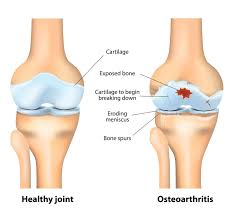
A nurse is assessing a client newly diagnosed with early-onset osteoarthritis. Which manifestation should the nurse expect?
Ulnar deviation.
Symmetric joints are affected.
Weight loss.
Joint stiffness and limited range of motion.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason:
Ulnar deviation, which is the angling of the fingers towards the little finger side of the hand, is more commonly associated with rheumatoid arthritis, not osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis typically affects the joint's cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness, rather than causing the fingers to deviate.
Choice B reason:
Symmetric joint involvement is also more characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually affects joints asymmetrically, meaning it's more likely to affect one side of the body or one particular joint at a time.
Choice C reason:
Weight loss is not a direct manifestation of osteoarthritis. In fact, being overweight is a risk factor for developing osteoarthritis due to the increased stress on weight-bearing joints. However, weight management through diet and exercise can be part of the treatment plan for osteoarthritis to alleviate symptoms and improve joint function.
Choice D reason:
Joint stiffness and limited range of motion are hallmark manifestations of osteoarthritis. These symptoms result from the breakdown of cartilage within the joints, which leads to pain and difficulty moving the affected joint. Stiffness is often most noticeable upon waking or after periods of inactivity, and the range of motion may decrease as the condition progresses.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
The statement "Forget him. There are other fish in the sea." minimizes the client's feelings and does not acknowledge the emotional pain they are experiencing. It is a cliché that can come across as dismissive rather than empathetic.
Choice B Reason:
"You must have been very upset to do what you did." This statement acknowledges the client's distress and does not judge their actions. It reflects an understanding of the depth of their emotional pain, which is a key component of empathy.
Choice C Reason:
"Don't worry, you'll get over him in time." While this statement may be intended to provide reassurance, it does not address the immediate emotional state of the client. It could be perceived as brushing aside their current feelings.
Choice D Reason:
"Why do you think your boyfriend broke up with you?" This question could be seen as probing for information rather than offering support. It might imply that the client is at fault for the breakup, which is not an empathetic approach.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Gas pains, while uncomfortable, are not typically a serious adverse effect of simvastatin and do not usually require immediate medical attention unless they are severe or persistent.
Choice B Reason:
Headaches are a common side effect of many medications, including simvastatin, and are not generally considered an emergency. However, if the headache is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms, it should be reported to a healthcare provider.
Choice C Reason:
Occasional constipation is another common side effect and is not usually a cause for immediate concern unless it becomes severe or chronic.
Choice D Reason:
Muscle weakness and pain, especially in the calves, can be a sign of a serious condition called rhabdomyolysis, which is a rare but serious adverse effect of statins like simvastatin. This condition involves the breakdown of muscle tissue and can lead to kidney damage. It should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
