A 35-year-old pregnant woman with irregular periods, G4 T2 PO A1 L2 is 28 weeks pregnant by the last ultrasound, when she experiences bright red and painless vaginal bleeding, fetal contour is easily assessed, and uterine tone is normal. On her arrival at the hospital, what would be an expected diagnostic procedure or test to confirm the diagnosis?
Select one:
Vaginal Ultrasound for placental location
Amniocentesis for fetal lung maturity
Abdominal Ultrasound for placental location
Contraction stress test (CST)
The Correct Answer is A
a. This would help determine the location of the placenta and whether placenta previa is present, which can cause painless vaginal bleeding.
b. This is not typically done for diagnosis of painless vaginal bleeding.
c. While an abdominal ultrasound can also determine the location of the placenta, a vaginal ultrasound is more accurate for this purpose.
d. This is not typically done for diagnosis of painless vaginal bleeding.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
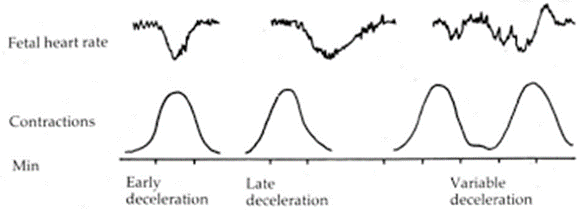
a. This is a common cause of variable decelerations, not early decelerations.
b. This is not a cause of early decelerations.
c. This is a common cause of variable decelerations, not early decelerations.
d. This is the cause of early decelerations and is a normal response to the pressure of the fetal head on the cervix during contractions.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
a. This is an important nursing intervention when a patient is receiving magnesium sulfate, as the medication can affect renal function.
b. Assessing cervix dilation is not related to magnesium sulfate toxicity.
c. This is an important nursing intervention when a patient is receiving magnesium sulfate, as the medication can affect neuromuscular function.
d. This is an important nursing intervention when a patient is receiving magnesium sulfate, as the medication can affect respiratory function.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
