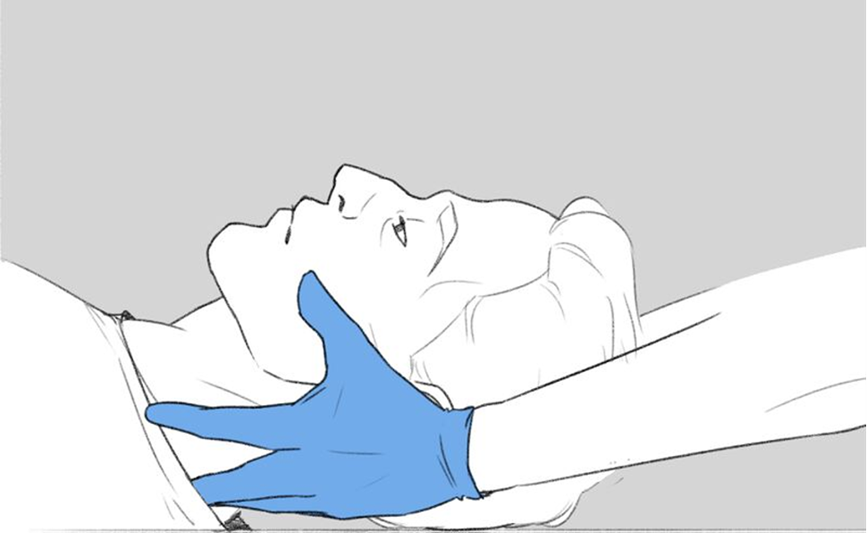
A nurse is caring for a client who was brought to the emergency department (ED) by EMS after diving into a lake and losing consciousness. The client was intubated in the field by the paramedics. A CT of the head and neck revealed a spinal cord injury at the level of C3-4. What is the priority nursing action?
Maintain the cervical collar in place.
Ask the client if they remember any events around the time of the injury.
Explain to the client that they will never be able to walk again.
Notify the client's parents that they are in the ED.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A Reason:
Maintaining the cervical collar in place is crucial for a client with a spinal cord injury at the level of C3-4. This action prevents further damage to the spinal cord by immobilizing the neck and maintaining proper alignment. Any movement could exacerbate the injury, potentially leading to more severe neurological deficits or even paralysis.
Choice B Reason:
Asking the client if they remember any events around the time of the injury is not the priority in this situation. While obtaining a history is important, it should not take precedence over stabilizing the spinal cord to prevent further injury. The primary focus should be on ensuring the client's safety and preventing additional harm.
Choice C Reason:
Explaining to the client that they will never be able to walk again is inappropriate and premature. The prognosis for spinal cord injuries can vary widely, and it is essential to provide accurate information based on a thorough assessment and consultation with specialists. Additionally, delivering such news requires sensitivity and should be done in a supportive manner.
Choice D Reason:
Notifying the client's parents that they are in the ED is important for family communication and support. However, it is not the immediate priority. The primary focus should be on stabilizing the client's condition and preventing further injury. Once the client is stabilized, the nurse can then inform the family.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
0.9% sodium chloride is an isotonic crystalloid solution often used for fluid resuscitation. However, it is not the preferred choice for burn patients because it lacks the necessary electrolytes to replace those lost through burn injuries. While it can be used if Lactated Ringer's is unavailable, it does not provide the same balanced electrolyte composition.
Choice B Reason:
Lactated Ringer's is the preferred fluid for initial resuscitation in burn patients. It is an isotonic crystalloid solution that closely mimics the body's plasma, providing essential electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and lactate. The lactate in the solution acts as a buffer, helping to correct metabolic acidosis, which is common in burn patients. The Parkland formula, widely used for calculating fluid needs in burn patients, specifically recommends Lactated Ringer's for the first 24 hours.
Choice C Reason:
Dextrose 5% in water is a hypotonic solution that provides free water and calories but lacks electrolytes. It is not suitable for initial fluid resuscitation in burn patients because it does not address the electrolyte imbalances and large fluid shifts that occur after a burn injury. Using this solution could lead to further complications such as hyponatremia.
Choice D Reason:
Dextrose 5% in 0.9% sodium chloride is a hypertonic solution that provides both glucose and electrolytes. However, it is not typically used for initial burn resuscitation because the high glucose content can lead to hyperglycemia, which is detrimental to burn patients. Additionally, the solution's osmolarity can exacerbate fluid shifts and worsen edema.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Elevating the client's head on two pillows can help reduce ICP by promoting venous drainage from the brain. However, it is important to ensure that the head is not elevated too high, as this can impede venous return and potentially increase ICP. The recommended elevation is typically 30 degrees. While this intervention is beneficial, it is not the most critical action compared to reducing environmental stimuli.
Choice B Reason:
Keeping the client well hydrated is essential for overall health, but excessive hydration can increase ICP by increasing the volume of cerebrospinal fluid and blood within the cranial vault. Fluid management must be carefully monitored to avoid exacerbating ICP. Therefore, while hydration is important, it must be balanced and not excessive.
Choice C Reason:
Decreasing the noise level in the client's room is crucial for minimizing external stimuli that can increase ICP. Noise and other environmental stressors can lead to increased agitation and stress, which in turn can elevate ICP. Creating a calm and quiet environment helps in maintaining a stable ICP and is a non-invasive, easily implementable intervention.
Choice D Reason:
Frequent suctioning of the endotracheal tube can cause transient increases in ICP due to the stimulation and potential for coughing. While suctioning is necessary to maintain airway patency, it should be performed judiciously and only when clinically indicated. Over-suctioning can lead to spikes in ICP and should be avoided.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
