A nurse assesses a patient who is prescribed a medication that inhibits aldosterone secretion and release. For which potential complications will the nurse assess? (Select all that apply.)
Serum potassium level of 3.2 mEq/L
Urine output of 1 200 mL in the last 2 hours
Blood osmolality of 250 mOsm/kg (250 mmol/kg)
Urine output of 25 mL/hr
Serum potassium level of 5.4 mEq/L:
Correct Answer : A,D,E
A serum potassium level of 3.2 mEq/L indicates hypokalemia, which is a potential complication of inhibiting aldosterone secretion and release. Aldosterone plays a key role in potassium regulation in the body by promoting potassium excretion in the kidneys. When aldosterone secretion is inhibited, potassium excretion decreases, leading to an accumulation of potassium in the bloodstream and resulting in hypokalemia. Symptoms of hypokalemia may include muscle weakness, cramping, irregular heartbeat, and fatigue.
B. Urine output of 1,200 mL in the last 2 hours:
This option does not directly relate to complications of inhibiting aldosterone secretion. A urine output of 1,200 mL in the last 2 hours indicates adequate urine production, which is generally a positive sign. However, in the context of inhibiting aldosterone secretion, the nurse would be more concerned about decreased urine output due to potential renal effects.
C. Blood osmolality of 250 mOsm/kg (250 mmol/kg):
Blood osmolality within the normal range (usually around 275-295 mOsm/kg) is not directly associated with complications of inhibiting aldosterone secretion. Blood osmolality reflects the concentration of solutes in the blood and is regulated by various factors, including water balance, electrolyte levels, and hormonal regulation. Inhibiting aldosterone secretion primarily affects electrolyte balance rather than blood osmolality.
D. Urine output of 25 mL/hr:
A urine output of 25 mL/hr is considered low and may indicate decreased renal perfusion or impaired kidney function. Inhibiting aldosterone secretion can affect renal function and urine output, leading to decreased urine production. Reduced urine output can contribute to fluid and electrolyte imbalances and may be a concern in patients with inhibited aldosterone secretion.
E. Serum potassium level of 5.4 mEq/L:
A serum potassium level of 5.4 mEq/L indicates hyperkalemia, which is another potential complication of inhibiting aldosterone secretion. Aldosterone helps regulate potassium levels by promoting potassium excretion in the kidneys. When aldosterone secretion is inhibited, potassium excretion decreases, leading to an accumulation of potassium in the bloodstream and resulting in hyperkalemia. Symptoms of hyperkalemia may include muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, nausea, and numbness or tingling.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
-
A. How many people live in your home?
This question pertains to social and environmental factors but is not directly related to assessing skin inflammation on the chest. While social factors can impact overall health, such as stress levels or exposure to infectious agents, the number of people living in the client's home is unlikely to be directly related to a new skin inflammation unless there are specific circumstances, such as sharing personal care products or close contact with others who have similar skin issues.
B. Did you have a recent exposure to irritants?
This question is highly relevant to assessing a new skin inflammation on the chest. Exposure to irritants or allergens can trigger or worsen skin conditions, such as contact dermatitis or allergic reactions. By asking about recent exposure to potential irritants like new detergents, soaps, fabrics, chemicals, or environmental factors, the nurse can gather important information to identify possible triggers for the skin inflammation.
C. Is nausea associated with your rash?
Nausea is typically not directly associated with a skin rash or inflammation unless there is a systemic condition or allergic reaction causing both symptoms. While it's important to assess for any systemic signs or symptoms that may be related to the skin condition, such as fever or malaise, specifically asking about nausea may not provide relevant information about the skin inflammation on the chest.
D. What is your body mass index?
Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body weight relative to height and is not directly related to assessing a new skin inflammation on the chest. While obesity or changes in body weight can sometimes contribute to skin issues, such as friction-related dermatitis or hormonal changes affecting skin health, BMI alone is not a primary assessment parameter for localized skin conditions unless there are specific concerns related to weight-related skin problems.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
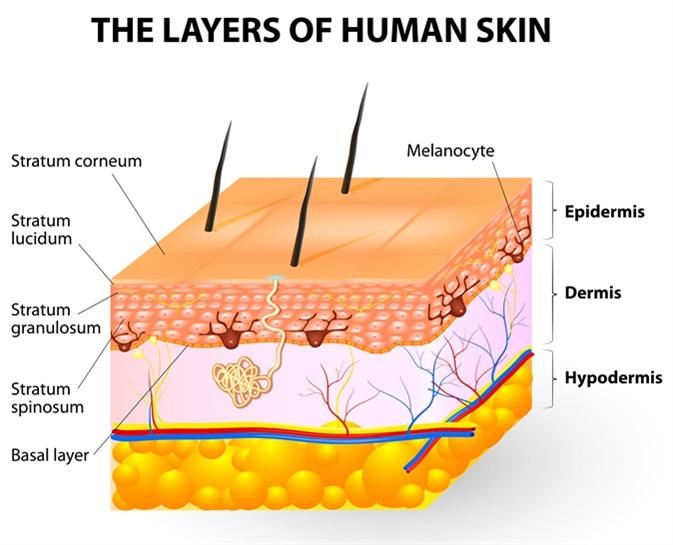
A. Loose connective tissue:
Melanocytes are not typically found in loose connective tissue. Their primary location is within the epidermis, specifically in the basal layer, where they interact with keratinocytes to produce melanin and contribute to skin color. Loose connective tissue contains collagen and elastin fibers, as well as fibroblasts, but it does not house melanocytes.
B. Epidermis:
This is the correct answer. Melanocytes are primarily located in the basal layer of the epidermis, which is the deepest layer of the epidermis. These cells produce melanin, a pigment that helps protect the skin from UV radiation and determines skin color. Melanocytes are interspersed among keratinocytes in the epidermis and transfer melanin to keratinocytes to provide skin pigmentation.
C. Dermis:
The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis and consists of connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. While the dermis plays a crucial role in supporting and nourishing the epidermis, melanocytes are not primarily located in the dermis. They are confined to the basal layer of the epidermis.
D. Superficial fascia:
The superficial fascia, also known as the subcutaneous tissue or hypodermis, lies beneath the dermis and consists of adipose (fat) tissue and connective tissue. It provides insulation, energy storage, and cushioning for underlying structures. However, melanocytes are not typically found in the superficial fascia. They are restricted to the epidermis, specifically the basal layer, where they carry out their function of melanin production.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
