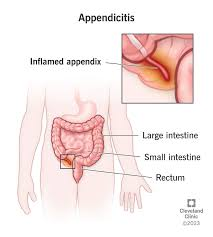
A client with suspected appendicitis is waiting for surgery. What should the nurse do?
Offer the client a warm beverage.
Monitor the client's gag reflex.
Help the client to a side-lying position with knees flexed.
Bring the client a heating pad to apply to the abdomen for comfort.
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason:
Offering a warm beverage to a client with suspected appendicitis is not advisable. Preoperative clients are typically required to have an empty stomach to reduce the risk of aspiration during anesthesia. Introducing fluids or food could delay surgery and increase the risk of complications.
Choice B reason:
Monitoring the client's gag reflex is not a priority in the care of a client with suspected appendicitis. The gag reflex is more relevant in neurological assessments or when evaluating swallowing function, not in the context of appendicitis.
Choice C reason:
Helping the client to a side-lying position with knees flexed can provide comfort and may help relieve abdominal pain. This position reduces tension on the abdominal muscles and can be a supportive measure while the client awaits surgery.
Choice D reason:
Applying a heating pad to the abdomen is contraindicated in clients with suspected appendicitis. Heat can cause the appendix to rupture, leading to peritonitis, which is a severe and potentially life-threatening complication. Therefore, this action should be avoided.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
A positive pregnancy test is crucial information that must be reported immediately as it has significant implications for the patient's health and treatment options. Pregnancy can impact the results of a Schilling's test, which is used to diagnose B12 deficiency anemia, as pregnancy itself can cause changes in B12 metabolism. Therefore, the healthcare provider must be informed to adjust the diagnostic approach and ensure the safety of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Choice B Reason:
While a hemoglobin level of 9.5 g/dL is below the normal range for adult females (11.6 to 15 g/dL) and a hematocrit of 32% is at the lower end of the normal range (36% to 44%)[^10^], these results are consistent with anemia but are not as immediately critical as a positive pregnancy test in the context of a Schilling's test.
Choice C Reason:
A glycosylated hemoglobin (A1c) level of 7.5% is above the normal range (4% to 5.9%), indicating poor blood sugar control over the past two to three months, which could suggest diabetes or prediabetes. However, this is not as urgent as a positive pregnancy test when considering the administration of a Schilling's test.
Choice D Reason:
A serum cholesterol level of 237 mg/dL is considered borderline high (200 to 239 mg/dL), which may increase the risk of heart disease over time. However, this does not require immediate reporting in the context of a Schilling's test for B12 deficiency anemia as compared to a positive pregnancy test.
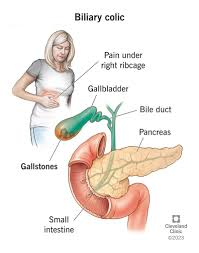
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice a reason:
A cream to soothe itching may be used if the client is experiencing pruritus, which can sometimes accompany biliary issues due to bile salts in the skin. However, pruritus is not a direct symptom of biliary colic, which is characterized primarily by pain.
Choice b reason:
Pain medication is the appropriate treatment for biliary colic. Biliary colic is caused by the temporary blockage of the bile duct by a gallstone, leading to intense pain in the upper right abdomen or the center of the abdomen. Pain relief is typically achieved with anti-inflammatory drugs or antispasmodics, and in some cases, opioids may be necessary.
Choice c reason:
An antibiotic would be prescribed if there was an infection, such as cholecystitis or cholangitis. Biliary colic itself does not necessarily indicate an infection unless accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or elevated white blood cell count.
Choice d reason:
A laxative is not typically used to treat biliary colic. While laxatives can help relieve constipation, biliary colic is a result of gallstones obstructing the bile duct, not bowel movement issues.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
