Which of the following is another term for muscle cell?
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Muscle Fiber
Sarcolemma
Myofilament
Correct Answer : B
- A. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum → A specialized endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells that stores and releases calcium for muscle contraction. ❌
- B. Muscle Fiber → Another name for a muscle cell, which is a long, cylindrical, multinucleated cell that makes up muscle tissue. ✅
- C. Sarcolemma → The cell membrane of a muscle fiber, which surrounds the muscle cell. ❌
- D. Myofilament → Protein structures (actin and myosin) within a muscle fiber that are responsible for contraction. ❌
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
- A. Nanolitres (nL) → Extremely small unit (1 nL = 0.000000001 L), used for microscopic measurements. ❌
- B. Microlitres (µL) → Also very small (1 µL = 0.000001 L), used in lab settings. ❌
- C. Litres (L) → Too large, as typical urine output per hour is much less than 1 L. ❌
- D. Millilitres (mL) → Suitable, since normal urine output per hour is about 30-80 mL. ✅
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
- A. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum → A specialized endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells that stores and releases calcium for muscle contraction. ❌
- B. Muscle Fiber → Another name for a muscle cell, which is a long, cylindrical, multinucleated cell that makes up muscle tissue. ✅
- C. Sarcolemma → The cell membrane of a muscle fiber, which surrounds the muscle cell. ❌
- D. Myofilament → Protein structures (actin and myosin) within a muscle fiber that are responsible for contraction. ❌
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Carbohydrates are one of the main types of biomolecules and are composed of monomers called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are usually composed of 3 to 7 carbon atoms and have a general formula of (CH2O)n, where n is a number between 3 and 7. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond, they form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Option a) is incorrect because it describes the composition of a disaccharide, not a monosaccharide. Option
c) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be found in both plants and animals.
Option d) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be used for energy storage and
structural purposes, depending on their specific structure and function in the organism.
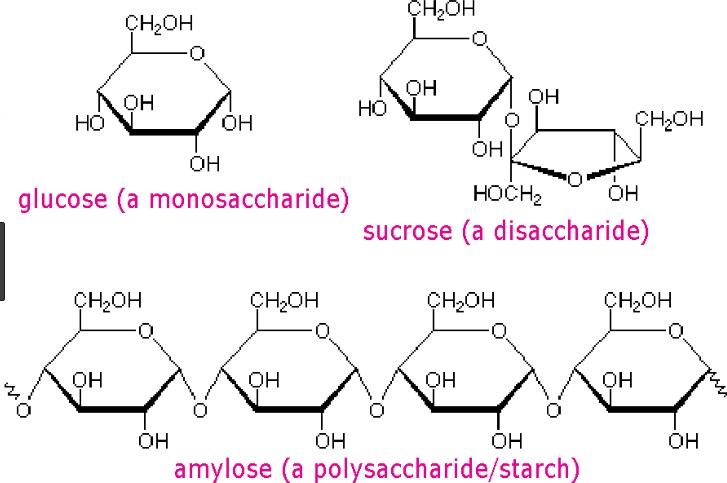 |
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a type of RNA molecule that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has a specific sequence of three nucleotides called an anticodon, which pairs with a complementary codon in the messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence. Each tRNA also carries a specific amino acid that corresponds to the codon it recognizes, allowing the ribosome to link the amino acids together in the correct order to form a protein.
In contrast, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of the ribosome itself, where it helps to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is involved in splicing of pre-mRNA molecules during post-transcriptional processing.
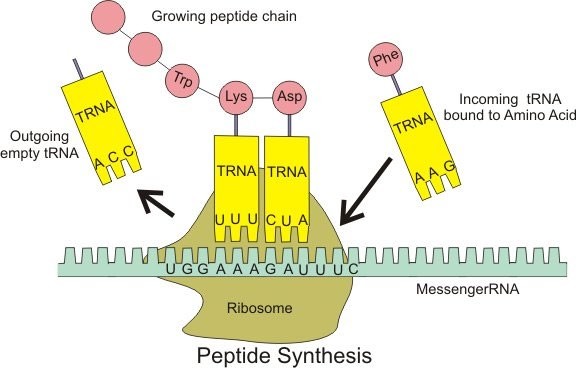 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Ligaments are tough bands of fibrous ssue that connect two bones together in a joint. They provide stability and support to the joint, prevenng excessive movement and helping to maintain proper alignment of the bones.
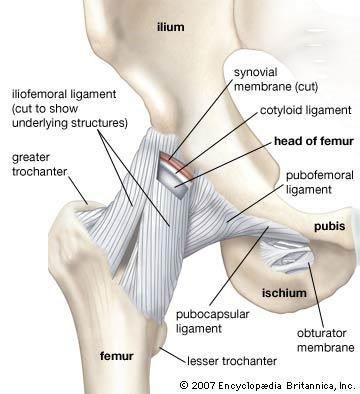
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Exothermic reactions are reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound. Burning wood is an example of an exothermic reaction because it releases heat and light. As the wood reacts with oxygen in the air, it undergoes a combustion reaction that releases energy in the form of heat and light. Melting ice is an endothermic reaction because it requires energy input to melt the solid ice into liquid water. Cooking an egg is a chemical reaction that involves denaturing the proteins in the egg, but it is not necessarily exothermic or endothermic. Dissolving sugar in water is also not an example of an exothermic reaction because it does not release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound.
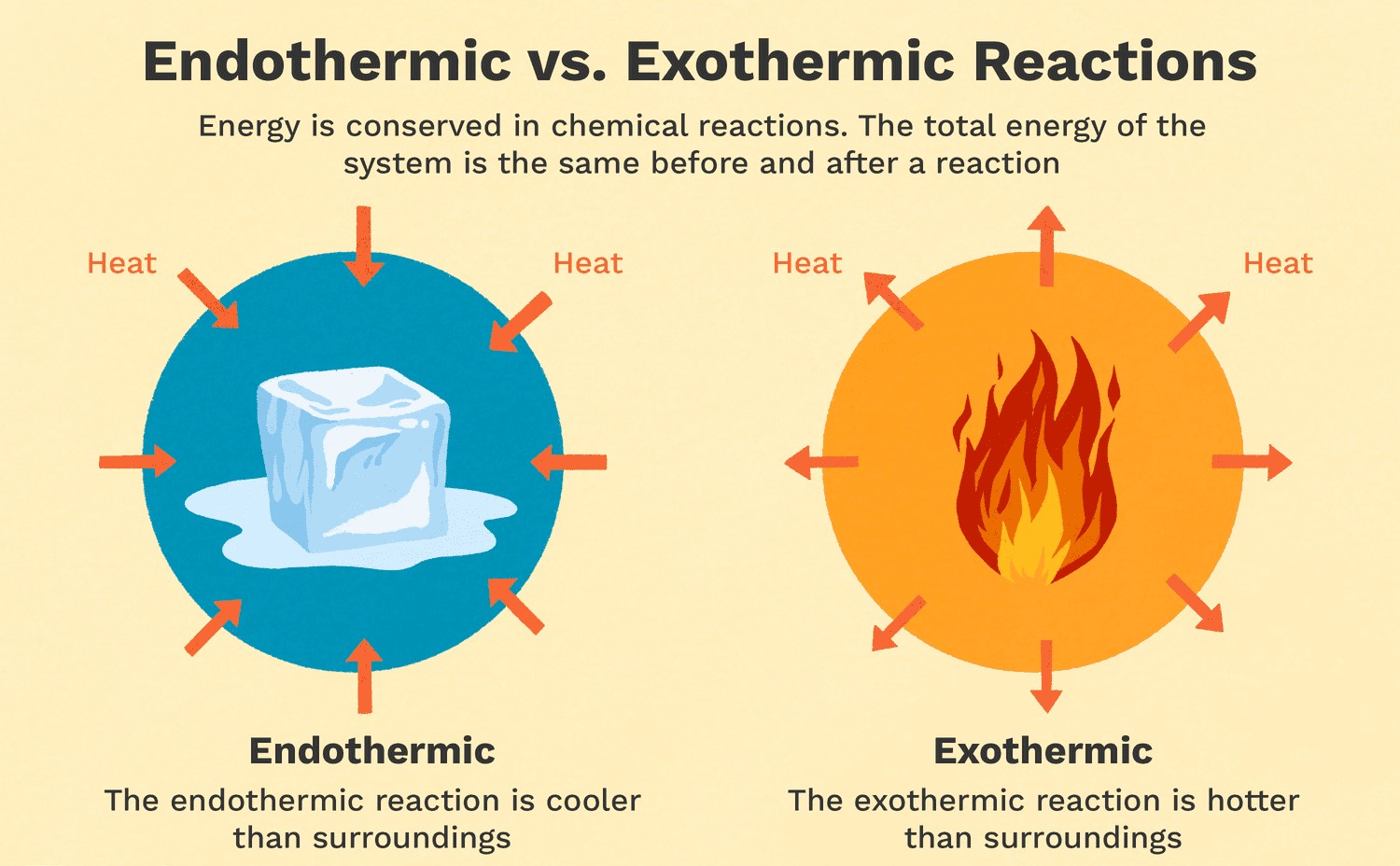
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
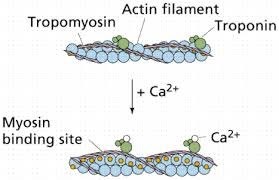
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The nurse can logically conclude that:
✅ Treatment A results in the shortest recovery time.
- The data shows that Treatment A has a mean recovery time of 3 days, which is the shortest compared to Treatment B (5 days) and Treatment C (7 days).
The other statements are not supported by the given data:
❌ "Treatment C enhances patient satisfaction more than the others."
- There is no information about patient satisfaction, only recovery times.
❌ "Treatment B is as effective as Treatment A."
- Treatment B has a longer recovery time (5 days) compared to Treatment A (3 days), so it is not equally effective in terms of recovery speed.
❌ "Treatments A and B provide the same rate of recovery."
- Treatment A has a faster recovery time than Treatment B, so they do not have the same recovery rate.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
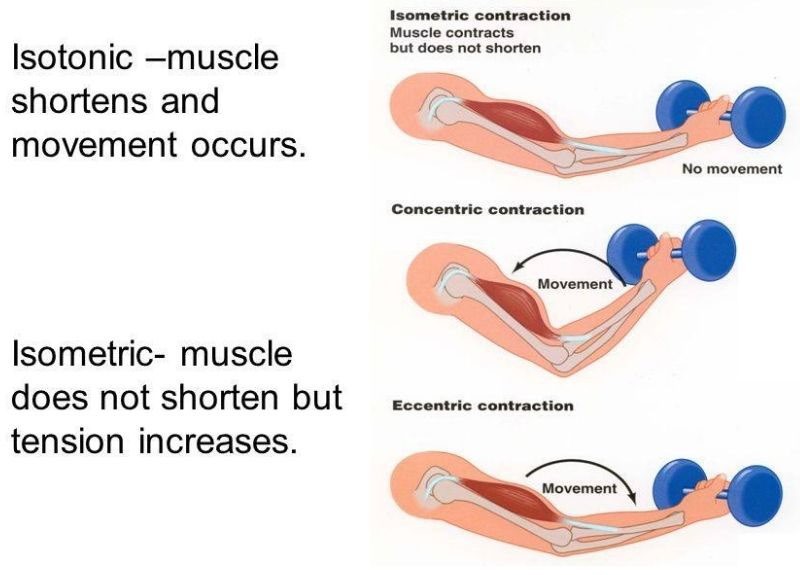
Isotonic and isometric contractions are two types of muscle contractions that differ in the amount of force produced and the movement of the muscle. In isotonic contractions, the muscle changes length and produces movement, such as lifting a weight. The force generated by the muscle remains constant throughout the movement. Isotonic contractions can be further classified as concentric contractions, in which the muscle shortens as it contracts, and eccentric contractions, in which the muscle lengthens as it contracts.
In contrast, isometric contractions occur when the muscle generates force without changing its length or producing movement. For example, holding a weight in a fixed position without moving it requires an isometric contraction. In an isometric contraction, the force generated by the muscle increases up to a maximum and then remains constant. Isometric contractions can be used to build strength and endurance in the muscle, but they do not produce movement.
 |
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
- The number of protons in an atom is equal to its atomic number.
- The periodic table shows that phosphorus (P) has an atomic number of 15.
- This means every phosphorus atom has 15 protons in its nucleus.
Analysis of Other Options:
- A. 30 → This is close to the atomic mass (30.97), but the atomic mass is not the same as the number of protons. ❌
- B. 16 → This is incorrect; sulfur (S) has an atomic number of 16, not phosphorus. ❌
- D. 31 → This is rounded from the atomic mass (30.97), but atomic mass ≠ number of protons. ❌
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
