What are the five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards?
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
Thoracic, cervical, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
Lumbar, thoracic, cervical, coccygeal, sacral
Sacral, lumbar, cervical, thoracic, coccygeal
Correct Answer : A
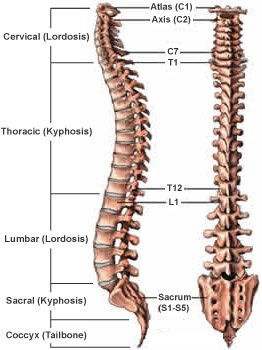
The vertebral column, also known as the spine or spinal column, is a series of bones called vertebrae that extend from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord. The five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards, are:
- Cervical: This region is made up of seven vertebrae and is located in the neck. The first two cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specialized to allow for head movement.
2. Thoracic: This region is made up of twelve vertebrae and is located in the upper and middle back. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae and articulate with the ribs.
3. Lumbar: This region is made up of five vertebrae and is located in the lower back. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebrae.
4. Sacral: This region is made up of five fused vertebrae and is located in the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior wall of the pelvis and articulates with the hip bones.
5. Coccygeal: This region is made up of four fused vertebrae and is located at the base of the vertebral column. The coccyx, or tailbone, provides atachment points for muscles and ligaments.
 |
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
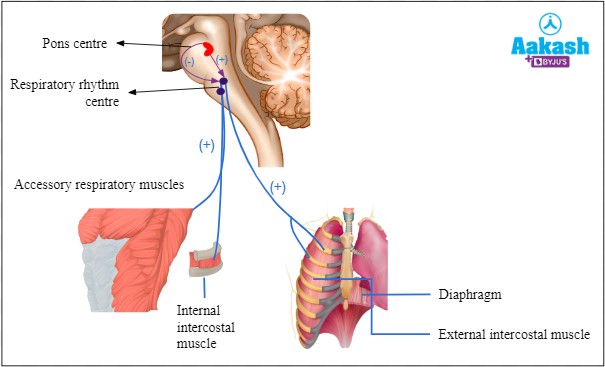
The diaphragm is responsible for regulating breathing rate and depth. It is a dome-shaped muscle located at the bottom of the chest cavity that contracts and relaxes to help move air in and out of the lungs.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Chemical properties are characteristics of a substance that describe its ability to undergo a chemical change or reaction with another substance. Reactivity with acid is a chemical property because it describes how a substance will react with an acid to produce a new substance.
Density, melting point, and boiling point are physical properties that describe how a substance behaves under certain conditions but do not involve a chemical change or reaction.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, play a crucial role in the circulatory system, primarily by facilitating the transportation of oxygen to body tissues. The other choices are also explained below:
A. Facilitation of gas exchange in the alveoli: While gas exchange occurs in the alveoli of the lungs, it is primarily carried out by the respiratory system and involves the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between air and blood. Red blood cells do not directly participate in this process.
B. Regulation of blood pH through the release of bicarbonate ions: The regulation of blood pH is mainly maintained by the bicarbonate buffering system, which involves the action of the respiratory and renal systems. Red blood cells do play a minor role in transporting carbon dioxide, which can indirectly influence pH, but it's not their primary function.
D. Synthesis of clotting factors in response to vascular injury: Clotting factors are primarily produced by the liver and are involved in the blood clotting process to prevent excessive bleeding. Red blood cells are not directly responsible for synthesizing these factors.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The kidneys secrete a number of hormones, which are important for normal functioning of the body.
If blood pressure falls, renin is secreted by the kidneys to constrict the small blood vessels, thereby increasing blood pressure. If the kidneys aren’t functioning correctly, too much renin can be produced, increasing blood pressure and sometimes resulting in hypertension (high blood pressure). This is why a number of people with kidney diseases also have high blood pressure.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The vertebral column, also known as the spine or spinal column, is a series of bones called vertebrae that extend from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord. The five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards, are:
- Cervical: This region is made up of seven vertebrae and is located in the neck. The first two cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specialized to allow for head movement.
2. Thoracic: This region is made up of twelve vertebrae and is located in the upper and middle back. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae and articulate with the ribs.
3. Lumbar: This region is made up of five vertebrae and is located in the lower back. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebrae.
4. Sacral: This region is made up of five fused vertebrae and is located in the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior wall of the pelvis and articulates with the hip bones.
5. Coccygeal: This region is made up of four fused vertebrae and is located at the base of the vertebral column. The coccyx, or tailbone, provides atachment points for muscles and ligaments.
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
- Frontal Plane (Coronal Plane) → Divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) halves. ❌
- Transverse Plane → A horizontal plane that divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) halves. ✅
- Sagittal Plane → Divides the body into left and right halves. ❌
- Coronal Plane → Another name for the Frontal Plane, which divides the body into front and back. ❌
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
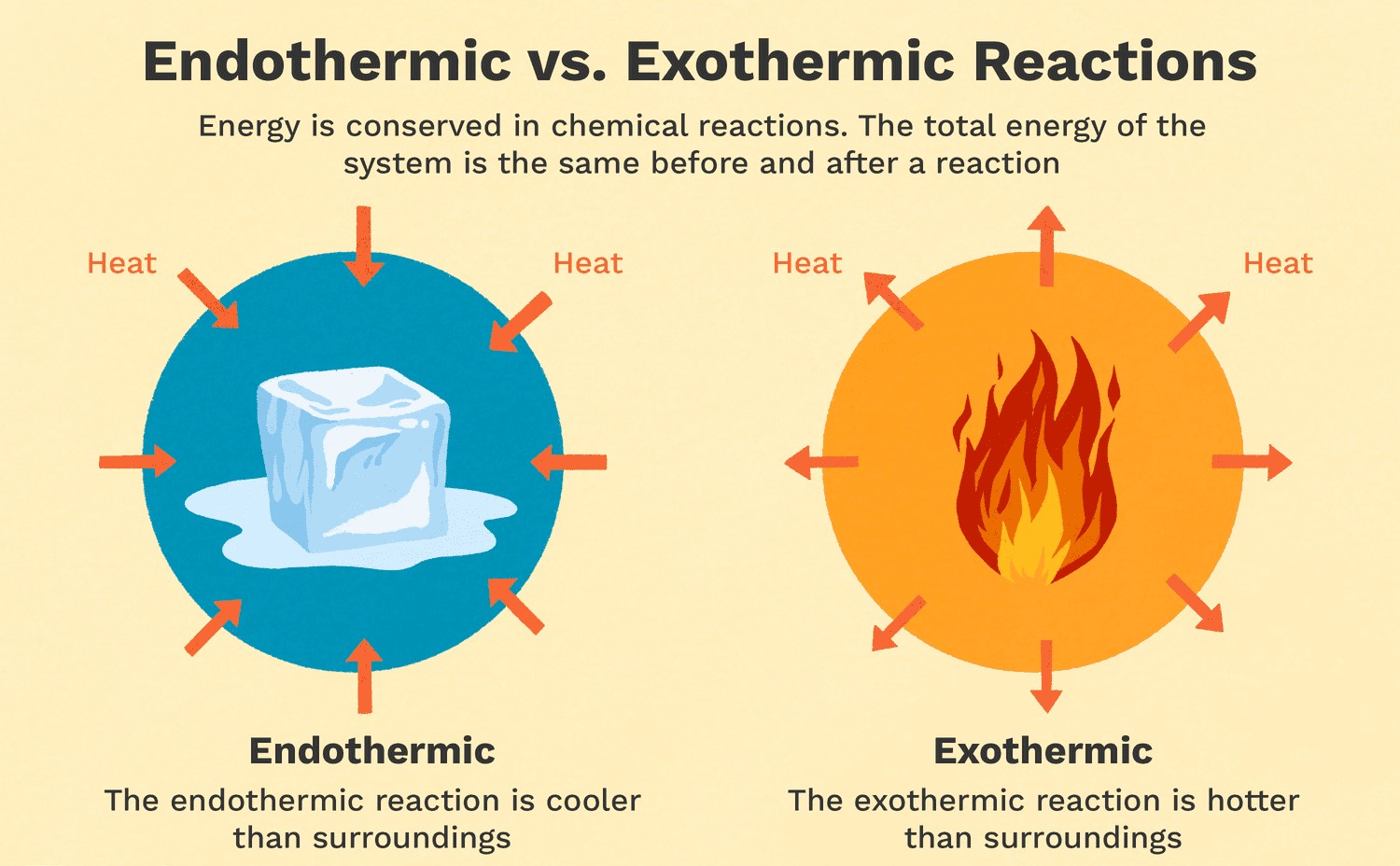
Exothermic reactions are reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound. Burning wood is an example of an exothermic reaction because it releases heat and light. As the wood reacts with oxygen in the air, it undergoes a combustion reaction that releases energy in the form of heat and light. Melting ice is an endothermic reaction because it requires energy input to melt the solid ice into liquid water. Cooking an egg is a chemical reaction that involves denaturing the proteins in the egg, but it is not necessarily exothermic or endothermic. Dissolving sugar in water is also not an example of an exothermic reaction because it does not release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
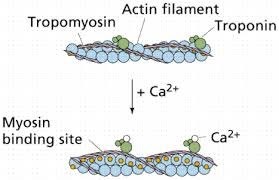
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
- The number of protons in an atom is equal to its atomic number.
- The periodic table shows that phosphorus (P) has an atomic number of 15.
- This means every phosphorus atom has 15 protons in its nucleus.
Analysis of Other Options:
- A. 30 → This is close to the atomic mass (30.97), but the atomic mass is not the same as the number of protons. ❌
- B. 16 → This is incorrect; sulfur (S) has an atomic number of 16, not phosphorus. ❌
- D. 31 → This is rounded from the atomic mass (30.97), but atomic mass ≠ number of protons. ❌
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
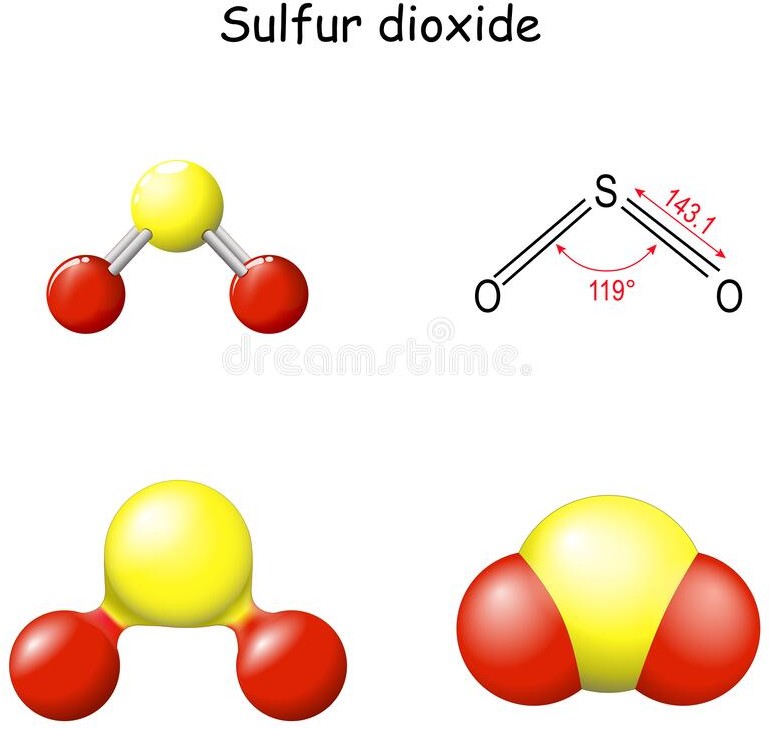
The molecular geometry of a molecule of sulphur dioxide (SO2) is bent or V-shaped. This is because of the presence of two lone pairs on the sulfur atom, which cause repulsion and distort the bond angles in the molecule.
SO2 has a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms by double bonds. The two double bonds and the two lone pairs of electrons on sulfur result in a trigonal planar arrangement of electron pairs around the sulfur atom. However, the repulsion between the lone pairs causes the two oxygen atoms to be pulled closer together, resulting in a bent or V-shaped molecular geometry.
The bent molecular geometry of SO2 affects its properties, such as its polarity and reactivity. SO2 is a polar molecule due to the asymmetric distribution of electrons, which results in a partial positive charge on the sulfur atom and partial negative charges on the oxygen atoms. This polarity makes SO2 a good solvent and reactant in chemical reactions, as well as a contributor to air pollution and acid rain.
 |
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
