What is the difference between innate and adaptive immunity?
Innate immunity is present at birth while adaptive immunity is acquired after exposure to pathogens.
Innate immunity is specific to particular pathogens while adaptive immunity is nonspecific.
Innate immunity is mediated by antibodies while adaptive immunity is mediated by T cells.
Innate immunity provides long-term protection while adaptive immunity provides only short-term protection.
Correct Answer : A
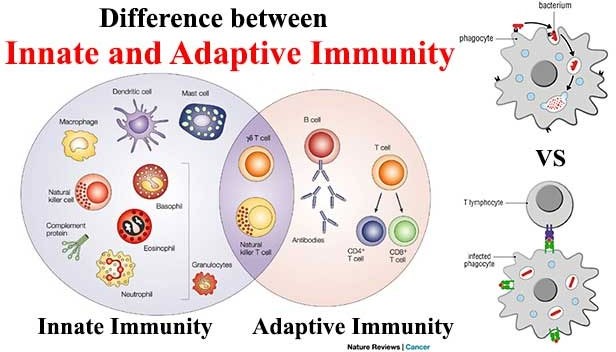
Innate immunity and adaptive immunity are two arms of the immune system that work together to protect the body from pathogens. Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is present at birth. It includes physical and chemical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes, and antimicrobial peptides, as well as cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells that can quickly recognize and atack pathogens. Innate immunity is nonspecific, meaning it responds to a wide variety of pathogens in a similar way.
Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is acquired after exposure to pathogens. It involves the production of antibodies and activation of T cells, which are specific to particular pathogens. Adaptive immunity takes longer to develop than innate immunity, but it provides a more specific and targeted response to pathogens. Once the adaptive immune system has been activated against a particular pathogen, it can provide long-term protection against future infections with that pathogen.
Option b) is incorrect because innate immunity is nonspecific while adaptive immunity is specific. Option c) is incorrect because antibodies are a part of adaptive immunity while T cells can be a part of both innate and adaptive immunity. Option d) is incorrect because adaptive immunity can provide long-term protection, while innate immunity provides immediate but short-lived protection.
 |
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The unit used to indicate length is the meter (m). It is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
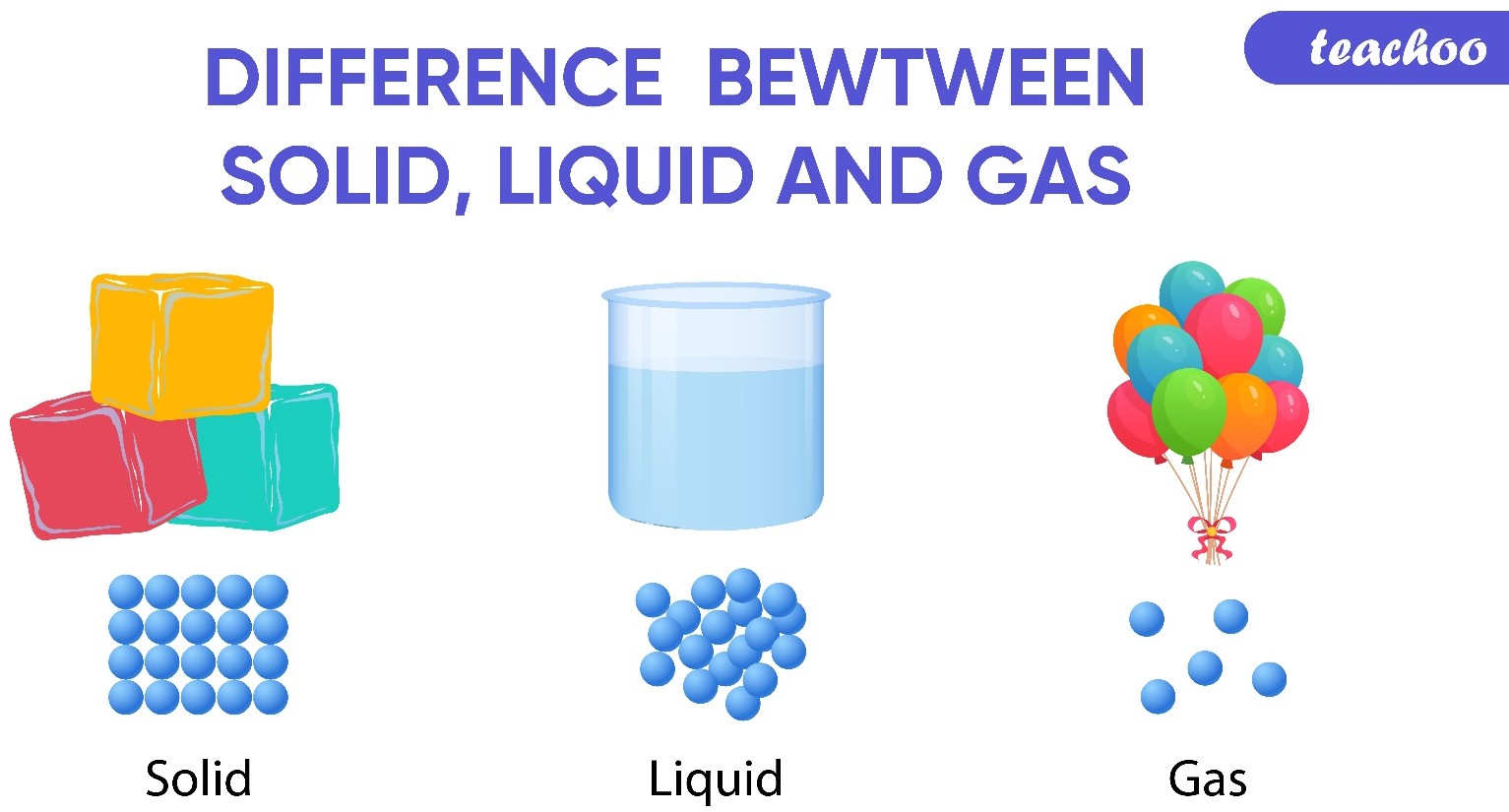
The main difference between a solid and a liquid is their physical state and the way their particles are arranged. In a solid, the particles are tightly packed together and have a fixed position, which gives the solid a definite shape and volume. Solids are also characterized by their high density, low compressibility, and high thermal conductivity.
In contrast, the particles in a liquid are more loosely packed and can move around each other, which allows the liquid to take the shape of its container. Liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape, which means they can be poured or spilled. Liquids also have a lower density than solids, are more compressible than solids, and have lower thermal conductivity than solids.
Option b) is incorrect because it describes the properties of a gas, not a liquid. Option c) is incorrect because solids and liquids have different physical properties. Option d) is incorrect because it describes the properties of a gas, not a liquid or a solid.
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
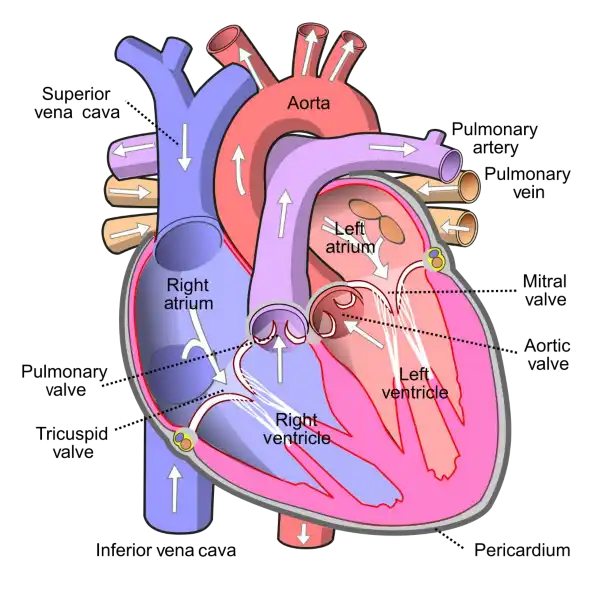
The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart and helps to regulate the flow of blood between these chambers. It consists of two leaflets or flaps that open and close in response to changes in pressure as the heart beats.
During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral valve opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. During systole, when the heart contracts to pump blood out of the left ventricle and into the systemic circulation, the mitral valve closes to prevent backflow of blood into the left atrium.
The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart that help to ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the circulatory system. Problems with the mitral valve, such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis, can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure.
 |
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Water molecules primarily enter cells through the process of facilitated diffusion, specifically via aquaporins, which are specialized channel proteins that facilitate the rapid transport of water across the cell membrane. This process does not require energy (ATP) as it relies on the concentration gradient of water, allowing water to move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration.
Here’s why the other options are not correct in the context of water transport:
- A. Gated channels: While aquaporins can be gated, this term generally refers to channels that open and close in response to specific signals, which is not the primary mechanism for water transport in most cells.
- B. Electrochemical gradients: This term relates to the combined effect of electrical and chemical gradients across a membrane, typically for ions rather than water molecules directly. Water movement can be influenced by osmotic gradients but is not solely dependent on electrochemical gradients.
- D. Proton pumps: These are involved in transporting protons (H⁺ ions) across membranes, primarily for establishing an electrochemical gradient, not for the transport of water.
Thus, water molecules enter cells mainly by facilitated diffusion through aquaporins.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
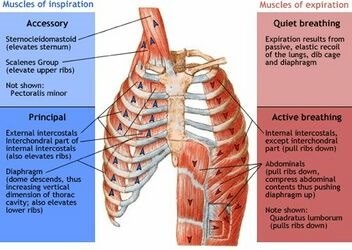
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing. It separates the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, allowing air to flow into the lungs. When it relaxes, it moves upward and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, forcing air out of the lungs.
 |
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
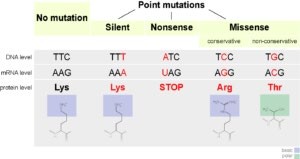 |
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Stomach acid is highly acidic, primarily composed of hydrochloric acid (HCl), which means it has a low pH (around 1 to 3). Acids release hydrogen ions (H⁺) in solution, which lowers the pH.
- A. It has a higher pH: Incorrect, as acidic solutions have a lower pH compared to neutral distilled water (which has a pH of 7).
- B. It contains nitrogen: Incorrect, stomach acid is composed mostly of HCl, not nitrogen-containing compounds.
- D. It has more hydroxyl ions: Incorrect, acidic solutions have fewer hydroxyl ions (OH⁻); hydroxyl ions are more common in basic (alkaline) solutions.
In comparison to distilled water, which is neutral, the stomach acid solution has significantly more hydrogen ions, making it more acidic.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of an acid or base are added. Buffers work by neutralizing added hydrogen ions (H⁺) or hydroxide ions (OH⁻), thereby maintaining a relatively stable pH. Buffers are made up of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
- A. It decreases the pH of the solution: This is incorrect because a buffer does not always decrease pH; it resists changes in both directions.
- C. It causes the pH of a solution to become neutral: Incorrect because buffers do not necessarily make a solution neutral; they stabilize pH around a certain value.
- D. It permanently binds hydrogen ions: Incorrect as the binding is reversible, which is essential for maintaining pH balance.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to. Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind. Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to. Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.
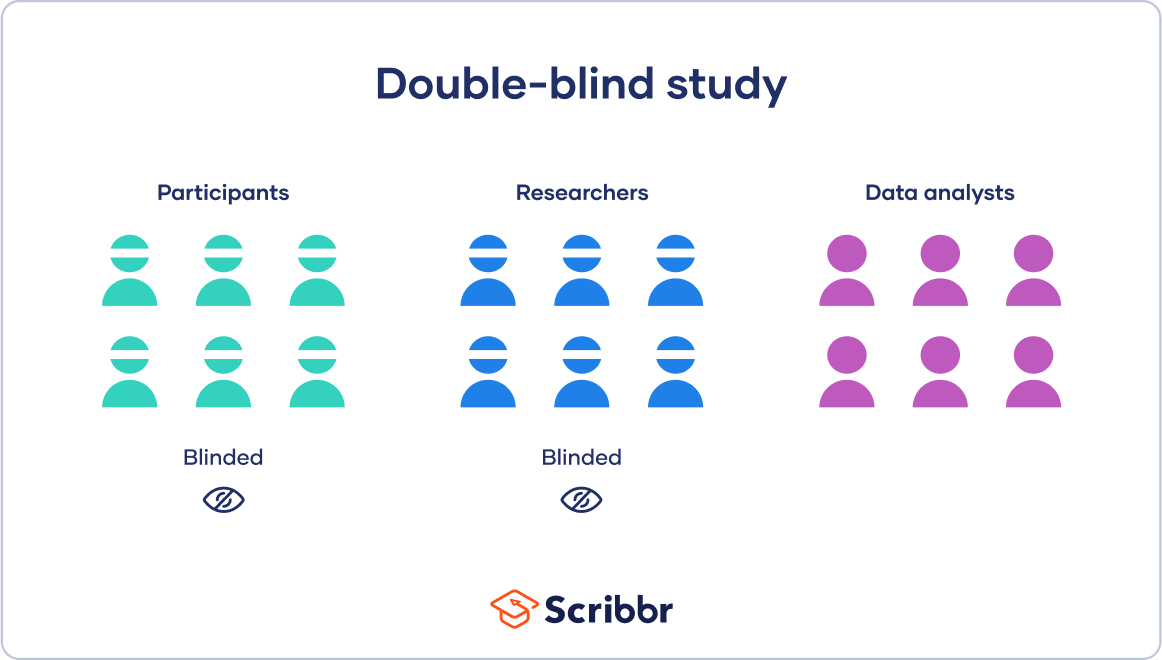
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Innate immunity and adaptive immunity are two arms of the immune system that work together to protect the body from pathogens. Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is present at birth. It includes physical and chemical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes, and antimicrobial peptides, as well as cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells that can quickly recognize and atack pathogens. Innate immunity is nonspecific, meaning it responds to a wide variety of pathogens in a similar way.
Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is acquired after exposure to pathogens. It involves the production of antibodies and activation of T cells, which are specific to particular pathogens. Adaptive immunity takes longer to develop than innate immunity, but it provides a more specific and targeted response to pathogens. Once the adaptive immune system has been activated against a particular pathogen, it can provide long-term protection against future infections with that pathogen.
Option b) is incorrect because innate immunity is nonspecific while adaptive immunity is specific. Option c) is incorrect because antibodies are a part of adaptive immunity while T cells can be a part of both innate and adaptive immunity. Option d) is incorrect because adaptive immunity can provide long-term protection, while innate immunity provides immediate but short-lived protection.
 |
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
