In a certain plant, red flowers are dominant over white flowers. A plant heterozygous for red flowers and a plant with white flowers are crossed. Which of the following is the expected proportion of phenotypes in the next generation?
1 red, 3 white
4 red, 0 white
2 red, 2 white
3 red, 1 white
Correct Answer : C
The law of segregation states that each individual has two alleles for each trait, and these alleles separate during gamete formation. The allele that each gamete receives is random. Therefore, the probability of getting a certain genotype or phenotype depends on the Punnett square. In this case, the plant heterozygous for red flowers has the genotype Rr, where R is the dominant allele for red flowers and r is the recessive allele for white flowers. The plant with white flowers has the genotype rr. half of the offspring will have the genotype Rr and half will have the genotype rr. Since R is dominant over r, the offspring with Rr will have red flowers and the offspring with rr will have white flowers. Therefore, the expected proportion of phenotypes in the next generation is 2 red, 2 white.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
An amine group is a nitrogen atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, and a carboxyl group is a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group. These groups are important for the formation of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
One way to assess the size of a cell is to measure its diameter, which is the length of a straight line that passes through the center of the cell and touches both sides. The measurement indicated by the line across the center of the cell in the diagram is best referred to as the diameter of the cell.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The answer lies in the environmental conditions of the Alps. The body was quickly frozen by the low temperature and covered by snow and ice, which prevented exposure to air, moisture, and microorganisms. The freezing also slowed down the chemical reactions that would normally break down the body's cells and tissues. Thus, the body was preserved in a natural mummy state until it was discovered by modern humans.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A totipotent cell is a type of stem cell that has the ability to develop into any kind of cell in the body, including the cells that make up the placenta and the umbilical cord. This means that a totipotent cell can generate a complete organism from a single cell. The only natural example of totipotent cells are the fertilized egg and the cells produced by the first few divisions of the egg. Totipotent cells are different from other types of stem cells, such as pluripotent cells, which can develop into any cell type except for the placenta and the umbilical cord, and multipotent cells, which can only develop into a limited range of cell types.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The pancreas releases sodium bicarbonate into the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. The main function of sodium bicarbonate is to neutralize the acidity of chyme, the semi-digested food that comes from the stomach. By doing so, sodium bicarbonate creates a more alkaline environment that is suitable for the action of pancreatic enzymes. Sodium bicarbonate does not affect peristalsis, the rhythmic contraction of the intestinal muscles, nor does it stimulate the pyloric sphincter, the valve that controls the passage of food from the stomach to the duodenum. Sodium bicarbonate is not a protease, an enzyme that digests proteins, nor does it digest carbohydrates.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The pulmonary vein is the only vessel in the list that carries oxygenated blood. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it gets oxygenated. The superior and inferior vena cava are large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the upper and lower body, respectively, to the heart.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
One of the essential aspects of scientific inquiry is the communication of results to peers and the public. Publishing new scientific findings allows other scientists to review, replicate, or challenge the methods and conclusions of a study. This way, science can advance by building on previous knowledge and correcting any errors or inconsistencies.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The atomic number of an atom is defined as the number of protons in its nucleus. Protons are positively charged particles that make up part of the atomic mass, along with neutrons, which have no charge. The number of neutrons can vary for atoms of the same element, resulting in different isotopes. However, the number of protons is always constant for a given element. Therefore, to find the atomic number of an atom that has 12 protons and 12 neutrons, we only need to look at the number of protons.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when the flow of blood to the heart is blocked. The blockage is usually due to a buildup of fat, cholesterol and other substances in the heart (coronary) arteries. The fatty, cholesterol-containing deposits are called plaques. The process of plaque buildup is called atherosclerosis. Sometimes, a plaque can rupture and form a clot that blocks blood flow. A lack of blood flow can damage or destroy part of the heart muscle.
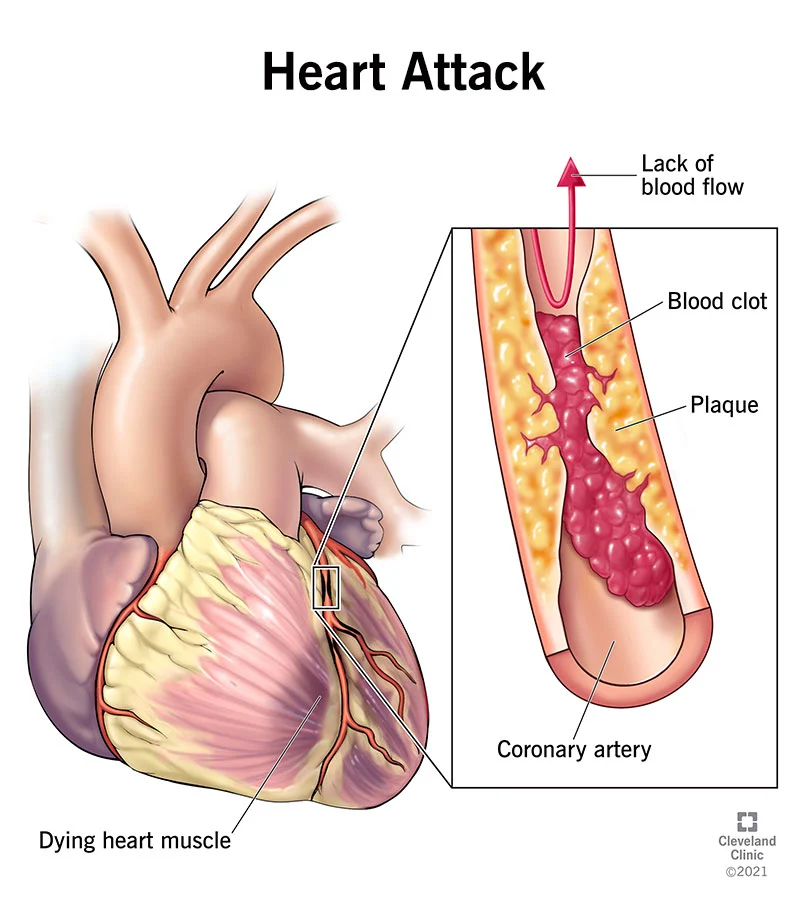
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The glomerulus is a network of capillaries that filters blood and forms the primary urine. The blood enters the glomerulus through the afferent arteriole and leaves through the efferent arteriole. The efferent arteriole has a smaller diameter than the afferent arteriole, creating a high pressure in the glomerulus that facilitates filtration.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
