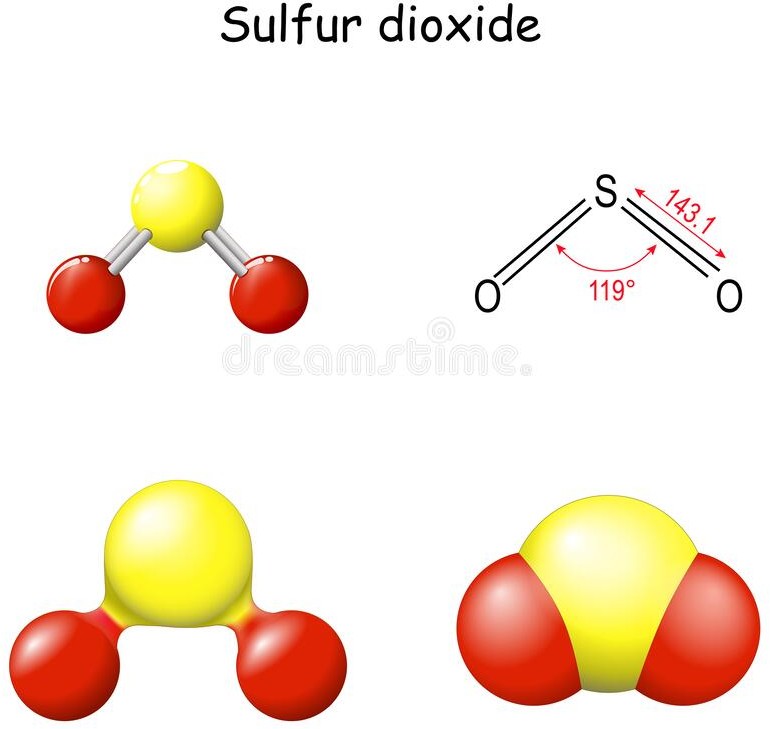
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule of sulphur dioxide (SO2)?
Linear
Trigonal planar
Bent
Tetrahedral
Correct Answer : C
The molecular geometry of a molecule of sulphur dioxide (SO2) is bent or V-shaped. This is because of the presence of two lone pairs on the sulfur atom, which cause repulsion and distort the bond angles in the molecule.
SO2 has a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms by double bonds. The two double bonds and the two lone pairs of electrons on sulfur result in a trigonal planar arrangement of electron pairs around the sulfur atom. However, the repulsion between the lone pairs causes the two oxygen atoms to be pulled closer together, resulting in a bent or V-shaped molecular geometry.
The bent molecular geometry of SO2 affects its properties, such as its polarity and reactivity. SO2 is a polar molecule due to the asymmetric distribution of electrons, which results in a partial positive charge on the sulfur atom and partial negative charges on the oxygen atoms. This polarity makes SO2 a good solvent and reactant in chemical reactions, as well as a contributor to air pollution and acid rain.
 |
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
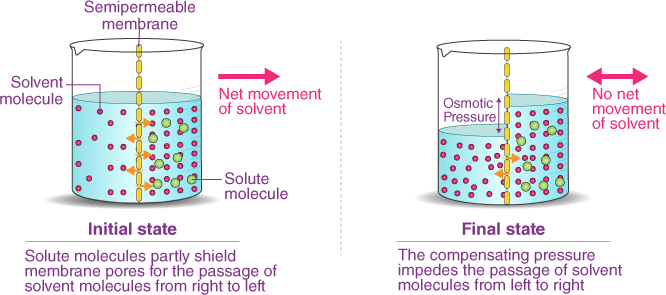
Osmosis is the process by which water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, in order to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane. Selectively permeable membranes allow only certain molecules to pass through, while preventing the passage of others.
In osmosis, the movement of water molecules is driven by the concentration gradient of solutes, which cannot pass through the membrane. If one side of the membrane has a higher concentration of solutes than the other, water molecules will move from the side with the lower concentration of solutes to the side with the higher concentration of solutes, in an atempt to dilute the solutes and equalize the concentration on both sides.
Osmosis is important in many biological processes, including the uptake of water by plant roots, the regulation of water balance in animal cells, and the preservation of food by adding salt or sugar to create a hypertonic environment that inhibits bacterial growth.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
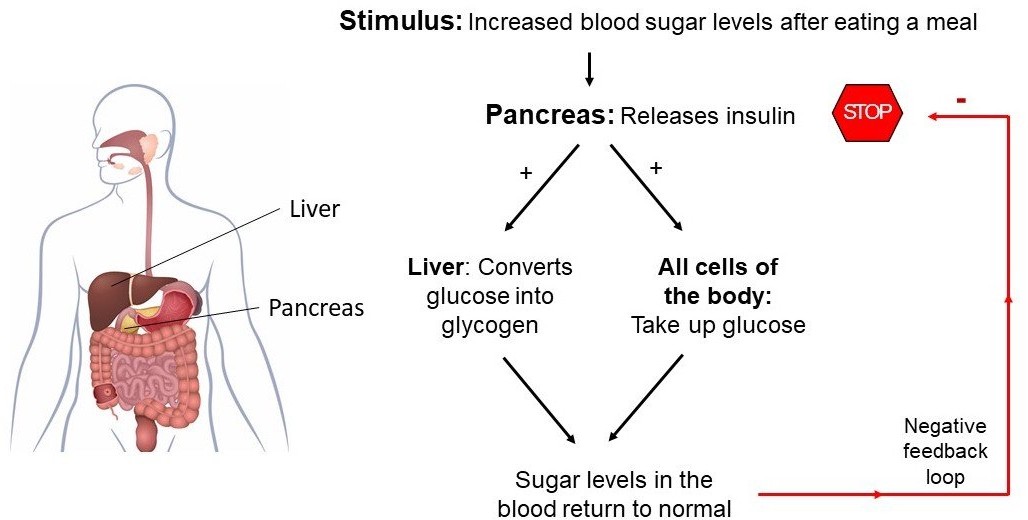
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating the levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. After a person eats a meal, the levels of glucose in the blood rise, which stimulates the pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin acts on various cells in the body, particularly those in the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue, to promote the uptake, use, and storage of glucose.
Insulin helps to lower the levels of glucose in the blood by increasing the uptake of glucose by cells, stimulating the liver and muscle cells to store glucose in the form of glycogen, and inhibiting the production and release of glucose by the liver. This process is known as glucose homeostasis, and it helps to keep the levels of glucose in the blood within a normal range.
Deficiencies or abnormalities in insulin production or function can lead to a range of metabolic disorders, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin, while in type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The unit used to indicate length is the meter (m). It is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Electrons are subatomic particles that possess a very small mass compared to protons and neutrons. The mass of an electron is approximately 11836of the mass of a proton or neutron, making it negligible when calculating the atomic mass of an atom.
In atomic mass calculations, protons and neutrons are considered because they make up the bulk of the atom's mass:
- Proton: Positively charged, and each proton has a mass of about 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
- Neutron: Neutral charge, with a mass also close to 1 amu.
- Electron: Negligible mass, contributing very little to the atomic mass, which is why the atomic mass number is typically determined by the number of protons and neutrons.
Quarks are the fundamental constituents of protons and neutrons but are not typically referred to in terms of atomic mass.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
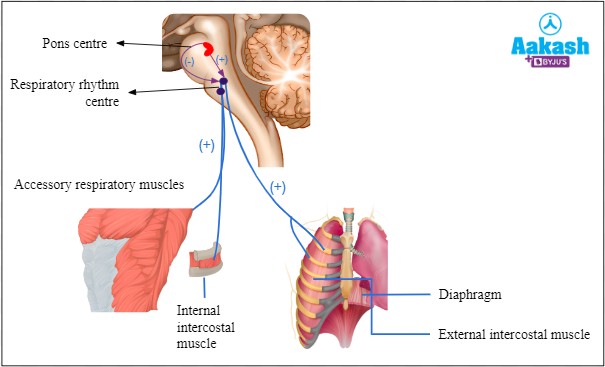
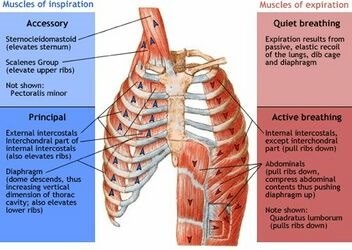
Diaphragm is responsible for regulating breathing rate and depth. It is a dome-shaped muscle located at the
bottom of the chest cavity that contracts and relaxes to help move air in and out of the lungs.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
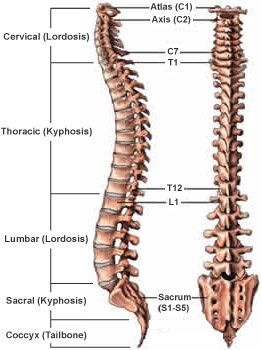
The vertebral column, also known as the spine or spinal column, is a series of bones called vertebrae that extend from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord. The five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards, are:
- Cervical: This region is made up of seven vertebrae and is located in the neck. The first two cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specialized to allow for head movement.
- Thoracic: This region is made up of twelve vertebrae and is located in the upper and middle back. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae and articulate with the ribs.
- Lumbar: This region is made up of five vertebrae and is located in the lower back. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebrae.
- Sacral: This region is made up of five fused vertebrae and is located in the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior wall of the pelvis and articulates with the hip bones.
- Coccygeal: This region is made up of four fused vertebrae and is located at the base of the vertebral column. The coccyx, or tailbone, provides atachment points for muscles and ligaments.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing. It separates the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, allowing air to flow into the lungs. When it relaxes, it moves upward and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, forcing air out of the lungs.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
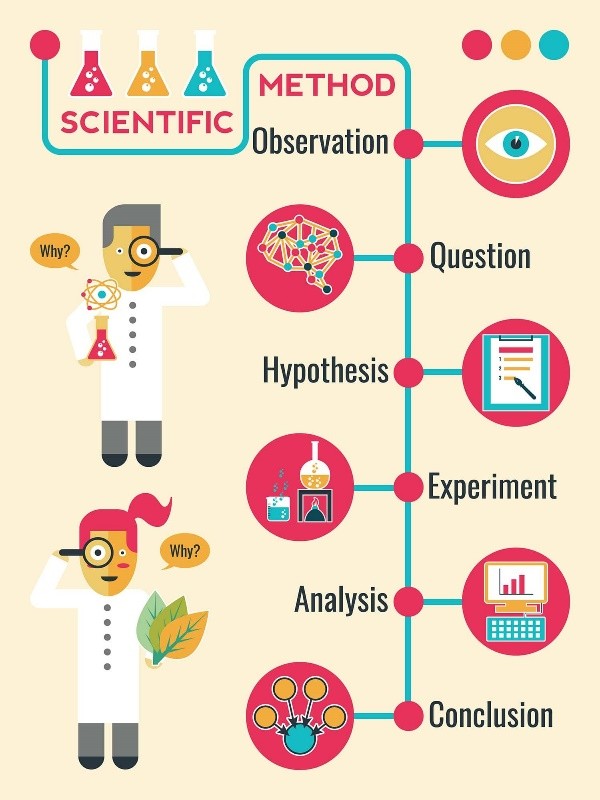
The scientific method is a systematic approach used to answer questions or test hypotheses about the natural world. The steps involved in the scientific method are:
- Observation: This is the first step in the scientific method. It involves observing a phenomenon or a problem and gathering information about it.
- Hypothesis: After making an observation, a scientist forms a hypothesis, which is a tentative explanation for the phenomenon or problem.
- Prediction: Based on the hypothesis, the scientist makes a prediction about what will happen in an experiment or what they will observe.
- Experimentation: The scientist designs and conducts an experiment to test the hypothesis and prediction.
- Analysis: The data collected from the experiment are analyzed to determine if they support or refute the hypothesis.
- Conclusion: Based on the analysis of the data, the scientist draws a conclusion about whether the hypothesis is supported or refuted.
Option b) is incorrect because it starts with hypothesis before observation. Option c) is incorrect because prediction comes before experimentation. Option d) is incorrect because hypothesis comes after observation and data collection.
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
One of the key differences between skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles is the presence of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle tissue. These discs are specialized structures that facilitate communication and synchronization between cardiac muscle cells, allowing the heart to contract as a unified organ.
The other options are incorrect:
- A. Skeletal muscles are autorhythmic, whereas cardiac muscles are not: This is incorrect because cardiac muscles are autorhythmic; they can generate their own rhythmic contractions. Skeletal muscles require nervous system stimulation to contract.
- C. Skeletal muscles are found in the viscera, whereas cardiac muscles are found in the cranium: This is incorrect; skeletal muscles are primarily associated with the skeleton (attached to bones) and are not typically found in the viscera, while cardiac muscle is found in the heart.
- D. Cardiac muscles are voluntary, whereas skeletal muscles are involuntary: This is incorrect; skeletal muscles are voluntary (under conscious control), while cardiac muscles are involuntary (not under conscious control).
Therefore, the correct distinction is that cardiac muscles contain intercalated discs, while skeletal muscles do not.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
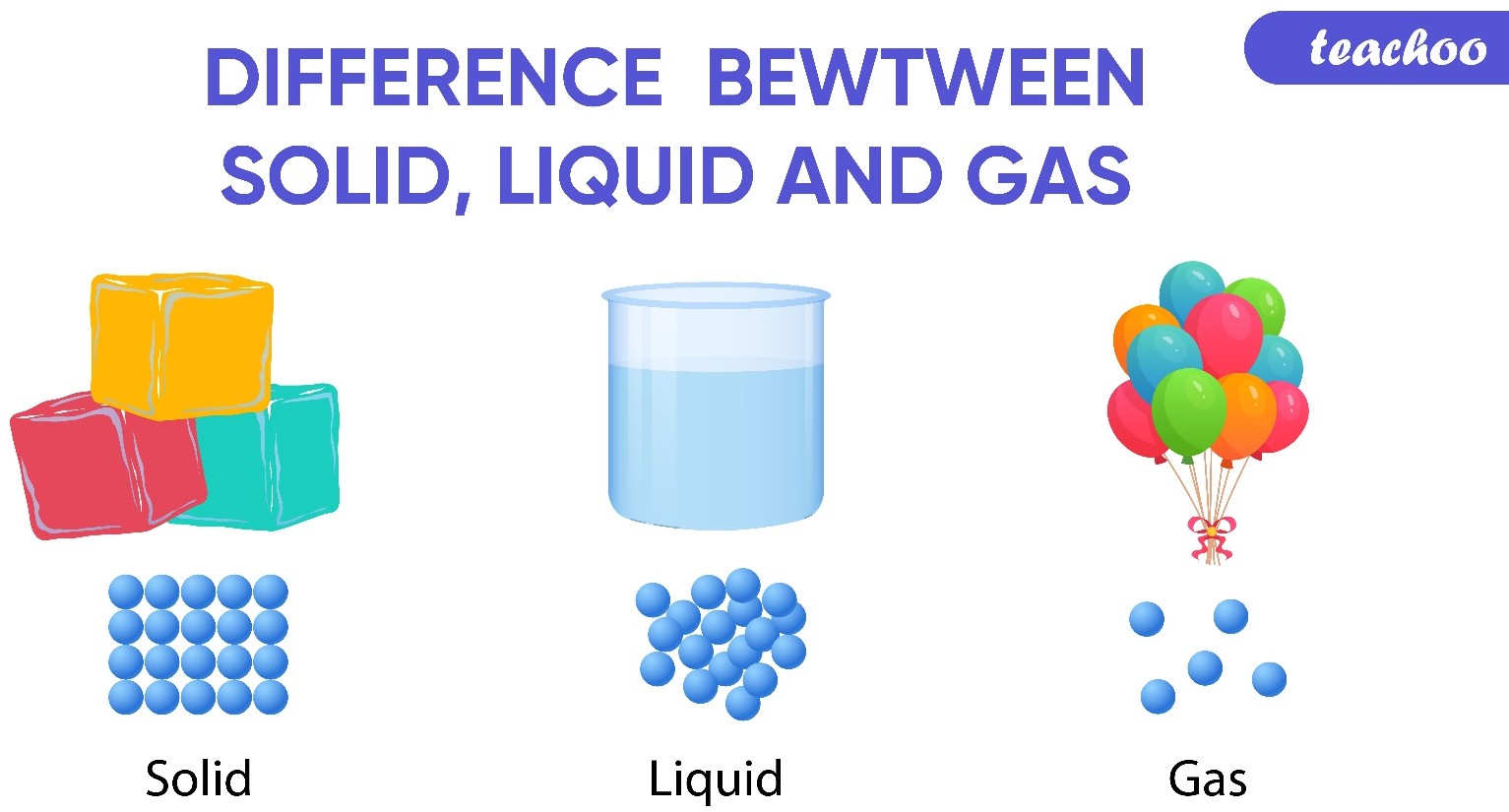
The main difference between a solid and a liquid is their physical state and the way their particles are arranged. In a solid, the particles are tightly packed together and have a fixed position, which gives the solid a definite shape and volume. Solids are also characterized by their high density, low compressibility, and high thermal conductivity.
In contrast, the particles in a liquid are more loosely packed and can move around each other, which allows the liquid to take the shape of its container. Liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape, which means they can be poured or spilled. Liquids also have a lower density than solids, are more compressible than solids, and have lower thermal conductivity than solids.
Option b) is incorrect because it describes the properties of a gas, not a liquid. Option c) is incorrect because solids and liquids have different physical properties. Option d) is incorrect because it describes the properties of a gas, not a liquid or a solid.
 |
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
