What type of bond forms between nitrogen and oxygen, and why?
Ionic, because electrons are shared
Covalent, because electrons are shared
Ionic, because electrons are transferred
Covalent, because electrons are transferred
Correct Answer : B
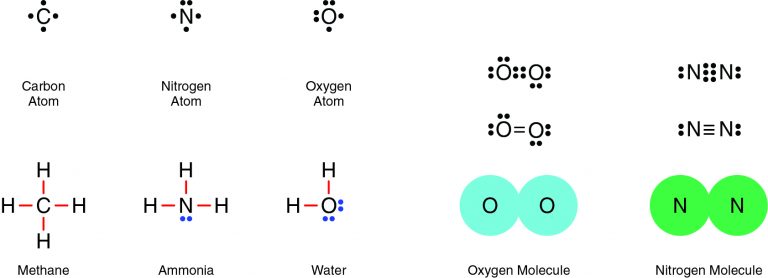
Nitrogen and oxygen are both nonmetals, which means they will share electrons in a covalent bond. For example, two oxygen atoms form a double bond, in which two pairs of electrons (four electrons total) are shared. Similarly, two nitrogen atoms form a molecule with a triple bond, in which three pairs of electrons (six electrons total) are shared.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Autotrophs are organisms that use basic raw materials in nature, like the sun, to make energy-rich biomolecules. Minerals are naturally inorganic.
Autotrophsare organisms that make energy-rich biomolecules from raw material in nature. They do this by using basic energy sources such the sun. This explains why most autotrophs rely on photosynthesis to transform sunlight into usable food that can produce energy necessary for life. Plants and certain species of bacteria are autotrophs.
Autotrophs, such as plants, use carbon dioxide (CO2) during photosynthesis to create chemical energy in the form of sugar molecules (like glucose) for growth.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
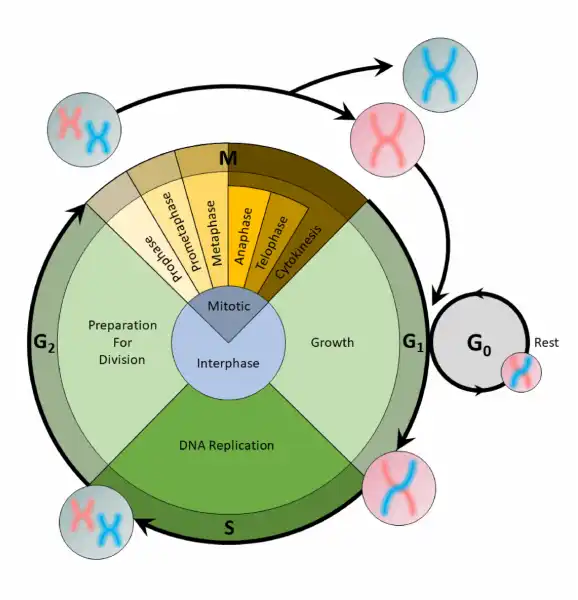
Before mitosis or meiosis occurs, interphase must happen. This is when the cell cycle takes place. The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases:interphaseand theM (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2phases make up interphase.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
After scientists were able to view cells under the microscope they formulated the cell theory. One part of this theory concluded that all cells are alive. They also represent the basic unit of life.
All living things are made of cells. Cells are the smallest structural units and basic building blocks of living things. Cells contain everything necessary to keep living things alive. Varying in size and shape, cells carry out specialized functions. This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Mendel developed theories of genetics that scientists around the world use today.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants eitherself-pollinateorcross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are eitherdominantorrecessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information calledgenes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual ishomozygousfor that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual isheterozygousfor that trait. Each copy of a factor, orgene, is called anallele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, orphenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is itsgenotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
One step of the scientific method is to analyze information or data collected from the experiment to conclude whether the hypothesis is supported.
Recall that these make up thescientific method,described below:
- Problem:The question created because of an observation.Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research:Reliable information available about what is observed.Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis:A predicted solution to the question or problem.Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment:A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of anindependent variablethat the researcher modifies and adependent variablethat changes due to the independent variable. They also include acontrol groupused as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe:Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion:State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate:Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The protein disc that holds two sister chromatids together is what collectively makes a chromosome. A gene is a segment of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, which transmits information from parent to offspring. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. A chromosome is a rod-shaped structure that forms when a single DNA molecule and its associated proteins coil tightly before cell division.
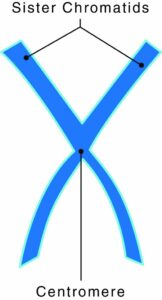
Chromosomes have two components:
- Chromatids: two copies of each chromosome
- Centromeres: protein discs that attach the chromatids together
Human cells have 23 sets of different chromosomes. The two copies of each chromosome are called homologous chromosomes, or homologues. An offspring receives one homologue from each parent. When a cell contains two homologues of each chromosome, it is termed diploid (2n). A haploid (n) cell contains only one homologue of each chromosome. The only haploid cells humans have are the sperm and eggs cells known as gametes.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The primary function of the respiratory system is to provide oxygen to and remove carbon dioxide from the body. In addition to gas exchange, the respiratory system enables a person to breathe. Breathing, or inhalation, is essential to life. It is the mechanism that provides oxygen to the body. Without oxygen, cells are unable to perform their functions necessary to keep the body alive. The primary muscle of inspiration is the diaphragm. Known as the chest cavity, this dome shaped structure flattens when it contracts. The rib cage moves outward, allowing outside air to be drawn into the lungs. During relaxation, the diaphragm returns to its dome shape and the rib cage moves back to its natural position. This causes the chest cavity to push air out of the lungs.
The respiratory system can be functionally divided into two parts:
- Air-conducting portion: Air is delivered to the lungs. This region consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract—specifically, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
- Gas exchange portion: Gas exchange takes place between the air and the blood. This portion includes the lungs, alveoli, and capillaries.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
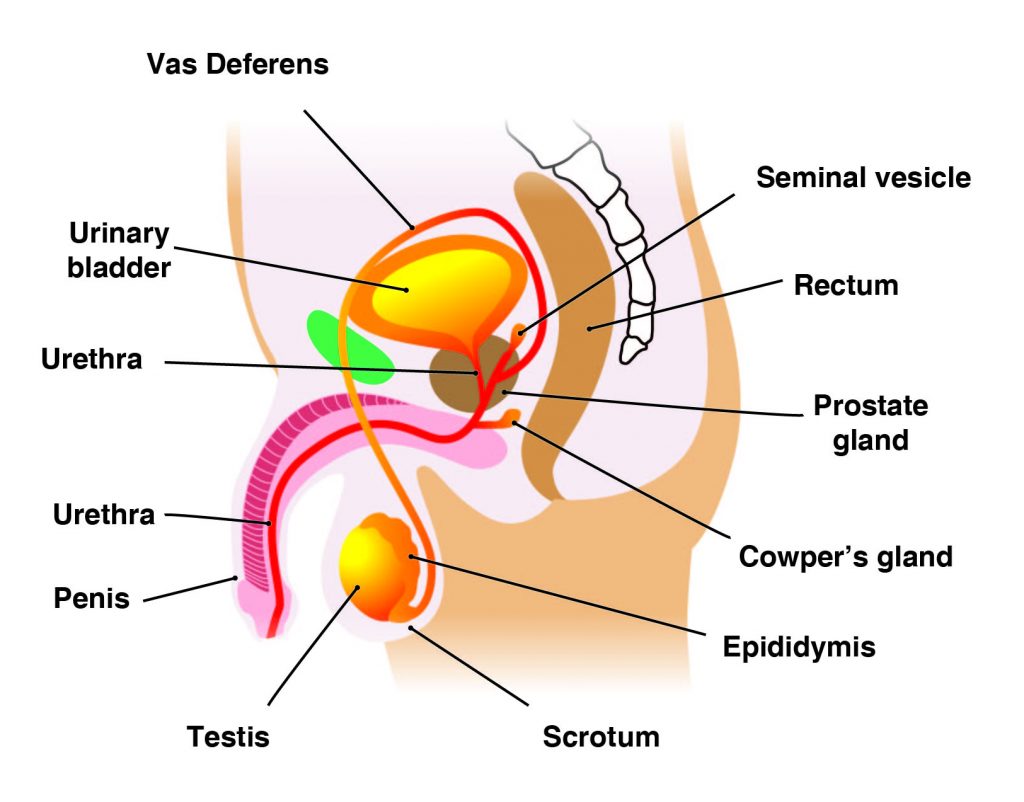
The main male reproductive organs are thepenisand thetesticles, which are located external to the body. The penis is composed of a long shaft and a bulbous end called the glans penis. The glans penis is usually surrounded by an extension of skin called the foreskin.
Thetestes(analogous to the female ovaries), or testicles, are retained in a pouch of skin called thescrotum, which descends from the base of the penis. The scrotum contains nerves and blood vessels needed to support the testicles’ functions. Each testicle (or testis) produces sperm (analogous to the female ova), which are passed into a series of coiled tubules called theepididymis. The epididymis stores and nurtures sperm until they are passed into thevas deferens, a tubule that is about 30 centimeters long, extending from the testicle into the pelvis and ending at the ejaculatory duct.
The epididymis and vas deferens are supported by several accessory glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the Cowper glands) that produce fluid components of semen and support the sperm cells.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Theaging processaffects hormone activity in one of three ways: their secretion can decrease, remain unchanged, or increase.
Hormones thatdecrease secretioninclude the following:
- Estrogen (in women)
- Testosterone (in men)
- Growth hormone
- Melatonin
Inwomen, the decline in estrogen levels leads to menopause. Inmen, testosterone levels usually decrease gradually. Decreased levels of growth hormone may lead to decreased muscle mass and strength. Decreased melatonin levels may play an important role in the loss of normal sleep-wake cycles (circadian rhythms) with aging.
Hormones that usually remainunchangedorslightly decreaseinclude the following:
- Cortisol
- Insulin
- Thyroid hormones
Hormones that mayincrease secretionslevels include the following:
Parathyroid hormone
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Norepinephrine
- Epinephrine, in the very old
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Nitrogen and oxygen are both nonmetals, which means they will share electrons in a covalent bond. For example, two oxygen atoms form a double bond, in which two pairs of electrons (four electrons total) are shared. Similarly, two nitrogen atoms form a molecule with a triple bond, in which three pairs of electrons (six electrons total) are shared.

This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
