Diagnostic Evaluation and GFR Calculation
- The diagnosis of CRF is based on the presence of kidney damage or decreased GFR for three or more months.
- The GFR can be estimated by using serum creatinine level and other factors such as age, sex, race, and body size.
- The most commonly used formula is the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation:
- GFR = 141 x min (Scr/κ, 1)^α x max(Scr/κ , 1)^-1.209 x 0.993^Age x 1.018 [if female] x 1.159 [if black]
where Scr is serum creatinine in mg/dL,
κ is 0.7 for females and 0.9 for males,
α is -0.329 for females and -0.411 for males,
min indicates the minimum of Scr/κ or 1,
and max indicates the maximum of Scr/κ or 1.
- The stages of CKD are defined by the GFR as follows:
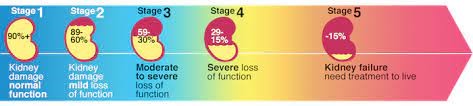
Stage 1: GFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2 with evidence of kidney damage
Stage 2: GFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73 m2 with evidence of kidney damage
Stage 3a: GFR 45-59 mL/min/1.73 m2
Stage 3b: GFR 30-44 mL/min/1.73 m2
Stage 4: GFR 15-29 mL/min/1.73 m2
Stage 5: GFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2 or on dialysis
- Other diagnostic tests that may be performed include:
- Blood tests: to measure electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone (PTH), albumin, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelets, coagulation factors
- Urine tests: to measure urine volume, specific gravity, osmolality, pH, sodium, potassium
- Urine culture: to rule out infection
- Urine protein electrophoresis: to identify the type of proteinuria
- Renal ultrasound: to assess the size and shape of the kidneys and detect any obstruction or cysts
- CT scan or MRI: to provide more detailed images of the kidneys and detect any masses or lesions. They can reveal structural changes, such as cysts, tumors, or kidney stones, that may be contributing to kidney damage.
- Kidney biopsy: to obtain a tissue sample for histological examination and diagnosis of the underlying cause
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Questions on Diagnostic Evaluation and GFR Calculation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Search Here
Related Topics
More on Nursing
- Pathophysiology of the Musculoskeletal System
- Pathophysiology of the Reproductive System
- Pathophysiology of the integumentary system
- Pathophysiology of the Hematologic System
- Pathophysiology of the respiratory system
- Pathophysiology of the Gastrointestinal System
- Pathophysiology of the Nervous System
- Basic Concepts of Pathophysiology
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
