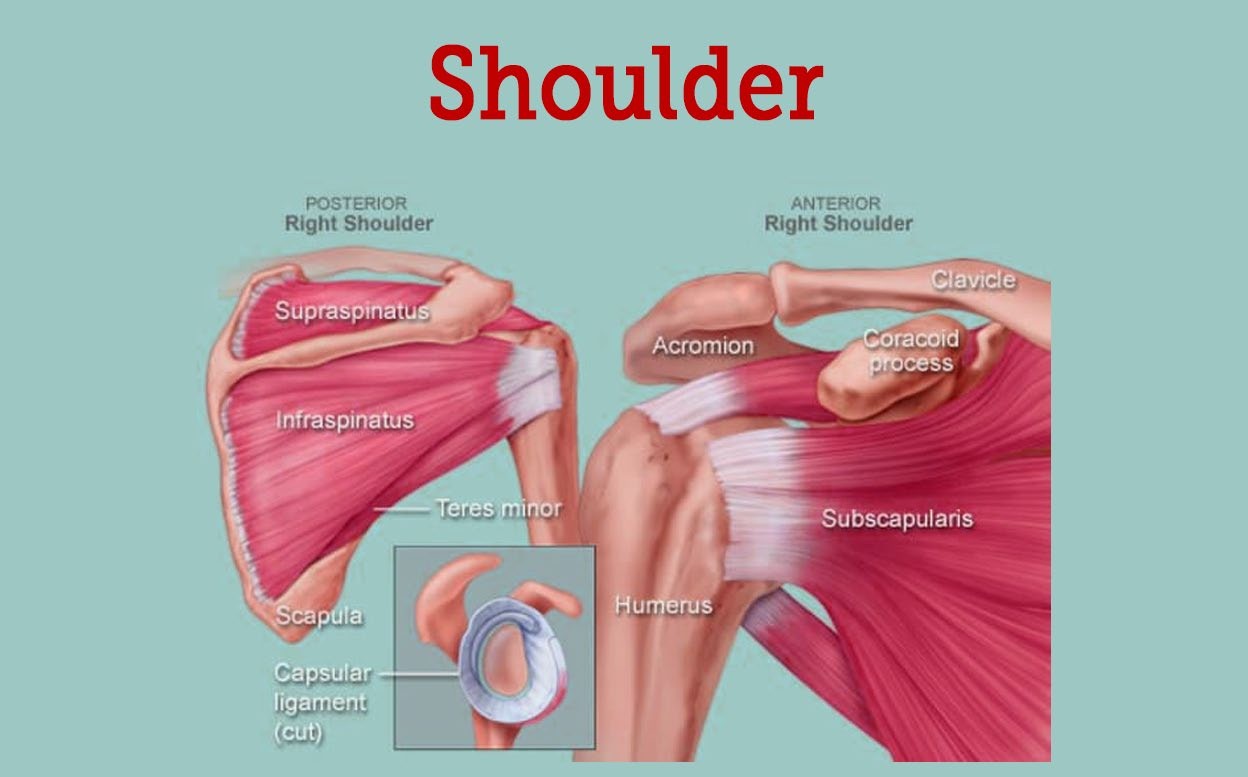
What is the name of the joint that allows for rotation of the arm at the shoulder?
Elbow joint
Hip joint
Knee joint
Shoulder joint
Correct Answer : D
 |
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
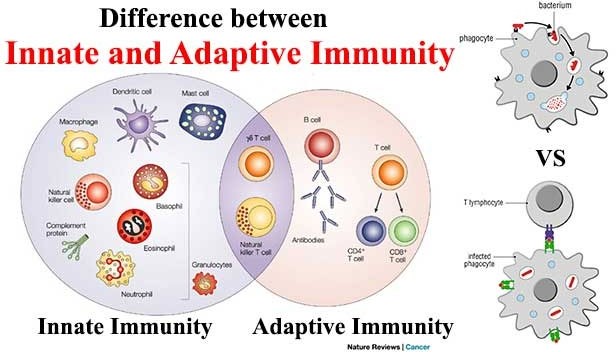
Innate immunity and adaptive immunity are two arms of the immune system that work together to protect the body from pathogens. Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is present at birth. It includes physical and chemical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes, and antimicrobial peptides, as well as cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells that can quickly recognize and atack pathogens. Innate immunity is nonspecific, meaning it responds to a wide variety of pathogens in a similar way.
Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is acquired after exposure to pathogens. It involves the production of antibodies and activation of T cells, which are specific to particular pathogens. Adaptive immunity takes longer to develop than innate immunity, but it provides a more specific and targeted response to pathogens. Once the adaptive immune system has been activated against a particular pathogen, it can provide long-term protection against future infections with that pathogen.
Option b) is incorrect because innate immunity is nonspecific while adaptive immunity is specific. Option c) is incorrect because antibodies are a part of adaptive immunity while T cells can be a part of both innate and adaptive immunity. Option d) is incorrect because adaptive immunity can provide long-term protection, while innate immunity provides immediate but short-lived protection.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The kidneys secrete a number of hormones, which are important for normal functioning of the body.
If blood pressure falls, renin is secreted by the kidneys to constrict the small blood vessels, thereby increasing blood pressure. If the kidneys aren’t functioning correctly, too much renin can be produced, increasing blood pressure and sometimes resulting in hypertension (high blood pressure). This is why a number of people with kidney diseases also have high blood pressure.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
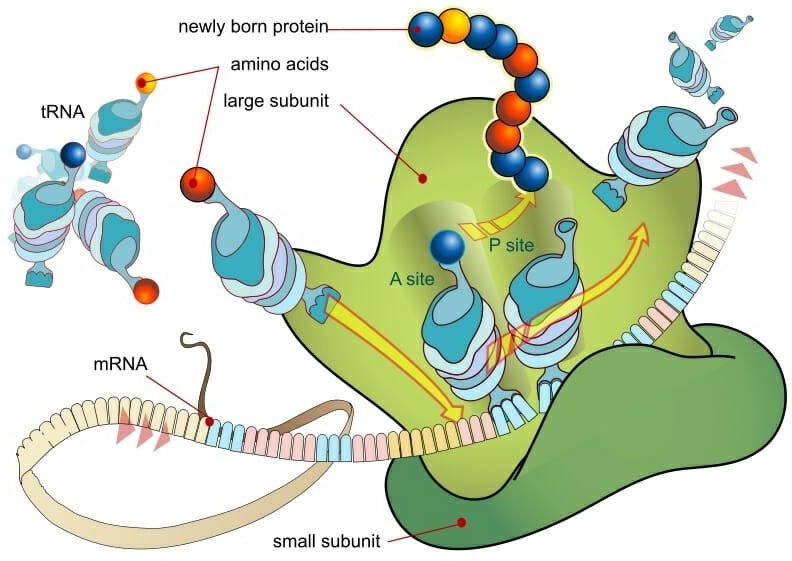
Ribosomes are small, spherical structures found in all living cells, including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Their primary function is to synthesize proteins using the genetic information stored in the cell's DNA. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, one large and one small, that come together during protein synthesis.
Ribosomes read the genetic information stored in mRNA (messenger RNA) and use this information to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing protein chain until it reaches the end of the mRNA and the protein is complete.
Proteins are essential for a wide variety of cellular functions, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and transporting molecules across cell membranes. Therefore, ribosomes play a critical role in the overall function and survival of a cell.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
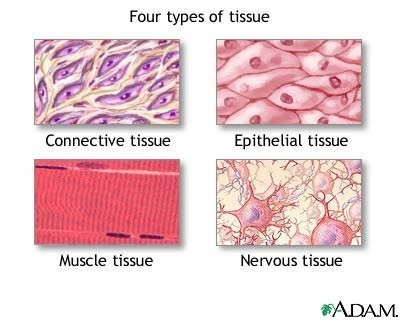
Exocrine glandular is not one of the four primary ssue types found in the human body. The four primary ssue types are epithelial, nervous, connective, and muscle.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
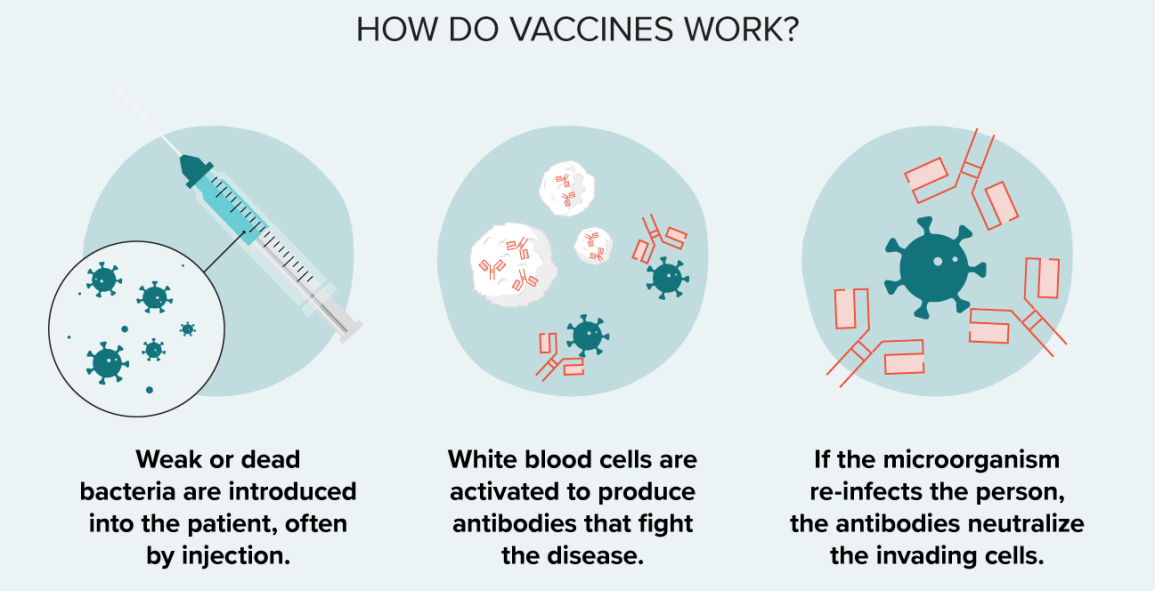
Vaccines are a type of preventative medicine that work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen (such as a virus or bacteria) or to a piece of the pathogen (such as a protein or sugar) that triggers an immune response in the body. This exposure allows the body to develop immunity to the pathogen without getting sick from the full-blown disease. Once the immune system has been primed, it can recognize and quickly respond to the pathogen if it is encountered again in the future, providing protection against the disease.
It is a common misconception that vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against. This is not true. While some vaccines may cause mild symptoms such as a low-grade fever or soreness at the injection site, they do not cause the full-blown disease.
Vaccines provide active immunity, meaning that the body produces its own antibodies against the pathogen, rather than receiving pre-made antibodies as in passive immunity. Additionally, vaccines can be effective against both bacterial and viral infections, depending on the specific vaccine.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
- A. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum → A specialized endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells that stores and releases calcium for muscle contraction. ❌
- B. Muscle Fiber → Another name for a muscle cell, which is a long, cylindrical, multinucleated cell that makes up muscle tissue. ✅
- C. Sarcolemma → The cell membrane of a muscle fiber, which surrounds the muscle cell. ❌
- D. Myofilament → Protein structures (actin and myosin) within a muscle fiber that are responsible for contraction. ❌
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
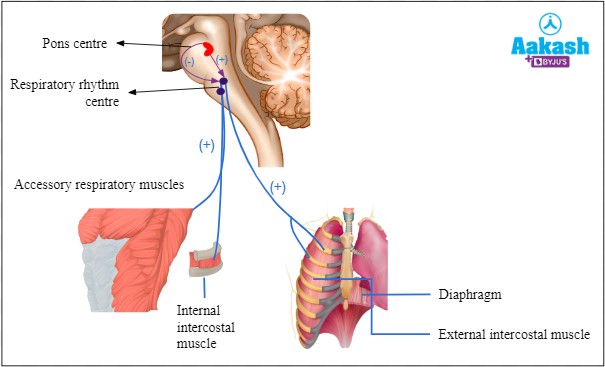
The diaphragm is responsible for regulating breathing rate and depth. It is a dome-shaped muscle located at the bottom of the chest cavity that contracts and relaxes to help move air in and out of the lungs.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
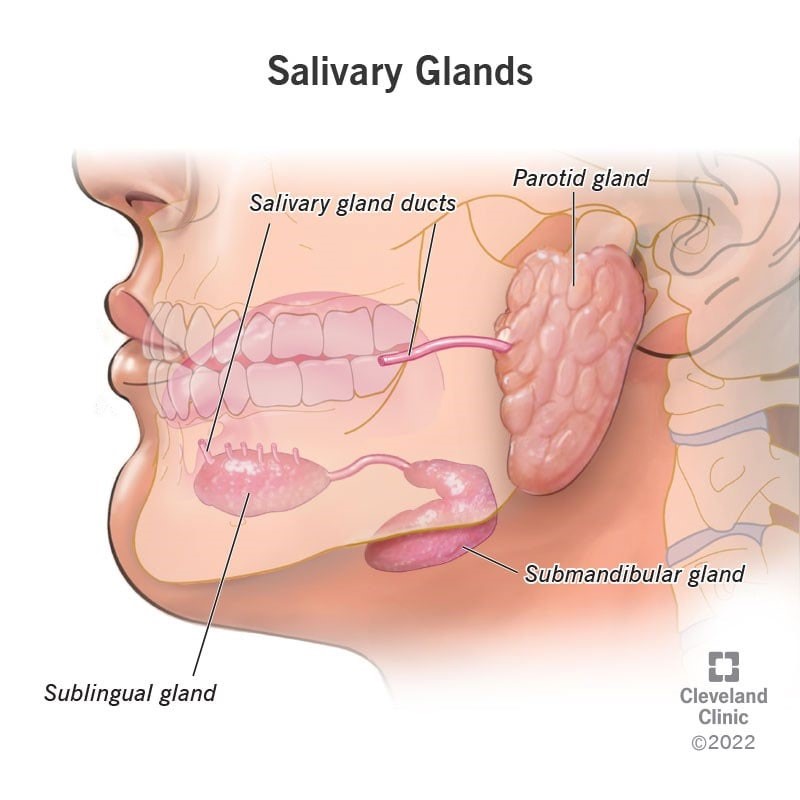
The three major pairs of salivary glands are the parod glands, sublingual glands, and submandibular glands. The parotid glands are located just in front of your ears. The sublingual glands are below either side of your tongue, under the floor of your mouth. The submandibular glands are located below your jaw ¹.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The nurse can logically conclude that:
✅ Treatment A results in the shortest recovery time.
- The data shows that Treatment A has a mean recovery time of 3 days, which is the shortest compared to Treatment B (5 days) and Treatment C (7 days).
The other statements are not supported by the given data:
❌ "Treatment C enhances patient satisfaction more than the others."
- There is no information about patient satisfaction, only recovery times.
❌ "Treatment B is as effective as Treatment A."
- Treatment B has a longer recovery time (5 days) compared to Treatment A (3 days), so it is not equally effective in terms of recovery speed.
❌ "Treatments A and B provide the same rate of recovery."
- Treatment A has a faster recovery time than Treatment B, so they do not have the same recovery rate.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
- Frontal Plane (Coronal Plane) → Divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) halves. ❌
- Transverse Plane → A horizontal plane that divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) halves. ✅
- Sagittal Plane → Divides the body into left and right halves. ❌
- Coronal Plane → Another name for the Frontal Plane, which divides the body into front and back. ❌
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
