A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for total parental nutrition (TPN).
Which of the following routes of administration should the nurse use?
Subcutaneous
Intraosseous
Midline catheter
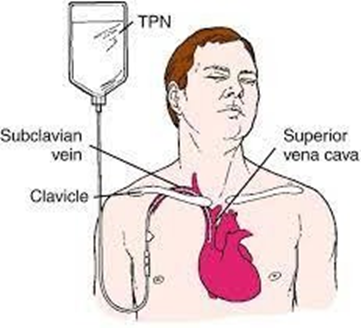
Central venous access device
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A rationale: TPN cannot be administered subcutaneously due to its composition.
Choice B rationale: Intraosseous access is for emergency situations when IV access isn't attainable.
Choice C rationale: A midline catheter might not be suitable for the hypertonic nature of TPN and can lead to complications.
Choice D rationale: Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) is a hypertonic solution that requires infusion into a large vein. The central venous access device allows for high-flow rates and avoids irritation or damage to smaller peripheral veins.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","C","D"]
Explanation
Choice A rationale: For subcutaneous injections like enoxaparin, the entire length of the needle needs to be inserted to ensure that the medication reaches the fatty tissue under the skin and reduces the risk of bleeding or bruising.
Choice B rationale: The client should not massage the insertion site after injecting the medication, as this may increase the risk of hematoma formation.
Choice C rationale: The client should alternate injection sites between the sides of the abdomen to prevent bruising and irritation.
Choice D rationale: The client should also grasp the skin between the thumb and forefinger while injecting the medication to create a fold of tissue. This ensures that the medication is delivered into the subcutaneous layer and not the muscle.
Choice E rationale: The client should not expel the air bubble from the prefilled syringe, as this helps to seal the medication in the tissue and prevent leakage while ensuring that you receive the full dose of medication.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale: An activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) of 90 seconds is prolonged, indicating that heparin is exerting an increased anticoagulant effect. To prevent bleeding, the nurse should decrease the infusion rate.
Choice B rationale: A platelet count within the normal range wouldn't necessarily prompt a decrease in heparin infusion.
Choice C rationale: The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is not directly related to heparin infusion.
Choice D rationale: An International Normalized Ratio (INR) of 1.2 suggests a low risk of bleeding, not requiring a decrease in heparin infusion.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
