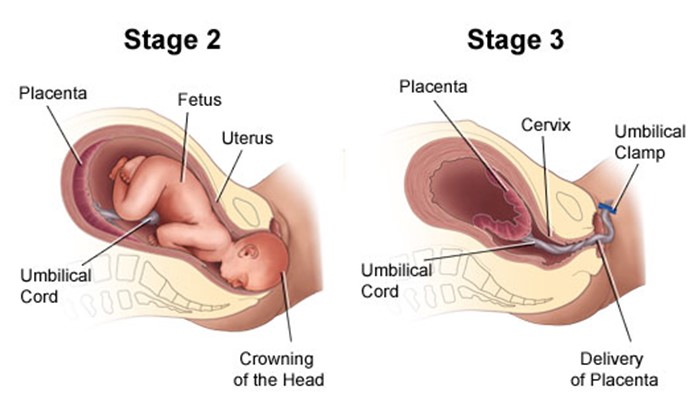
What nursing intervention is particularly indicated for the second stage of labor?
Providing pain medication to increase the client's tolerance of labor pains
Assessing the fetal heart rate and pattern for signs of fetal distress
Assisting the client to push effectively so that expulsion of the fetus can be achieved
Monitoring effects of oxytocin administration to help achieve cervical dilation
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason: Providing pain medication to increase the client's tolerance of labor pains is not a specific intervention for the second stage of labor. Pain medication is a drug that relieves pain by blocking pain signals or reducing inflammation. Pain medication can be given during any stage of labor, depending on the client's preference and condition. However, pain medication may have side effects such as sedation, nausea, or respiratory depression, and may affect the fetal heart rate or the progress of labor.
Choice B reason: Assessing the fetal heart rate and pattern for signs of fetal distress is not a particular intervention for the second stage of labor. Fetal heart rate and pattern are indicators of fetal well-being and oxygenation. Fetal heart rate and pattern should be monitored throughout labor, especially during contractions, to detect any abnormalities or complications such as bradycardia, tachycardia, or decelerations.
Choice D reason: Monitoring effects of oxytocin administration to help achieve cervical dilation is not a relevant intervention for the second stage of labor. Oxytocin is a hormone that stimulates uterine contractions and cervical dilation. Oxytocin can be administered during labor to augment or induce labor, especially if there is prolonged or dysfunctional labor. However, oxytocin is not needed in the second stage of labor, when the cervix is already fully dilated and the focus is on pushing and delivering the baby.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice B reason: Elevating the head of the bed to a 45-degree angle is not a sufficient intervention for the nurse to implement before leaving the client. Elevating the head of the bed can help reduce snoring and improve breathing by preventing the tongue and soft palate from falling back and obstructing the airway. However, it may not be enough to prevent apnea episodes in clients with obstructive sleep apnea, especially if they have other risk factors such as obesity, enlarged tonsils, or nasal congestion. The nurse should also use other interventions such as a positive airway pressure device, weight loss, or surgery.
Choice C reason: Removing dentures or other oral appliances is not a relevant intervention for the nurse to implement before leaving the client. Dentures or other oral appliances are devices that replace missing teeth or improve dental alignment. They may help improve speech, chewing, and appearance, but they do not have a direct impact on obstructive sleep apnea. The nurse should instruct the client to remove dentures or other oral appliances before going to bed to prevent discomfort, infection, or damage.
Choice D reason: Lifting and locking the side rails in place is not a necessary intervention for the nurse to implement before leaving the client. Side rails are bars that attach to the sides of the bed frame to prevent falls or injuries. They may provide safety and security for some clients, but they may also pose risks such as entrapment, strangulation, or agitation. The nurse should assess the need for side rails on an individual basis and consider alternative measures such as bed alarms, low beds, or floor mats.
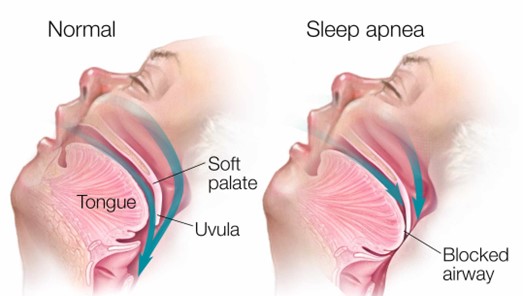
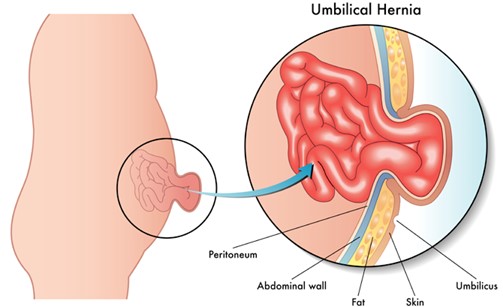
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A: An abdominal binder can be worn daily to reduce the protrusion is not a correct explanation for the nurse to provide, as this is not an effective or recommended method to treat a hernia. This is a distractor choice.
Choice B: This hernia is a normal variation that resolves without treatment is a correct explanation for the nurse to provide, as this refers to an umbilical hernia, which is a common and harmless condition in infants that usually disappears by age 2. Therefore, this is the correct choice.
Choice C: The quarter should be secured with an elastic bandage wrap is not a correct explanation for the nurse to provide, as this is a folk remedy that has no scientific basis and can cause skin irritation and infection. This is another distractor choice.
Choice D: Restrictive clothing will be adequate to help the hernia go away is not a correct explanation for the nurse to provide, as this is not a proven or safe way to treat a hernia. This is another distractor choice.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
