What is the difference between a monosaccharide and a disaccharide?
Monosaccharides are composed of two sugar molecules while disaccharides are composed of a single sugar molecule.
Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars while disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars.
Monosaccharides are only found in plants while disaccharides are only found in animals.
Monosaccharides are used for energy storage while disaccharides are used for structural purposes.
Correct Answer : B
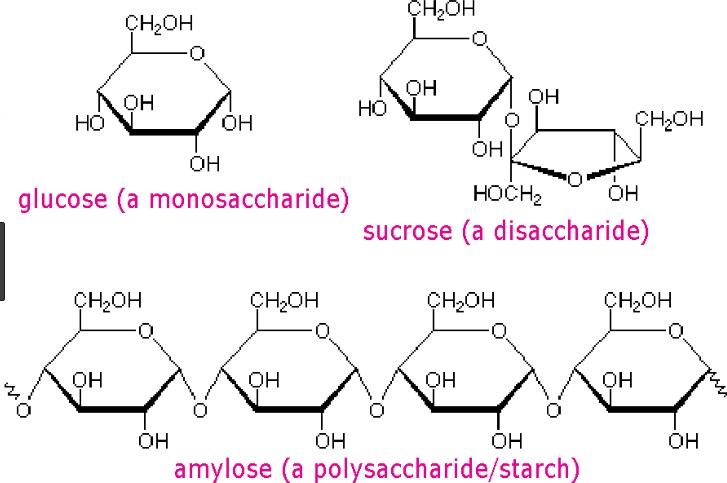
Carbohydrates are one of the main types of biomolecules and are composed of monomers called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are usually composed of 3 to 7 carbon atoms and have a general formula of (CH2O)n, where n is a number between 3 and 7. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond, they form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Option a) is incorrect because it describes the composition of a disaccharide, not a monosaccharide. Option
c) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be found in both plants and animals.
Option d) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be used for energy storage and
structural purposes, depending on their specific structure and function in the organism.
 |
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
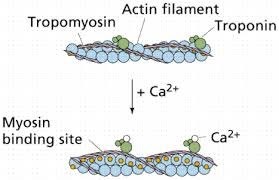
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The nurse can logically conclude that:
✅ Treatment A results in the shortest recovery time.
- The data shows that Treatment A has a mean recovery time of 3 days, which is the shortest compared to Treatment B (5 days) and Treatment C (7 days).
The other statements are not supported by the given data:
❌ "Treatment C enhances patient satisfaction more than the others."
- There is no information about patient satisfaction, only recovery times.
❌ "Treatment B is as effective as Treatment A."
- Treatment B has a longer recovery time (5 days) compared to Treatment A (3 days), so it is not equally effective in terms of recovery speed.
❌ "Treatments A and B provide the same rate of recovery."
- Treatment A has a faster recovery time than Treatment B, so they do not have the same recovery rate.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
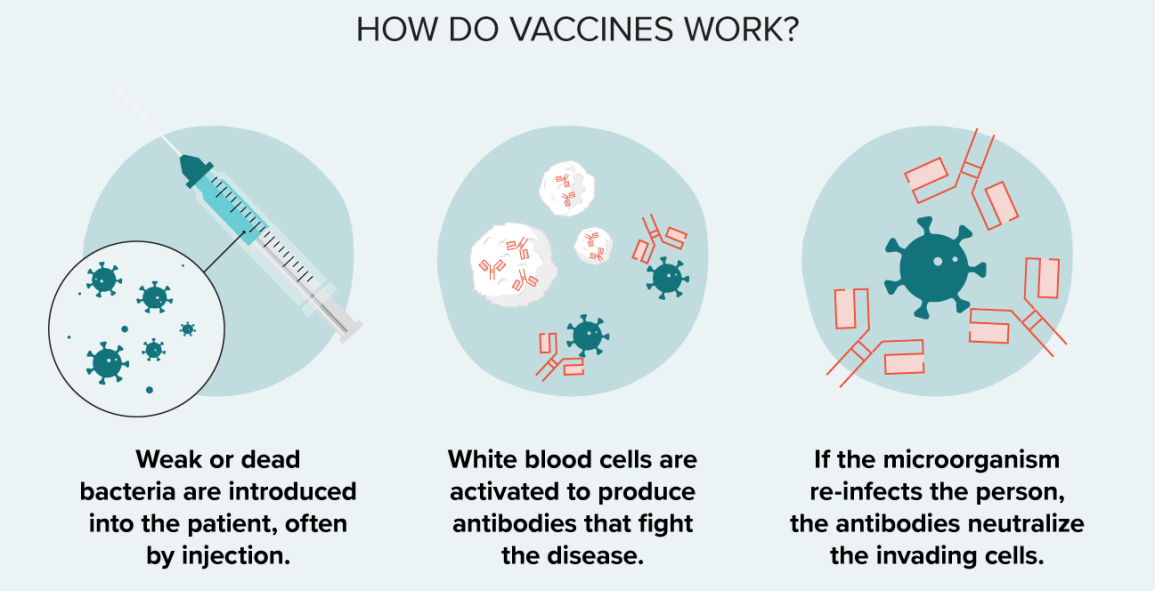
Vaccines are a type of preventative medicine that work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen (such as a virus or bacteria) or to a piece of the pathogen (such as a protein or sugar) that triggers an immune response in the body. This exposure allows the body to develop immunity to the pathogen without getting sick from the full-blown disease. Once the immune system has been primed, it can recognize and quickly respond to the pathogen if it is encountered again in the future, providing protection against the disease.
It is a common misconception that vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against. This is not true. While some vaccines may cause mild symptoms such as a low-grade fever or soreness at the injection site, they do not cause the full-blown disease.
Vaccines provide active immunity, meaning that the body produces its own antibodies against the pathogen, rather than receiving pre-made antibodies as in passive immunity. Additionally, vaccines can be effective against both bacterial and viral infections, depending on the specific vaccine.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
- A. Adduction → Moving a limb toward the midline of the body. ❌
- B. Extension → Increasing the angle of a joint (e.g., straightening the arm or leg). ❌
- C. Flexion → Decreasing the angle of a joint (e.g., bending the elbow or knee). ❌
- D. Abduction → Moving a limb away from the midline (e.g., raising the arm or leg sideways). ✅
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The data collected by the researcher on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month would be most useful to analyze traffic patterns during rush hour.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
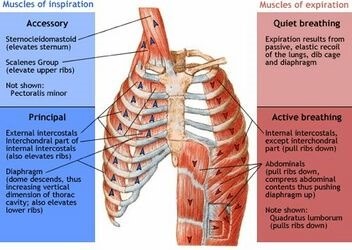
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing. It separates the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, allowing air to flow into the lungs. When it relaxes, it moves upward and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, forcing air out of the lungs.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
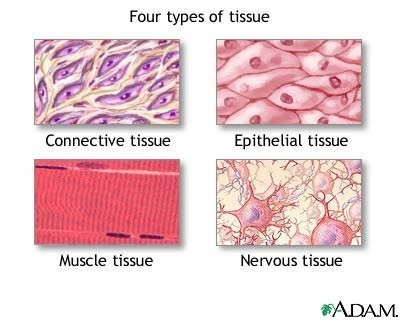
Exocrine glandular is not one of the four primary ssue types found in the human body. The four primary ssue types are epithelial, nervous, connective, and muscle.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
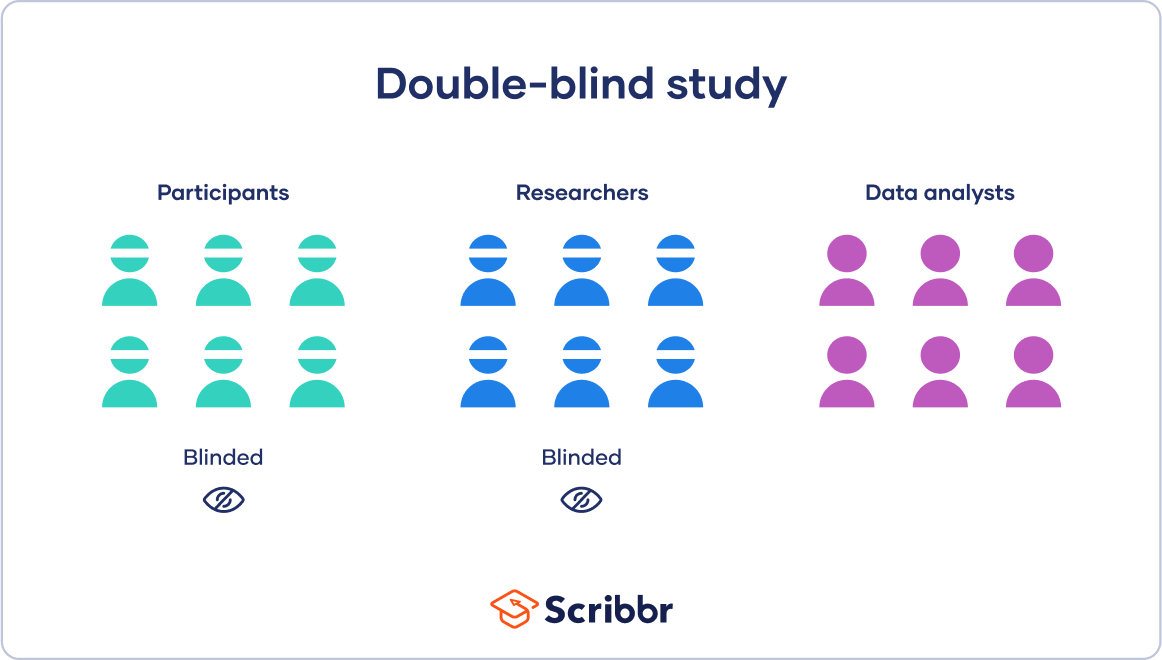
A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to.
Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind.
Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to.
Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
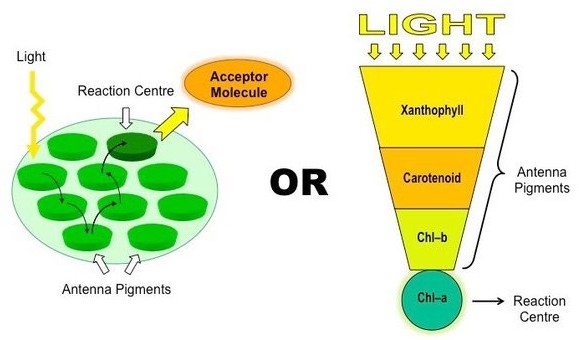
Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants. It is a green pigment that is essential for capturing light energy from the sun and converting it into chemical energy that can be used by the plant. Chlorophyll a absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red parts of the spectrum, and reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic green color
Chlorophyll b is another type of chlorophyll that is also involved in photosynthesis, but it is not as abundant as chlorophyll a. Chlorophyll b absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and orange parts of the spectrum and reflects yellow-green light.
Carotenoids are pigments that are present in many plants and are involved in photosynthesis as well as protecting the plant from damage caused by excess light. Carotenoids are responsible for the orange, yellow, and red colors of many fruits and vegetables.
Anthocyanins are pigments that give plants their red, purple, and blue colors. While they are not directly involved in photosynthesis, they play a role in atracting pollinators and protecting the plant from damage caused by UV radiation.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
- The number of protons in an atom is equal to its atomic number.
- The periodic table shows that phosphorus (P) has an atomic number of 15.
- This means every phosphorus atom has 15 protons in its nucleus.
Analysis of Other Options:
- A. 30 → This is close to the atomic mass (30.97), but the atomic mass is not the same as the number of protons. ❌
- B. 16 → This is incorrect; sulfur (S) has an atomic number of 16, not phosphorus. ❌
- D. 31 → This is rounded from the atomic mass (30.97), but atomic mass ≠ number of protons. ❌
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
