseases.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Some autoimmune diseases, such as vasculitis, can cause inflammation and damage to blood vessels in the peripheral circulation.
Assessment and Diagnostic Tests
Assessment and Diagnostic Tests for Aneurysms:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider may perform a thorough physical examination to check for signs of aneurysm, such as a pulsating mass, tenderness, or bruits (abnormal sounds) over the affected area.
- Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the blood vessels and can help visualize aneurysms.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of blood vessels and can help identify the location and size of aneurysms.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI can produce high-resolution images of blood vessels, aiding in the detection and assessment of aneurysms.
- Angiography: In this procedure, a contrast dye is injected into the blood vessels, followed by X-rays or other imaging techniques, to visualize the blood flow and identify aneurysms.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis: In cases of suspected ruptured cerebral aneurysms, a lumbar puncture may be performed to examine the cerebrospinal fluid for signs of bleeding and other abnormalities.
Assessment and Diagnostic Tests for Peripheral Vascular Disorders:
- AnkleBrachial Index (ABI): ABI is a simple and non-invasive test that compares the blood pressure in the ankles to that in the arms. It is used to assess peripheral artery disease (PAD) and determine the extent of arterial blockage.
- Doppler Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to measure blood flow in the arteries and veins, helping to diagnose PAD and assess blood flow in peripheral vessels.
- Angiography: Similar to the procedure for aneurysms, angiography can also be used to visualize the blood flow in peripheral arteries and identify blockages or narrowing.
- Treadmill Exercise Testing: This test is used to evaluate the severity of PAD by monitoring the patient's ability to walk on a treadmill and assessing any symptoms of claudication (pain or discomfort in the legs during walking).
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): Both CTA and MRA are imaging tests that provide detailed images of blood vessels to evaluate peripheral vascular disorders.
- Arteriography: In this procedure, a contrast dye is injected directly into the arteries, and X-rays are taken to visualize the blood flow and identify any abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can be used to assess lipid levels, glucose levels (in the case of diabetes), and other markers of inflammation and vascular health that may contribute to peripheral vascular disorders.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: For conditions involving peripheral neuropathy, nerve conduction studies may be performed to assess nerve function and detect abnormalities in nerve signals.
Complications and Potential Consequences
- The main complications of aneurysms and peripheral vascular disorders are thrombosis, embolism, rupture, and bleeding
- Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside the aneurysm or artery, which can block blood flow and cause ischemia
- Embolism is the detachment of a blood clot or a piece of plaque from the aneurysm or artery, which can travel to other organs and cause infarction
- Rupture is the tearing of the aneurysm or artery wall, which can cause massive hemorrhage and shock
- Bleeding is the loss of blood from the aneurysm or artery, which can cause anemia and hypotension
Treatment Options
Treatment Options for Aneurysms:
- Monitoring: Small, stable aneurysms may be monitored regularly through imaging tests to track their growth and determine if intervention is necessary.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers, may be prescribed to manage blood pressure and reduce the risk of aneurysm rupture.
- Endovascular Repair: For certain types of aneurysms, endovascular repair may be an option. This minimally invasive procedure involves the insertion of a stent or a graft through the blood vessels to reinforce the weakened area and divert blood flow away from the aneurysm.
- Open Surgical Repair: In cases where the aneurysm is large or has a high risk of rupture, open surgical repair may be performed. During this procedure, the weakened portion of the blood vessel is replaced with a synthetic graft.
- Coil Embolization: For certain types of cerebral aneurysms, a technique called coil embolization may be used. Soft platinum coils are inserted into the aneurysm to promote clotting and reduce the risk of rupture.
- Blood Pressure Management: Maintaining optimal blood pressure through lifestyle modifications or medications is essential to prevent further weakening of arterial walls.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Vascular Disorders:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle changes, including regular exercise, smoking cessation, a balanced diet, and weight management, can help improve blood flow and manage peripheral vascular disorders.
- Medications: Various medications may be prescribed to manage peripheral vascular disorders, such as antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), statins to control cholesterol levels, and medications to manage blood pressure and blood sugar in diabetes.
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: In cases of peripheral artery disease (PAD) with arterial blockages, angioplasty may be performed. During this procedure, a balloon is inflated to widen the narrowed artery, and a stent may be placed to keep the artery open.
- Bypass Surgery: In severe cases of peripheral artery disease (PAD), bypass surgery may be performed. During this procedure, a graft is used to bypass the blocked or narrowed artery, allowing blood to flow freely to the affected area.
- Endarterectomy: Endarterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove plaque buildup from the inner lining of an artery, improving blood flow.
- Compression Therapy: Compression stockings or bandages may be used to improve blood flow and reduce swelling in individuals with peripheral vascular disorders.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Post-op Care and Rehabilitation for Aneurysms
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Monitoring: After surgical repair of an aneurysm, the patient is usually closely monitored in the ICU to assess vital signs, neurological status, and signs of complications.
- Pain Management: Adequate pain management is provided to ensure the patient's comfort and reduce postoperative pain.
- Wound Care: Careful monitoring and dressing changes for surgical incisions are essential to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Blood Pressure Management: Maintaining stable blood pressure is crucial post-surgery to prevent stress on the repaired blood vessel and reduce the risk of further complications.
- Early Mobilization: Encouraging early mobilization helps prevent complications such as blood clots and promotes faster recovery.
- Respiratory Care: Monitoring and supporting respiratory function is crucial, especially if the aneurysm is located in the thoracic region.
- Neurological Assessment: Frequent neurological assessments are conducted to monitor for any changes that might indicate complications affecting the brain or spinal cord.
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Monitoring and managing fluid and electrolyte levels are vital to maintain overall health and support proper healing.
- Medication Management: The patient may receive medications, such as antihypertensives or anticoagulants, to manage blood pressure and prevent clot formation.
- Diet and Nutrition: A well-balanced diet is important for wound healing and overall recovery.
Rehabilitation for Aneurysms
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy focuses on improving strength, mobility, and function. It may include exercises to improve walking, balance, and overall physical conditioning.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy helps patients regain skills necessary for daily activities and promotes independence.
- Speech Therapy: For aneurysms affecting the brain, speech therapy may be needed to address any speech or language deficits that may have occurred.
- Neurological Rehabilitation: Patients with neurological deficits may benefit from specialized neurological rehabilitation programs tailored to their needs.
- Psychological Support: Rehabilitation often involves psychological support to address emotional and cognitive challenges that may arise after aneurysm repair.
Post-op Care and Rehabilitation for Peripheral Vascular Disorders:
- Wound Care: For individuals who underwent procedures like angioplasty, stent placement, or bypass surgery, careful wound care and monitoring are essential to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Activity and Mobility: Gradual and supervised mobilization is encouraged to prevent complications and improve blood flow.
- Medication Management: Compliance with prescribed medications, such as antiplatelets and statins, is essential to manage the underlying vascular condition and prevent complications.
- Compression Therapy: For individuals with venous insufficiency or chronic venous ulcers, compression therapy may be utilized to improve blood flow and promote wound healing.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging and supporting lifestyle changes,
Summary
- Aneurysms and peripheral vascular disorders are serious conditions that can affect any artery in the body and cause life-threatening complications
- The causes and risk factors of these conditions are mainly related to atherosclerosis and its associated factors
- The assessment and diagnostic tests for these conditions are based on physical examination and imaging studies
- The treatment options for these conditions are aimed at preventing rupture, restoring blood flow, relieving symptoms, and preventing further damage to the arteries
- The surgical interventions and endovascular repair for these conditions involve using grafts or stents to repair the aneurysm or artery
- The postoperative care and rehabilitation for these conditions involve monitoring, education, and support
Conclusion
- Aneurysms and peripheral vascular disorders are complex and potentially life-threatening conditions that can arise due to the weakening of arterial walls and various risk factors.
- Early detection and diagnosis are crucial as these conditions often remain asymptomatic until complications arise.
- Diagnostic tests such as ultrasonography, MRA, CT, and angiography play a vital role in confirming the presence and extent of these disorders.
- Complications such as thrombosis, embolism, rupture, and bleeding can lead to severe consequences, making timely intervention essential.
- Treatment options include medical therapy, endovascular repair, and surgical repair, tailored to the specific characteristics and severity of each case.
- Medical therapy aims to manage risk factors and alleviate symptoms, while endovascular and surgical interventions seek to restore vascular integrity.
- Postoperative care and rehabilitation are critical for successful outcomes, involving close monitoring, patient education, and support.
- Nurses play a central role in the comprehensive care of patients with aneurysms and peripheral vascular disorders, contributing to their recovery and overall well-being.
- Continued research and advancements in medical technology are vital to improving outcomes and reducing the burden of these vascular conditions.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Introduction
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure that combines chest compressions often with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest.
- CPR can keep oxygen-rich blood flowing to the brain and other organs until emergency medical treatment can restore a normal heart rhythm.
- CPR can double or triple the chances of survival after cardiac arrest.
- CPR is a critical step in the American Heart Association's (AHA) Chain of Survival.

Basic Life Support (BLS) Guidelines
- The AHA develops science-based CPR guidelines and is the leader in first aid, CPR, and AED training.
- The AHA recommends starting CPR with hard and fast chest compressions.
- The AHA recommends two versions of CPR:
- For healthcare providers and those trained: conventional CPR using chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth breathing at a ratio of 30:2 compressions-to-breaths.
- For the general public or bystanders who witness an adult suddenly collapse: compression-only CPR, or Hands-Only CPR.
- In adult victims of cardiac arrest, it is reasonable for rescuers to perform chest compressions at a rate of 100 to 120/min and to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) for an average adult while avoiding excessive chest compression depths (greater than 2.4 inches [6 cm]).
Chain of Survival
- The term Chain of Survival provides a useful metaphor for the elements of the emergency cardiovascular care (ECC) systems concept.
- The 6 links in the adult out-of-hospital Chain of Survival are:
- Recognition of cardiac arrest and activation of the emergency response system (calling 91-1 in the US)
- Early CPR with an emphasis on chest compressions
- Rapid defibrillation
- Advanced resuscitation by Emergency Medical Services and other healthcare providers
- Postcardiac arrest care
- Recovery (including additional treatment, observation, rehabilitation, and psychological support)
- A strong Chain of Survival can improve the chances of survival and recovery for victims of cardiac arrest.
Cardiac Arrest Recognition and Response
- Cardiac arrest is when the heart stops beating or beats too ineffectively to circulate blood to the brain and other vital organs.
- Cardiac arrest can be caused by many factors, such as heart attack, drowning, electrocution, drug overdose, choking, trauma, or infection.
- Cardiac arrest can happen to anyone, at any age, at any time.
- Cardiac arrest is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate action.
- The signs of cardiac arrest are :
- Sudden collapse or loss of consciousness
- No breathing or gasping breaths
- No pulse or movement
- The steps to respond to cardiac arrest are :
- Check for safety and responsiveness
- Call 9-1-1 or the local emergency number and get an AED if available
- Start chest compressions (and rescue breaths if trained)
- Use an AED as soon as possible
- Continue CPR until help arrives or the person shows signs of life
CPR Techniques and Compression Ratios
- The technique for performing chest compressions varies depending on the age and size of the victim.
- The general principles are :
- Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, between the nipples
- Place the other hand on top of the first hand, interlocking your fingers
- Keep your arms straight and your shoulders directly over your hands
- Push hard and fast, compressing the chest at least one-third of its depth
- Allow the chest to recoil fully after each compression
- Minimize interruptions in chest compressions
- The compression ratio for conventional CPR (with rescue breaths) is 30:2 for all age groups, except for newborns.
- The compression ratio for compression-only CPR (without rescue breaths) is continuous chest compressions without pauses.
- The compression rate for both types of CPR is 100 to 120/min for all age groups.
Use of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs)
- An AED is a portable device that can analyze the heart rhythm and deliver an electric shock to restore a normal heartbeat in a person who is in cardiac arrest.
- AEDs can greatly increase a cardiac arrest victim's chances of survival.
- AEDs are designed to be easy to use by anyone, even without formal training.
- The steps to use an AED are :
- Turn on the AED and follow the voice and/or visual prompts
- Expose the person's chest and wipe it dry
- Attach the AED pads to the person's chest as shown on the pad's diagram
- Plug in the connector if necessary
- Make sure no one is touching the person, including yourself
- Push the \"analyze\" button if necessary and let the AED analyze the heart rhythm
- If the AED advises a shock, make sure no one is touching the person, including yourself
- Push the \"shock\" button as prompted
- Perform CPR as instructed by the AED or until emergency help arrives
Team Dynamics and Communication during CPR
- CPR is often performed by more than one rescuer, especially in healthcare settings.
- Effective team dynamics and communication are essential for high-quality CPR and improved outcomes.
- The key elements of team dynamics and communication are :
- Clear roles and responsibilities for each team member
- Leadership and followership skills
- Closed-loop communication and feedback
- Mutual respect and trust among team members
- Shared mental model and situational awareness
- Rehearsal and debriefing of CPR performance
Summary
- CPR is a lifesaving procedure that can restore blood flow and oxygen to the brain and other organs in a person who is in cardiac arrest.
- CPR involves chest compressions with or without rescue breaths, depending on the type of CPR and the training level of the rescuer.
- CPR follows the basic life support guidelines developed by the AHA, which are based on scientific evidence and best practices.
- CPR is part of the Chain of Survival, which consists of six links that can improve survival and recovery for cardiac arrest victims.
- CPR should be performed as soon.
Conclusion
- CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is a critical emergency procedure designed to save lives by restoring blood circulation and oxygenation to vital organs during cardiac arrest or respiratory failure.
- When performed promptly and correctly, CPR can significantly increase the chances of survival for individuals experiencing life-threatening emergencies.
- The key components of CPR, including chest compressions and rescue breaths, work together to maintain blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain and other organs.
- Proper training in CPR is crucial for individuals to effectively respond to emergencies and provide immediate assistance to those in need.
- CPR should be initiated immediately when someone is unresponsive, not breathing, or without a pulse, even before professional medical help arrives.
- Continuous practice and regular updates in CPR skills are essential to maintain proficiency and ensure confidence in performing the procedure effectively.
- Public awareness and education campaigns play a vital role in promoting CPR knowledge and empowering communities to be proactive in lifesaving situations.
- Integrating automated external defibrillators (AEDs) with CPR can further enhance the chances of successful resuscitation for individuals experiencing sudden cardiac arrest.
- CPR is a fundamental skill that can be the difference between life and death, and everyone should be encouraged to learn and be prepared to act in emergency situations.
Leukemia
Introduction
- Leukemia is a group of malignant disorders that affect the blood and blood-forming tissues of the bone marrow, lymph system, and spleen
- Leukemia is classified according to the type of white blood cell (WBC) involved (lymphocytic or myelogenous) and the rate of progression (acute or chronic)
- Leukemia is the most common cancer in children and adolescents, accounting for about 30% of all childhood cancers
- Leukemia can also affect adults of any age, with the highest incidence in older adults
Overview and Types of Leukemia
- Leukemia results from the abnormal proliferation of immature or abnormal WBCs that interfere with the normal production and function of blood cells
- The four main types of leukemia are:
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL): The most common type in children; involves immature lymphocytes that originate from the lymphoid stem cell; has a good prognosis with a 5year survival rate of about 85% in children and less than 50% in adults
- Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML): The most common type in adults; involves immature myeloid cells that originate from the myeloid stem cell; has a poor prognosis with a 5year survival rate of about 25% in adults and children; a subtype called acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is the most curable of adult leukemias
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): Mostly affects older adults; involves mature but abnormal lymphocytes that accumulate in the blood, bone marrow, and lymphoid tissues; has a slow progression and a variable prognosis; watchful waiting is often used until symptoms appear
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML): Mostly affects young adults; involves mature but abnormal myeloid cells that proliferate in the blood, bone marrow, and spleen; has a rapid progression and a poor prognosis; divided into three phases: chronic, accelerated, and blast
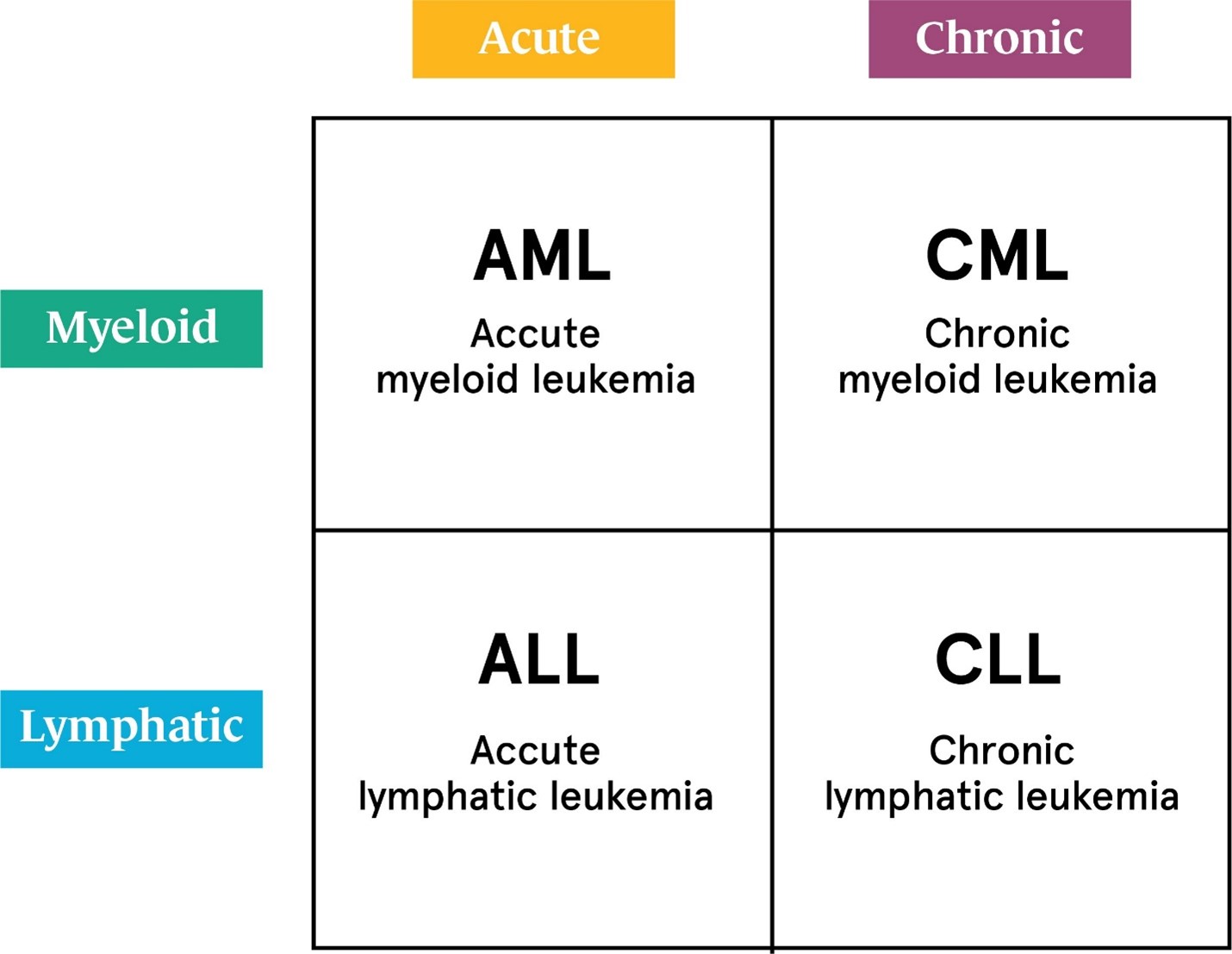
Etiology and Risk Factors
- The exact cause of leukemia is unknown, but it is likely multifactorial, involving genetic, environmental, and immunologic factors
- Some possible risk factors for leukemia are:
- Exposure to ionizing radiation, such as from atomic bombs, nuclear power plants, or medical radiation therapy
- Exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene, formaldehyde, or pesticides
- Exposure to certain viruses, such as human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- Genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, Fanconi anemia, or Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Family history of leukemia or other hematologic malignancies
- Smoking or tobacco use

Pathophysiology
- Leukemia involves a clonal expansion of abnormal hematopoietic stem cells that have acquired mutations that disrupt their differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis
- These abnormal stem cells give rise to immature or dysfunctional WBCs that crowd out the normal blood cells in the bone marrow and peripheral blood
- The lack of normal WBCs leads to immunosuppression and increased susceptibility to infections
- The lack of normal red blood cells (RBCs) leads to anemia and decreased oxygen delivery to tissues
- The lack of normal platelets leads to thrombocytopenia and an increased risk of bleeding
- The abnormal WBCs can also infiltrate other organs, such as the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, brain, testes, and skin, causing organ enlargement, dysfunction, or damage
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
- The signs and symptoms of leukemia vary depending on the type, stage, and extent of involvement
- Some common signs and symptoms are:
- Fever, chills, night sweats, or recurrent infections
- Fatigue, weakness, pallor, or shortness of breath
- Bleeding, bruising, petechiae, or purpura
- Bone pain, joint pain, or tenderness
- Lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, or splenomegaly
- Headache, nausea, vomiting, or visual disturbances
- Weight loss, anorexia, or malaise
Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnosis of leukemia is based on the history, physical examination, and laboratory tests
- Some diagnostic tests for leukemia are:
-
- Complete blood count (CBC) with differential: Shows abnormal WBC count (high or low), low RBC count (anemia), and low platelet count (thrombocytopenia); also shows the presence and percentage of blast cells (immature WBCs) in the blood
- Peripheral blood smear: Shows the morphology and characteristics of the blood cells; helps to identify the type of leukemia and the degree of maturation of the WBCs
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: Shows the cellularity and histology of the bone marrow; confirms the diagnosis of leukemia and the subtype; also helps to evaluate the response to treatment and the remission status
- Cytogenetic analysis: Shows the chromosomal abnormalities and genetic mutations of the leukemic cells; helps to classify the leukemia and to predict the prognosis and response to treatment
- Immunophenotyping: Shows the surface markers and antigens of the leukemic cells; helps to identify the lineage and subtype of leukemia and to monitor the minimal residual disease
- Lumbar puncture: Shows the presence of leukemic cells in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); helps to diagnose and treat central nervous system (CNS) involvement
Treatment Approaches
- The treatment of leukemia depends on the type, stage, and risk factors of the disease; the goal is to eliminate all leukemic cells and to prevent relapse
- Some treatment modalities for leukemia are:
- Chemotherapy: The use of cytotoxic drugs that kill or inhibit the growth of cancer cells; usually given in combination and in different phases (induction, consolidation, maintenance); may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, hair loss, mucositis, neuropathy, myelosuppression, or infertility
- Targeted therapy: The use of drugs that target specific molecules or pathways that are involved in the growth or survival of cancer cells; may be more effective and less toxic than chemotherapy; examples include tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) for CML or APL, monoclonal antibodies for CLL or ALL, or immunomodulatory agents for AML
- Immunotherapy: The use of drugs that stimulate or enhance the immune system's ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells; examples include chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for ALL or NHL, bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) for ALL or AML, or checkpoint inhibitors for HL or NHL
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT): The infusion of healthy stem cells from a donor (allogeneic) or from oneself (autologous) to restore normal blood cell production after high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy; may offer a chance of cure for some patients with high-risk or relapsed leukemia; may cause complications such as graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), infection, bleeding, organ damage, or graft failure
- Radiation therapy: The use of high-energy rays or particles to kill or damage cancer cells; may be used to treat localized disease such as CNS involvement, lymph node enlargement, or splenic enlargement; may cause side effects such as skin irritation, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or infertility
- Supportive care: The use of drugs or interventions to prevent or treat the complications or side effects of leukemia or its treatment; examples include antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, blood transfusions, growth factors, antiemetics, analgesics, hydration, nutrition, or palliative care
Patient Assessment, Monitoring and Patient Education
- Monitor complete blood counts (CBC) regularly to detect changes in blood cell counts
- Assess for signs of infection, bleeding, and anemia
- Observe for skin pallor, petechiae, and bruising
- Monitor for fever and initiate appropriate infection control measures
- Assess for signs of pain and implement pain management strategies
- Monitor for side effects of chemotherapy and other treatments
- Provide information about leukemia, its types, and treatment options
- Educate patients on the importance of adherence to prescribed medications and treatment plans
- Teach patients about managing side effects and self-care measures
- Encourage a balanced diet and hydration to support the immune system
- Discuss the importance of rest and stress reduction techniques
- Provide emotional support and active listening to patients and their families
- Facilitate support groups to connect patients with others experiencing similar challenges
- Offer counseling services for coping with the emotional impact of diagnosis and treatment
- Encourage participation in leisure activities to improve quality of life
- Collaborate with social workers to address financial and practical concerns
- Initiate palliative care to improve symptom control and enhance quality of life
- Manage pain and other distressing symptoms through appropriate interventions
- Monitor for signs of fatigue and implement energy conservation strategies
- Support patients in advanced care planning and end-of-life decision-making
- Implement strict infection control measures to minimize the risk of infections
- Educate patients and their families about the importance of hand hygiene
- Restrict visitors with signs of illness to prevent exposure to infections
- Ensure appropriate isolation precautions for patients with neutropenia
Summary
- Leukemias is a group of cancers that affect the blood and bone marrow, characterized by the uncontrolled production of abnormal white blood cells.
- There are four main types of leukemia: acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
- Leukemia can affect people of all ages, but some types are more common in children (ALL) or adults (AML, CLL, and CML).
- Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, fever, easy bruising or bleeding, frequent infections, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Diagnosis is based on blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and cytogenetic analysis to identify specific genetic abnormalities.
- Treatment options for leukemia include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, stem cell transplantation, and immunotherapy.
- Prognosis varies depending on the type and stage of leukemia, with some types having high cure rates, while others may be more challenging to treat.
- Supportive care is essential to manage side effects and improve the quality of life for individuals undergoing leukemia treatment.
- Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and timely treatment play a crucial role in improving the survival rates and overall prognosis for leukemia patients.
Conclusion
- Leukemias are a diverse group of blood cancers affecting various age groups and characterized by abnormal white blood cell proliferation.
- The four main types include acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
- Timely diagnosis through blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and genetic analysis is crucial for appropriate treatment planning.
- Treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, stem cell transplantation, and immunotherapy, tailored to the specific leukemia type and stage.
- Prognosis varies, with some types having high cure rates, while others may require more intensive and prolonged treatment.
- Supportive care is essential in managing treatment side effects and enhancing patients' quality of life.
- Ongoing research continues to improve leukemia treatments and uncover new therapeutic approaches.
- Early detection and effective treatment are vital for better survival rates and improved outcomes in leukemia patients.
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Introduction
- DVT is a condition where a blood clot forms in one or more of the deep veins in the body, usually in the legs.
- DVT can cause leg pain, swelling, redness, warmth, or no symptoms at all.
- DVT is a serious condition because the clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE), which can be fatal.
- DVT is part of a condition called venous thromboembolism (VTE), which also includes PE and chronic venous insufficiency (CVI).
Risk Factors and Causes
- DVT is caused by a combination of factors that affect the blood flow, the blood vessel wall, and the blood coagulation system. These factors are known as Virchow's triad.
- The risk factors for DVT include:
- Immobility or reduced physical activity, such as bed rest, hospitalization, surgery, paralysis, or long-distance travel.
- Injury or damage to the blood vessel wall, such as trauma, fracture, dislocation, infection, inflammation, or catheter insertion.
- Hypercoagulability or increased tendency of the blood to clot, such as genetic disorders, cancer, pregnancy, oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy, or smoking.
Clinical Manifestations and Assessment
- The signs and symptoms of DVT depend on the location and size of the clot. Some patients may have no symptoms at all.
- The common signs and symptoms include:
- Limb pain: a feeling of fullness or heaviness in the affected leg after standing or walking. The pain may be worse when flexing the foot or extending the knee.
- Limb swelling: a sudden onset of edema in the affected leg that may extend to the thigh or groin. The leg may appear larger than the other leg.
- Limb warmth: an increased temperature in the affected leg compared to the other leg.
- Limb redness: a change in skin color in the affected leg that may be bluish or purple.
- Limb induration: a hardening or thickening of the skin or subcutaneous tissue over the affected vein.
- Shortness of breath and chest pain: these are signs of PE and require immediate medical attention.
- The assessment of a patient with suspected DVT includes:
- A detailed medical history to identify the risk factors and symptoms of DVT.
- A physical examination is to inspect and palpate the affected leg for signs of DVT. The examiner should also check for signs of PE, such as tachypnea, tachycardia, hypoxia, or hemoptysis.
- A comparison of the circumference of both legs at different levels to detect any difference in size.
- A measurement of the calf muscle squeeze test (Homan's sign) to elicit pain in the calf when squeezing it. However, this test is not reliable and may be positive in other conditions or negative in some cases of DVT.
Diagnostic Tests and Imaging
- The diagnosis of DVT is confirmed by laboratory tests and imaging studies. The common tests include:
- Ddimer: a blood test that measures fibrin degradation products that are released when a clot is formed. A positive test indicates that a clot is likely present somewhere in the body. However, this test is not specific for DVT and may be elevated in other conditions such as infection, inflammation, or cancer.
- Venous duplex scan: an ultrasound test that uses high-frequency sound waves to provide a real-time picture of blood flow through the veins. This test can detect clots in the deep veins by showing reduced or absent flow. It can also measure the diameter and compressibility of the veins.
- Doppler flow study: an ultrasound test that uses sound waves to measure the speed and direction of blood flow through the veins. This test can detect clots by showing changes in flow patterns or sounds. It can also assess for valve function and reflux in the veins.
- Impedance plethysmography: a noninvasive test that uses electrodes attached to the leg to measure changes in electrical resistance caused by variations in blood volume in the veins. This test can detect clots by showing abnormal venous flow in the affected leg.
- Venogram: an invasive test that uses contrast material injected into a vein to visualize the veins on an X-ray. This test can detect clots by showing filling defects or obstructions in the veins. It can also assess for collateral circulation and valve function. This test is usually reserved for cases where other tests are inconclusive or contraindicated.
Management and Treatment
- The main goals of treatment for DVT are to prevent the clot from growing or breaking off, to dissolve the clot, to prevent the recurrence of clots, and to prevent complications such as PE or CVI.
- The treatment options for DVT include:
- Anticoagulation therapy: the use of medications that inhibit the formation or extension of clots or enhance the natural clot dissolution process. The common anticoagulants used for DVT are:
- Unfractionated heparin (UFH): a parenteral anticoagulant that binds to antithrombin III and inhibits several clotting factors. It is given intravenously or subcutaneously and requires frequent monitoring of activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) to adjust the dose. It also requires monitoring of platelet count to detect heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), a serious complication that causes low platelets and increased clotting. The antidote for UFH is protamine sulfate, which can reverse its effects in case of bleeding.
- Lowmolecular-weight heparin (LMWH): a parenteral anticoagulant that binds to antithrombin III and inhibits factor Xa. It is given subcutaneously and does not require frequent monitoring of aPTT. It has a lower risk of HIT than UFH. The antidote for LMWH is also protamine sulfate, but it is less effective than for UFH.
- Warfarin: an oral anticoagulant that inhibits the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. It takes 3 to 4 days to achieve its therapeutic effect, so it is usually started while the patient is still on heparin. It requires frequent monitoring of prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) to adjust the dose. It has many drug and food interactions, especially with vitamin K-rich foods, that can affect its efficacy. The antidote for warfarin is vitamin K, which can reverse its effects in case of bleeding.
- Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs): a newer class of oral anticoagulants that directly inhibit factor Xa or thrombin. They include rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban, and dabigatran. They have a rapid onset and offset of action, do not require frequent monitoring of coagulation tests, and have fewer drug and food interactions than warfarin. However, they are expensive, have limited antidotes available, and may not be suitable for patients with renal impairment or high bleeding risk.
- Thrombolytic therapy: the use of medications that dissolve existing clots by activating plasminogen to plasmin, which breaks down fibrin. The common thrombolytics used for DVT are streptokinase, urokinase, and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). They are given intravenously or through a catheter-directed into the clot. They are reserved for patients with severe or life-threatening DVT or PE who have no contraindications such as active bleeding, recent surgery, or stroke. They have a high risk of bleeding complications and require close monitoring of vital signs and coagulation tests.
- Mechanical methods: the use of devices or procedures that physically remove or prevent clots from forming or traveling to the lungs. They include:
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter: a metal device that is inserted into the IVC through a catheter and acts as a trap for clots that may break off from the legs and travel to the lungs. It is used for patients who have contraindications or complications from anticoagulation therapy or recurrent DVT despite adequate anticoagulation therapy. It does not prevent new clots from forming and may cause complications such as filter migration, fracture, infection, or perforation.
- Thrombectomy: a surgical procedure that involves removing the clot from the vein through an incision or a catheter. It is used for patients who have large or extensive clots that cause severe symptoms or compromise blood flow to the limb. It may be combined with thrombolytic therapy to enhance clot dissolution.
- Compression devices: devices that apply intermittent or continuous pressure to the legs to enhance venous return and prevent stasis. They include pneumatic compression devices, compression stockings, or compression bandages. They are used for patients who are at high risk of developing DVT due to immobility, or surgery.
Preventive Measures and Patient Education
- Encourage early ambulation and frequent leg movement for immobilized patients
- Utilize compression stockings or intermittent pneumatic compression devices to promote blood flow
- Educate patients on the importance of staying hydrated and avoiding dehydration
- Implement pharmacological prophylaxis, such as anticoagulant medications, for high-risk patients
- Teach patients about signs and symptoms of DVT and when to seek immediate medical attention
- Promote a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet to reduce risk factors
- Advise travelers to perform leg exercises during long flights or journeys
- Educate patients on the need for compliance with prescribed medications and follow-up appointments
- Encourage smoking cessation to minimize the risk of blood clot formation
Summary
- DVT is a medical condition where a blood clot (thrombus) forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs, but it can occur in other parts of the body as well.
- Several factors increase the risk of developing DVT, including prolonged immobility, surgery, trauma, obesity, pregnancy, hormonal contraception, smoking, and a history of previous DVT or family history of blood clotting disorders.
- DVT usually occurs due to Virchow's triad, which involves venous stasis (slow blood flow), endothelial injury (damage to the blood vessel lining), and hypercoagulability (increased blood clotting potential).
- Clinical Presentation: Common symptoms of DVT include swelling, pain, warmth, and redness in the affected limb. However, some cases may be asymptomatic or present with atypical symptoms, making diagnosis challenging.
- DVT is diagnosed through a combination of clinical assessment, patient history, and diagnostic tests such as compression ultrasound, D-dimer blood test, and venography.
- If left untreated, DVT can lead to serious complications, such as pulmonary embolism (a blood clot traveling to the lungs) and postthrombotic syndrome (chronic leg pain and swelling).
- The mainstay of DVT treatment is anticoagulation therapy, which helps prevent clot extension and reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism. Thrombolytic therapy may be considered in severe cases.
- Early ambulation, leg exercises, compression stockings, and prophylactic measures are crucial in preventing DVT, especially in high-risk patients.
- In some cases, DVT may be associated with genetic or acquired conditions that increase the risk of abnormal blood clotting, known as thrombophilia.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about DVT risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures is essential for early detection and better outcomes.
- Ongoing research is exploring new diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive strategies to improve DVT management and patient outcomes.
Conclusion
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a significant medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in deep veins, mainly in the legs.
- Various risk factors contribute to DVT development, including immobility, surgery, pregnancy, and family history of clotting disorders.
- Understanding the pathophysiology of DVT is crucial in recognizing the importance of venous stasis, endothelial injury, and hypercoagulability in its formation.
- Prompt and accurate diagnosis of DVT is essential through clinical assessment and appropriate diagnostic tests like ultrasound and D-dimer testing.
- DVT can lead to severe complications, such as pulmonary embolism and postthrombotic syndrome, emphasizing the significance of timely treatment.
- Anticoagulation therapy remains the mainstay of DVT treatment, along with nonpharmacological preventive measures to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Special populations require tailored DVT management, considering the unique risk factors and physiological changes they may experience.
- Educating patients about DVT, its symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures is vital in early detection and prevention.
- Ongoing research aims to advance diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive strategies for enhanced DVT management and patient outcomes.
Peripheral vascular disease
Introduction
- Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a blood circulation disorder that causes the blood vessels outside of the heart and brain to narrow, block, or spasm.
- This can affect any blood vessel, including the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels, but it most commonly affects the legs and feet. PVD can cause pain, fatigue, skin changes, wounds that do not heal, and gangrene. PVD can also increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and limb loss.
- There are two main types of PVD: functional and organic.
- Functional PVD means there is no physical damage to the blood vessels, but they react abnormally to factors such as stress, temperature, or vibration. Organic PVD means there is structural damage to the blood vessels, such as inflammation, plaque buildup, or tissue damage.
- The most common cause of organic PVD is atherosclerosis, which is the hardening and narrowing of the arteries due to plaque accumulation. Plaque is made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances that stick to the inner walls of the arteries. Plaque reduces the blood flow and oxygen supply to the organs and limbs. Plaque can also rupture and form clots that block the arteries completely.
Etiology and Contributing Factors
The exact cause of PVD is not known, but there are several factors that increase the risk of developing it. Some of these factors are modifiable, meaning they can be changed or controlled by lifestyle changes or medication. Some of these factors are nonmodifiable, meaning they cannot be changed.
The modifiable risk factors for PVD include:
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
The nonmodifiable risk factors for PVD include:
- Age (older than 50 years)
- Gender (male)
- Family history of PVD or heart disease
- Postmenopausal women
Clinical Features and Symptoms
The symptoms of PVD depend on the location and severity of the blood vessel narrowing or blockage. Some people with PVD may not have any symptoms at all. Others may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Painful leg cramping that occurs with exercise and is relieved by rest (intermittent claudication)
- Numbness, weakness, or heaviness in the muscles
- Burning or aching pain at rest, especially in the toes and at night while lying flat
- Changes in the skin color or temperature of the legs or feet (pale, bluish, or reddish)
- Hair loss on the legs
- Thickened, brittle, or opaque toenails
- Wounds that do not heal over pressure points such as heels or ankles
- Gangrene (dead tissue due to lack of blood flow)
- Impotence (erectile dysfunction)
Diagnostic Evaluation
The diagnosis of PVD is based on the medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The medical history includes questions about the symptoms, risk factors, medications, and family history of PVD or heart disease. The physical examination includes checking the pulses, skin color and temperature, hair growth, toenails, wounds, and sensation in the legs and feet.
The diagnostic tests for PVD include:
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI): This test compares the blood pressure in the ankles with the blood pressure in the arms. A low ABI indicates reduced blood flow in the legs.
- Doppler ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to create images of the blood flow in the arteries and veins. It can detect narrowing, blockage, or clots in the blood vessels.
- Angiography: This test uses a contrast dye injected into an artery to show the blood flow in an X-ray image. It can identify the location and extent of narrowing or blockage in the arteries.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA): This test uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create images of the blood vessels. It can provide more detailed information than angiography.
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA): This test uses X-rays and a computer to create images of the blood vessels. It can also provide more detailed information than angiography.
Management and Treatment Strategies
- The treatment of PVD aims to improve the blood flow in the affected vessels, relieve the symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. The treatment options depend on the type, location, and severity of PVD, as well as the overall health and preferences of the patient.
The treatment options for PVD include:
- Medications: These include antiplatelet drugs (such as aspirin or clopidogrel) to prevent blood clots, statins (such as atorvastatin or simvastatin) to lower cholesterol, antihypertensives (such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers) to lower blood pressure, and vasodilators (such as cilostazol or pentoxifylline) to improve blood flow and reduce leg pain.
- Angioplasty: This is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a thin tube (catheter) with a balloon at its tip to widen a narrowed or blocked artery. The balloon is inflated to compress the plaque against the artery wall and restore blood flow. Sometimes, a small metal mesh tube (stent) is inserted to keep the artery open.
- Bypass surgery: This is a surgical procedure that uses a graft (a piece of vein or synthetic material) to create a detour around a blocked artery and restore blood flow. The graft is attached above and below the blockage, bypassing it.
- Endarterectomy: This is a surgical procedure that removes the plaque from the inner lining of an artery and restores blood flow. It is usually done for blockages in the carotid arteries (the arteries that supply blood to the brain).
- Amputation: This is a surgical procedure that removes part or all of a limb that has been severely damaged by PVD. It is usually done as a last resort when other treatments have failed or are not possible.
Lifestyle Modifications and Self-Care
Lifestyle modifications and self-care are important aspects of managing PVD. They can help improve the symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. They include:
- Quitting smoking or tobacco use
- Controlling diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol
- Losing weight if overweight or obese
- Eating a healthy diet that is low in saturated fat, salt, and sugar, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein
- Exercising regularly, preferably under the guidance of a healthcare provider or physical therapist
- Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing
- Elevating the legs when resting
- Wearing comfortable shoes that fit well and do not cause pressure points
- Wearing compression stockings or socks to improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the legs
- Keeping the skin clean and moisturized to prevent dryness, cracking, and infection
- Inspecting the legs and feet daily for any signs of injury, infection, or gangrene
- Seeking medical attention promptly for any wounds that do not heal or show signs of infection (such as redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or fever)
Nursing Interventions and Patient Support
Nursing interventions and patient support are essential for providing holistic care for patients with PVD. They include:
- Assessing the patient's medical history, risk factors, symptoms, physical examination findings, and diagnostic test results
- Educating the patient about PVD, its causes, complications, treatment options, and prevention strategies
- Encouraging the patient to adhere to the prescribed medications, lifestyle modifications, and self-care measures
- Monitoring the patient's vital signs, blood glucose levels, cholesterol levels, wound healing status, and signs of infection or gangrene
- Administering medications as ordered by the healthcare provider
- Assisting with angioplasty, bypass surgery, endarterectomy, or amputation as needed
- Providing wound care and dressing changes as needed
- Providing pain management as needed
- Providing emotional support and counseling as needed
- Referring the patient to other healthcare professionals or support groups as needed
Summary
- Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a term that refers to disorders of the blood vessels outside the heart and brain, such as the arteries and veins.
- There are two main types of PVD: peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and peripheral venous disease (PVD).
- PAD affects the arteries that carry blood away from the heart to the limbs and organs. It is usually caused by atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arterial walls, narrowing the lumen and reducing blood flow.
- PAD can cause symptoms such as pain, cramping, numbness, or tingling in the legs or feet, especially during exercise or at night. It can also lead to complications such as ulcers, gangrene, infection, or amputation of the affected limb.
- PAD is diagnosed by various tests that measure the blood pressure, pulse, and blood flow in the arteries, such as Doppler ultrasound, anklebrachial index (ABI), segmental systolic blood pressure measurements, plethysmography, and arteriography.
- PAD is treated by lifestyle changes, medications, and interventions that aim to improve blood flow and prevent further damage to the arteries. Lifestyle changes include quitting smoking, managing diabetes and cholesterol levels, exercising regularly, and avoiding cold temperatures and tight clothing. Medications include antiplatelets, anticoagulants, vasodilators, and statins. Interventions include angioplasty, stenting, atherectomy, bypass surgery, and endarterectomy.
- PVD affects the veins that carry blood back to the heart from the limbs and organs. It is usually caused by venous insufficiency, which is the inability of the veins to return blood to the heart efficiently due to damaged valves or walls.
- PVD can cause symptoms such as swelling, heaviness, aching, or cramping in the legs or feet, especially after standing or sitting for long periods. It can also lead to complications such as varicose veins, skin changes, ulcers, infection, or thrombosis.
- PVD is diagnosed by various tests that measure the blood pressure, pulse, and blood flow in the veins, such as Doppler ultrasound, venous duplex scan, venography, and impedance plethysmography.
- PVD is treated by lifestyle changes, medications, and interventions that aim to improve blood flow and prevent further damage to the veins. Lifestyle changes include elevating the legs above the heart level, wearing compression stockings or bandages, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged standing or sitting. Medications include diuretics, anti-inflammatories, antibiotics, and anticoagulants. Interventions include sclerotherapy, laser therapy, radiofrequency ablation, vein stripping, or ligation.
Conclusion
- Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
- It can have serious consequences for the quality of life and health of the affected individuals.
- Therefore, it is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of PVD and seek medical attention promptly.
- PVD can be managed effectively by a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and interventions that aim to restore blood flow and prevent further complications.
- However, prevention is always better than cure. Therefore, it is advisable to adopt healthy habits that reduce the risk factors for PVD such as smoking cessation,
Congestive Cardiac Failure
Introduction
- Congestive cardiac failure (CCF) is a clinical syndrome characterized by signs and symptoms of fluid overload or inadequate tissue perfusion due to impaired cardiac function.
- CCF can be classified into two types: left-sided heart failure (LHF) and right-sided heart failure (RHF).
- LHF occurs when the left ventricle cannot effectively pump blood out of the ventricle into the aorta and the systemic circulation, leading to pulmonary congestion and impaired gas exchange.
- RHF occurs when the right ventricle cannot effectively pump blood into the pulmonary artery and accommodate the venous return, leading to peripheral and visceral congestion and edema.
- CCF can also be classified according to the ejection fraction (EF), which is the percentage of blood ejected from the ventricle during systole.
- Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) occurs when the EF is less than 40%, indicating systolic dysfunction or impaired contraction of the ventricle.
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) occurs when the EF is greater than or equal to 50%, indicating diastolic dysfunction or impaired relaxation of the ventricle.
- Heart failure with midrange ejection fraction (HFmrEF) occurs when the EF is between 40% and 49%, indicating a combination of systolic and diastolic dysfunction.
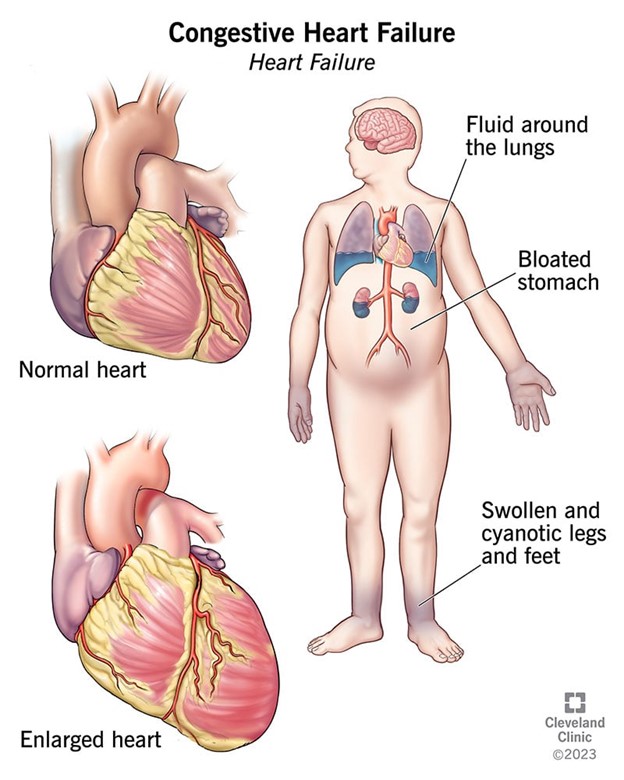
Etiology and Precipitating Factors
- The etiology of CCF is any condition that affects the structure or function of the heart, such as :
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Hypertension
- Valvular heart disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Congenital heart defects
- Arrhythmias
- Pulmonary embolism
- The precipitating factors of CCF are any conditions that increase the workload or oxygen demand of the heart, such as :
- Anemia
- Infection
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Pregnancy
- Fluid overload
- Renal failure
- Noncompliance with medications or dietary restrictions
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
- The clinical presentation and symptoms of CCF vary depending on the type, severity, and chronicity of heart failure. Some common manifestations are :
- Dyspnea on exertion or at rest
- Orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
- Cough with frothy or pink-tinged sputum
- Fatigue, weakness, or malaise
- Tachycardia, palpitations, or irregular pulse
- Edema of the lower extremities, sacrum, or abdomen
- Weight gain or loss
- Jugular venous distension (JVD)
- Hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
- Ascites or pleural effusion
- Crackles or wheezes in the lungs
- S3 or S4 gallop sounds in the heart
- Cheyne-Stokes respiration or central sleep apnea
Diagnostic Assessment
- The diagnostic assessment of CCF involves various tests and criteria to confirm the diagnosis, determine the etiology, evaluate the severity, and guide the treatment. Some common tests and criteria are:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to detect arrhythmias, ischemia, infarction, hypertrophy, or conduction abnormalities.
- Chest x-ray to assess cardiac size, shape, position, and pulmonary congestion.
- Echocardiogram to measure EF, cardiac output, stroke volume, and structural abnormalities.
- Cardiac catheterization to evaluate coronary artery patency, pressure gradients, and oxygen saturation.
- Laboratory tests to measure biomarkers, electrolytes, renal function, liver function, thyroid function, and blood count.
- The New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification to assess the impact of heart failure on the patient's daily activities and quality of life.
- The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) staging system to assess the progression of heart failure and the need for interventions.
Treatment and Management
- The treatment and management of CCF aim to improve cardiac function, reduce symptoms, prevent complications, and prolong survival. Some common strategies are :
- Lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation, weight management, sodium and fluid restriction, regular exercise, and stress reduction.
- Pharmacologic therapy such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), diuretics, digoxin, nitrates, hydralazine, ivabradine, and sacubitril/valsartan.
- Nonpharmacologic therapy such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), ventricular assist device (VAD), intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP), extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), or heart transplantation.
- Palliative care or hospice care for patients with end-stage or refractory heart failure who have a poor prognosis or quality of life.

Medications and Therapies
- The medications and therapies used for CCF are based on the type, etiology, and severity of heart failure. Some common medications and therapies are :
- ACE inhibitors or ARBs reduce afterload, preload, and neurohormonal activation, and prevent ventricular remodeling. Examples are captopril, enalapril, lisinopril, losartan, valsartan, and candesartan.
- ARNIs enhance the effects of ACE inhibitors or ARBs by inhibiting neprilysin, an enzyme that degrades natriuretic peptides. An example is sacubitril/valsartan.
- Beta-blockers to reduce heart rate, blood pressure, and myocardial oxygen demand, and to prevent ventricular remodeling. Examples are metoprolol, carvedilol, and bisoprolol.
- MRAs to reduce fluid retention, blood pressure, and neurohormonal activation, and to prevent ventricular remodeling. Examples are spironolactone and eplerenone.
- Diuretics to reduce fluid overload, edema, and pulmonary congestion. Examples are furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide, hydrochlorothiazide, and metolazone.
- Digoxin increases the contractility and stroke volume of the heart and decreases the heart rate and conduction velocity. It also has a positive inotropic effect and a negative chronotropic effect.
- Nitrates dilate the veins and arteries, reducing preload and afterload. Examples are nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate, and isosorbide mononitrate.
- Hydralazine dilates the arteries, reducing afterload. It is often combined with nitrates for patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors or ARBs.
- Ivabradine lowers the heart rate by inhibiting the sinoatrial node pacemaker. It is used for patients with HFrEF who have a resting heart rate greater than 70 beats per minute despite optimal medical therapy.
- Sacubitril/valsartan lowers blood pressure by inhibiting neprilysin and blocking angiotensin II receptors. It is used for patients with HFrEF who have NYHA class IIIV symptoms despite optimal medical therapy.
- CRT to synchronize the contraction of the right and left ventricles using a biventricular pacemaker. It is used for patients with HFrEF who have a QRS duration greater than 120 milliseconds and NYHA class IIIV symptoms despite optimal medical therapy.
- ICD to monitor the heart rhythm and deliver electrical shocks if needed to correct life-threatening arrhythmias. It is used for patients with HFrEF who have an EF of less than or equal to 35% and are at high risk of sudden cardiac death.
- VAD assists the pumping function of the ventricle using a mechanical device that is implanted in the chest or abdomen. It is used for patients with end-stage or refractory heart failure who are awaiting heart transplantation or as a destination therapy.
- IABP to increase the coronary perfusion pressure and decrease the afterload using a balloon catheter.
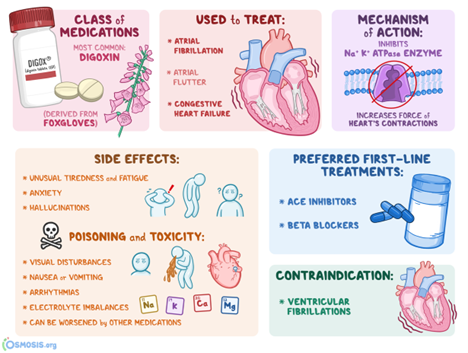
Nursing Considerations and Patient Education
- Assess the patient's vital signs, oxygen saturation, weight, fluid intake and output, and peripheral edema.
- Monitor the patient's cardiac rhythm, blood pressure, and urine output for signs of worsening CCF or fluid overload.
- Administer medications as prescribed, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), beta-blockers, diuretics, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2Is).
- Educate the patient about the importance of medication adherence, dietary sodium restriction, fluid management, daily weight monitoring, and regular follow-up visits.
- Teach the patient to recognize and report signs of worsening CCF, such as increased dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, cough, weight gain, or swelling.
- Encourage the patient to engage in physical activity as tolerated and prescribed by the health care provider.
- Provide emotional support and counseling to the patient and family members.
Summary
- CCF stands for Congestive Cardiac Failure, also known as Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body.
- CCF can be caused by various underlying conditions such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, heart valve disorders, and cardiomyopathy.
- Symptoms of CCF include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling (edema) in the legs, ankles, and feet, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and persistent coughing or wheezing.
- The diagnosis of CCF involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, chest X-rays, echocardiography, and other imaging tests to assess the heart's function.
- Treatment for CCF includes lifestyle modifications, medication management, diuretics to reduce fluid retention, and in severe cases, surgical interventions like heart valve repair or heart transplantation.
- It is crucial for patients with CCF to adhere to their treatment plan, follow up with healthcare providers regularly, and make necessary lifestyle changes to manage the condition effectively.
- CCF is a chronic condition that requires ongoing care and monitoring to prevent complications and improve the patient's quality of life.
- Education and support for patients and their caregivers play a vital role in managing CCF and promoting a better understanding of the condition's management and prognosis.
- Ongoing research aims to discover new treatments and interventions to enhance the outcomes for individuals living with CCF.
Conclusion
- Congestive Cardiac Failure (CCF) is a serious medical condition characterized by the heart's inability to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body.
- It is commonly caused by underlying heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, or valvular heart disease.
- The hallmark symptoms of CCF include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling of the legs and ankles, and difficulty lying flat.
- Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging tests like echocardiography, and blood tests.
- Treatment strategies focus on managing the underlying cause, controlling symptoms, and improving heart function.
- Medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and vasodilators are often prescribed to alleviate symptoms and improve cardiac function.
- Lifestyle modifications, including a low-sodium diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking, play a vital role in managing CCF.
- In severe cases, advanced interventions like cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), implantable defibrillators (ICD), or heart transplantation may be considered.
- Regular follow-up and adherence to the treatment plan are essential to optimize outcomes and improve the patient's quality of life.
- CCF requires a multidisciplinary approach involving cardiologists, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care.
- Public awareness about heart health and early intervention for risk factors can contribute to reducing the burden of CCF in the population.
Myocardial Infarction (MI) and Angina Pectoris
Introduction
- MI is a condition in which an area of the myocardium is permanently destroyed due to plaque rupture and subsequent thrombus formation that results in complete occlusion of a coronary artery
- Angina pectoris is a condition in which there is reduced blood flow in a coronary artery, often due to rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, but the artery is not completely occluded
- There are three types of angina: stable, unstable, and variant
- Stable angina occurs with exercise or emotional stress and is relieved by rest or nitroglycerin
- Unstable angina occurs with exercise or emotional stress, but it increases in occurrence, severity, and duration over time
- Variant angina is due to a coronary artery spasm, often occurring during periods of rest
- MI and angina pectoris are both manifestations of acute coronary syndrome (ACS), which is a spectrum of ischemic heart disease that can result in myocardial death
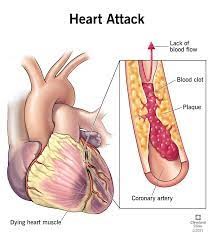
Pathophysiology and Risk Factors
- The pathophysiology of MI and angina pectoris involves an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand
- The supply of oxygen is determined by the coronary blood flow, which can be impaired by atherosclerosis, thrombosis, vasospasm, or hypotension
- The demand for oxygen is determined by the cardiac workload, which can be increased by tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, or cocaine use
- The risk factors for MI and angina pectoris are similar to those for coronary artery disease (CAD), which include :
- Male gender or postmenopausal women
- Hypertension
- Tobacco use
- Hyperlipidemia
- Metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism)
- Methamphetamine or cocaine use
- Stress (occupational, physical exercise, sexual activity)
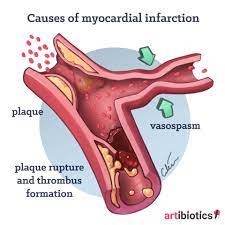
Clinical Manifestations and Assessment
- The clinical manifestations and assessment of MI and angina pectoris depend on the severity, location, and duration of ischemia
- The cardinal symptom of both conditions is chest pain, which is usually described as heavy, squeezing, or crushing and may radiate to the left arm, jaw, neck, or shoulder blades
- The pain of MI is more severe, persistent (lasting more than 15 minutes), and unrelieved by rest or nitroglycerin
- The pain of angina is less severe, intermittent (lasting less than 15 minutes), and relieved by rest or nitroglycerin
- Other symptoms that may accompany chest pain include:
- Shortness of breath
- Indigestion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diaphoresis
- Pallor
- Cool, clammy skin
- Tachycardia and/or palpitations
- Decreased level of consciousness
- Anxiety or fear of death
Diagnostic Tests and Imaging
- The diagnostic tests and imaging for MI and angina pectoris aim to confirm the presence of ischemia or infarction, identify the location and extent of myocardial damage, evaluate the cardiac function and hemodynamics, and rule out other causes of chest pain
- The main tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): recording of electrical activity of the heart over time that can show changes indicative of ischemia (ST depression or T wave inversion), injury (ST elevation), or necrosis (abnormal Q wave)
- Cardiac biomarkers: enzymes released with myocardial injury that can indicate the onset, duration, and severity of infarction; the most specific ones are troponin I or T, creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), and myoglobin
- Chest x-ray: imaging of the chest that can show cardiomegaly (enlarged heart), pulmonary congestion, or other causes of chest pain such as pneumonia or pneumothorax
- Echocardiogram: ultrasound of the heart that can show the structure and function of the heart, including the ejection fraction, wall motion, and valvular abnormalities
- Coronary angiography: invasive procedure that involves injecting contrast dye into the coronary arteries and taking x-rays to visualize the degree and location of stenosis or occlusion
- Thallium scan: nuclear imaging that involves injecting radioisotopes into the bloodstream and taking images of the heart to assess for ischemia or necrosis; areas with decreased or absent perfusion appear as "cold spots"
Emergency Management and Interventions
- The emergency management and interventions for MI and angina pectoris aim to restore blood flow to the ischemic myocardium, reduce myocardial oxygen demand, prevent complications, and provide comfort and support
- The main interventions include :
- Oxygen therapy: to increase oxygen supply to the myocardium and reduce ischemia
- Nitroglycerin: to dilate coronary arteries and improve blood flow to the myocardium; also reduces preload and afterload and decreases myocardial oxygen demand
- Aspirin: to inhibit platelet aggregation and prevent thrombus formation; also has anti-inflammatory effects that may limit plaque rupture
- Morphine: to relieve pain and anxiety; also reduces preload and afterload and decreases myocardial oxygen demand
- Beta-blockers: to reduce heart rate, blood pressure, and contractility and decrease myocardial oxygen demand; also have antiarrhythmic effects that may prevent ventricular fibrillation
- Anticoagulants: to prevent further thrombus formation and reduce the risk of embolization; examples include heparin, enoxaparin, or bivalirudin
- Antiplatelets: to inhibit platelet activation and aggregation and prevent thrombus formation; examples include clopidogrel, ticagrelor, or prasugrel
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: to reduce blood pressure and afterload and decrease myocardial oxygen demand; also prevent ventricular remodeling and improve survival after MI
- Statins: to lower cholesterol levels and stabilize atherosclerotic plaques; also have anti-inflammatory effects that may limit plaque rupture
Pharmacological and Revascularization Therapies
- The main goals of pharmacological therapy for MI and angina are to restore blood flow to the ischemic myocardium, reduce myocardial oxygen demand, relieve pain and discomfort, prevent complications, and improve survival and quality of life.
- The main classes of drugs used for these purposes are:
- Antiplatelet agents: These drugs inhibit platelet aggregation and prevent thrombus formation. Examples are aspirin, clopidogrel, ticagrelor, and prasugrel.
- Anticoagulants: These drugs prevent the extension or formation of clots by interfering with the coagulation cascade. Examples are heparin, enoxaparin, bivalirudin, and warfarin.
- Thrombolytics: These drugs dissolve existing clots by activating plasminogen, which breaks down fibrin. Examples are alteplase, reteplase, tenecteplase, and streptokinase.
- Nitrates: These drugs dilate coronary arteries and peripheral veins, reducing preload and afterload on the heart. This lowers myocardial oxygen demand and improves blood flow to the ischemic areas. Examples are nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate, and isosorbide mononitrate.
- Beta-blockers: These drugs block the effects of catecholamines on the heart, reducing heart rate, contractility, and blood pressure. This lowers myocardial oxygen demand and reduces the risk of arrhythmias. Examples are metoprolol, atenolol, propranolol, and carvedilol.
- Calcium channel blockers: These drugs block the influx of calcium into cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells, causing vasodilation and reduced contractility. This lowers myocardial oxygen demand and improves blood flow to the ischemic areas. Examples are verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine, and amlodipine.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: These drugs block the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor and stimulator of aldosterone secretion. This lowers blood pressure, reduces preload and afterload on the heart, and prevents ventricular remodeling. Examples are lisinopril, enalapril, captopril, and ramipril.
- Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs): These drugs block the binding of angiotensin II to its receptors, producing similar effects as ACE inhibitors. Examples are losartan, valsartan, candesartan, and irbesartan.
- Statins: These drugs inhibit the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in cholesterol synthesis in the liver. This lowers serum cholesterol levels, especially low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and prevents plaque formation in the arteries. Examples are atorvastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin, and pravastatin.
- Revascularization therapies are invasive procedures that aim to restore blood flow to the ischemic myocardium by bypassing or opening the occluded coronary arteries.
- The main types of revascularization therapies are:
- Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery: This is a surgical procedure that involves grafting a healthy vessel (usually from the leg or chest) to bypass the blocked coronary artery.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): This is a catheter-based procedure that involves inserting a balloon-tipped catheter into the occluded coronary artery and inflating it to compress the plaque against the arterial wall. A stent (a metal mesh tube) may be deployed to keep the artery open.
- Transmyocardial laser revascularization (TMR): This is a surgical procedure that involves creating channels in the myocardium with a laser to improve blood flow to the ischemic areas.
Rehabilitation and Lifestyle Changes after MI
- Rehabilitation after MI is a multidisciplinary process that involves physical, psychological, and social aspects of care. The main goals of rehabilitation are to restore functional capacity, prevent complications, reduce the risk of recurrent events, and improve quality of life.
- The main components of rehabilitation are:
- Cardiac rehabilitation program: This is a structured program that involves exercise training, education, counseling, and behavioral interventions to help patients recover from MI and adopt a healthy lifestyle. The program is usually divided into four phases: phase I (inpatient), phase II (early outpatient), phase III (late outpatient), and phase IV (maintenance).
- Risk factor modification: This involves identifying and managing the modifiable risk factors for MI and angina, such as smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, obesity, physical inactivity, and stress. Patients are advised to quit smoking, follow a low-fat, low-sodium, high-fiber diet, control blood pressure and blood glucose levels, lose weight if overweight or obese, exercise regularly, and manage stress effectively.
- Medication adherence: This involves taking the prescribed medications as directed by the health care provider, and monitoring for any adverse effects or interactions. Patients are educated about the purpose, dosage, frequency, route, and side effects of each medication and the importance of compliance.
- Psychosocial support: This involves providing emotional support and counseling to patients and their families to cope with the psychological impact of MI and angina, such as anxiety, depression, fear, anger, guilt, and low self-esteem. Patients are encouraged to express their feelings, seek professional help if needed, join support groups, and participate in leisure activities.
Summary
- Myocardial infarction (MI) is the permanent destruction of myocardial cells due to severe ischemia caused by complete occlusion of a coronary artery.
- Angina pectoris is the chest pain or discomfort that occurs when the myocardial oxygen demand exceeds the supply due to partial or transient occlusion of a coronary artery.
- There are three types of angina: stable, unstable, and variant.
- Stable angina is triggered by exertion or stress and relieved by rest or nitroglycerin.
- Unstable angina is more frequent, severe, and prolonged than stable angina and may precede an MI.
- Variant angina is caused by coronary artery spasm and usually occurs at rest.
- The main goals of treatment for MI and angina are to restore blood flow, reduce oxygen demand, relieve pain, prevent complications, and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
- MI and angina are serious conditions that require prompt diagnosis and management to prevent further damage to the heart muscle and reduce mortality and morbidity.
- Nurses play a vital role in assessing, monitoring, educating, and caring for patients with MI and angina.
- Nurses should be familiar with the signs and symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic tests, pharmacologic interventions, and nursing interventions for MI and angina.
- Nurses should also promote health promotion and disease prevention strategies to reduce the incidence and recurrence of MI and angina.
Anemia
Introduction
- Anemia is a condition in which the hemoglobin concentration is lower than normal, reflecting the presence of fewer than the normal number of erythrocytes within the circulation
- Anemia is not a specific disease state but an underlying disorder and the most common hematologic condition
- Anemia can be classified according to whether the deficiency in erythrocytes is caused by a defect in their production, by their destruction, or by their loss
- Anemia can have various causes, such as blood loss, nutritional deficiencies, bone marrow disorders, chronic diseases, infections, genetic disorders, or medications
- Anemia can cause various clinical manifestations, such as fatigue, weakness, pallor, dyspnea, tachycardia, chest pain, dizziness, headache, or cognitive impairment
- Anemia can be diagnosed by laboratory tests, such as complete blood count (CBC), reticulocyte count, peripheral blood smear, serum iron, total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), serum ferritin, serum vitamin B12, serum folate, or bone marrow aspiration
- Anemia can be treated and managed by various approaches, such as blood transfusions, iron and vitamin supplementation, erythropoietin therapy, immunosuppressive therapy, or bone marrow transplantation
- Anemia requires nursing considerations and patient education to prevent complications, promote recovery, and improve quality of life.
Classification of Anemia
- Hypoproliferative anemias: In hypoproliferative anemias, the marrow cannot produce adequate numbers of erythrocytes. Examples include iron deficiency anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency anemia (pernicious anemia), folate deficiency anemia, aplastic anemia, or anemia of chronic disease
- Hemolytic anemias: In hemolytic anemias, there is premature destruction of erythrocytes that results in the liberation of hemoglobin from the erythrocytes into the plasma. Examples include sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, or drug-induced hemolytic anemia
- Bleeding anemias: In bleeding anemias, there is loss of erythrocytes due to hemorrhage. Examples include trauma-induced bleeding, gastrointestinal bleeding (ulcerative colitis), menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia), or surgery-related bleeding
Etiology and Causes
- Iron deficiency anemia: Iron deficiency anemia is caused by inadequate intake or absorption of dietary iron, increased iron requirements (pregnancy), or chronic blood loss (menstruation)
- Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia: Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia is caused by inadequate intake or absorption of dietary vitamin B12 (vegan diet), lack of intrinsic factor (pernicious anemia), or malabsorption disorders (Crohn's disease)
- Folate deficiency anemia: Folate deficiency anemia is caused by inadequate intake or absorption of dietary folate (alcoholism), increased folate requirements (pregnancy), or medications that interfere with folate metabolism (methotrexate)
- Aplastic anemia: Aplastic anemia is caused by bone marrow failure due to exposure to toxins (radiation), infections (hepatitis), autoimmune disorders (lupus), or medications that suppress bone marrow function (chemotherapy)
- Anemia of chronic disease: Anemia of chronic disease is caused by inflammation or infection that inhibits erythropoiesis and iron utilization. Examples include rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, cancer, or HIV/AIDS
- Sickle cell anemia: Sickle cell anemia is caused by a genetic mutation that results in abnormal hemoglobin (HbS) that causes the erythrocytes to sickle and hemolyze under conditions of hypoxia, acidosis, or dehydration
- Thalassemia: Thalassemia is caused by a genetic mutation that results in reduced or absent synthesis of alpha or beta globin chains of hemoglobin, leading to microcytic and hypochromic erythrocytes that are prone to hemolysis
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia: Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is caused by the production of antibodies against one's own erythrocytes, leading to their destruction by the immune system. It can be idiopathic or secondary to other diseases, such as lupus, lymphoma, or leukemia
- Drug-induced hemolytic anemia: Drug-induced hemolytic anemia is caused by the reaction of certain drugs with erythrocytes, leading to their damage or lysis. Examples include penicillin, cephalosporins, sulfonamides, or quinine
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
- The clinical presentation and symptoms of anemia depend on the severity, duration, and type of anemia. However, some common manifestations include:
- Fatigue, weakness, and malaise
- Pallor of the skin, mucous membranes, and conjunctiva
- Dyspnea on exertion and at rest
- Tachycardia and palpitations
- Chest pain and angina
- Dizziness and orthostatic hypotension
- Headache and impaired concentration
- Cognitive impairment and mood changes
- Pica (craving for non-food substances)
- Glossitis (inflammation of the tongue)
- Cheilitis (inflammation of the lips)
- Jaundice and splenomegaly (in hemolytic anemias)
- Bone pain and joint swelling (in sickle cell anemia)
- Neurologic symptoms (in vitamin B12 deficiency anemia)
Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnostic evaluation of anemia involves various laboratory tests that measure the quantity and quality of erythrocytes and hemoglobin. Some common tests include :
- Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures the number and percentage of erythrocytes (red blood cell count), hemoglobin (Hgb), hematocrit (Hct), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), and red cell distribution width (RDW). It also measures the number and percentage of leukocytes (white blood cell count) and platelets (platelet count).
- A low RBC count, Hgb, and Hct indicate anemia.
- A low MCV indicates microcytic anemia (iron deficiency, thalassemia).
- A high MCV indicates macrocytic anemia (vitamin B12 deficiency, folate deficiency).
- A low MCH and MCHC indicate hypochromic anemia (iron deficiency).
- A high RDW indicates increased variation in RBC size (anisocytosis), which can be seen in iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, or folate deficiency.
- Reticulocyte count: This test measures the number and percentage of immature erythrocytes (reticulocytes) in the blood. It reflects the bone marrow's response to anemia.
- A high reticulocyte count indicates increased erythropoiesis due to hemolysis or bleeding.
- A low reticulocyte count indicates decreased erythropoiesis due to bone marrow suppression or nutritional deficiencies.
- Peripheral blood smear: This test examines the morphology of erythrocytes under a microscope. It can reveal various abnormalities in the shape, size, color, or inclusion bodies of erythrocytes.
- Poikilocytosis: Abnormal shape of erythrocytes. Examples include sickle cells (sickle cell anemia), spherocytes (autoimmune hemolytic anemia), schistocytes (microangiopathic hemolytic anemia), or elliptocytes (hereditary elliptocytosis).
- Anisocytosis: Abnormal size of erythrocytes. Examples include microcytes (iron deficiency, thalassemia), macrocytes (vitamin B12 deficiency, folate deficiency), or normocytes (anemia of chronic disease).
- Hypochromia: Abnormal color of erythrocytes due to reduced hemoglobin content. It is commonly seen in iron deficiency anemia.
- Serum iron studies: These tests measure the levels of serum iron, total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), and ferritin.
- Low serum iron and high TIBC are indicative of iron deficiency anemia.
- Low serum iron and low TIBC may indicate anemia of chronic disease.
- High serum iron and high TIBC may suggest hemochromatosis or iron overload conditions.
- Vitamin B12 and Folate levels: Measuring the levels of vitamin B12 and folate in the blood helps identify deficiencies that can lead to macrocytic anemia.
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis: This test is performed to identify abnormal hemoglobin variants, such as in sickle cell anemia or thalassemias.
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: In certain cases where the cause of anemia remains unclear, a bone marrow examination is performed to assess the production and maturation of blood cells in the bone marrow.
- Additional tests: Depending on the clinical presentation and suspected underlying cause of anemia, additional tests may be conducted, such as erythropoietin levels, Coombs test (to detect autoimmune hemolytic anemia), or hemoglobinopathies screening.
Treatment and Management Approaches
- Transfusion of packed red blood cells to increase hemoglobin level and improve oxygen delivery.
- Administration of erythropoietin or other hematopoietic growth factors to stimulate red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
- Correction of nutritional deficiencies, such as iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid, that impair red blood cell synthesis.
- Treatment of the primary disease or condition that causes anemia, such as ulcerative colitis, kidney disease, or cancer.
- Prevention or management of complications, such as infection, bleeding, or organ damage.
Iron and Vitamin Supplementation
- Iron supplements should be taken with food or juice to enhance absorption and reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
- Vitamin C can increase iron absorption, while calcium, antacids, and tetracycline can decrease it.
- Iron supplements can cause dark stools, which should not be confused with occult blood.
- Vitamin B12 supplements can be given orally, intramuscularly, or intranasally, depending on the patient's preference and ability to absorb the vitamin.
- Folic acid supplements should be taken with food to prevent nausea and abdominal cramps.
Nursing Considerations and Patient Education
- Assessing the patient's history, symptoms, vital signs, laboratory values, and potential complications of anemia.
- Monitoring the patient's hemoglobin level, oxygen saturation, blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and urine output during transfusion or administration of erythropoietin or other medications.
- Providing assistance with activities of daily living, ambulation, and exercise as tolerated by the patient.
- Encouraging adequate fluid intake and a balanced diet rich in iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid.
- Teaching the patient about the signs and symptoms of anemia, such as fatigue, pallor, dyspnea, chest pain, dizziness, or headache.
- Teaching the patient about the causes and treatment of anemia and the importance of compliance with medication regimen and follow-up appointments.
- Teaching the patient about the prevention of anemia by avoiding excessive blood loss, infections, exposure to toxins or drugs that can damage red blood cells, and dietary restrictions that can impair the absorption of iron or vitamins.
Summary
- Anemia is a medical condition characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells or a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood.
- It is one of the most common hematologic disorders worldwide, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds.
- Anemia can result from various underlying causes, including nutritional deficiencies (iron, vitamin B12, folate), chronic diseases, infections, genetic disorders, and blood loss.
- The clinical presentation of anemia includes fatigue, weakness, pallor, shortness of breath, dizziness, and increased heart rate.
- Diagnosis is made through a complete blood count (CBC), reticulocyte count, peripheral blood smear, serum iron studies, vitamin B12, and folate levels, and sometimes bone marrow examination.
- Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve iron or vitamin supplementation, blood transfusions, erythropoietin therapy, or addressing the primary disease.
- Nursing considerations play a vital role in assessing patients, monitoring treatment responses, providing supportive care, and educating patients about self-management and prevention.
- Anemia management is essential to improve a patient's quality of life, prevent complications, and enhance overall well-being.
Public awareness about anemia risk factors and early detection is crucial in reducing the global burden of this condition.
Conclusion
- Anemia is a prevalent medical condition characterized by low red blood cell count or hemoglobin levels, impacting individuals of all ages worldwide.
- It can stem from various factors, including nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, infections, genetics, and blood loss.
- Recognizing anemia's clinical signs, such as fatigue and pallor, aids in early detection and intervention.
- Accurate diagnosis through CBC and other tests facilitates appropriate treatment planning.
- Managing anemia involves addressing the underlying cause, administering iron or vitamin supplementation, or resorting to transfusions and erythropoietin therapy.
- Nurses play a vital role in patient care, including assessment, monitoring, and patient education.
- Effective anemia management enhances patients' well-being, prevents complications, and promotes a better quality of life.
- Public awareness and timely intervention are crucial in mitigating the global impact of anemia.
Complications of Intravenous therapy
Introduction
- Intravenous therapy is the administration of fluids, medications, blood products, or nutrients through a vein
- IV therapy is used for various purposes, such as hydration, nutrition, medication delivery, blood transfusion, or fluid replacement
- IV therapy has many advantages, such as rapid onset of action, precise dosage control, and bypassing of the gastrointestinal tract
- However, IV therapy also carries some risks and potential complications that can affect the patient's safety and comfort
- Nurses play a vital role in preventing, detecting, and managing IV complications
Indications
- Some common indications for IV therapy are:
- Dehydration or fluid imbalance
- Malnutrition or electrolyte imbalance
- Infection or sepsis
- Pain or inflammation
- Anemia or bleeding
- Shock or hypotension
Potential Complications of IV Therapy
- Some potential complications of IV therapy are:
- Infiltration and extravasation
- Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
- Infection and sepsis
- Allergic reactions and hypersensitivity
Infiltration and Extravasation
- Infiltration occurs when the IV fluid leaks into the surrounding tissue due to a dislodged or punctured catheter
- Extravasation occurs when a vesicant (a substance that causes tissue damage) infiltrates into the surrounding tissue
- Both infiltration and extravasation can cause pain, swelling, redness, blanching, coolness, or dampness at the IV site
- Extravasation can also cause tissue necrosis, ulceration, or blistering
- The treatment for infiltration and extravasation includes:
- Stopping the infusion and removing the catheter
- Applying cold or warm compresses depending on the type of fluid or medication
- Elevating the affected limb and assessing the circulation
- Aspirating the residual fluid if possible
- Administering antidotes or medications as ordered
- Documenting the incident and notifying the provider
Phlebitis and Thrombophlebitis
- Phlebitis is the inflammation of the vein wall due to mechanical, chemical, or bacterial irritation from the catheter or the IV fluid or medication
- Thrombophlebitis is the formation of a blood clot in the inflamed vein that can obstruct the blood flow and cause embolism
- Both phlebitis and thrombophlebitis can cause pain, warmth, redness, swelling, or a palpable cord along the vein
- The treatment for phlebitis and thrombophlebitis includes:
- Stopping the infusion and removing the catheter
- Applying warm compresses to the affected area
- Administering anti-inflammatory or anticoagulant medications as ordered
- Documenting the incident and notifying the provider
Infection and Sepsis
- Infection is the invasion of microorganisms into the bloodstream through a break in the skin barrier or a contaminated catheter or IV fluid or medication
- Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) caused by a severe infection that can lead to organ failure and death
- Both infection and sepsis can cause fever, chills, malaise, headache, nausea, vomiting, or increased heart rate or respiratory rate
- Sepsis can also cause hypotension, altered mental status, oliguria, or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- The treatment for infection and sepsis includes:
- Stopping the infusion and removing the catheter
- Obtaining blood cultures and other laboratory tests as ordered
- Administering antibiotics or other medications as ordered
- Monitoring vital signs and organ functions closely
- Documenting the incident and notifying the provider
Allergic Reactions and Hypersensitivity
- Allergic reactions are immune-mediated responses to foreign substances (allergens) that can cause mild to severe symptoms depending on the type and severity of the reaction
- Hypersensitivity is an exaggerated or inappropriate allergic reaction that can be classified into four types: type I (anaphylactic), type II (cytotoxic), type III (immune complex), or type IV (delayed)
- Both allergic reactions and hypersensitivity can cause itching, rash, hives, or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Anaphylactic reactions can also cause bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, hypotension, tachycardia, or cardiac arrest
- The treatment for allergic reactions and hypersensitivity includes:
- Stopping the infusion and removing the catheter
- Administering epinephrine, antihistamines, corticosteroids, or other medications as ordered
- Providing oxygen and airway support as needed
- Monitoring vital signs and symptoms closely
- Documenting the incident and notifying the provider
Preventive Measures and Nursing Management
- Some preventive measures and nursing management for IV complications are:
-
- Choosing the appropriate vein, catheter size, and insertion site for the IV therapy
- Using an aseptic technique and following the infection control policies when inserting, maintaining, or changing the IV catheter or tubing
- Securing the catheter and dressing properly and checking for patency and placement regularly
- Monitoring the infusion rate and adjusting the flow as needed
- Assessing the IV site and surrounding tissue for signs of complications at least every hour
- Educating the patient about the IV therapy and encouraging them to report any discomfort or changes at the IV site
- Documenting the IV therapy and any complications or interventions accurately and timely
Summary
- IV therapy, also known as intravenous therapy, involves the administration of fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into the bloodstream through a vein using a needle or catheter.
- It is commonly used in medical settings to provide rapid and efficient delivery of various substances to treat dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, infections, and other medical conditions.
- IV therapy allows for precise dosing and immediate effects as the substances bypass the digestive system and are quickly distributed throughout the body.
- The procedure is typically performed by trained healthcare professionals, such as nurses or doctors, in a sterile environment to minimize the risk of infection and complications.
- Different types of IV solutions are available, including crystalloids (electrolyte solutions), colloids (protein-based solutions), and blood products (red blood cells, plasma, platelets).
- IV therapy can be used for short-term treatments, such as during hospitalization, or for long-term management of chronic conditions in outpatient settings.
- Potential risks and side effects of IV therapy include vein irritation, infection, allergic reactions, and fluid overload, so careful monitoring and proper assessment are essential during the procedure.
Conclusion
- IV therapy is a crucial and commonly used medical intervention for administering fluids, medications, and nutrients directly into the bloodstream.
- It offers rapid and efficient delivery, allowing for precise dosing and immediate effects in treating various medical conditions.
- IV therapy is performed by trained healthcare professionals in a sterile environment to minimize risks and complications.
- Different types of IV solutions are available to meet specific patient needs, including crystalloids, colloids, and blood products.
- While IV therapy provides significant benefits, careful monitoring and proper assessment are essential to manage potential risks and side effects effectively.
- Overall, IV therapy plays a vital role in improving patient outcomes and supporting their health and recovery.
Naxlex
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Blood and Cardiovascular Disorders
This filled cannot be empty
Join Naxlex Nursing for nursing questions & guides! Sign Up Now


