A nurse is caring for a client who is taking montelukast. Which of the following outcomes indicates a therapeutic effect of the medication?
The client's seizure threshold is reduced.
The client experiences less muscle pain.
The client experiences an increased ease of breathing.
The client's platelet count is increased
The Correct Answer is C
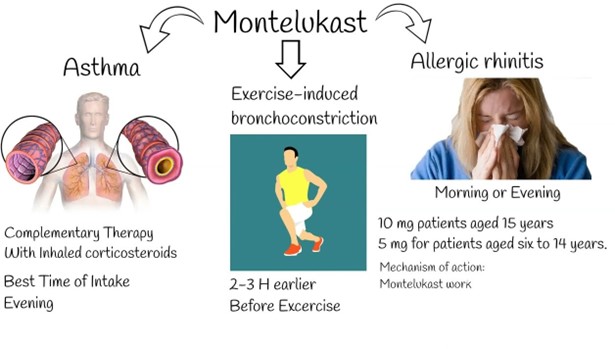
Montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist commonly used to manage asthma and allergic rhinitis. Its primary therapeutic effect is to improve respiratory symptoms by reducing inflammation and constriction of the airways. Therefore, an increased ease of breathing would be an expected outcome indicating that the medication is working effectively.
The other options are incorrect because:
A. The client's seizure threshold is reduced: Montelukast does not have any effect on the seizure threshold. This outcome is unrelated to the medication and may be indicative of a different condition or treatment.
B. The client experiences less muscle pain: Montelukast is not indicated for reducing muscle pain. This outcome is unrelated to the medication and may be indicative of a different condition or treatment.
D. The client's platelet count is increased: Montelukast does not have an effect on platelet count. This outcome is unrelated to the medication and may be indicative of a different condition or treatment.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","D"]
Explanation
The nurse should include the following information in the teaching about medication reconciliation:
● Provide a list of the client's current medications during admission to a healthcare facility.
● Provide a list of the client's current medications during the change of shift report.
Medication reconciliation is a critical process that involves comparing the medications a patient is currently taking with the medications ordered or intended to be prescribed. It helps ensure accurate and safe medication management during transitions of care. The nurse should emphasize the importance of providing a list of the client's current medications during admission to a healthcare facility. This information helps establish a baseline for the patient's medication regimen and allows healthcare providers to verify and reconcile the medications accurately.
Additionally, the nurse should instruct the class to provide a list of the client's current medications during the change of shift report. This allows for effective communication between healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and preventing medication errors or omissions.
While not specifically mentioned in the options, it is important to note that medication reconciliation should be performed at various points, including during the discharge process from a healthcare facility. Discharge medication reconciliation helps ensure a smooth transition to home or another healthcare setting, reduces the risk of medication-related issues, and promotes patient safety and adherence to the prescribed medication regimen.
Regarding over-the-counter medications, it is crucial to include them in the medication reconciliation process. Over-the-counter medications can interact with prescription medications and have potential side effects. Including them in the reconciliation report helps identify any potential interactions or duplications and ensures comprehensive medication management.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Dry mouth is a common side effect of diphenhydramine, which is an antihistamine medication commonly used to relieve symptoms of allergies, including itching and rash. Chewing on sugarless gum or sucking on hard, sour candies can help stimulate saliva production and alleviate the discomfort of dry mouth.
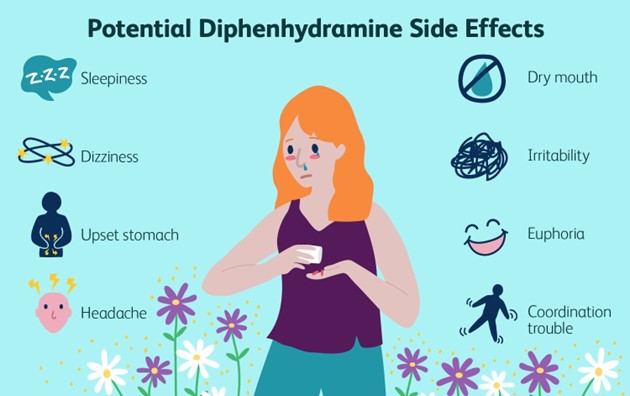
A. "Administer the medication with food": While taking diphenhydramine with food may help reduce the risk of stomach upset, it does not directly address the dry mouth side effect.
B. "Discontinue the medication and notify your provider": Discontinuing the medication without consulting the healthcare provider is not recommended unless specifically instructed to do so. Dry mouth is a common side effect of diphenhydramine and can be managed with supportive measures.
C. "Place a humidifier at your bedside every evening": While using a humidifier can help add moisture to the air and potentially alleviate dryness in the environment, it is not a specific instruction for managing dry mouth caused by diphenhydramine.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
