A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who has fluid volume deficit. The nurse would expect which of the following findings?
Urine specific gravity 1.035.
BUN 19 mg/dL.
Hematocrit 44.9%.
Sodium 155 mEq/L.
The Correct Answer is A
Sodium 155 mEq/L. Choice A rationale:
A urine specific gravity of 1.035 indicates concentrated urine and is consistent with fluid volume deficit. However, it is not the most specific finding for this condition.
Choice B rationale:
A BUN (blood urea nitrogen) level of 19 mg/dL can be a normal value. It is within the reference range (usually around 7-20 mg/dL) and does not provide specific information about fluid volume deficit.
Choice C rationale:
A hematocrit of 44.9% can also be within the normal range for some individuals, and while it can be elevated in cases of fluid volume deficit, it is not as sensitive as other parameters for detecting this condition.
Choice D rationale:
This is the correct answer because a sodium level of 155 mEq/L is elevated and indicates hypernatremia, which is associated with fluid volume deficit. Hypernatremia occurs when there is a relative lack of water in relation to the sodium concentration in the blood, and it can lead to dehydration
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. The client who has gastroenteritis and is febrile.
Choice A rationale:
The client with end-stage renal failure scheduled for dialysis would not be at risk for fluid volume deficit because dialysis is a treatment that removes waste, salt, and extra water to prevent them from building up in the body, keeping a safe level of certain chemicals in the blood, and controlling blood pressure.
Choice B rationale:
Being NPO (nothing by mouth) since midnight for endoscopy typically involves a short period of fasting. While it could potentially contribute to a mild fluid volume deficit, it is not as significant as other causes like vomiting or diarrhea, which can lead to more substantial fluid losses.
Choice C rationale:
A client with left-sided heart failure and an elevated BNP level is more likely to experience fluid volume overload rather than a deficit. BNP is released in response to ventricular volume expansion and pressure overload, which are indicative of heart failure, not fluid volume deficit.
Choice D rationale:
The client with gastroenteritis and a fever is at risk for fluid volume deficit due to increased fluid losses from vomiting, diarrhea, and fever-induced perspiration. These symptoms align with the common risk factors for fluid volume deficit, which include vomiting, diarrhea, and sweating.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Widened QRS Complexes.
Choice A rationale:
Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes are not typical findings in respiratory acidosis. They are more commonly associated with conditions like hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia.
Choice B rationale:
Warm, flushed skin is not directly related to respiratory acidosis. It is not a typical manifestation of this acid-base imbalance.
Choice C rationale:
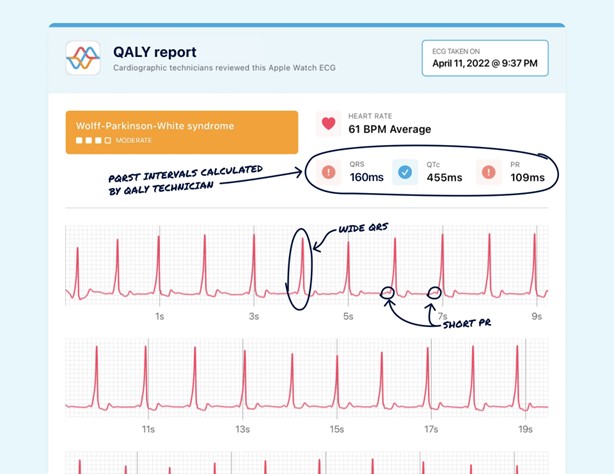
Widened QRS complexes on an ECG are characteristic findings in respiratory acidosis. Acidosis can lead to changes in the electrical conduction of the heart, resulting in QRS complex widening.
Choice D rationale:
Bounding peripheral pulses are not directly associated with respiratory acidosis. They may be seen in conditions like hyperthyroidism or anemia but are not specific to respiratory acidosis. Remember, always interpret lab results and clinical findings in the context of the patient's overall condition, medical history, and other relevant factors to provide the best care possible.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
