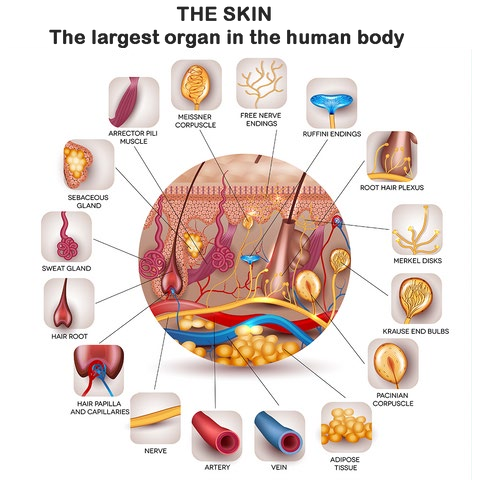
What is the largest organ in the human body by surface area?
Brain
Heart
Liver
Skin
Correct Answer : D
The largest organ in the human body by surface area is the skin. It covers the entire external surface of the body and has an average surface area of about 20 square feet in adults.
 |
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
In the given exothermic reaction:
CaO + H2O ⇌ Ca(OH)2 + heat
To increase the total yield of lime water (Ca(OH)₂), you can apply Le Chatelier's Principle, which states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the disturbance.
- A. Continuously remove Ca(OH)₂: By removing the product (Ca(OH)₂) as it forms, the equilibrium will shift to the right, favoring the formation of more Ca(OH)₂. This is the most effective way to increase the yield.
The other options are less effective or counterproductive:
- B. Increase the temperature: Since the reaction is exothermic, increasing the temperature would shift the equilibrium to the left (toward the reactants), reducing the yield of Ca(OH)₂.
- C. Increase the pressure: This reaction does not involve gases, so changing the pressure would not significantly affect the equilibrium.
- D. Add an enzyme that can catalyze this reaction: While a catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction, it does not affect the equilibrium position or the total yield of products. It simply allows the system to reach equilibrium faster.
Thus, continuously removing Ca(OH)₂ is the best way to increase the total yield of lime water.
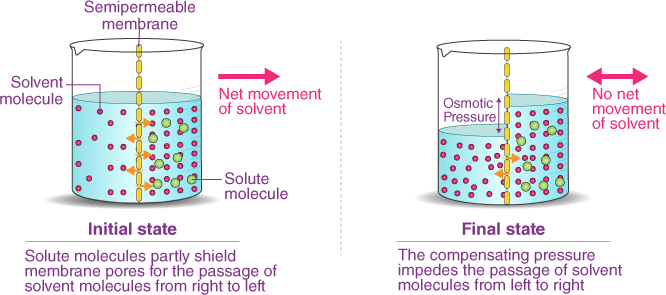
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Osmosis is the process by which water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, in order to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane. Selectively permeable membranes allow only certain molecules to pass through, while preventing the passage of others.
In osmosis, the movement of water molecules is driven by the concentration gradient of solutes, which cannot pass through the membrane. If one side of the membrane has a higher concentration of solutes than the other, water molecules will move from the side with the lower concentration of solutes to the side with the higher concentration of solutes, in an atempt to dilute the solutes and equalize the concentration on both sides.
Osmosis is important in many biological processes, including the uptake of water by plant roots, the regulation of water balance in animal cells, and the preservation of food by adding salt or sugar to create a hypertonic environment that inhibits bacterial growth.
 |
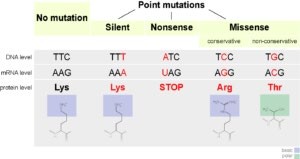
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
 |
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
This reaction is exothermic (releases heat), as indicated by the presence of "Heat" on the product side (C + Heat). According to Le Chatelier's Principle, when the temperature of an exothermic reaction is increased, the equilibrium shifts to counteract the added heat by favoring the reverse reaction (where heat is absorbed).
- As a result, the system will shift towards the left (toward the reactants, A and B), to consume the excess heat.
- Therefore, the concentrations of A and B will increase, and the concentration of C will decrease.
The other options do not align with this behavior:
- A. Incorrect, as the concentration of C will change (decrease).
- B. Incorrect, the reaction will shift away from equilibrium due to the temperature change.
- C. Incorrect, the concentration of C will not increase; it will decrease.
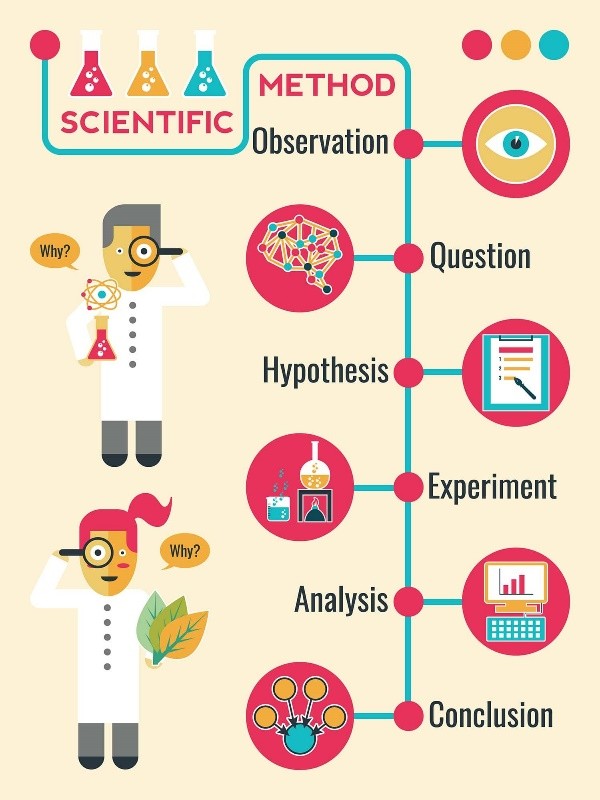
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The scientific method is a systematic approach used to answer questions or test hypotheses about the natural world. The steps involved in the scientific method are:
- Observation: This is the first step in the scientific method. It involves observing a phenomenon or a problem and gathering information about it.
- Hypothesis: After making an observation, a scientist forms a hypothesis, which is a tentative explanation for the phenomenon or problem.
- Prediction: Based on the hypothesis, the scientist makes a prediction about what will happen in an experiment or what they will observe.
- Experimentation: The scientist designs and conducts an experiment to test the hypothesis and prediction.
- Analysis: The data collected from the experiment are analyzed to determine if they support or refute the hypothesis.
- Conclusion: Based on the analysis of the data, the scientist draws a conclusion about whether the hypothesis is supported or refuted.
Option b) is incorrect because it starts with hypothesis before observation. Option c) is incorrect because prediction comes before experimentation. Option d) is incorrect because hypothesis comes after observation and data collection.
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
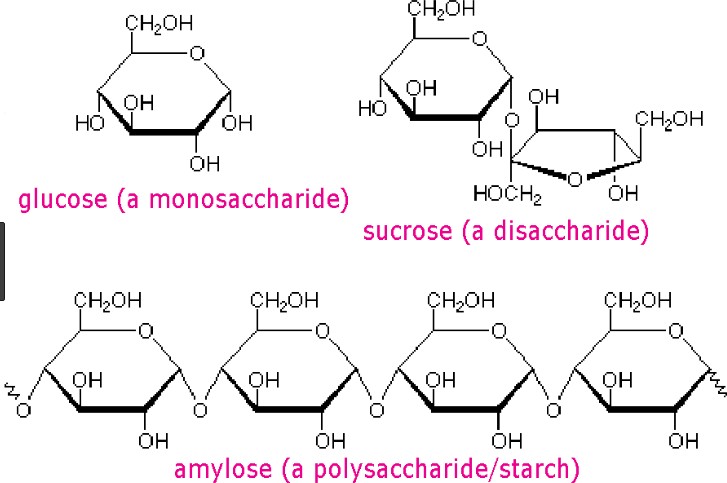
Carbohydrates are one of the main types of biomolecules and are composed of monomers called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are usually composed of 3 to 7 carbon atoms and have a general formula of (CH2O)n, where n is a number between 3 and 7. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond, they form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Option a) is incorrect because it describes the composition of a disaccharide, not a monosaccharide. Option
c) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be found in both plants and animals.
Option d) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be used for energy storage and
structural purposes, depending on their specific structure and function in the organism.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Electrons are subatomic particles that possess a very small mass compared to protons and neutrons. The mass of an electron is approximately 11836of the mass of a proton or neutron, making it negligible when calculating the atomic mass of an atom.
In atomic mass calculations, protons and neutrons are considered because they make up the bulk of the atom's mass:
- Proton: Positively charged, and each proton has a mass of about 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
- Neutron: Neutral charge, with a mass also close to 1 amu.
- Electron: Negligible mass, contributing very little to the atomic mass, which is why the atomic mass number is typically determined by the number of protons and neutrons.
Quarks are the fundamental constituents of protons and neutrons but are not typically referred to in terms of atomic mass.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
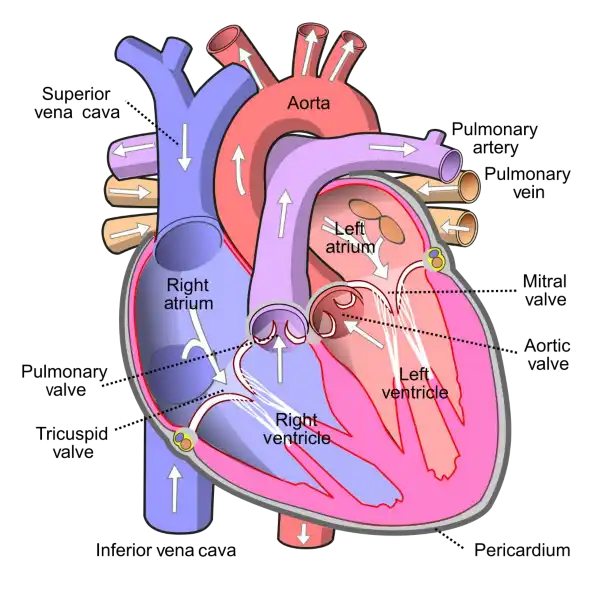
The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart and helps to regulate the flow of blood between these chambers. It consists of two leaflets or flaps that open and close in response to changes in pressure as the heart beats.
During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral valve opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. During systole, when the heart contracts to pump blood out of the left ventricle and into the systemic circulation, the mitral valve closes to prevent backflow of blood into the left atrium.
The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart that help to ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the circulatory system. Problems with the mitral valve, such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis, can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The scientific purpose of retracing the steps of a fatal expedition, such as the 1924 climb of Mount Everest, would primarily be to assess the factors that contributed to the earlier expedition's failure. By analyzing the conditions, decisions made, and circumstances surrounding the previous climb, the mountaineer can gain insights into potential dangers, challenges, and mistakes that were encountered, which can inform current climbing practices and safety measures.
Here's why the other options are less appropriate as primary scientific purposes:
- B. To measure the oxygen levels at high elevation: While measuring oxygen levels can be a scientific goal, it is not the main focus if the intent is to understand the failure of the previous expedition specifically.
- C. To identify routes that can be explored in future climbs: This could be a minor aspect of the climb, but the emphasis is on understanding the past tragedy rather than route exploration.
- D. To show that modern technology makes climbing safer: Although modern technology may improve safety, the primary purpose of the climb, given the context, would be to learn from historical events rather than to prove a point about technology.
Thus, the scientific purpose of such a climb would be to assess why the earlier expedition failed.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Water molecules primarily enter cells through the process of facilitated diffusion, specifically via aquaporins, which are specialized channel proteins that facilitate the rapid transport of water across the cell membrane. This process does not require energy (ATP) as it relies on the concentration gradient of water, allowing water to move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration.
Here’s why the other options are not correct in the context of water transport:
- A. Gated channels: While aquaporins can be gated, this term generally refers to channels that open and close in response to specific signals, which is not the primary mechanism for water transport in most cells.
- B. Electrochemical gradients: This term relates to the combined effect of electrical and chemical gradients across a membrane, typically for ions rather than water molecules directly. Water movement can be influenced by osmotic gradients but is not solely dependent on electrochemical gradients.
- D. Proton pumps: These are involved in transporting protons (H⁺ ions) across membranes, primarily for establishing an electrochemical gradient, not for the transport of water.
Thus, water molecules enter cells mainly by facilitated diffusion through aquaporins.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
