A woman presents to the emergency department with complaints of bleeding and cramping. The initial nursing history is significant for the last menstrual period 6 weeks ago. On sterile speculum examination, the primary care provider finds that the cervix is closed. The anticipated plan of care for this woman would be based on a probable diagnosis of which type of spontaneous abortion? Select one:
Inevitable
Septic
c Incomplete
Missed
Threatened
The Correct Answer is E
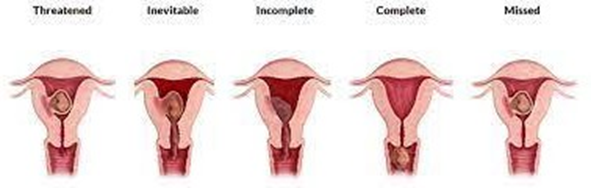
a. Inevitable abortion is characterized by vaginal bleeding, cramping, and dilated cervical os.
b. Septic abortion is associated with infection and may present with fever, chills, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
c. Incomplete abortion involves vaginal bleeding, cramping, and dilation of the cervical os with passage of some products of conception.
d. A missed abortion is when there is no bleeding or cramping, but the pregnancy has stopped developing and there is no fetal heartbeat. The cervix may be closed or slightly open, and the uterus may be smaller than expected for gestational age.
e. Threatened abortion involves vaginal bleeding with a closed cervical os and no passage of products of conception. It signifies a potential abortion, but the pregnancy may continue.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
a. Multipara refers to a woman who has given birth to two or more children.
b. Primipara refers to a woman who has given birth to one child.
c. Nullipara refers to a woman who has never given birth.
d. Nulligravida refers to a woman who has never been pregnant.

Correct Answer is A
Explanation
a. Bulging of the vulva: This indicates that the fetal head is descending but does not necessarily mean the woman is almost ready to give birth. This indicates that the fetal head is crowning and putting pressure on the perineum, which means that delivery is imminent.
b. This indicates that the amniotic sac has ruptured but does not necessarily mean the woman is almost ready to give birth.
c. The fetal head at 0 station means that it is at the level of the maternal ischial spines, but it still needs to descend further to reach the perineum.
d. This indicates that the woman is in the early stages of labor but does not necessarily mean she is almost ready to give birth.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
