Which of the following is a component of a chromosome?
Centromere
Gamete
Homologue
Ribose
Correct Answer : A
The protein disc that holds two sister chromatids together is what collectively makes a chromosome. A gene is a segment of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, which transmits information from parent to offspring. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. A chromosome is a rod-shaped structure that forms when a single DNA molecule and its associated proteins coil tightly before cell division.
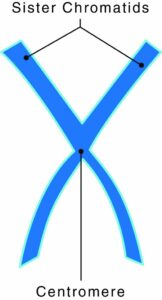
Chromosomes have two components:
- Chromatids: two copies of each chromosome
- Centromeres: protein discs that attach the chromatids together
Human cells have 23 sets of different chromosomes. The two copies of each chromosome are called homologous chromosomes, or homologues. An offspring receives one homologue from each parent. When a cell contains two homologues of each chromosome, it is termed diploid (2n). A haploid (n) cell contains only one homologue of each chromosome. The only haploid cells humans have are the sperm and eggs cells known as gametes.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The particles in a sample of gas are farther apart than in solids or liquids and therefore have the lowest amount of cohesion.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A cell copies its DNA during the S phase, and nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. Thus, the step preceding the S phase, theG1phase, is the phase of the cell cycle when the cell would contain the most nucleotides.
For a cell to divide into more cells, it must grow, copy its DNA, and produce new daughter cells. Thecell cycleregulates cellular division. This process can either prevent a cell from dividing or trigger it to start dividing.
The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases:interphaseand theM (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2phases make up interphase.
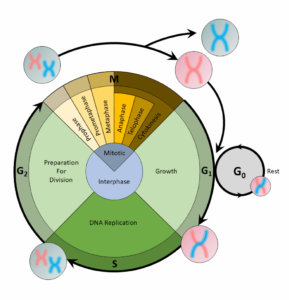
- G1:The first gap phase, during which the cell prepares to copy its DNA
- S:The synthesis phase, during which DNA is copied
- G2:The second gap phase, during which the cell prepares for cell division
It may appear that little is happening in the cell during the gap phases. Most of the activity occurs at the level of enzymes and macromolecules. The cell produces things like nucleotidesfor synthesizing new DNA strands, enzymes for copying the DNA, and tubulin proteins for building the mitotic spindle. During the S phase, the DNA in the cell doubles, but few other signs are obvious under the microscope. All the dramatic events that can be seen under a microscope occur during the M phase: the chromosomes move, and the cell splits into two new cells with identical nuclei.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
In this reaction, two elements are trading places hence double-replacement. In the reactants, zinc and bromide ions are together, and potassium and hydroxide ions are together. In the products, zinc and hydroxide ions are together, and potassium and bromide ions are together.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
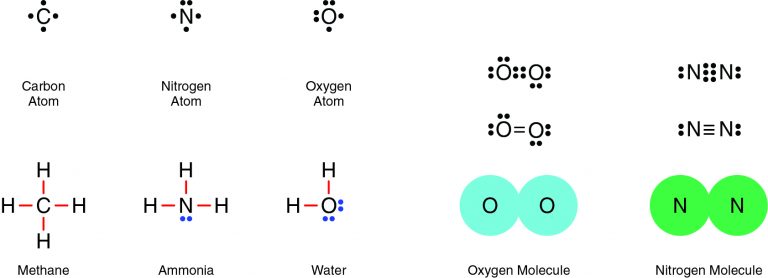
Nitrogen and oxygen are both nonmetals, which means they will share electrons in a covalent bond. For example, two oxygen atoms form a double bond, in which two pairs of electrons (four electrons total) are shared. Similarly, two nitrogen atoms form a molecule with a triple bond, in which three pairs of electrons (six electrons total) are shared.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Human intercourse consists of the male introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive system. Sperm may then pass through the female’s reproductive system to the Fallopian tubes where one sperm fertilizes an ovum, creating azygote. The zygote passes out of the Fallopian tube and implants into the uterine wall to begin gestation. Over nine months, the zygote develops and grows into an embryo and then a fetus. An infant is the baby that is born.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Because this is a positive correlation, if the nutrient concentration increases or decreases, plant height will either increase or decrease accordingly.
While analyzing data, scientists tend to observe cause-and-effect relationships. These relationships can be quantified using correlations.Correlationsmeasure the amount of linear association between two variables. There are three types of correlations:
Positive correlation:
As one variable increases, the other variable also increases. This is also known as a direct correlation.
Negative correlation:
As one variable increases, the other decreases. The opposite is true if one variable decreases. A negative correlation is also known as an inverse correlation or an indirect correlation.
No correlation:
There is no connection or relationship between two variables.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Mendel developed theories of genetics that scientists around the world use today.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants eitherself-pollinateorcross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are eitherdominantorrecessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information calledgenes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual ishomozygousfor that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual isheterozygousfor that trait. Each copy of a factor, orgene, is called anallele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, orphenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is itsgenotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Unlike condensation, deposition, and melting, evaporation is dependent not only on the temperature, but also on the amount of a substance available.
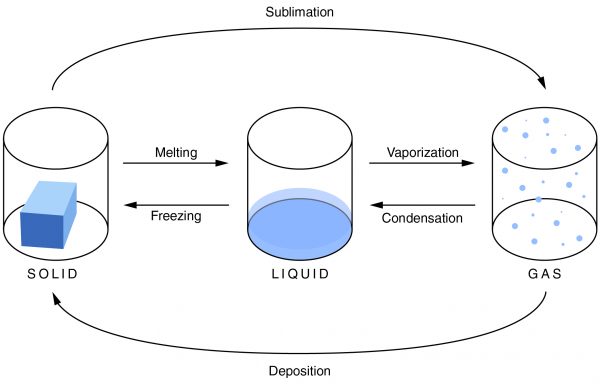
Condensationis the change of a gas or vapor to a liquid. A change in the pressure and the temperature of a substance causes this change. The condensation point is the same as the boiling point of a substance. It is most noticeable when there is a large temperature difference between an object and the atmosphere. Condensation is also the opposite of evaporation.
Evaporationis the change of a liquid to a gas on the surface of a substance. This is not to be confused with boiling, which is a phase transition of an entire substance from a liquid to a gas. The evaporation point is the same as the freezing point of a substance. As the temperature increases, the rate of evaporation also increases. Evaporation depends not only on the temperature, but also on the amount of substance available.
Freezingis the change of a liquid to a solid. It occurs when the temperature drops below the freezing point. The amount of heat that has been removed from the substance allows the particles of the substance to draw closer together, and the material changes from a liquid to a solid. It is the opposite of melting.
Meltingis the change of a solid into a liquid. For melting to occur, enough heat must be added to the substance. When this is done, the molecules move around more, and the particles are unable to hold together as tightly as they can in a solid. They break apart, and the solid becomes a liquid.
Sublimationis a solid changing into a gas. As a material sublimates, it does not pass through the liquid state. An example of sublimation is carbon dioxide, a gas, changing into dry ice, a solid. It is the reverse of deposition.
Depositionis a gas changing into a solid without going through the liquid phase. It is an uncommon phase change. An example is when it is extremely cold outside and the cold air comes in contact with a window. Ice will form on the window without going through the liquid state.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
There are two major types of receptor molecules that respond to an intercellular chemical signal:
- Intracellular receptors: These receptors are located in either the cytoplasm or the nucleus of the cell. Signals diffuse across the cell membrane and bind to the receptor sites on intracellular receptors, of the same cell.
- Membrane-bound receptors: These receptors extend across the cell membrane, with their receptor sites on the outer surface of the cell membrane. They respond to intercellular chemical signals that are large, water-soluble molecules that do not diffuse across the cell membrane.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A person can be a universal blood donor or acceptor. A universal blood donor has type O blood, while a universal blood acceptor has type AB blood.
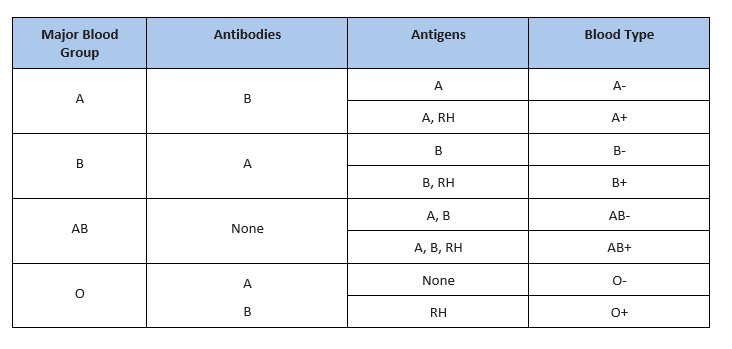
There are several different types or groups of blood, andthe major groups are A, B, AB, and O. Blood group is a way to classify blood according to inherited differences of red blood cellantigensfound on the surface of a red blood cell. The type ofantibodyin blood also identifies a particular blood group. Antibodies are proteins found in the plasma. They function as part of the body’s natural defense to recognize foreign substances and alert the immune system.
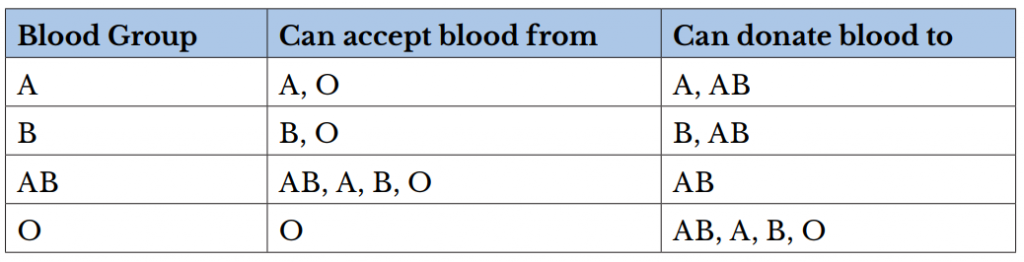
Depending on which antigen is inherited, parental offspring will have one of the four major blood groups. Collectively, the following major blood groups comprise the ABO system:
- Blood group A: Displays type A antigens on the surface of a red blood cell and contains B antibodies in the plasma.
- Blood group B: Displays type B antigens on the red blood cell’s surface and contains A antibodies in the plasma.
- Blood group O: Does not display A or B antigens on the surface of a red blood cell. Both A and B antibodies are in the plasma.
- Blood group AB: Displays type A and B antigens on the red blood cell’s surface, but neither A nor B antibodies are in the plasma
In addition to antigens, the Rh factor protein may exist on a red blood cell’s surface. Because this protein can be either present (+) or absent (-), it increases the number of major blood groups from four to eight: A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O-, AB+, and AB-.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
