A nurse is caring for a 3-year-old child who has had 160 mL of urine output over the past 8-hour period.
The child weighs 33 lb.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Notify the provider.
Continue to monitor the client.
Perform a bladder scan at the bedside.
Provide oral rehydration fluids.
The Correct Answer is B
Normal urine output for a child is 1-2 ml/kg/hr.
The child weighs 33 lb (15 kg), so their expected urine output over an 8-hour period would be between 120 mL and 240 mL.
The child’s urine output of 160 mL falls within this range.
Choice A, Notifying the provider, is not necessary because the child’s urine output
is within the normal range.
Choice C, Perform a bladder scan at the bedside, is not necessary because there is no indication of urinary retention.
Choice D, Providing oral rehydration fluids, is not necessary because the child’s urine output is within the normal range.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes your body to pass too much protein in your urine.
Swelling around the eyes is the most common sign of nephrotic syndrome in children 2.
Choice A is incorrect because smokey brown urine is not a symptom of nephrotic syndrome.
Choice C is incorrect because hypertension (high blood pressure) is a complication of nephrotic syndrome, not a symptom.
Choice D is incorrect because polyuria (frequent urination) is not a symptom of nephrotic syndrome.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
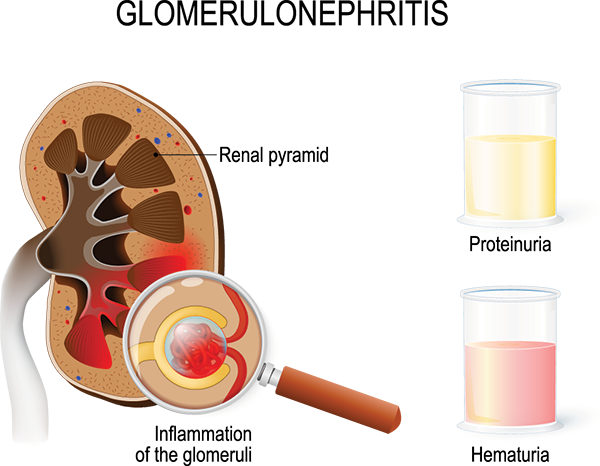
Nursing care planning goals for a child with acute glomerulonephritis are directed toward the excretion of excess fluid through urination.
Monitoring fluid status is very important and daily weights are an effective way to monitor fluid retention, as weight gain is the earliest sign of fluid retention.
Choice B, Educating the parents about potential complications, is important but not the nurse’s priority.
Choice C, Place the child on a no-salt-added diet, which may be part of the treatment
plan but is not the nurse’s priority.
Choice D, Maintaining a saline lock, may be necessary for administering medications but is not the nurse’s priority.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
