The sequence of amino acids in a gene determines
the primary structure of a codon
the primary structure of a protein
the primary structure of a nucleotide
the primary structure of a nucleic acid.
Correct Answer : B
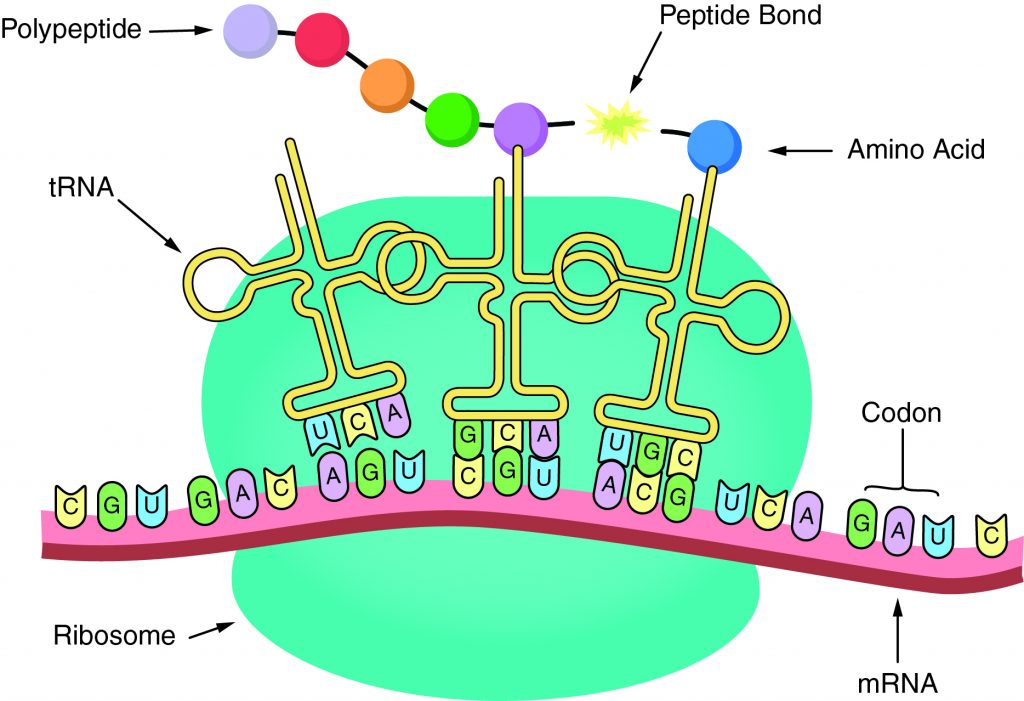
The sequence of amino acids in a gene determines the primary structure of a protein. The components necessary for translation are located in the cytoplasm. Translation is the making of proteins by mRNA binding to a ribosome with the start codon that initiates the production of amino acids. A peptide bond forms and connects the amino acids together. The sequence of amino acids determines the protein’s structure, which determines its function.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Because it has more protons than electrons, this atom has a positive charge and can be classified as a cation. When a metal such as sodium reacts to become stable, it loses its valence electrons. At first, it is a neutral atom with 11 protons and 11 electrons. When it loses an electron, the number of protons does not change, and the atom has 11 protons and 10 electrons. Because there is one more positively charged proton, acationforms. A cation is an ion with a net positive charge.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Because more solute could be added and dissolve, the solution has not yet reached its limit and is considered unsaturated. Because all the solute dissolves, the particles in the mixture are evenly distributed as a homogenous mixture.
- Amixtureis when elements and compounds are physically, but not chemically, combined.
- Ahomogeneousmixture is when substances mix evenly and it is impossible to see individual components. Aheterogeneousmixture is when the substances mix unevenly and it is possible to see individual components.
- Asolutionis a type of homogeneous mixture that is formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
- The concentration of a solution is the amount of a substance in a given amount of solution. Anunsaturatedsolution has the ability to dissolve more solute and asaturatedsolution has already reached the limit of solute it can dissolve.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Robert Hooke discovered the first cells in the mid-eighteenth century. The cell theory is a theory because it is supported by a significant number of experimental findings. The cell theory took many years to be developed because microscopes were not powerful enough to make such observations.
This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
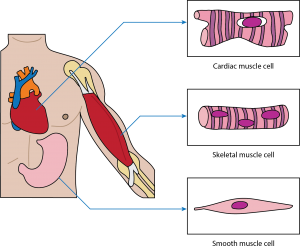
Skeletal muscle: This muscle cell is striated, long, and cylindrical. There are many nuclei in a skeletal muscle cell. Attached to bones in the body, skeletal muscle contracts voluntarily, meaning that it is under conscious control.
Smooth muscle: This muscle consists of nonstriated muscle cells that are spindle-shaped. Like cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle cells contain one nucleus. This muscle type is found in the walls of internal organs like the bladder and stomach. Smooth muscle contraction is involuntary and controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Cardiac muscle: This muscle consists of muscle cells that are striated, short, and branched. These cells contain one nucleus, are branched, and are rectangular. Cardiac muscle contraction is an involuntary process, which is why it is under the control of the autonomic nervous system. This muscle is found in the walls of the heart.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Human intercourse consists of the male introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive system. Sperm may then pass through the female’s reproductive system to the Fallopian tubes where one sperm fertilizes an ovum, creating azygote. The zygote passes out of the Fallopian tube and implants into the uterine wall to begin gestation. Over nine months, the zygote develops and grows into an embryo and then a fetus. An infant is the baby that is born.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
In this reaction, chlorine (Cl2) is an element in the reaction that replaces iodine in the compound sodium iodide (NaI). This allows chlorine to form a compound with sodium (NaCl) and leaves iodine (I2) as an element.
Synthesisreactions involve two or more reactants (A and B) combining to form one product (AB). In the example provided, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) begin as separate elements. At the end of the reaction, the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are bonded in a molecule of water (H2O).
Decompositionreactions have only one reactant (AB) that breaks apart into two or more products (A and B). In the example above, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) breaks apart into two smaller molecules: water (H2O) and oxygen (O2).
Single-replacementreactions involve two reactants, one compound (AB) and one element (C). In this type of reaction, one element replaces another to form a new compound (AC), leaving one element by itself (B). In the example, zinc replaces hydrogen in hydrochloric acid (HCl). As a result, zinc forms a compound with chlorine, zinc chloride (ZnCl2), and hydrogen (H2) is left by itself.
Double-replacementreactions involve two reactants, both of which are compounds made of two components (AB and CD). In the example, silver nitrate, composed of silver (Ag1+) and nitrate (NO31-) ions, reacts with sodium chloride, composed of sodium (Na1+) and chloride (Cl1-) ions. The nitrate and chloride ions switch places to produce two compounds that are different from those in the reactants.
Combustionreactions occur when fuels burn, and they involve specific reactants and products, as seen in the examples below. Some form of fuel that contains carbon and hydrogen is required. Examples of such fuels are methane, propane in a gas grill, butane in a lighter, and octane in gasoline. Notice that these fuels all react with oxygen, which is necessary for anything to burn. In all combustion reactions, carbon dioxide, water, and energy are produced. When something burns, energy is released, which can be felt as heat and seen as light.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A neutralization reaction is a type of acid-base reaction where an acid and base react to form a salt and water.
In an aqueous solution, a base increases the hydroxide concentration (OH–), while an acid increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Sometimes,neutralization reactionsalso occur. This type of reaction happens when an acid and a base react with each other to form water and salt. Salt is typically defined as anionic compoundthat includes any cation except H+and any anion except OH–. Consider the following example of a neutralization reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
HBr+KOH→KBr+H2O
Not all neutralization reactions proceed in the manner where all reactants are in the aqueous phase. In some chemical reactions, one reactant may be a solid. The neutralization reaction can still proceed to completion.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Autotrophs are organisms that use basic raw materials in nature, like the sun, to make energy-rich biomolecules. Minerals are naturally inorganic.
Autotrophsare organisms that make energy-rich biomolecules from raw material in nature. They do this by using basic energy sources such the sun. This explains why most autotrophs rely on photosynthesis to transform sunlight into usable food that can produce energy necessary for life. Plants and certain species of bacteria are autotrophs.
Autotrophs, such as plants, use carbon dioxide (CO2) during photosynthesis to create chemical energy in the form of sugar molecules (like glucose) for growth.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
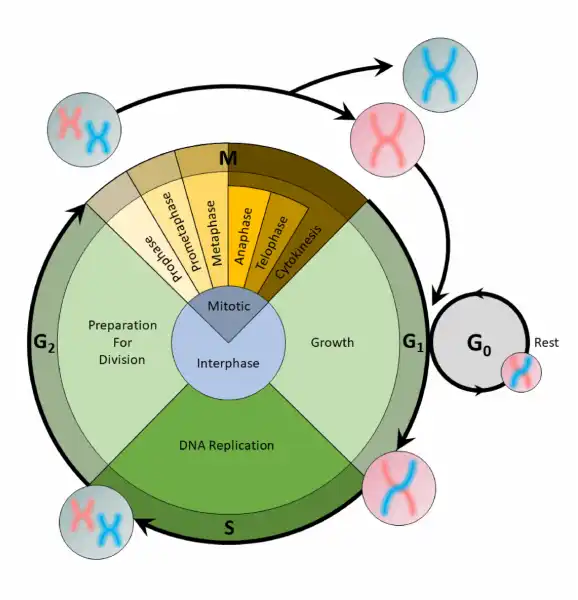
Before mitosis or meiosis occurs, interphase must happen. This is when the cell cycle takes place. The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases:interphaseand theM (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2phases make up interphase.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
