Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms
- The signs and symptoms of glomerulonephritis vary depending on the type, severity, and duration of the condition.
- Some of the common signs and symptoms are:
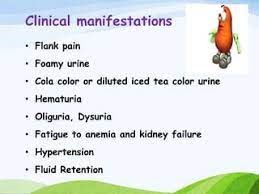
- Hematuria: Blood in urine can make it appear pink or brown-colored. It indicates the presence of red blood cells in urine due to damage to the glomeruli.
- Proteinuria: Protein in urine can make it appear foamy. It indicates the loss of protein from the blood due to increased permeability of the glomeruli.
- Azotemia: Increased waste products such as creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in the blood indicate the reduced filtration function of the kidneys.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can result from fluid retention, activation of the RAAS, or damage to the renal arteries.
- Edema: Swelling can result from fluid retention due to decreased urine output or loss of protein from the blood. It is usually seen in the face, hands, feet, and abdomen.
- Weight gain: Weight gain can result from fluid retention due to decreased urine output or loss of protein from the blood.
- Oliguria or anuria: Decreased or absent urine output can result from severe damage to the glomeruli or acute kidney failure.
- Fatigue: Fatigue can result from anemia, electrolyte imbalance, or uremia (buildup of waste products in the blood).
- Headache: Headache can result from hypertension, electrolyte imbalance, or uremia.
- Nausea and vomiting: Nausea and vomiting can result from electrolyte imbalance or uremia.
- Dyspnea: Difficulty breathing can result from pulmonary edema due to fluid overload or uremic pleuritis (inflammation of the lining of the lungs).
- Flank pain: Pain in the back or side can result from inflammation or enlargement of the kidneys.
Nursing Test Bank
Quiz #1: RN Exams Pharmacology Exams
Quiz #2: RN Exams Medical-Surgical Exams
Quiz #3: RN Exams Fundamentals Exams
Quiz #4: RN Exams Maternal-Newborn Exams
Quiz #5: RN Exams Anatomy and Physiology Exams
Quiz #6: RN Exams Obstetrics and Pediatrics Exams
Quiz #7: RN Exams Fluid and Electrolytes Exams
Quiz #8: RN Exams Community Health Exams
Quiz #9: RN Exams Promoting Health across the lifespan Exams
Quiz #10: RN Exams Multidimensional care Exams
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Quiz #1: Naxlex RN Comprehensive online practice 2019 B with NGN
Quiz #2: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023
Quiz #3: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 Exit Exam A
Quiz #4: Naxlex HESI Exit LPN Exam
Quiz #5: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor PN 2020
Quiz #6: Naxlex VATI PN Comprehensive Predictor 2020
Quiz #8: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 - Exam 1
Quiz #10: Naxlex HESI PN Exit exam
Quiz #11: Naxlex HESI PN EXIT Exam 2
Questions on Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Incorrect. The renal medulla is not the primary site of glomerulonephritis; it is deeper within the kidney and not directly involved in this condition.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Incorrect. Dysuria refers to painful urination and is not typically associated with dark, cola-colored urine.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Incorrect. Familial history may be a risk factor for some kidney diseases, but it is not a direct cause of PSGN.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Incorrect. While the kidneys play a role in blood pressure regulation, this function involves other structures in addition to the glomeruli.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct. Renal artery stenosis, a narrowing of the renal artery supplying the kidney, is a common complication of glomerulonephritis and can lead to hypertension and heart failure.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Incorrect. Excessive reabsorption of sodium is not a primary factor in the development of glomerulonephritis.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Incorrect. Tolerance induction is a process by which the immune system recognizes self-antigens and does not directly relate to the development of glomerulonephritis.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct. PSGN is most commonly associated with streptococcal infections, particularly group A streptococci.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Incorrect. Acute pyelonephritis is a different kidney condition caused by a bacterial infection of the renal pelvis and is not characterized by crescent-shaped structures in the glomeruli.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Incorrect. Fiber is an important dietary component for overall health but is not specifically related to reducing proteinuria or managing blood pressure in glomerulonephritis.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Incorrect. While a familial history of kidney disease may be a risk factor for some kidney conditions, it is not a primary risk factor for PSGN.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Incorrect. High dietary intake of calcium is not a common predisposing factor for APSGN.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Incorrect. Osteoarthritis is unrelated to RPGN.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Incorrect. Adequate fluid intake is generally recommended for kidney health and does not increase the risk of chronic glomerulonephritis.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Incorrect. Elevated blood cholesterol levels may have cardiovascular implications but are not typically a predisposing factor for membranous glomerulonephritis.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct. Periorbital edema (swelling around the eyes) and edema in the lower extremities are often early indicators of glomerulonephritis due to fluid retention.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Incorrect. Hypercalcemia (high blood calcium levels) is not a common cause of hypertension in glomerulonephritis.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Incorrect. Proteinuria refers to the presence of excess protein in the urine and is not specifically related to the color of urine in glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect. Excessive fluid intake is not a likely cause of fatigue, weakness, and pallor in glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect. Edema refers to swelling due to fluid retention and is not related to decreased urine output.
Incorrect. Hyponatremia is an electrolyte imbalance and is not a direct indicator of hematuria in glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect. PET scans are not typically used for kidney imaging in the context of glomerulonephritis.
Correct. Kidney biopsies are essential for diagnosing glomerulonephritis because they help identify the specific type of glomerulonephritis, its cause, and the extent of renal damage.
Correct. Proteinuria, the presence of excessive protein in the urine, is a common abnormality associated with glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a marker of inflammation and is not typically used to assess kidney function or GFR in glomerulonephritis.
Correct. A low-sodium diet helps manage hypertension and reduces edema, which are common complications of glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect. Antacids are used to relieve symptoms of gastrointestinal conditions and do not play a primary role in managing blood pressure in glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect. Avoiding protein-rich foods is not a non-pharmacological intervention for reducing edema in glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect. While ACE inhibitors can affect aldosterone levels, their primary role in glomerulonephritis is to reduce proteinuria and manage blood pressure.
Incorrect. Monthly dental check-ups are important for oral health but are not specifically related to glomerulonephritis follow-up care.
Correct. A low-sodium diet helps manage hypertension and reduces edema, common complications of glomerulonephritis.
Correct. ACE inhibitors are commonly prescribed in glomerulonephritis to reduce proteinuria and manage hypertension, helping to protect kidney function.
Incorrect. Limiting fluid intake should be individualized and is not a universal measure to prevent recurrent episodes of glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect. Avoiding all movement is not necessary and may not effectively reduce fluid accumulation in edematous areas.
Correct. The primary goal of follow-up visits for glomerulonephritis is to monitor kidney function, blood pressure, and overall health to ensure the client's well-being and the effectiveness of treatment.
Search Here
Related Topics
More on Nursing
- Pathophysiology of the Musculoskeletal System
- Pathophysiology of the Reproductive System
- Pathophysiology of the integumentary system
- Pathophysiology of the Hematologic System
- Pathophysiology of the respiratory system
- Pathophysiology of the Gastrointestinal System
- Pathophysiology of the Nervous System
- Basic Concepts of Pathophysiology
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
