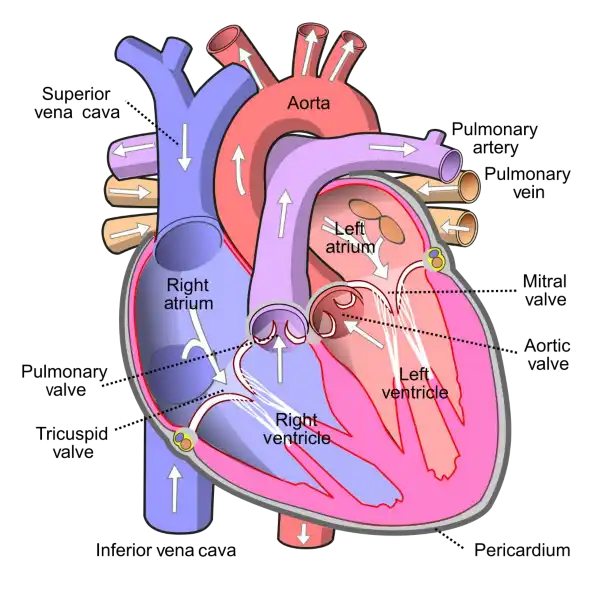
What is the name of the valve that separates the left atrium and left ventricle in the heart?
Aortic valve
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
Pulmonary valve
Correct Answer : B
The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart and helps to regulate the flow of blood between these chambers. It consists of two leaflets or flaps that open and close in response to changes in pressure as the heart beats.
During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral valve opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. During systole, when the heart contracts to pump blood out of the left ventricle and into the systemic circulation, the mitral valve closes to prevent backflow of blood into the left atrium.
The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart that help to ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the circulatory system. Problems with the mitral valve, such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis, can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure.
 |
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
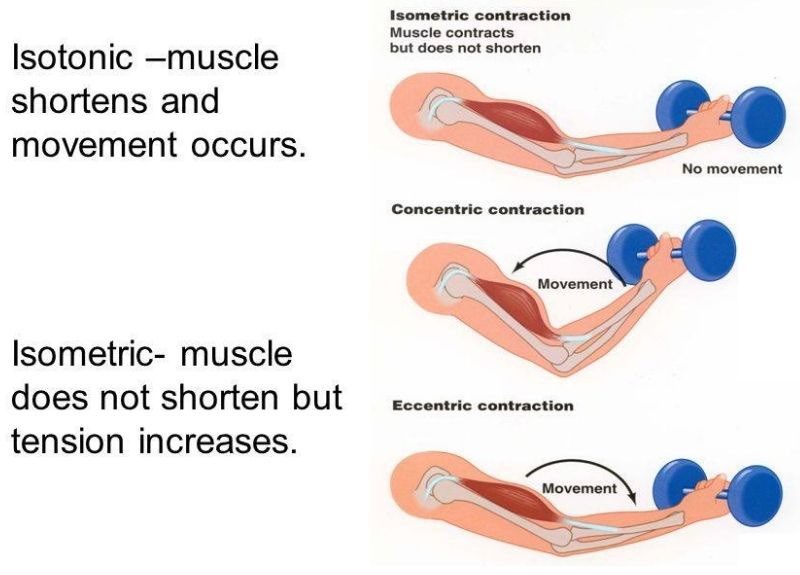
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Isotonic and isometric contractions are two types of muscle contractions that differ in the amount of force produced and the movement of the muscle. In isotonic contractions, the muscle changes length and produces movement, such as lifting a weight. The force generated by the muscle remains constant throughout the movement. Isotonic contractions can be further classified as concentric contractions, in which the muscle shortens as it contracts, and eccentric contractions, in which the muscle lengthens as it contracts.
In contrast, isometric contractions occur when the muscle generates force without changing its length or producing movement. For example, holding a weight in a fixed position without moving it requires an isometric contraction. In an isometric contraction, the force generated by the muscle increases up to a maximum and then remains constant. Isometric contractions can be used to build strength and endurance in the muscle, but they do not produce movement.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The renal vein is responsible for draining oxygen-depleted blood from the kidneys and carrying it back to the heart through the inferior vena cava.
The other options refer to different structures:
- B. Renal Artery: Brings oxygenated blood to the kidneys, not draining it.
- C. Urethra: Transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, not involved in blood flow.
- D. Ureter: Carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder, also not related to blood drainage.
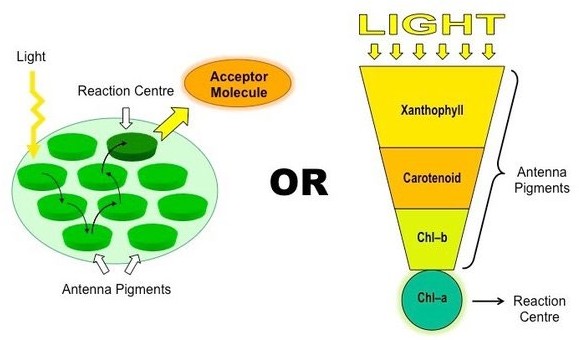
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants. It is a green pigment that is essential for capturing light energy from the sun and converting it into chemical energy that can be used by the plant. Chlorophyll a absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red parts of the spectrum, and reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic green color
Chlorophyll b is another type of chlorophyll that is also involved in photosynthesis, but it is not as abundant as chlorophyll a. Chlorophyll b absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and orange parts of the spectrum and reflects yellow-green light.
Carotenoids are pigments that are present in many plants and are involved in photosynthesis as well as protecting the plant from damage caused by excess light. Carotenoids are responsible for the orange, yellow, and red colors of many fruits and vegetables.
Anthocyanins are pigments that give plants their red, purple, and blue colors. While they are not directly involved in photosynthesis, they play a role in atracting pollinators and protecting the plant from damage caused by UV radiation.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of an acid or base are added. Buffers work by neutralizing added hydrogen ions (H⁺) or hydroxide ions (OH⁻), thereby maintaining a relatively stable pH. Buffers are made up of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
- A. It decreases the pH of the solution: This is incorrect because a buffer does not always decrease pH; it resists changes in both directions.
- C. It causes the pH of a solution to become neutral: Incorrect because buffers do not necessarily make a solution neutral; they stabilize pH around a certain value.
- D. It permanently binds hydrogen ions: Incorrect as the binding is reversible, which is essential for maintaining pH balance.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Spirometry is a common pulmonary function test that measures pulmonary ventilation, specifically assessing the volume and flow of air that can be inhaled and exhaled from the lungs. It provides important information about lung function and can help diagnose various respiratory conditions.
The other options do not relate to spirometry:
- A. Urinary capacity of the bladder: This is measured by urodynamics or bladder capacity tests, not spirometry.
- B. Volume of blood in the body: This can be estimated using different methods, such as dilution techniques or imaging, but not spirometry.
- D. Number of turns in the small intestine: This relates to the anatomy and function of the digestive system and is not measured by spirometry.
Thus, spirometry specifically evaluates how well the lungs are functioning in terms of air movement.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
In the given exothermic reaction:
CaO + H2O ⇌ Ca(OH)2 + heat
To increase the total yield of lime water (Ca(OH)₂), you can apply Le Chatelier's Principle, which states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the disturbance.
- A. Continuously remove Ca(OH)₂: By removing the product (Ca(OH)₂) as it forms, the equilibrium will shift to the right, favoring the formation of more Ca(OH)₂. This is the most effective way to increase the yield.
The other options are less effective or counterproductive:
- B. Increase the temperature: Since the reaction is exothermic, increasing the temperature would shift the equilibrium to the left (toward the reactants), reducing the yield of Ca(OH)₂.
- C. Increase the pressure: This reaction does not involve gases, so changing the pressure would not significantly affect the equilibrium.
- D. Add an enzyme that can catalyze this reaction: While a catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction, it does not affect the equilibrium position or the total yield of products. It simply allows the system to reach equilibrium faster.
Thus, continuously removing Ca(OH)₂ is the best way to increase the total yield of lime water.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
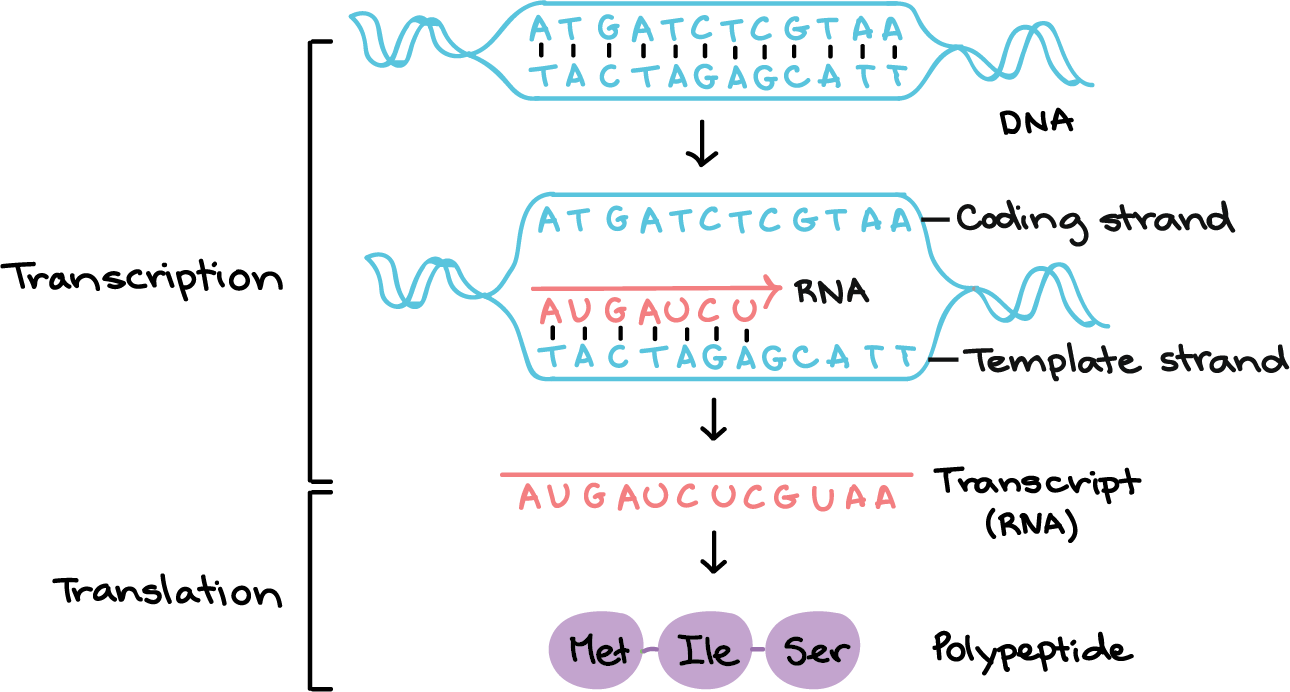
Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied into RNA. During transcription, the DNA molecule unwinds and RNA polymerase reads the DNA sequence and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule using the DNA as a template.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
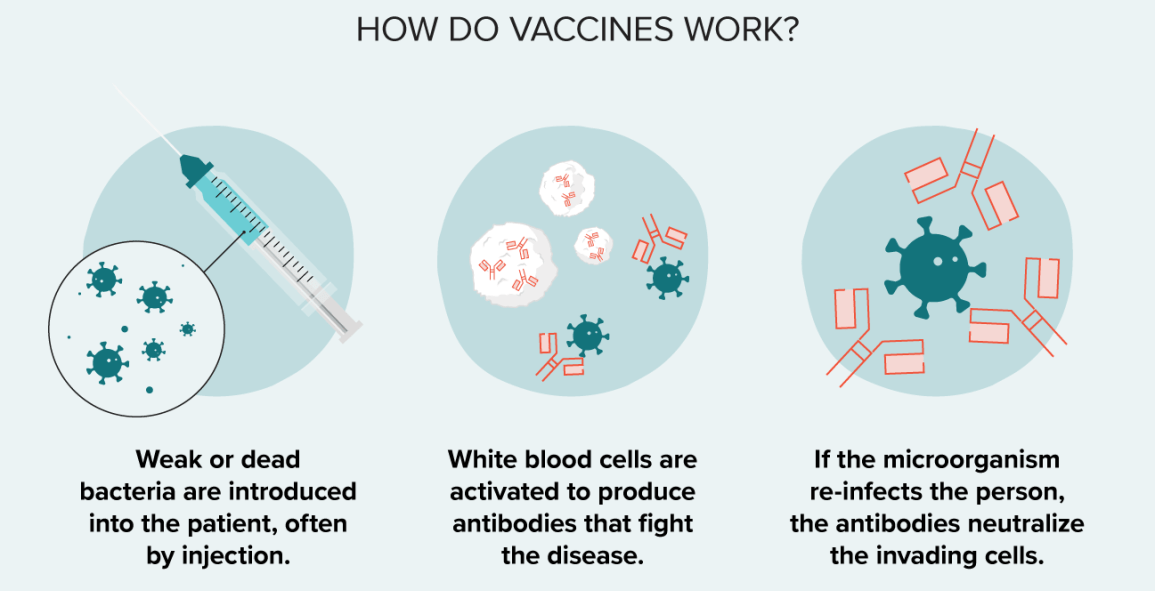
Vaccines are a type of preventative medicine that work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen (such as a virus or bacteria) or to a piece of the pathogen (such as a protein or sugar) that triggers an immune response in the body. This exposure allows the body to develop immunity to the pathogen without getting sick from the full-blown disease. Once the immune system has been primed, it can recognize and quickly respond to the pathogen if it is encountered again in the future, providing protection against the disease.
It is a common misconception that vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against. This is not true. While some vaccines may cause mild symptoms such as a low-grade fever or soreness at the injection site, they do not cause the full-blown disease.
Vaccines provide active immunity, meaning that the body produces its own antibodies against the pathogen, rather than receiving pre-made antibodies as in passive immunity. Additionally, vaccines can be effective against both bacterial and viral infections, depending on the specific vaccine.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
In the case of methanol poisoning, the metabolism of methanol to formaldehyde is a critical concern because formaldehyde is highly toxic. Ethanol is used as a treatment because it competes with methanol for the same enzyme, methanol oxidase (or alcohol dehydrogenase), effectively inhibiting the metabolism of methanol. By inhibiting the enzyme, ethanol reduces the conversion of methanol to formaldehyde, thereby minimizing its toxic effects.
Here’s why the other options are not suitable treatments:
- A. Methanol oxidase, which would increase the rate of the reaction: This would not be a treatment; it would worsen the situation by promoting the conversion of methanol to toxic formaldehyde.
- B. Methanol, which would saturate the methanol oxidase: This option would also be harmful, as adding more methanol would only lead to more formaldehyde production.
- C. Ice, which would shift the equilibrium of the reaction: The reaction is not a typical equilibrium reaction in this context, and cooling the body does not address the metabolic conversion of methanol to formaldehyde.
Thus, administering ethanol is an effective treatment to prevent the toxic effects of methanol metabolism.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
