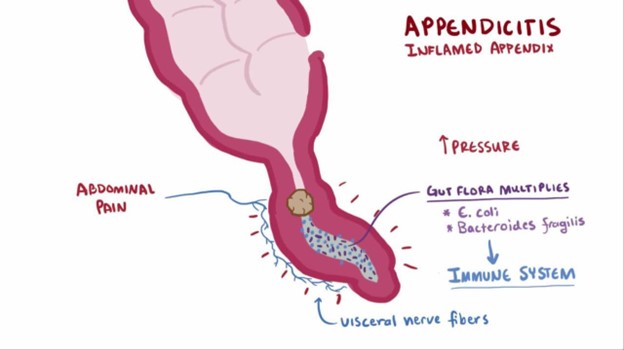
A nurse is caring for a child who has suspected appendicitis. Which of the following provider prescriptions should the nurse clarify?
Monitor oral temperature every 4 hr.
Administer sodium biphosphate/sodium phosphate.
Maintain NPO status.
Medicate the client for pain every 4 hr as needed.
The Correct Answer is B
The nurse should clarify the prescription to administer sodium biphosphate/sodium phosphate because it is a laxative and is contraindicated in a child with suspected appendicitis. The use of laxatives or enemas can potentially worsen the condition by increasing the risk of perforation or rupture of the inflamed appendix.
A. Monitoring oral temperature every 4 hours is important to assess for signs of infection or worsening condition.
C. Maintaining NPO status is essential to avoid stimulating the digestive system and to prepare for possible surgery.
D. Medicating the client for pain every 4 hours as needed is appropriate to manage pain and provide comfort while the child awaits further evaluation or treatment.
Remember, it's crucial to avoid the use of laxatives, enemas, or any other interventions that can potentially aggravate the inflamed appendix in a child with suspected appendicitis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Gastrointestinal:
Kawasaki disease primarily affects blood vessels, and the gastrointestinal system is not the main target of this condition. While gastrointestinal symptoms can occur as part of the overall inflammatory response, such as abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea, they are not the primary focus of concern in Kawasaki disease. The most critical system to monitor in Kawasaki disease is the cardiovascular system, specifically the coronary arteries.
B. Respiratory:
The respiratory system is not the primary system affected by Kawasaki disease. While respiratory symptoms can occur as part of the overall inflammatory response and fever associated with the disease, such as coughing or runny nose, they are not the main concern in Kawasaki disease. The primary system to monitor in this condition is the cardiovascular system, especially the coronary arteries.
C. Cardiovascular:
This is the correct answer. Kawasaki disease is primarily a vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels) that affects various blood vessels, including the coronary arteries. The inflammation of the coronary arteries can lead to coronary artery aneurysms and other cardiac complications. Monitoring the cardiovascular system is essential to detect any signs of coronary artery involvement and ensure timely intervention to prevent potential long-term cardiac problems.
D. Integumentary:
The integumentary system (skin) is not the primary focus of Kawasaki disease. While some skin changes can occur during the acute phase of the disease, such as a rash or peeling skin on the hands and feet, these are not the primary concerns. Monitoring the cardiovascular system is critical in Kawasaki disease due to the risk of coronary artery inflammation and potential complications.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
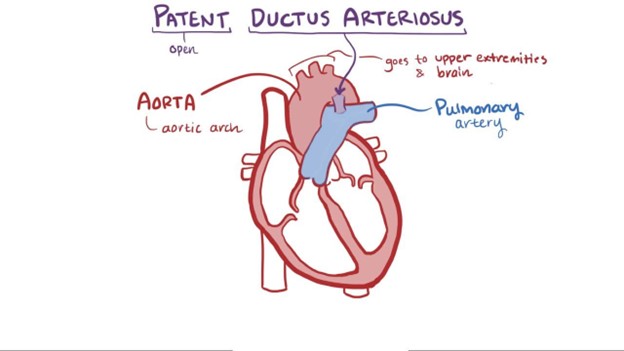
A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect associated with increased pulmonary blood flow. In normal fetal circulation, the ductus arteriosus allows blood to bypass the lungs since the baby receives oxygen from the mother's placenta. After birth, the ductus arteriosus should close, redirecting blood flow to the lungs for oxygenation. However, in some infants with PDA, the ductus arteriosus remains open, causing an abnormal connection between the aorta and the pulmonary artery. As a result, oxygenated blood from the aorta flows back into the pulmonary artery, increasing the workload on the lungs.
The other options are as follows:
A. Coarctation of the aorta - Coarctation of the aorta is a narrowing of the aorta, which obstructs blood flow and leads to increased blood pressure in the upper body and reduced blood flow to the lower body.
C. Tetralogy of Fallot - Tetralogy of Fallot is a combination of four heart defects that results in decreased pulmonary blood flow due to a ventricular septal defect (VSD), overriding aorta, pulmonary stenosis, and right ventricular hypertrophy.
D. Tricuspid atresia - Tricuspid atresia is a congenital heart defect where the tricuspid valve does not develop correctly, resulting in an absent or abnormal tricuspid valve. This defect prevents blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle and, therefore, reduces pulmonary blood flow.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
