Escherichia coli is plated on nutrient agar plates that each contain a different type of antibiotic. The shaded area represents growth of the bacteria. Which of the following plates contains bacteria that were most resistant to the antibiotic?
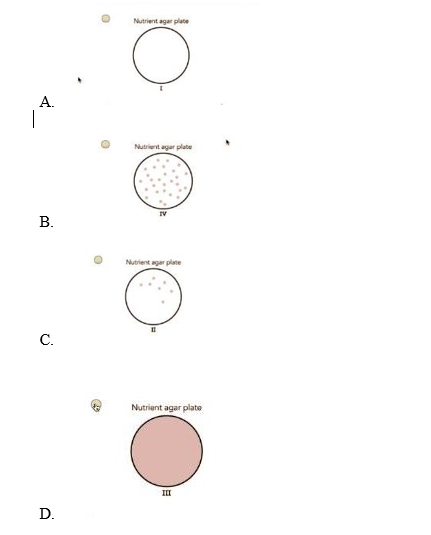
A
B
C
D
Correct Answer : B
A. This plate represents good antibiotic activity against Escherichia.
B. This is the plate that represents the highest number of bacteria. The bacteria that grow on this plate are the most resistant to the antibiotic because they can survive in a high concentration of the substance. In the other plates, the antibiotic inhibits the growth of the bacteria to a greater or lesser extent, depending on their sensitivity.
C. This plate represents partial antibiotic activity against Escherichia.
D. This represents no activity that may be due to inappropriate media.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Organs are more complex than tissues hence this sequence is not correct.
B. This is the most accurate sequence. Atoms are the basic units of matter and the defining structure of elements. Cells are the basic structural, functional, and biological units of all living organisms. They are the smallest units of life that can replicate independently. Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Organs are structures made up of two or more types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function in the body. For example, the heart is an organ composed of all four types of tissue, working together to pump blood throughout the body.
C. Organs are more complex than tissues, cells and atoms hence this sequence is incorrect.
D. Atoms are less complex than cells and tissues hence they should start the sequence.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. 5’ TCGUTCGCU 3’: This sequence is incorrect because it contains 'U', which is a base found in RNA, not DNA. DNA contains the base 'T' for thymine, not 'U' for uracil.
B. 5’ UCGAUCGCA 3’: This option is also incorrect for the same reason as option A; it includes 'U', indicating it is an RNA sequence, not a DNA sequence.
C. 3’ AGCTAGCGT 5’: This sequence is simply the original strand read in the opposite direction, not the complementary strand.
D. 3’ TCGATCGCA 5’: This is the correct complementary DNA sequence. In DNA, adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). Therefore, for the original DNA sequence 5' AGCTAGCGT 3', the complementary strand must read 3' TCGATCGCA 5', with each base pairing correctly according to the rules of base pairing in DNA. This sequence is antiparallel to the original, as indicated by the 3' and 5' ends, which is a key characteristic of DNA structure.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Urea is a waste product formed in the liver through the metabolic breakdown of proteins and is excreted by the sweat glands. When proteins are broken down, ammonia is formed, which is toxic to the body. The liver converts ammonia into urea, which is less toxic and can be safely transported in the bloodstream to be eliminated through sweat and urine.
B. Lysozymes are enzymes that are part of the immune system and are found in various body fluids, including sweat. However, they are not specifically related to the breakdown of proteins and the formation of ammonia.
C. Sebum is an oily substance produced by sebaceous glands, not sweat glands. It helps to lubricate and protect the skin but is not involved in the excretion of waste products from protein metabolism.
D. Water is a major component of sweat and is excreted by sweat glands to help regulate body temperature through evaporative cooling. While it is a component of sweat, it is not specifically excreted in response to protein breakdown and ammonia formation.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. The nucleus is the command center of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's genetic material and regulating gene expression to control cell growth, division, and differentiation.
B. Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes for digesting macromolecules, old cell parts, and foreign invaders, acting as the waste disposal system of the cell.
C. Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. They are responsible for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy-carrying molecule, through a process called cellular respiration.
D. Centrioles are cylindrical structures that are involved in the organization of microtubules during cell division, playing a crucial role in the formation of the spindle fibers that separate chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. The browning of an apple slice is caused by the enzyme polyphenol oxidase, which is present in the apple, not the lemon juice.
B. This acidic environment can denature the polyphenol oxidase enzyme in the apple, rendering it inactive and thus preventing the browning reaction.
C. The browning is a result of a chemical reaction, and dilution would not prevent the reaction from occurring.
D. The browning is due to the formation of melanin, which are pigments resulting from the enzymatic reaction. Lemon juice's acidity affects the enzyme responsible for this reaction, not the pigments themselves.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Melanocytes are specialized cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis. They are responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Melanocytes transfer pigment granules to adjacent keratinocytes, which then distribute the pigment throughout the epidermis, providing protection against ultraviolet radiation.
B. Keratinocytes are the most prevalent cell type in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. While they receive pigment granules from melanocytes, they do not transfer them; instead, they integrate the pigment into their own structure, contributing to skin color and protection.
C. Langerhans cells are a type of dendritic cell found in the epidermis. They are part of the immune system and are involved in the body's defense mechanisms. They do not participate in the transfer of pigment granules.
D. Merkel cells are sensory cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis. They are associated with nerve endings and are involved in the sensation of touch. Merkel cells are not involved in the transfer of pigment granules to other cells.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Potassium, with an atomic number of 19, has one electron in its outermost shell. This makes it more likely to lose that electron to achieve a stable electron configuration, resulting in a positively charged ion or cation.
B. Oxygen, with an atomic number of 8, has six electrons in its outer shell. It is more likely to gain two electrons to fill its outer shell and become an anion, not a cation.
C. Helium, with an atomic number of 2, has a full outer shell of electrons, making it very stable and unlikely to form ions under normal conditions.
D. Fluorine, with an atomic number of 9, has seven electrons in its outer shell. It tends to gain one electron to complete its outer shell and become an anion, not a cation.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Centrosomes are the microtubule-organizing centers in cells, playing a critical role in the spatial arrangement of cell structures and in cell division.
B. Ribosomes are the molecular machines within the cell that facilitate the production of proteins by translating messenger RNA into polypeptide chains.
C. Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell, generating most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy.
D. Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes capable of breaking down all types of biological polymers—proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. They are essential for intracellular digestion, the recycling of a cell's organic materials, and programmed cell death (apoptosis).
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Choice: D: A-1, Z-1
Choice D: A−1,Z−1
- Explanation: This is the correct description of what happens when a proton is emitted:
- The atomic number ZZZ decreases by 1 (because a proton is lost).
- The atomic mass AAA decreases by 1 (because the proton is no longer contributing to the mass).
Incorrect Choice:
Choice A: A+1,Z+1
- Explanation: This suggests that both the atomic mass and atomic number increase, which would happen if a proton were added to the nucleus. This does not describe the emission of a proton, so it’s incorrect.
Choice B: A−1,Z+1
- Explanation: This suggests that the atomic mass decreases by 1, but the atomic number increases. However, when a proton is emitted, the atomic number should decrease, so this is also incorrect.
Choice C: A+1,Z−1
- Explanation: This suggests that the atomic mass increases while the atomic number decreases. Emitting a proton does not increase the atomic mass, so this choice is incorrect.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. The cervical canal is the narrow passage through the cervix, connecting the vagina to the uterus. It is not typically the site of fertilization but rather serves as a gateway for sperm to enter the uterus and subsequently the Fallopian tubes where fertilization can occur.
B. The ovary is the female reproductive organ that produces eggs, or ova. While it is crucial for providing the egg, it is not the location where fertilization takes place.
C. The Fallopian tube, also known as the uterine tube or oviduct, is the site where fertilization usually occurs. After ovulation, the egg is captured by the fimbriae at the end of the Fallopian tube and is transported towards the uterus. If sperm are present in the Fallopian tube, fertilization can occur here.
D. The uterus is the muscular organ where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus. However, it is not the typical site of fertilization; this process usually occurs in the Fallopian tubes before the zygote travels to the uterus for implantation.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
