A client admitted with acute diverticulitis has experienced a sudden increase in temperature and reports a sudden onset of extreme abdominal tenderness. The nurse's rapid assessment reveals that the client's abdomen is uncharacteristically rigid on palpation. What is the nurse's best response?
Call the primary provider and report that the client may be obstructed.
Position the client supine and insert an NG tube.
Administer a fleet enema as prescribed and remain with the client.
Contact the primary provider promptly and report these signs of perforation.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason: This is not the best response because it does not accurately describe the client's condition. Obstruction is a possible complication of diverticulitis, but it is not indicated by fever and abdominal rigidity. Obstruction is more likely to cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, constipation, and abdominal distension.
Choice B reason: This is not the best response because it can worsen the client's condition. Positioning the client supine and inserting an NG tube are interventions for gastric outlet obstruction, not diverticulitis. An NG tube can increase the risk of infection and perforation in the inflamed colon. Supine position can also increase the pressure on the abdomen and cause more pain and discomfort.
Choice C reason: This is not the best response because it can be harmful to the client. Administering a fleet enema is contraindicated for diverticulitis, as it can cause more inflammation, bleeding, or perforation in the colon. A fleet enema is a type of laxative that contains sodium phosphate and is used to relieve constipation or prepare for colonoscopy.
Choice D reason: This is the best response because it is the most appropriate and urgent action for the client. Contacting the primary provider promptly and reporting these signs of perforation is essential for the client's safety and treatment. Perforation is a life-threatening complication of diverticulitis, where the colon wall ruptures and causes peritonitis, which is inflammation of the abdominal cavity. Perforation can cause symptoms such as fever, abdominal rigidity, tenderness, and rebound pain. Perforation requires immediate surgical intervention and antibiotic therapy.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
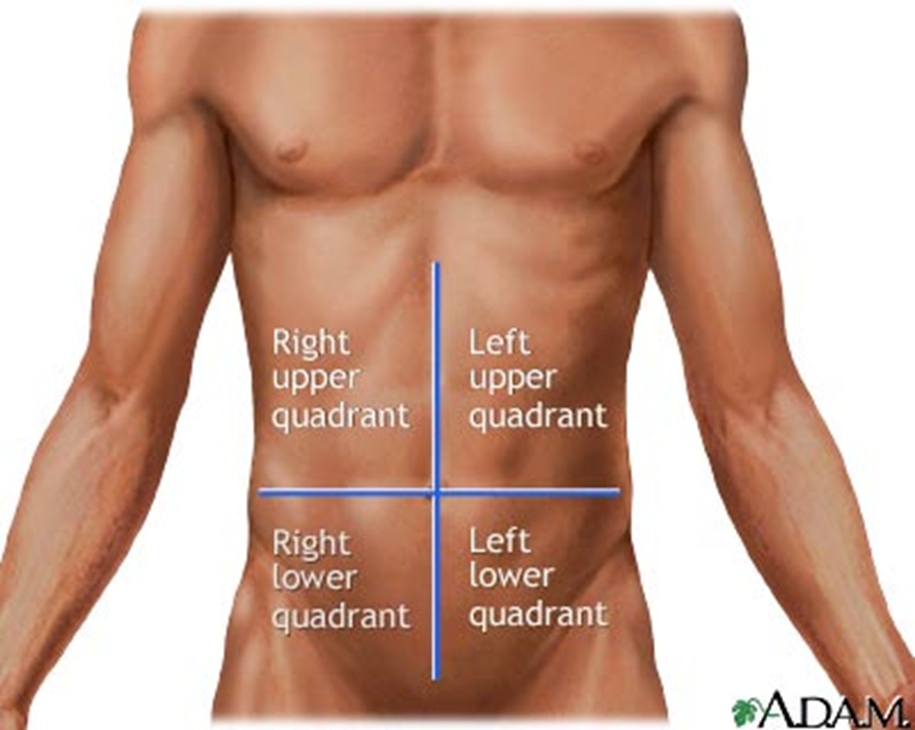
Choice A reason: The upper right quadrant is not the correct location for McBurney's point. This quadrant contains the liver, gallbladder, right kidney, and part of the colon. Pain in this area may indicate problems with these organs, such as hepatitis, gallstones, or kidney infection.
Choice B reason: The upper left quadrant is not the correct location for McBurney's point. This quadrant contains the stomach, spleen, left kidney, and part of the colon. Pain in this area may indicate problems with these organs, such as gastritis, splenomegaly, or kidney stones.
Choice C reason: The lower right quadrant is the correct location for McBurney's point. This quadrant contains the appendix, right ovary, and right fallopian tube. McBurney's point is a point on the abdomen that is one-third of the distance from the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus. Pain in this area may indicate appendicitis, ovarian cyst, or ectopic pregnancy.
Choice D reason: The lower left quadrant is not the correct location for McBurney's point. This quadrant contains the sigmoid colon, left ovary, and left fallopian tube. Pain in this area may indicate problems with these organs, such as diverticulitis, ovarian torsion, or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: Normal saline is not contraindicated for a dehydrated client with a skull fracture. Normal saline is an isotonic solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the blood plasma. It can help restore fluid balance and prevent cerebral edema.
Choice B reason: Dextrose in water 5% is contraindicated for a dehydrated client with a skull fracture. Dextrose in water 5% is a hypotonic solution that has a lower concentration of solutes than the blood plasma. It can cause fluid to shift from the blood vessels into the brain cells, increasing the intracranial pressure and worsening the skull fracture.
Choice C reason: Lactated Ringer's (LR) is not contraindicated for a dehydrated client with a skull fracture. Lactated Ringer's (LR) is an isotonic solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the blood plasma. It can also provide electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and lactate, which can help correct acid-base imbalances.
Choice D reason: Dextrose in normal saline is not contraindicated for a dehydrated client with a skull fracture. Dextrose in normal saline is a hypertonic solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than the blood plasma. It can cause fluid to shift from the brain cells into the blood vessels, reducing the intracranial pressure and cerebral edema.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
