In the following single-replacement reaction, ______ replaces ______.
Cl2+2NaI→2NaCl+I2
sodium, iodine
chlorine, iodine
chlorine, sodium
sodium, chlorine
Correct Answer : B
In this reaction, chlorine (Cl2) is an element in the reaction that replaces iodine in the compound sodium iodide (NaI). This allows chlorine to form a compound with sodium (NaCl) and leaves iodine (I2) as an element.
Synthesis reactions involve two or more reactants (A and B) combining to form one product (AB). In the example provided, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) begin as separate elements. At the end of the reaction, the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are bonded in a molecule of water (H2O).
Decomposition reactions have only one reactant (AB) that breaks apart into two or more products (A and B). In the example above, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) breaks apart into two smaller molecules: water (H2O) and oxygen (O2).
Single-replacement reactions involve two reactants, one compound (AB) and one element (C). In this type of reaction, one element replaces another to form a new compound (AC), leaving one element by itself (B). In the example, zinc replaces hydrogen in hydrochloric acid (HCl). As a result, zinc forms a compound with chlorine, zinc chloride (ZnCl2), and hydrogen (H2) is left by itself.
Double-replacement reactions involve two reactants, both of which are compounds made of two components (AB and CD). In the example, silver nitrate, composed of silver (Ag1+) and nitrate (NO31-) ions, reacts with sodium chloride, composed of sodium (Na1+) and chloride (Cl1-) ions. The nitrate and chloride ions switch places to produce two compounds that are different from those in the reactants.
Combustion reactions occur when fuels burn, and they involve specific reactants and products, as seen in the examples below. Some form of fuel that contains carbon and hydrogen is required. Examples of such fuels are methane, propane in a gas grill, butane in a lighter, and octane in gasoline. Notice that these fuels all react with oxygen, which is necessary for anything to burn. In all combustion reactions, carbon dioxide, water, and energy are produced. When something burns, energy is released, which can be felt as heat and seen as light.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Because this is a positive correlation, if the nutrient concentration increases or decreases, plant height will either increase or decrease accordingly.
While analyzing data, scientists tend to observe cause-and-effect relationships. These relationships can be quantified using correlations.Correlationsmeasure the amount of linear association between two variables. There are three types of correlations:
Positive correlation:
As one variable increases, the other variable also increases. This is also known as a direct correlation.
Negative correlation:
As one variable increases, the other decreases. The opposite is true if one variable decreases. A negative correlation is also known as an inverse correlation or an indirect correlation.
No correlation:
There is no connection or relationship between two variables.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Homeostasisis the existence and maintenance of a relatively constant environment within the body. Each cell of the body is surrounded by a small amount of fluid, and the normal functions of each cell depend on the maintenance of its fluid environment within a narrow range of conditions, including temperature, volume, and chemical content. These conditions are known asvariables. For example, body temperature is a variable that can increase in a hot environment or decrease in a cold environment.
There are two types of feedback mechanisms in the human body: negative and positive.
- Negative Feedback: Most systems of the body are regulated by negative feedback mechanisms, which maintain homeostasis. Negative means that any deviation from the set point is made smaller or is resisted. The maintenance of normal blood pressure is a negative-feedback mechanism. Normal blood pressure is important because it is responsible for moving blood from the heart to tissues.
- Positive Feedback: Positive-feedback mechanisms are not homeostatic and are rare in healthy individuals. Positive means that when a deviation from a normal value occurs, the response of the system is to make the deviation even greater. Positive feedback therefore usually creates a cycle leading away from homeostasis and, in some cases, results in death. Inadequate delivery of blood to cardiac muscle is an example of positive feedback.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
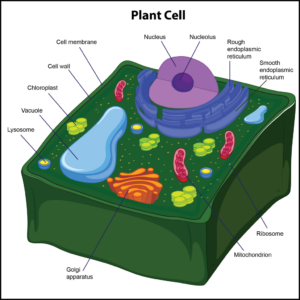
Only plant cells have cell walls, which help protect the cell and provide structural support. The cell wall also enforces the overall structural integrity of the plant cell, and it is found outside the cell membrane. The next organelle is a chloroplast. It is found in the cytoplasm of only plant cells.Chloroplastsare photosynthetic compounds usedto make food for plant cells by harnessing energy from the sun. These organelles play a role in photosynthesis.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
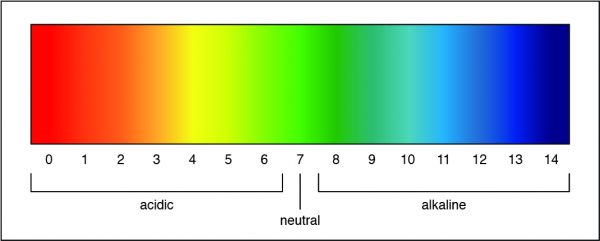
A pH of 7 is a neutral solution, which is how pure water is classified. Researchers can determine the strength of an acid or a base by measuring the pH of a solution. The pH value describes how acidic or basic a solution is. On pH scale, shown below, if the number is less than 7 the solution is acidic. A pH greater than 7 means the solution is basic. When the pH is exactly 7, the solution is neutral.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Mendel was accurately able to predict the patterns of heredity by studying rules related to genetics. These rules helped shape his theory of heredity. Heredity is the characteristics offspring inherit from their parents.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants eitherself-pollinateorcross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are eitherdominantorrecessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information calledgenes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual ishomozygousfor that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual isheterozygousfor that trait. Each copy of a factor, orgene, is called anallele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, orphenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is itsgenotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
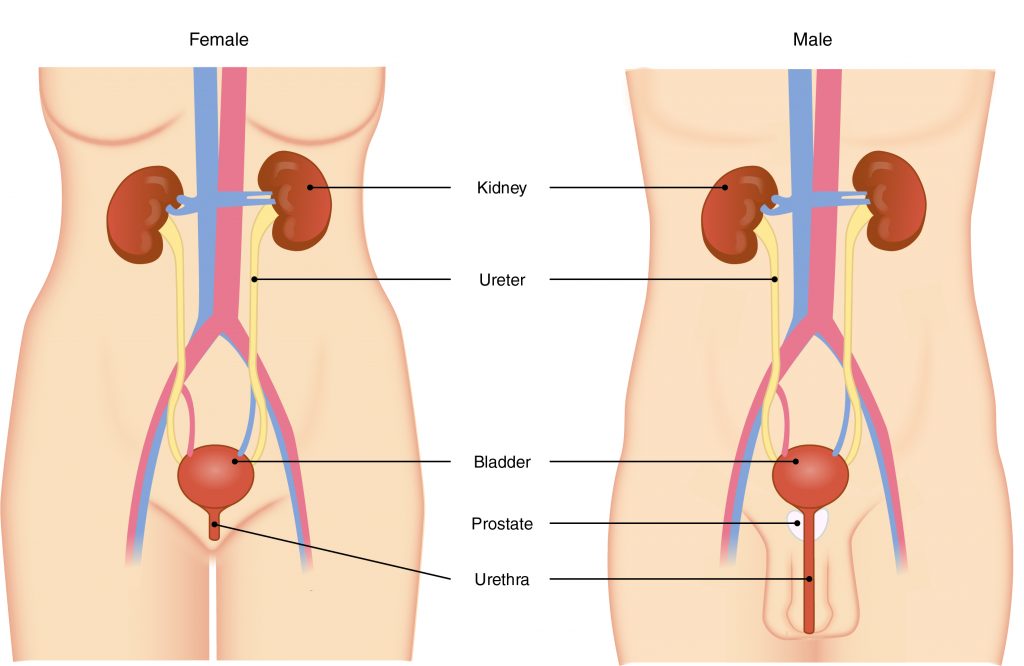
The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A control group is a factor that does not change during an experiment. Due to this, it is used as a standard for comparison with variables that do change such as a dependent variable.
Recall that these make up thescientific method,described below:
- Problem:The question created because of an observation.Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research:Reliable information available about what is observed.Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis:A predicted solution to the question or problem.Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment:A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of anindependent variablethat the researcher modifies and adependent variablethat changes due to the independent variable. They also include acontrol groupused as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe:Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion:State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate:Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
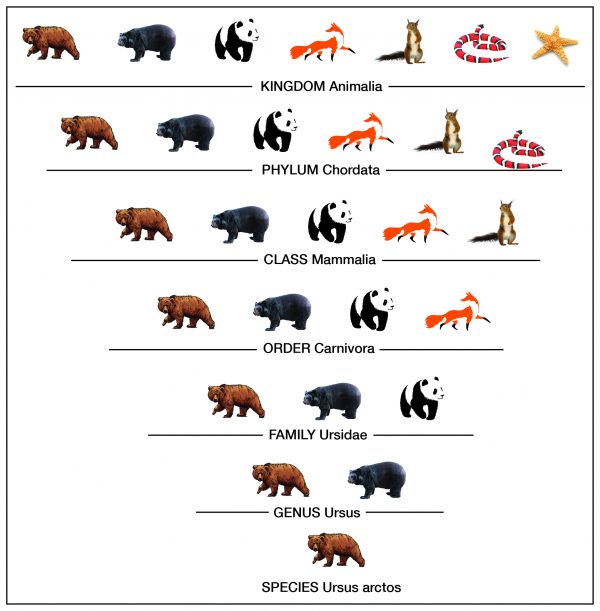
Taxonomy is the process of classifying, describing, and naming organisms. There are seven levels in the Linnaean taxonomic system, starting with the broadest level, kingdom, and ending with the species level. For example, in the image the genus level contains two types of bears, but the species level shows one type. Additionally,organisms in each level are found in the level above it. For example, organisms in the order level are part of the class level. This classification system is based on physical similarities across living things. It does not account for molecular or genetic similarities.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A neutralization reaction is a type of acid-base reaction where an acid and base react to form a salt and water.
In an aqueous solution, a base increases the hydroxide concentration (OH–), while an acid increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Sometimes,neutralization reactionsalso occur. This type of reaction happens when an acid and a base react with each other to form water and salt. Salt is typically defined as anionic compoundthat includes any cation except H+and any anion except OH–. Consider the following example of a neutralization reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
HBr+KOH→KBr+H2O
Not all neutralization reactions proceed in the manner where all reactants are in the aqueous phase. In some chemical reactions, one reactant may be a solid. The neutralization reaction can still proceed to completion.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
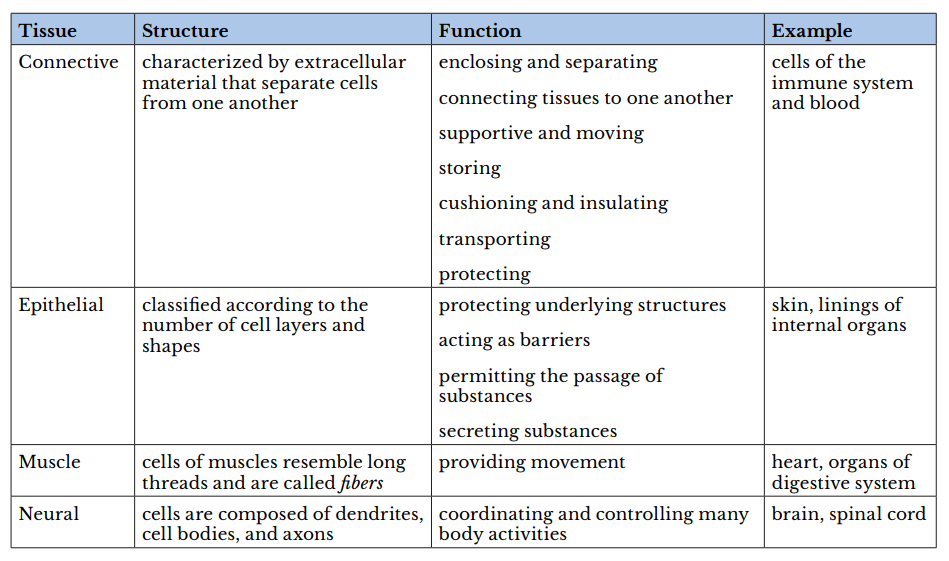
Atissueis a group of cells with similar structure and function and similar extracellular substances located between the cells. The table below describes the four primary tissues found in the human body.
body.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
