Blood oxygen levels are most likely low when blood _____.
leaves the aorta
fills the right atrium
reaches body tissues
flows through arteries
Correct Answer : B
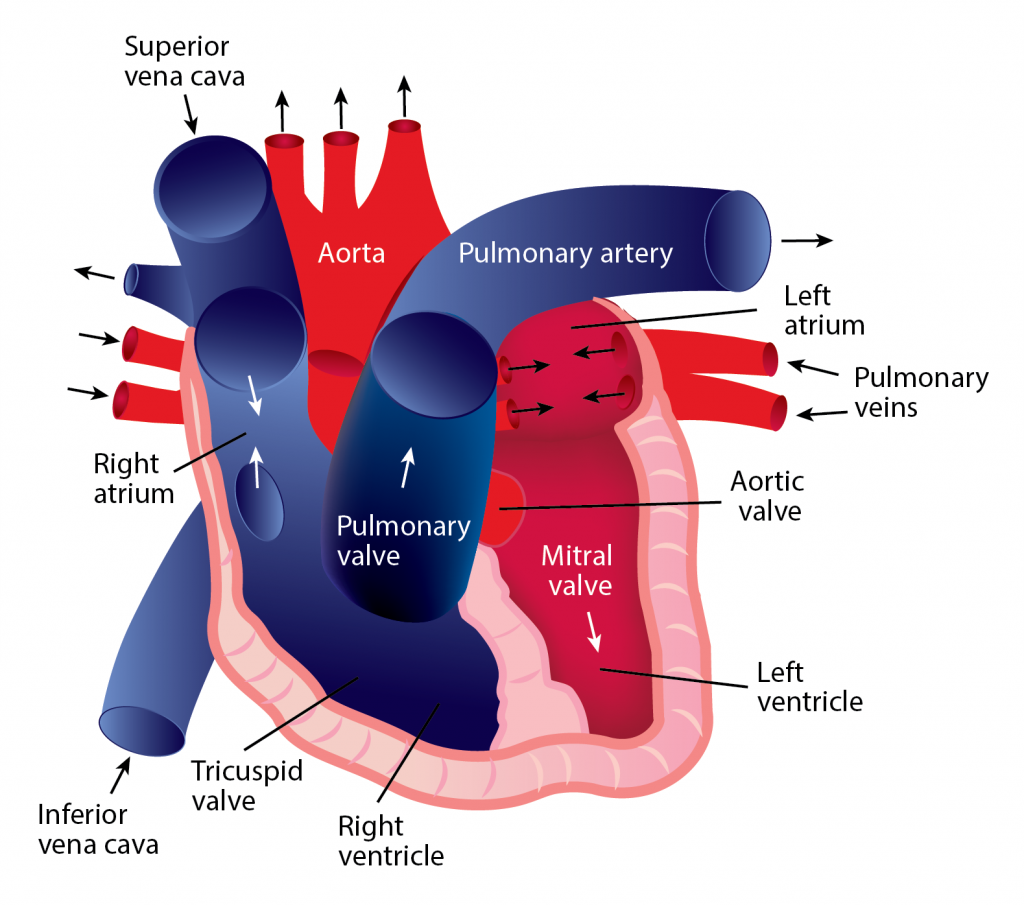
Blood continually flows in one direction, beginning in the heart and proceeding to the arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. When blood reaches the capillaries, exchanges occur between blood and tissues. After this exchange happens, blood is collected into venules, which feed into veins and eventually flow back to the heart’s atrium. The heart must relax between two heartbeats for blood circulation to begin.
Two types of circulatory processes occur in the body:
Systemic circulation
- The pulmonary vein pushes oxygenated blood into the left atrium.
- As the atrium relaxes, oxygenated blood drains into the left ventricle through the mitral valve. 3. The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta.
- Blood travels through the arteries and arterioles before reaching the capillaries that surround the tissues.
Pulmonary circulation
- Two major veins, the Superior Vena Cava and the Inferior Vena Cava, brings deoxygenated blood from the upper and lower half of the body.
- Deoxygenated blood is pooled into the right atrium and then sent into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve, which prevents blood from flowing backward.
- The right ventricle contracts, causing the blood to be pushed through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery.
- Deoxygenated blood becomes oxygenated in the lungs.
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
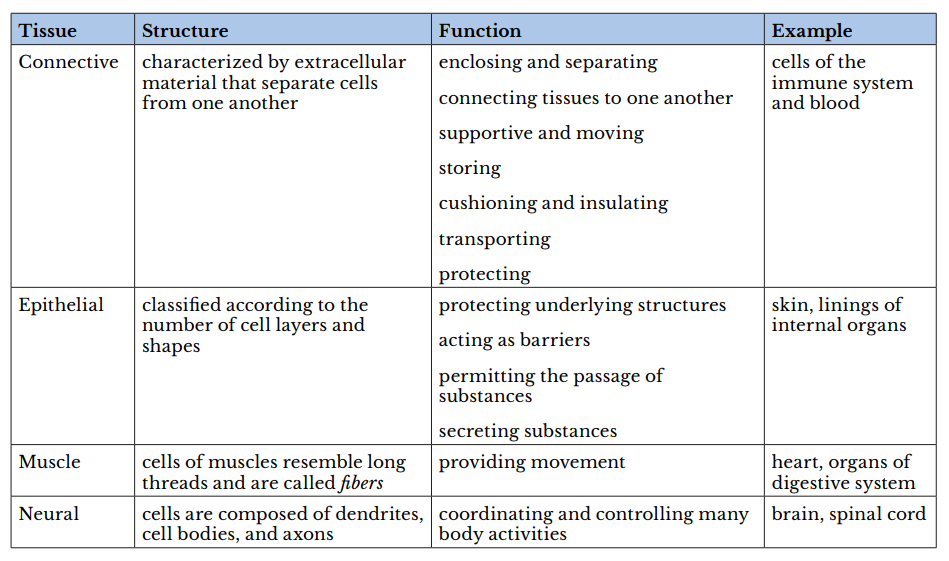
Atissueis a group of cells with similar structure and function and similar extracellular substances located between the cells. The table below describes the four primary tissues found in the human body.
body.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
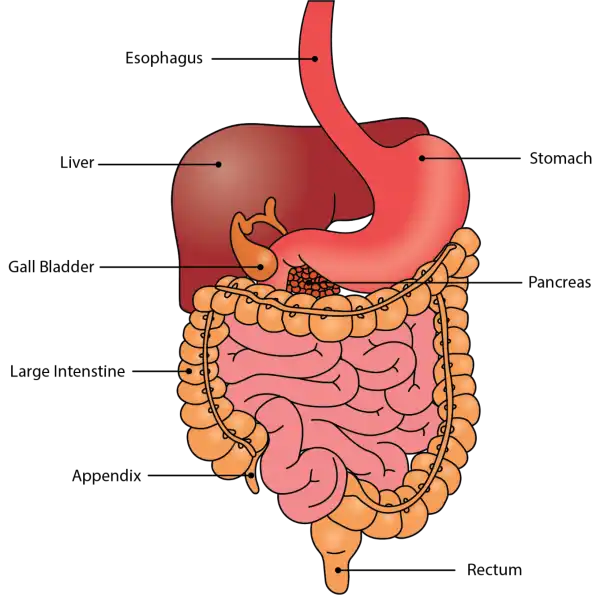
Oral Cavityis the first part of the digestive system. It is bounded by the lips and cheeks and contains the teeth and tongue. Its primary function is to masticate, or chew, and moisten the food.
Pharynx, or throat, connects the mouth to the esophagus.
Esophagusis a muscular tube about 25 centimeters long. Food travels down it to the cardiac sphincter of the stomach.
Pyloric sphincter. The exit of the stomach.
Small intestineis about 6 meters long and consists of three parts: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Large intestine, consists of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. The cecum is located where the small and large intestine meet. The primary function of the large intestine is to compress the waste and collect any excess water that can be recycled.
Colonis about 1.5 to 1.8 meters long and consists of four parts: the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Unlike condensation, deposition, and melting, evaporation is dependent not only on the temperature, but also on the amount of a substance available.
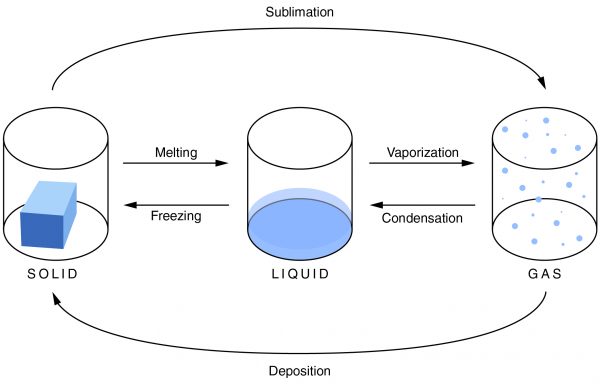
Condensationis the change of a gas or vapor to a liquid. A change in the pressure and the temperature of a substance causes this change. The condensation point is the same as the boiling point of a substance. It is most noticeable when there is a large temperature difference between an object and the atmosphere. Condensation is also the opposite of evaporation.
Evaporationis the change of a liquid to a gas on the surface of a substance. This is not to be confused with boiling, which is a phase transition of an entire substance from a liquid to a gas. The evaporation point is the same as the freezing point of a substance. As the temperature increases, the rate of evaporation also increases. Evaporation depends not only on the temperature, but also on the amount of substance available.
Freezingis the change of a liquid to a solid. It occurs when the temperature drops below the freezing point. The amount of heat that has been removed from the substance allows the particles of the substance to draw closer together, and the material changes from a liquid to a solid. It is the opposite of melting.
Meltingis the change of a solid into a liquid. For melting to occur, enough heat must be added to the substance. When this is done, the molecules move around more, and the particles are unable to hold together as tightly as they can in a solid. They break apart, and the solid becomes a liquid.
Sublimationis a solid changing into a gas. As a material sublimates, it does not pass through the liquid state. An example of sublimation is carbon dioxide, a gas, changing into dry ice, a solid. It is the reverse of deposition.
Depositionis a gas changing into a solid without going through the liquid phase. It is an uncommon phase change. An example is when it is extremely cold outside and the cold air comes in contact with a window. Ice will form on the window without going through the liquid state.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Autotrophs are organisms that use basic raw materials in nature, like the sun, to make energy-rich biomolecules. Minerals are naturally inorganic.
Autotrophsare organisms that make energy-rich biomolecules from raw material in nature. They do this by using basic energy sources such the sun. This explains why most autotrophs rely on photosynthesis to transform sunlight into usable food that can produce energy necessary for life. Plants and certain species of bacteria are autotrophs.
Autotrophs, such as plants, use carbon dioxide (CO2) during photosynthesis to create chemical energy in the form of sugar molecules (like glucose) for growth.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Human intercourse consists of the male introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive system. Sperm may then pass through the female’s reproductive system to the Fallopian tubes where one sperm fertilizes an ovum, creating azygote. The zygote passes out of the Fallopian tube and implants into the uterine wall to begin gestation. Over nine months, the zygote develops and grows into an embryo and then a fetus. An infant is the baby that is born.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
One step of the scientific method is to analyze information or data collected from the experiment to conclude whether the hypothesis is supported.
Recall that these make up thescientific method,described below:
- Problem:The question created because of an observation.Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research:Reliable information available about what is observed.Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis:A predicted solution to the question or problem.Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment:A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of anindependent variablethat the researcher modifies and adependent variablethat changes due to the independent variable. They also include acontrol groupused as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe:Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion:State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate:Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Mendel was accurately able to predict the patterns of heredity by studying rules related to genetics. These rules helped shape his theory of heredity. Heredity is the characteristics offspring inherit from their parents.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants eitherself-pollinateorcross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are eitherdominantorrecessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information calledgenes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual ishomozygousfor that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual isheterozygousfor that trait. Each copy of a factor, orgene, is called anallele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, orphenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is itsgenotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Mendel developed theories of genetics that scientists around the world use today.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants eitherself-pollinateorcross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are eitherdominantorrecessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information calledgenes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual ishomozygousfor that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual isheterozygousfor that trait. Each copy of a factor, orgene, is called anallele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, orphenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is itsgenotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The autonomic nervous systemis responsible for activities that arenonvoluntaryand under unconscious control. This system controls glands and the smooth muscles of internal organs, heart rate, breathing, and digestion. The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the following:
- Sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic nervous system focuses on emergency situations by preparing the body forfight or flight. (Sympathetic = Stress)
- Parasympathetic nervous system: The parasympathetic nervous system controls involuntary processes unrelated to emergencies. This system deals with “rest or digest” activities. (Parasympathetic = Peace)
Thesomatic nervous systemprimarily controlsvoluntaryactivities such as walking and riding a bicycle. Thus, this system sends information to the CNS and motor nerve fibers that are attached to skeletal muscle.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Inductive reasoning involves making specific observations and using them to make broad statements. The student observes that all of the tigers have the same stripe pattern. He can use this observation to make the broad statement that all the tigers’ offspring will have the same stripe pattern.
Inductive reasoninginvolves drawing a general conclusion from specific observations. This form of reasoning is referred to as the “from the bottom up” approach. Information gathered from specific observations can be used to make a general conclusion about the topic under investigation. In other words, conclusions are based on observed patterns in data.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
