Following surgery, a patient's central venous pressure (CVP) monitor indicates high pressures. Which action will the nurse anticipate taking?
Increase the IV fluid infusion rate.
Administer IV diuretic medications.
Elevate the head of the patient's bed to 45 degrees.
Document the CVP and continue to monitor.
The Correct Answer is B
Central venous pressure (CVP) is a measurement of the pressure in the central veins, which reflects the blood volume and right-sided cardiac function. High CVP readings may indicate fluid overload or impaired cardiac function, and intervention is necessary to address the underlying cause.
Administering IV diuretic medications can help reduce fluid volume by increasing urine output and promoting fluid elimination. By removing excess fluid, the diuretic medications can help lower the CVP and alleviate the high pressures.
The other options mentioned are not the anticipated actions for addressing high CVP:
A. Increasing the IV fluid infusion rate in (option A) is incorrect because: If the CVP is already indicating high pressures, increasing the IV fluid infusion rate would further contribute to fluid overload and exacerbate the problem. This action would not be appropriate for high CVP readings.
C. Elevating the head of the patient's bed to 45 degrees in (option C) is incorrect because Positioning the patient with the head of the bed elevated is commonly done to prevent complications such as aspiration or improve respiratory function. While it may have other benefits, it does not directly address the high CVP.
D. Documenting the CVP and continuing to monitor in (option D) is incorrect because Documenting the CVP and continuing to monitor is important for ongoing assessment and evaluation. However, in the presence of high CVP readings, intervention is necessary to address the underlying issue rather than solely documenting and monitoring.
Therefore, when a patient's CVP monitor indicates high pressures following surgery, the nurse would anticipate administering IV diuretic medications to help reduce fluid volume and lower the CVP.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Arterial pressure monitoring involves the insertion of an arterial catheter, typically in the radial artery, to directly measure blood pressure. Complications can arise from this invasive procedure, and one potential complication is inadequate blood flow to the hand, leading to numbness or ischemia.
A. The Allen's test is positive in (option A) is incorrect because The Allen's test is performed before arterial catheter insertion to assess the collateral circulation of the hand. A positive Allen test indicates adequate collateral circulation, which is desirable before performing the procedure. However, it does not directly indicate a complication during or after arterial pressure monitoring.
B. The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is 90 mm Hg in (option B) is incorrect because The mean arterial pressure (MAP) represents the average pressure in the arterial system during one cardiac cycle. While changes in MAP can be significant for patient management, it does not specifically indicate a complication of arterial pressure monitoring.
C. The dicrotic notch visible in the waveform in (option C) is incorrect because The dicrotic notch represents the closure of the aortic valve and is a normal finding in arterial waveforms. Its presence does not indicate a complication.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
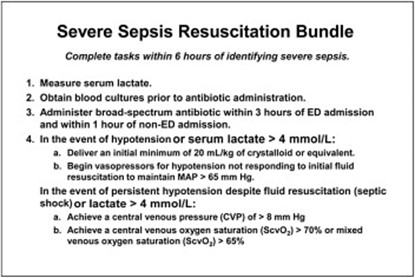
The patient's symptoms of fever and elevated white blood cell count suggest a potential infection and sepsis. Broad-spectrum antibiotics should be initiated promptly to cover a wide range of possible pathogens until further diagnostic tests and identification of the specific causative agent are obtained. Early administration of appropriate antibiotics is crucial in sepsis management to target the suspected infection and improve patient outcomes.
A. Cooling baths in (option A) is incorrect because: Cooling baths are typically used in the management of hyperthermia or specific conditions like heatstroke. While the patient has an elevated temperature, it is likely due to the systemic inflammatory response rather than solely hyperthermia.
C. Blood transfusion in (option C) is incorrect because Blood transfusion may be required in certain cases of sepsis if there is evidence of significant anemia or active bleeding. However, based on the information provided, there is no immediate indication of a blood transfusion.
D. NPO status in (option D) is incorrect because NPO status (nothing by mouth) is a general precautionary measure used in various situations, such as prior to surgery or to manage gastrointestinal complications. It is not a specific intervention in the sepsis resuscitation bundle.
Therefore, the nurse should initiate the intervention of administering broad-spectrum antibiotics in this scenario.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
