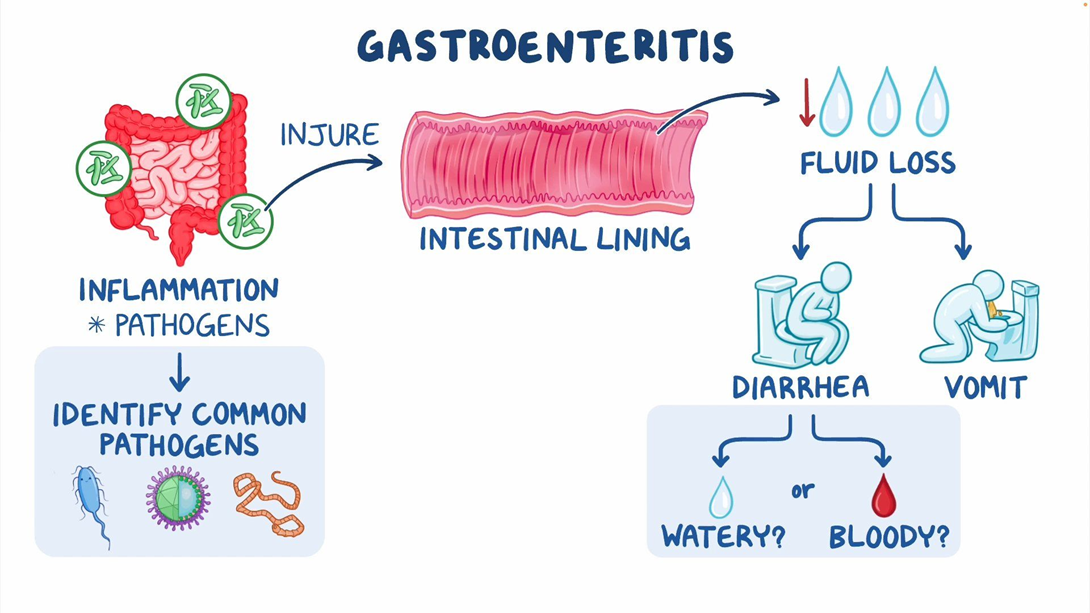
A nurse is caring for a client who has gastroenteritis and is reviewing the client's findings from two days ago and today. Which of the following findings require immediate follow-up?
The client is confused and appears weak.
The client's oral mucosa is dry and tongue is furrowed.
The client's temperature is 37.4° C (99.3° F).
The client's blood pressure is 90/58 mm Hg.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason: Confusion and weakness are signs of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance, which can result from vomiting and diarrhea. These are serious complications that can affect the client's mental status, blood pressure, heart rate, and kidney function. The nurse should report these findings to the provider and monitor the client's vital signs and fluid status.
Choice B reason: Dry oral mucosa and furrowed tongue are also signs of dehydration, but they are less severe than confusion and weakness. The nurse should report these findings to the provider as well, but they are not the most urgent ones.
Choice C reason: A temperature of 37.4° C (99.3° F) is slightly elevated, but not indicative of a fever or infection. The nurse should document this finding, but it does not require immediate follow-up.
Choice D reason: A blood pressure of 90/58 mm Hg is low, but not hypotensive. The nurse should document this finding, but it does not require immediate follow-up.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D"]
Explanation
Choice A reason: Administering antiemetics following the meal is not an appropriate action for a client who is at risk for malnutrition. Antiemetics are medications that prevent or treat nausea and vomiting, which can interfere with oral intake and hydration. However, antiemetics should be given before the meal, not after, to reduce the likelihood of postprandial nausea and vomiting. ¹²
Choice B reason: Providing mouth care before feeding is an appropriate action for a client who is at risk for malnutrition. Mouth care can improve the client's appetite, taste, and comfort, as well as prevent oral infections and dental problems that can affect food intake. ³⁴
Choice C reason: Assessing for pain prior to mealtime is an appropriate action for a client who is at risk for malnutrition. Pain can reduce the client's appetite, mood, and ability to eat comfortably. The nurse should assess the client's pain level and provide adequate pain relief before offering food. ⁵⁶
Choice D reason: Removing the bedpan from the client's sight is an appropriate action for a client who is at risk for malnutrition. The presence of a bedpan or other unpleasant stimuli can cause the client to lose appetite, feel nauseated, or associate food with negative emotions. The nurse should create a pleasant and comfortable environment for the client to eat. ⁷⁸
Choice E reason: Discouraging snacks between meals is not an appropriate action for a client who is at risk for malnutrition. Snacks can provide additional calories, protein, and micronutrients that the client may not get from regular meals. Snacks can also help prevent hunger, fatigue, and hypoglycemia between meals. The nurse should encourage the client to have healthy snacks that are high in energy and nutrient density.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: Confusion and weakness are signs of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance, which can result from vomiting and diarrhea. These are serious complications that can affect the client's mental status, blood pressure, heart rate, and kidney function. The nurse should report these changes to the provider and monitor the client's vital signs and fluid status.
Choice B reason: Dry oral mucosa and furrowed tongue are also signs of dehydration, but they are less severe than confusion and weakness. The nurse should report these changes to the provider as well, but they are not the most urgent ones.
Choice C reason: Clear lungs bilaterally are a normal finding and do not indicate any change in the client's condition. The nurse should document this finding, but it does not require reporting to the provider.
Choice D reason: A soft and non-tender abdomen is a normal finding and does not indicate any change in the client's condition. The nurse should document this finding, but it does not require reporting to the provider.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
