A 61-year-old female patient with hypovolemic shock has these vital signs: temperature 97.9°F (36.6°C): pulse 123 beats/min: blood pressure 85/48 mamite respirations 24 breaths/min; urine output 20 mL for last 2 hours: skin cool and clammy. Which prescription order for this patient does the nurse question?
Doasive Nitrogen 12m mi
Dobutamine Doubters) 5 mcg/kg/min
Plasmanate 1 unit
Bumetanide (Bumex) 1 mg IV
The Correct Answer is C
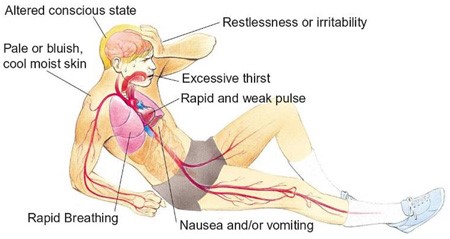
Hypovolemic shock is a life-threatening condition resulting from severe blood or fluid loss. The patient in this scenario exhibits signs of hypovolemic shock, such as low blood pressure, tachycardia, cool and clammy skin, and decreased urine output.
When assessing the prescription options, the nurse should consider the appropriateness of each intervention for hypovolemic shock. Plasmanate is a type of plasma protein fraction that is used for volume expansion in certain situations. However, in hypovolemic shock, the primary intervention is to restore intravascular volume promptly. Plasmanate alone may not be sufficient for rapid-volume resuscitation.
In hypovolemic shock, the initial management typically involves the administration of crystalloid solutions, such as Lactated Ringers or Normal Saline, to restore intravascular volume. Therefore, the prescription of Plasmanate as the primary intervention raises concerns and should be questioned by the nurse.
A. Dopamine (Intropin) 12 mcg/min in (option A) is incorrect because: Dopamine is a vasopressor medication used to increase blood pressure and cardiac output. It is a suitable option for hypovolemic shock to support blood pressure and tissue perfusion.
B. Dobutamine (Dobutrex) 5 mcg/kg/min in (option B) is incorrect because: Dobutamine is an inotropic medication that helps improve cardiac contractility and cardiac output. It can be beneficial in cases of hypovolemic shock with signs of poor cardiac function.
D. Bumetanide (Bumex) 1 mg IV in (option D) is incorrect because: Bumetanide is a loop diuretic used to promote diuresis. However, in the context of hypovolemic shock, diuretics are generally not the first-line treatment as they can further reduce intravascular volume and worsen the patient's condition.
It is essential for the nurse to consult with the healthcare provider regarding the prescription order of Plasmanate and consider alternative interventions for rapid volume resuscitation in hypovolemic shock.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Arterial pressure monitoring involves the insertion of an arterial catheter, typically in the radial artery, to directly measure blood pressure. Complications can arise from this invasive procedure, and one potential complication is inadequate blood flow to the hand, leading to numbness or ischemia.
A. The Allen's test is positive in (option A) is incorrect because The Allen's test is performed before arterial catheter insertion to assess the collateral circulation of the hand. A positive Allen test indicates adequate collateral circulation, which is desirable before performing the procedure. However, it does not directly indicate a complication during or after arterial pressure monitoring.
B. The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is 90 mm Hg in (option B) is incorrect because The mean arterial pressure (MAP) represents the average pressure in the arterial system during one cardiac cycle. While changes in MAP can be significant for patient management, it does not specifically indicate a complication of arterial pressure monitoring.
C. The dicrotic notch visible in the waveform in (option C) is incorrect because The dicrotic notch represents the closure of the aortic valve and is a normal finding in arterial waveforms. Its presence does not indicate a complication.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Urine output is an essential indicator of renal perfusion and overall fluid status. In a patient in shock, maintaining an adequate urine output is a crucial goal of fluid resuscitation. A urine output of 0.5 to 1 mL/kg/hour is generally considered adequate in adults. The given value of 35 ml over the last hour suggests that the patient is producing urine, which indicates that fluid resuscitation is effective in restoring perfusion to the kidneys.
A. The patient's mean arterial pressure (MAP) is 50 mm Hg in (option A) is incorrect because While mean arterial pressure is an important hemodynamic parameter, a single value alone may not provide a comprehensive assessment of the patient's response to fluid resuscitation.
B. The patient's GCS score is 9 in (option B) is incorrect because The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) assesses the level of consciousness and neurological function but does not directly reflect fluid resuscitation effectiveness.
D. The patient's hemoglobin is within normal limits: (option D) is incorrect because Haemoglobin levels are important for assessing oxygen-carrying capacity but do not directly indicate the effectiveness of fluid resuscitation.
Therefore, the nurse can evaluate that fluid resuscitation for a 70 kg patient in shock is effective by observing a urine output of 35 ml over the last hour.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
