A client converts from normal sinus rhythm at 80 bpm to atrial fibrillation with a ventricular response at 165 bpm.
Blood pressure is 162/74 mm Hg. Respiratory rate is 20 breaths per minute with normal chest expansion and clear lungs bilaterally.
IV heparin and Diltiazem are given.
What is the main goal of treatment?
Maintain anticoagulation
Improve oxygenation
Control ventricular heart rate
Decrease SA node conduction
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A rationale:
While maintaining anticoagulation is important in atrial fibrillation to prevent blood clots, it is not the main goal of treatment in this specific scenario.
The client's blood pressure is elevated, suggesting that the rapid heart rate is the more immediate concern.
Additionally, the prompt indicates that heparin has already been administered, addressing the anticoagulation need.
Choice B rationale:
The client's respiratory rate and lung sounds are normal, indicating that oxygenation is not a primary concern at this time.
The fast heart rate is the more pressing issue, as it can lead to decreased cardiac output and potential complications.
Choice C rationale:
Controlling the ventricular heart rate is the main goal of treatment in this case.
Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response can lead to several detrimental consequences, including:
Decreased cardiac output due to shortened ventricular filling time
Increased myocardial oxygen demand, potentially causing angina or heart failure
Increased risk of stroke or other thromboembolic events
Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, is a medication commonly used to slow the heart rate in atrial fibrillation.
By slowing the conduction of electrical impulses through the atrioventricular (AV) node, it effectively reduces the number of impulses that reach the ventricles, thereby controlling the ventricular response.
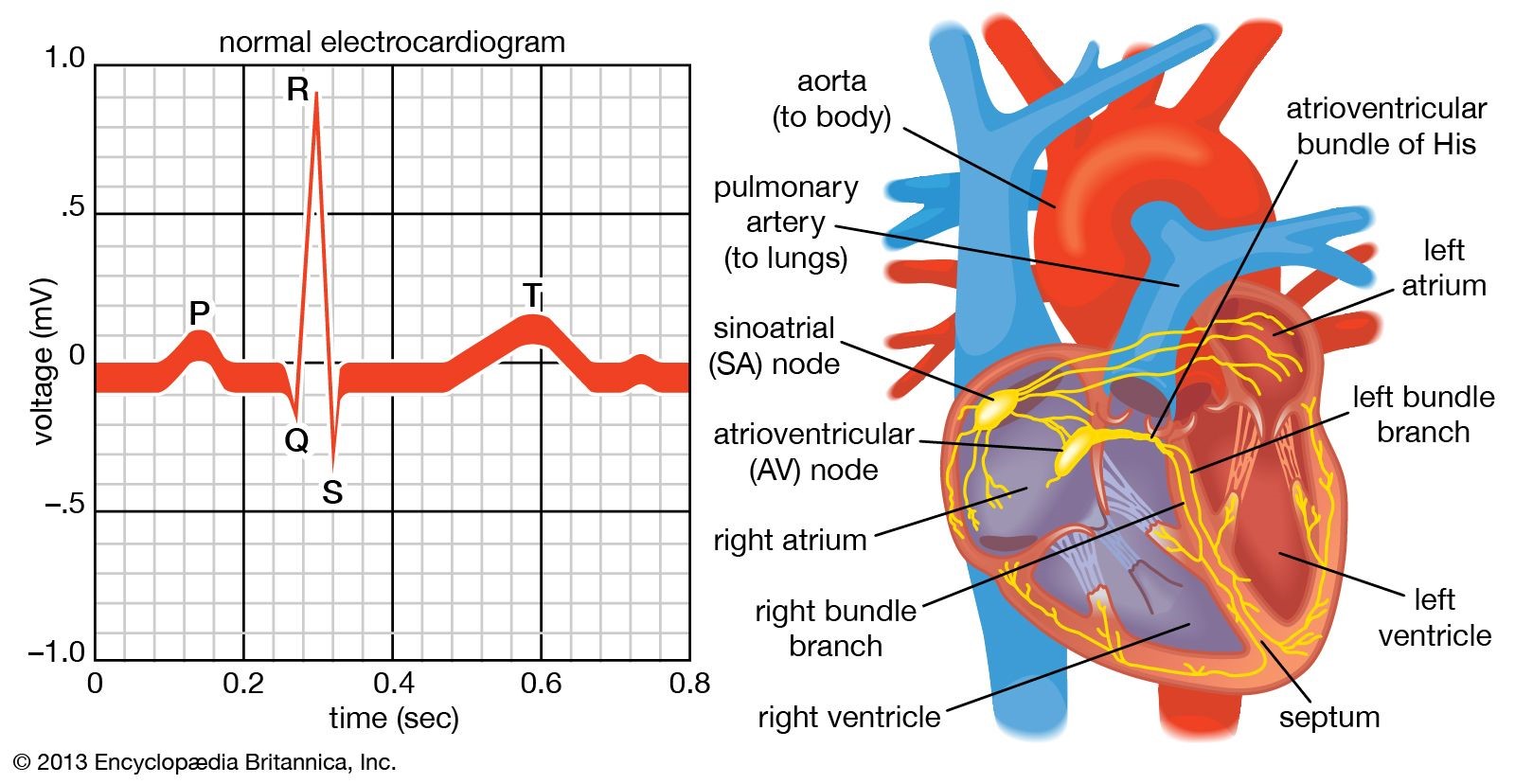
Choice D rationale:
Decreasing SA node conduction is not a primary goal in this situation.
The SA node is responsible for initiating the normal electrical impulses that trigger heart contractions.
In atrial fibrillation, the electrical activity is chaotic and originates from multiple foci within the atria, rather than the SA node.
Therefore, targeting the SA node would not effectively address the underlying rhythm disturbance.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Answer and explanation
The correct answer is C. Normal Sinus Rhythm.
Choice A rationale:
Asystole is the absence of all electrical activity in the heart, as evidenced by a flat line on the electrocardiogram (ECG). It is a medical emergency that requires immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation.
Key features of asystole on ECG:
No discernible P waves, QRS complexes, or T waves.
A completely flat or nearly flat line on the ECG tracing.
Choice B rationale:
Atrial flutter is a rapid heart rhythm that arises from abnormal electrical activity in the atria. It is characterized by a sawtooth pattern on the ECG, with atrial rates typically between 250 and 350 beats per minute.
Key features of atrial flutter on ECG:
Absence of distinct P waves, instead replaced by flutter waves (sawtooth pattern).
Regular, rapid atrial rate (typically 250-350 bpm).
QRS complexes may be normal or slightly irregular in appearance.
Choice C rationale:
Normal sinus rhythm is the natural, healthy rhythm of the heart. It originates in the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart's natural pacemaker, and is characterized by a regular rate of 60-100 beats per minute, with consistent P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves on the ECG.
Key features of normal sinus rhythm on ECG:
Presence of distinct P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves.
Regular rhythm with a rate of 60-100 beats per minute.
PR interval (the time between the P wave and QRS complex) is 0.12-0.20 seconds.
QRS duration (the time it takes for the ventricles to depolarize) is less than 0.12 seconds.
Choice D rationale:
Sinus bradycardia is a slow heart rhythm, with a rate below 60 beats per minute. It is often a normal finding in healthy individuals, especially athletes or during sleep. However, it can also be a sign of underlying medical conditions.
Key features of sinus bradycardia on ECG:
Presence of distinct P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves.
Regular rhythm with a rate less than 60 beats per minute.
PR interval and QRS duration are typically normal.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Clearance of partially occluded coronary arteries is not a primary goal of catheter ablation therapy. This procedure is not designed to remove blockages in the coronary arteries. Instead, it focuses on targeting and disrupting abnormal electrical signals within the heart.
While coronary artery disease (CAD) can coexist with heart rhythm problems, and both may share risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol, catheter ablation specifically addresses electrical disturbances, not structural blockages in blood vessels.
Procedures like angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) are used to address coronary artery blockages.
Choice B rationale:
Resetting of the heart’s contractility is not the primary mechanism of catheter ablation. While the procedure can sometimes improve heart function by reducing abnormal heart rhythms, its primary aim is to eliminate the abnormal electrical signals that cause arrhythmias, not directly enhance the heart's pumping ability.
Medications like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers are often used to address contractility issues.
Choice C rationale:
Destruction of specific cardiac cells is the correct answer. Catheter ablation works by using energy (usually radiofrequency or cryoablation) to destroy small areas of heart tissue that are responsible for generating or conducting abnormal electrical signals.
By targeting these specific cells, the procedure can interrupt the pathways that cause arrhythmias, effectively eliminating or significantly reducing their occurrence.
This targeted approach is what distinguishes catheter ablation from medications, which often act on the entire heart rather than specific areas.
Choice D rationale:
Correction of structural cardiac abnormalities is not a goal of catheter ablation. This procedure is designed to address electrical problems within the heart, not structural defects like valve problems or holes in the heart walls.
Surgical procedures are typically used to correct structural abnormalities.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
