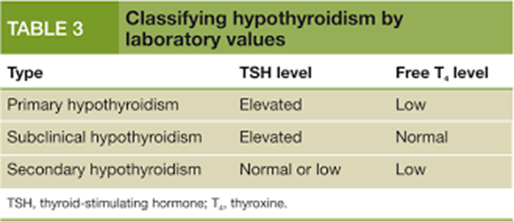
A nurse in a clinic is reviewing the laboratory values of a client who has primary hypothyroidism.
Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse anticipate an elevation of?
Free T4
Serum T3
Serum T4
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
The Correct Answer is D
A. In primary hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient thyroid hormone.
Consequently, free T4 levels are typically decreased.
B. Although serum T3 levels may also decrease in primary hypothyroidism due to impaired thyroid function, TSH is the primary marker used for diagnosis and monitoring.
C. Similarly, serum T4 levels may decrease in primary hypothyroidism due to decreased synthesis by the thyroid gland.
D. In primary hypothyroidism, the anterior pituitary gland releases more TSH to stimulate the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. Therefore, elevated TSH levels are characteristic of primary hypothyroidism.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Metabolic Acidosis, Uncompensated, is ruled out because the elevated PaCO2 and low pH indicate a respiratory problem rather than a metabolic one.
B. Respiratory Alkalosis. Partially Compensated is ruled out because the pH and PaCO2 levels are both abnormal and indicate acidosis rather than alkalosis.
C. The low pH (acidosis) along with the high PaCO2 indicate respiratory acidosis, and there is no evidence of compensation by the kidneys (normal HCO3).
D. Metabolic Alkalosis. Partially Compensated, is ruled out because the pH is low (acidosis) rather than high (alkalosis), and the PaCO2 is elevated, suggesting a respiratory problem rather than a metabolic one.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Increasing sodium intake is generally not recommended in chronic kidney disease, as it can exacerbate hypertension and fluid retention.
B. Epoetin alfa is a medication used to treat anemia associated with chronic kidney disease, and iron supplementation is often necessary to support erythropoiesis.
C. Potassium intake may need to be restricted in chronic kidney disease, especially in later stages when kidney function declines.
D. Protein intake may need to be adjusted in chronic kidney disease, but it's not directly related to the prescription of epoetin alfa.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
