Which of the following is a key teaching point when educating a client about disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)?
Consuming a diet high in vitamin K to promote clotting
Stopping all medications to prevent interactions with clotting factors
Engaging in physical activity to promote blood flo
Avoiding activities that may cause injury or bleeding
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason:
Consuming a diet high in vitamin K to promote clotting is not typically recommended for patients with DIC. While vitamin K is essential for clotting, DIC involves both excessive clotting and bleeding. Increasing vitamin K intake could exacerbate clotting issues without addressing the underlying imbalance.
Choice B Reason:
Stopping all medications to prevent interactions with clotting factors is not advisable. Patients with DIC often require medications to manage their condition, including anticoagulants and treatments for the underlying cause. Discontinuing all medications could lead to uncontrolled symptoms and complications.
Choice C Reason:
Engaging in physical activity to promote blood flow is generally beneficial for overall health, but in the context of DIC, it must be approached with caution. Physical activity can increase the risk of injury and bleeding, which is a significant concern for patients with DIC. Therefore, any exercise regimen should be carefully monitored and tailored to the patient's condition.
Choice D Reason:
Avoiding activities that may cause injury or bleeding is crucial for patients with DIC. Due to the risk of spontaneous bleeding and the potential for minor injuries to lead to significant blood loss, patients must take precautions to minimize these risks. This includes avoiding contact sports, using soft-bristled toothbrushes, and being cautious with sharp objects.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","C"]
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
First-degree heart block is a condition where the electrical signals in the heart are delayed but still reach the ventricles. It is generally considered benign and does not typically lead to heart failure. It is often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally on an ECG.
Choice B Reason:
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common arrhythmia associated with heart failure. AFib causes the atria to beat irregularly and often rapidly, which can lead to poor blood flow and increased risk of stroke. In heart failure patients, AFib can exacerbate symptoms and worsen the prognosis due to the loss of atrial contraction and irregular ventricular response.
Choice C Reason:
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a serious arrhythmia that is often associated with heart failure. VT originates in the ventricles and can lead to hemodynamic instability and sudden cardiac death if not treated promptly. It is a common complication in patients with heart failure and cardiomyopathy.
Choice D Reason:
Sinus bradycardia is a slower than normal heart rate, typically less than 60 beats per minute. While it can occur in healthy individuals, especially athletes, it is not specifically associated with heart failure. In some cases, severe bradycardia can lead to symptoms of heart failure, but it is not a primary arrhythmia linked to the condition.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
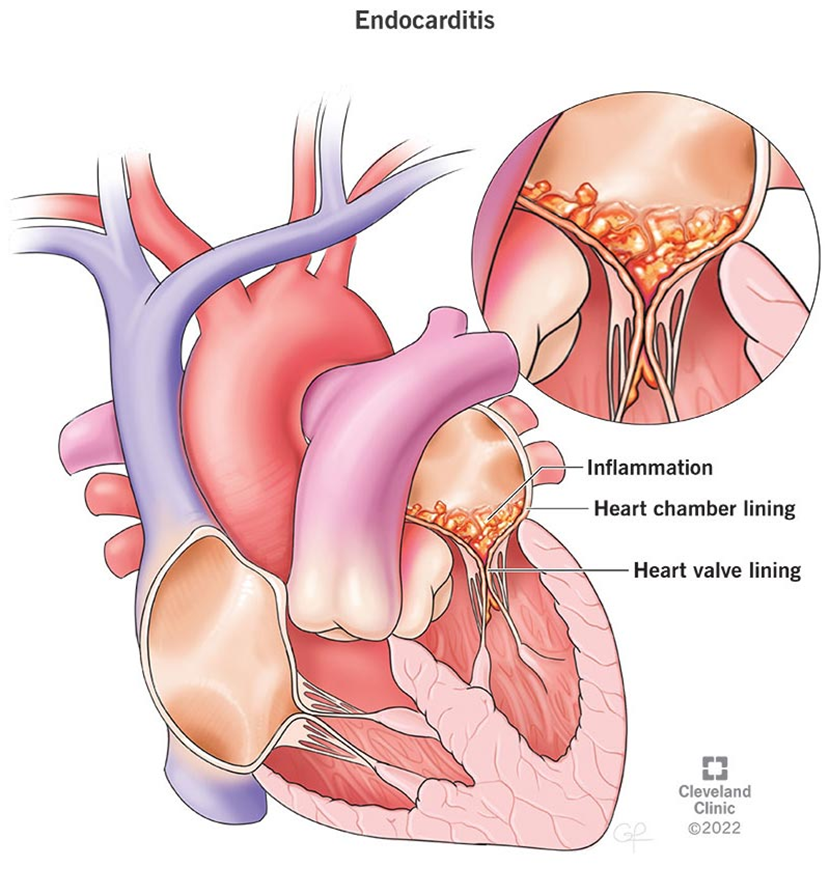
Reduced blood pressure is not a specific complication of infective endocarditis. While hypotension can occur in severe cases due to septic shock, it is not a hallmark of the disease. Infective endocarditis primarily affects the heart valves and can lead to embolic events, heart failure, and other complications.
Choice B Reason:
Osler's nodes are a classic sign of infective endocarditis. These are painful, red or purple, raised lesions found on the hands and feet. They are caused by immune complex deposition and are indicative of the systemic nature of the infection. Their presence can help in the clinical diagnosis of infective endocarditis.
Choice C Reason:
Clear lung sounds are not a complication of infective endocarditis. In fact, clear lung sounds would generally indicate that there is no pulmonary involvement or congestion. Complications of infective endocarditis are more likely to involve the heart, kidneys, and other organs through embolic events.
Choice D Reason:
Increased appetite is not associated with infective endocarditis. Patients with this condition often experience symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and weight loss due to the chronic infection. Increased appetite would be an unusual finding and not related to the disease process.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
