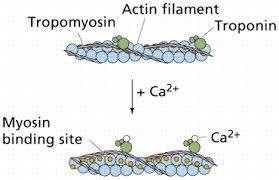
What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
Calcium binds to tropomyosin to expose the myosin-binding sites on actin.
Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum to initiate the sliding of actin and myosin filaments.
Calcium activates the motor neurons to stimulate muscle contraction.
Calcium is required for the relaxation of muscles after contraction.
Correct Answer : B
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Innate immunity is the first line of defense against pathogens and is present at birth. It provides immediate, non-specific protection against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Innate immunity involves physical barriers, such as skin and mucous membranes, as well as cellular and molecular components, such as phagocytes and cytokines.
Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is developed over time and provides specific protection against particular pathogens. It involves the recognition of antigens, which are specific components of pathogens, by immune cells called lymphocytes. The lymphocytes then produce antibodies that are specific to the antigens, allowing for a targeted response to the pathogen. This process takes time to develop, as the immune system needs to encounter the pathogen and mount a response.
Overall, innate immunity provides immediate, non-specific protection while adaptive immunity provides specific protection that is tailored to the particular pathogen. Both forms of immunity work together to protect the body against pathogens.
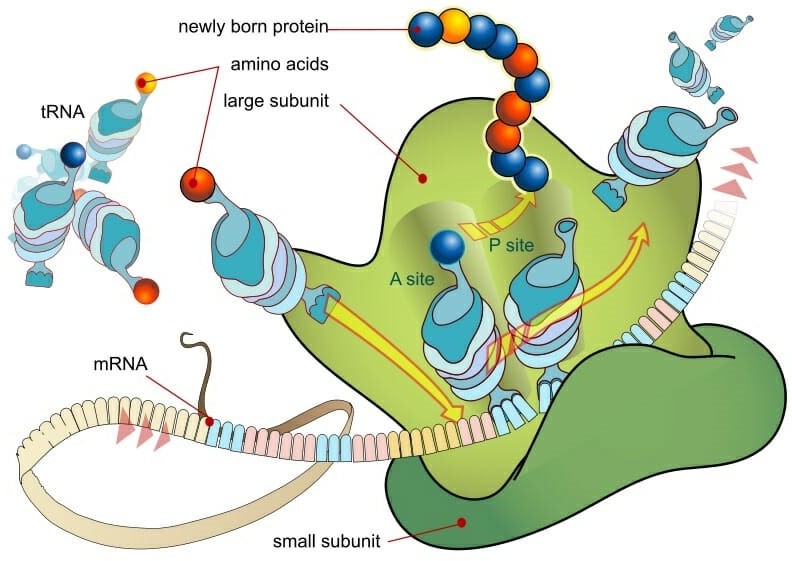
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Ribosomes are small, spherical structures found in all living cells, including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Their primary function is to synthesize proteins using the genetic information stored in the cell's DNA. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, one large and one small, that come together during protein synthesis.
Ribosomes read the genetic information stored in mRNA (messenger RNA) and use this information to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing protein chain until it reaches the end of the mRNA and the protein is complete.
Proteins are essential for a wide variety of cellular functions, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and transporting molecules across cell membranes. Therefore, ribosomes play a critical role in the overall function and survival of a cell.
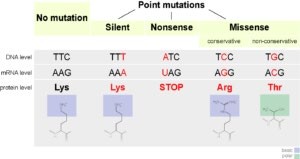
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
 |
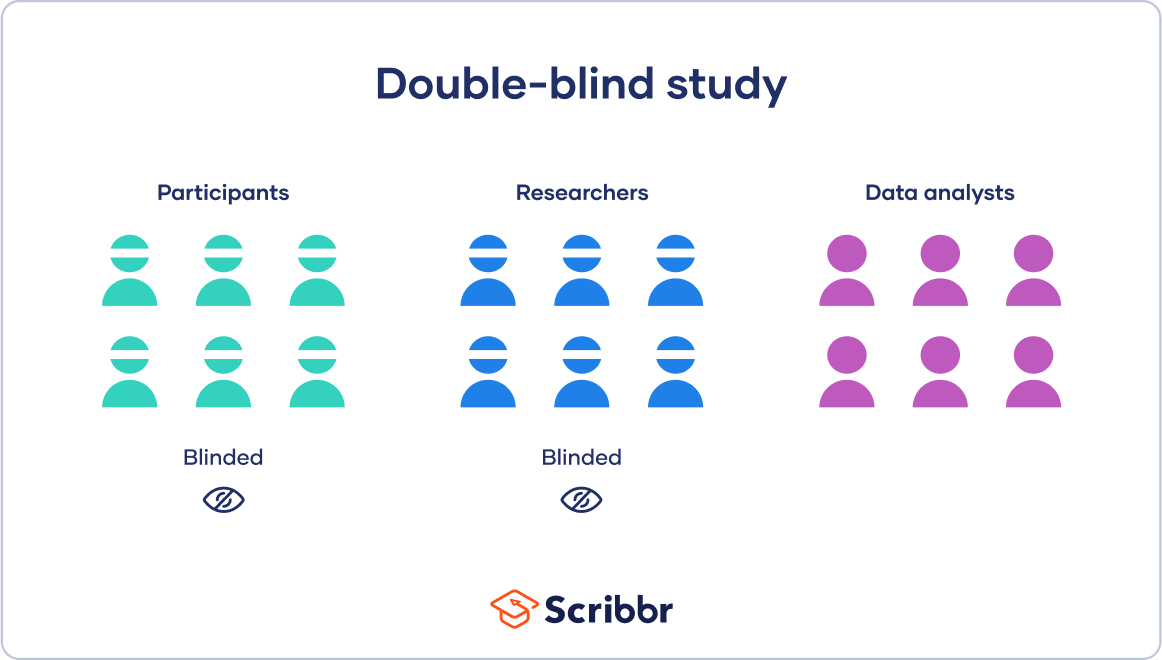
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to. Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind. Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to. Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Electrons are subatomic particles that possess a very small mass compared to protons and neutrons. The mass of an electron is approximately 11836of the mass of a proton or neutron, making it negligible when calculating the atomic mass of an atom.
In atomic mass calculations, protons and neutrons are considered because they make up the bulk of the atom's mass:
- Proton: Positively charged, and each proton has a mass of about 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
- Neutron: Neutral charge, with a mass also close to 1 amu.
- Electron: Negligible mass, contributing very little to the atomic mass, which is why the atomic mass number is typically determined by the number of protons and neutrons.
Quarks are the fundamental constituents of protons and neutrons but are not typically referred to in terms of atomic mass.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Facial acne is commonly caused by the blockage and inflammation of the sebaceous glands. These glands are responsible for secreting sebum, an oily substance that helps to lubricate the skin and hair. When these glands become overactive, or their ducts are blocked by excess sebum and dead skin cells, it can lead to the formation of pimples, blackheads, or whiteheads, which are typical signs of acne.
- Sebaceous glands are found near hair follicles and are primarily responsible for acne when they become clogged.
The other options are not related to acne:
- A. Lacrimal glands: These produce tears and are associated with the eye, not the skin.
- B. Sudoriferous glands: These are sweat glands, which are involved in perspiration, not typically linked to acne.
- D. Ceruminous glands: These are found in the ear canal and produce earwax, not involved in facial skin health.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Spirometry is a common pulmonary function test that measures pulmonary ventilation, specifically assessing the volume and flow of air that can be inhaled and exhaled from the lungs. It provides important information about lung function and can help diagnose various respiratory conditions.
The other options do not relate to spirometry:
- A. Urinary capacity of the bladder: This is measured by urodynamics or bladder capacity tests, not spirometry.
- B. Volume of blood in the body: This can be estimated using different methods, such as dilution techniques or imaging, but not spirometry.
- D. Number of turns in the small intestine: This relates to the anatomy and function of the digestive system and is not measured by spirometry.
Thus, spirometry specifically evaluates how well the lungs are functioning in terms of air movement.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The data collected by the researcher on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month would be most useful to analyze traffic paterns during rush hour.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The chemical formula for water is H2O. It consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
 |
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
This reaction involves an acid (hydrochloric acid, HCl) and a base (magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)₂) reacting to form water (H₂O) and a salt (magnesium chloride, MgCl₂). This is a classic neutralization reaction, where an acid reacts with a base to neutralize each other, producing water and a salt.
- Neutralization Reaction: Acid + Base → Water + Salt
- In this case:
- Acid: HCl (hydrochloric acid)
- Base: Mg(OH)₂ (magnesium hydroxide)
- Products: H₂O (water) and MgCl₂ (magnesium chloride)
The other options do not apply:
- A. Decomposition: A single compound breaks down into two or more substances. Not the case here.
- B. Combustion: A substance reacts with oxygen, often producing heat and light (usually with organic compounds). Not the case here.
- C. Synthesis: Two or more substances combine to form a single product. Not applicable to this reaction.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
