A nurse is assessing a client who is in labor and has meconium-stained amniotic fluid.
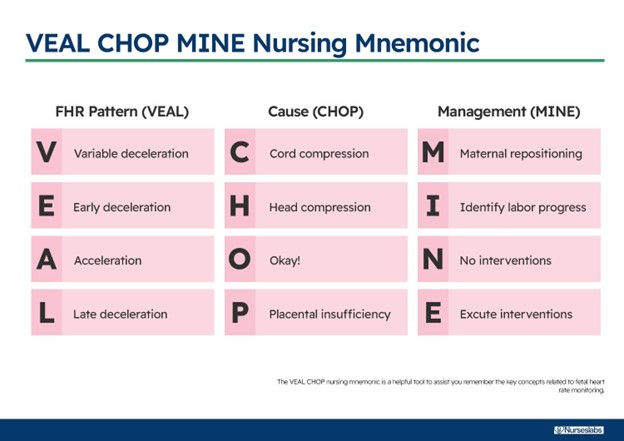
The nurse observes variable decelerations on the EFM tracing, which are decelerations that have an abrupt onset and vary in shape, duration, and degree of fall below the baseline FHR.
What is the most appropriate nursing intervention for this situation?
Reposition the client to improve placental blood flow
Administer oxygen to the client to increase fetal oxygenation
Prepare for an amnioinfusion to dilute the meconium and relieve cord compression
Notify the provider and prepare for an emergency cesarean delivery
The Correct Answer is C
Prepare for an amnioinfusion to dilute the meconium and relieve cord compression.
An amnioinfusion is a procedure in which sterile fluid is infused into the uterus through a catheter to increase the volume of amniotic fluid and reduce the risk of fetal distress caused by meconium aspiration or cord compression.
Variable decelerations are a sign of cord compression and can be alleviated by an amnioinfusion.
Choice A is wrong because repositioning the client may not be enough to improve placental blood flow and prevent fetal hypoxia.
Choice B is wrong because administering oxygen to the client may not be sufficient to increase fetal oxygenation if the cord is compressed.
Choice D is wrong because an emergency cesarean delivery may not be necessary if an amnioinfusion can resolve the variable decelerations and improve fetal well-being.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Prepare for an amnioinfusion to dilute the meconium and relieve cord compression.
An amnioinfusion is a procedure in which sterile fluid is infused into the uterus through a catheter to increase the volume of amniotic fluid and reduce the risk of fetal distress caused by meconium aspiration or cord compression.
Variable decelerations are a sign of cord compression and can be alleviated by an amnioinfusion.
Choice A is wrong because repositioning the client may not be enough to improve placental blood flow and prevent fetal hypoxia.
Choice B is wrong because administering oxygen to the client may not be sufficient to increase fetal oxygenation if the cord is compressed.
Choice D is wrong because an emergency cesarean delivery may not be necessary if an amnioinfusion can resolve the variable decelerations and improve fetal well-being.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Accelerations.According to the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) terminology, accelerations are defined as transient increases in the FHR of at least 15 bpm above the baseline for at least 15 seconds.Accelerations are a reassuring sign of fetal well-being and oxygenation.
Early decelerations are decreases in the FHR that coincide with the onset and end of a uterine contraction.They are caused by fetal head compression and are usually benign.
Late decelerations are decreases in the FHR that begin after the peak of a uterine contraction and do not return to baseline until after the contraction ends.They are caused by uteroplacental insufficiency and are a sign of fetal hypoxia.
Variable decelerations are abrupt decreases in the FHR that vary in timing.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
