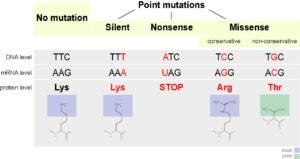
Which of the following is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence?
Silent mutation
Nonsense mutation
Frameshift mutation
Missense mutation
Correct Answer : C
A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
In the diagram, the circular molecules represent sugar. The square molecules represent hormones that regulate blood sugar levels. Among the answer choices:
- Insulin (A): Lowers blood sugar by promoting glucose uptake in cells.
- Norepinephrine (B): Involved in the fight-or-flight response, not directly related to blood sugar regulation.
- Calcitonin (C): Regulates calcium levels, not glucose.
- Glucagon (D): Raises blood sugar by promoting glucose release from the liver.
Since the diagram involves sugar regulation and the square molecules are coming from the liver, the square molecules represent glucagon hormones.
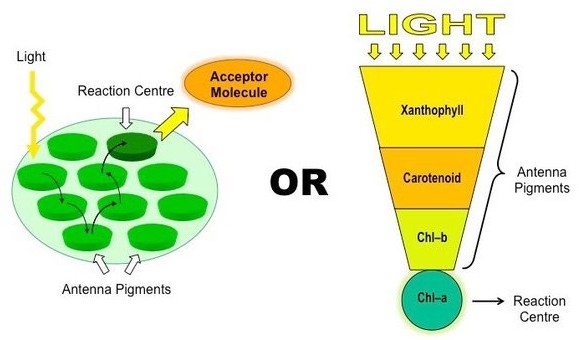
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants. It is a green pigment that is essential for capturing light energy from the sun and converting it into chemical energy that can be used by the plant. Chlorophyll a absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red parts of the spectrum, and reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic green color
Chlorophyll b is another type of chlorophyll that is also involved in photosynthesis, but it is not as abundant as chlorophyll a. Chlorophyll b absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and orange parts of the spectrum and reflects yellow-green light.
Carotenoids are pigments that are present in many plants and are involved in photosynthesis as well as protecting the plant from damage caused by excess light. Carotenoids are responsible for the orange, yellow, and red colors of many fruits and vegetables.
Anthocyanins are pigments that give plants their red, purple, and blue colors. While they are not directly involved in photosynthesis, they play a role in atracting pollinators and protecting the plant from damage caused by UV radiation.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
- A. Nanolitres (nL) → Extremely small unit (1 nL = 0.000000001 L), used for microscopic measurements. ❌
- B. Microlitres (µL) → Also very small (1 µL = 0.000001 L), used in lab settings. ❌
- C. Litres (L) → Too large, as typical urine output per hour is much less than 1 L. ❌
- D. Millilitres (mL) → Suitable, since normal urine output per hour is about 30-80 mL. ✅
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The kidneys secrete a number of hormones, which are important for normal functioning of the body.
If blood pressure falls, renin is secreted by the kidneys to constrict the small blood vessels, thereby increasing blood pressure. If the kidneys aren’t functioning correctly, too much renin can be produced, increasing blood pressure and sometimes resulting in hypertension (high blood pressure). This is why a number of people with kidney diseases also have high blood pressure.
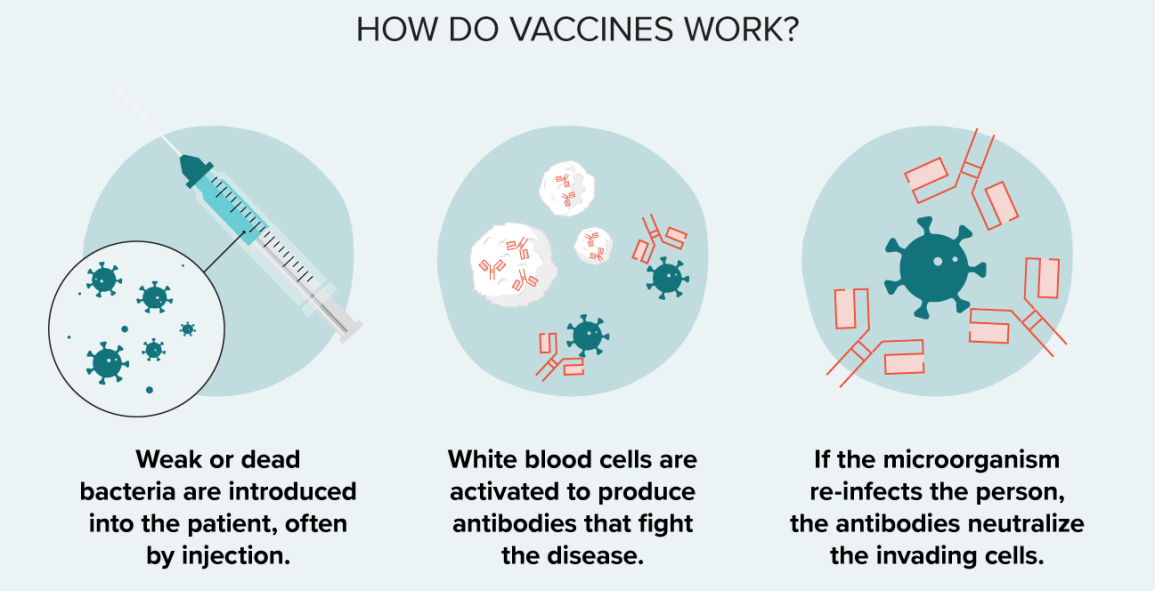
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Vaccines are a type of preventative medicine that work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen (such as a virus or bacteria) or to a piece of the pathogen (such as a protein or sugar) that triggers an immune response in the body. This exposure allows the body to develop immunity to the pathogen without getting sick from the full-blown disease. Once the immune system has been primed, it can recognize and quickly respond to the pathogen if it is encountered again in the future, providing protection against the disease.
It is a common misconception that vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against. This is not true. While some vaccines may cause mild symptoms such as a low-grade fever or soreness at the injection site, they do not cause the full-blown disease.
Vaccines provide active immunity, meaning that the body produces its own antibodies against the pathogen, rather than receiving pre-made antibodies as in passive immunity. Additionally, vaccines can be effective against both bacterial and viral infections, depending on the specific vaccine.
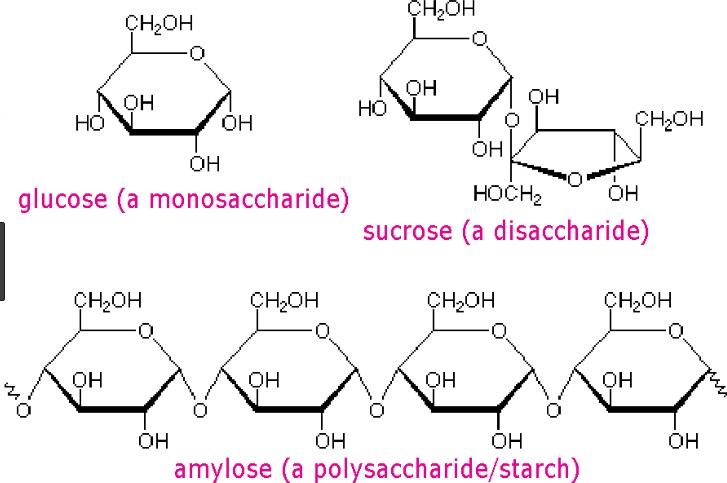
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Carbohydrates are one of the main types of biomolecules and are composed of monomers called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are usually composed of 3 to 7 carbon atoms and have a general formula of (CH2O)n, where n is a number between 3 and 7. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond, they form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Option a) is incorrect because it describes the composition of a disaccharide, not a monosaccharide. Option
c) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be found in both plants and animals.
Option d) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be used for energy storage and
structural purposes, depending on their specific structure and function in the organism.
 |
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
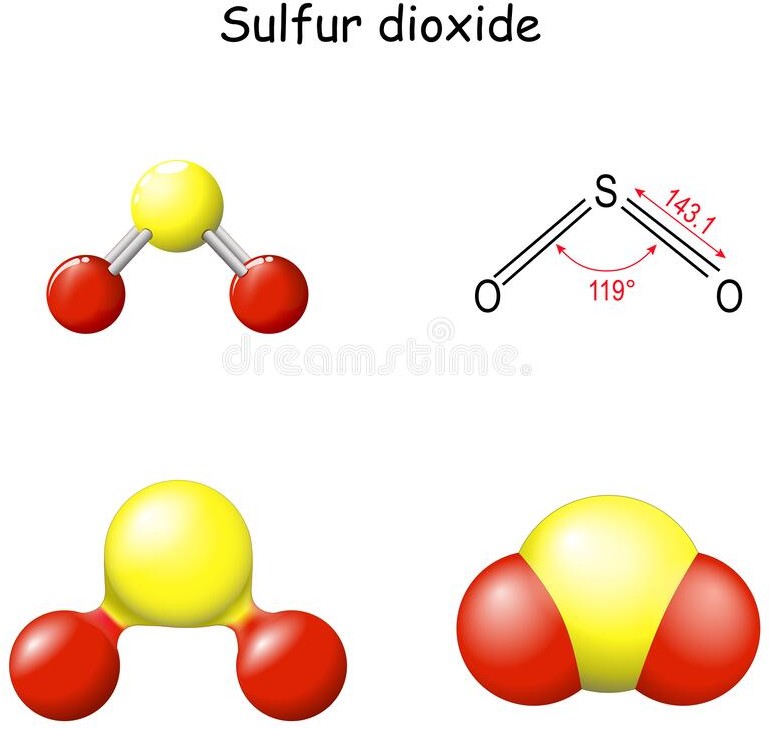
The molecular geometry of a molecule of sulphur dioxide (SO2) is bent or V-shaped. This is because of the presence of two lone pairs on the sulfur atom, which cause repulsion and distort the bond angles in the molecule.
SO2 has a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms by double bonds. The two double bonds and the two lone pairs of electrons on sulfur result in a trigonal planar arrangement of electron pairs around the sulfur atom. However, the repulsion between the lone pairs causes the two oxygen atoms to be pulled closer together, resulting in a bent or V-shaped molecular geometry.
The bent molecular geometry of SO2 affects its properties, such as its polarity and reactivity. SO2 is a polar molecule due to the asymmetric distribution of electrons, which results in a partial positive charge on the sulfur atom and partial negative charges on the oxygen atoms. This polarity makes SO2 a good solvent and reactant in chemical reactions, as well as a contributor to air pollution and acid rain.
 |
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
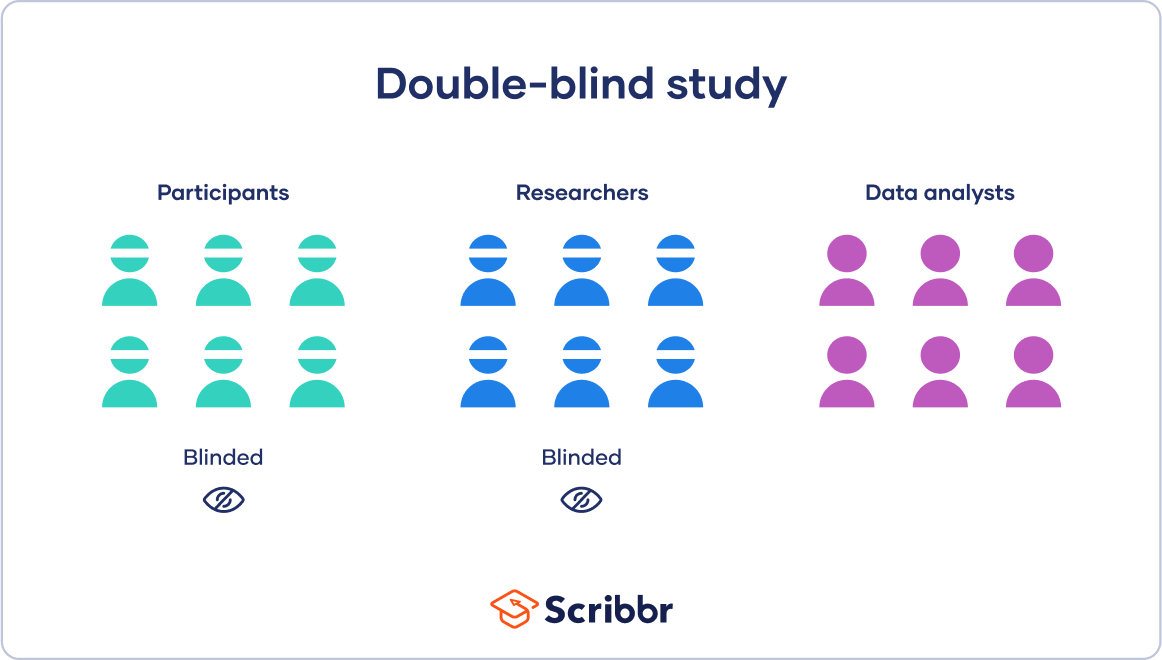
A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to.
Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind.
Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to.
Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The data collected by the researcher on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month would be most useful to analyze traffic patterns during rush hour.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
- The image shown is a highly detailed 3D surface view of a blood clot, which suggests that it was captured using a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
- SEM produces high-resolution, three-dimensional images by scanning a sample with a focused beam of electrons, making it ideal for studying surface structures like blood cells and clots.
Analysis of Other Options:
- A. Compound Light Microscope → Uses visible light to magnify samples but lacks the resolution and 3D detail seen in the image. ❌
- B. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) → Produces 2D images of ultra-thin sections, not detailed 3D surface views. ❌
- D. Stereoscope → A low-magnification microscope used for viewing larger objects, not detailed cellular structures. ❌
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
