A nurse is providing teaching to a parent of a child who has celiac disease. The nurse should include which of the following food choices for this child?
Barley
Rice
Rye
wheat
The Correct Answer is B
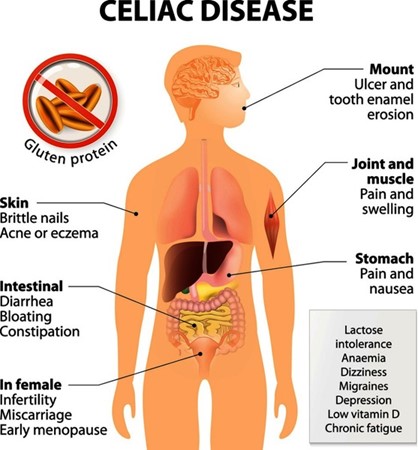
When providing teaching to a parent of a child with celiac disease, the nurse should recommend food choices that are gluten-free. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, which is a protein found in wheat, barley, rye, and their derivatives. Gluten damages the small intestine lining in individuals with celiac disease, leading to various gastrointestinal and nutritional issues.
The correct food choice for a child with celiac disease is B. Rice. Rice is naturally gluten-free and can be a safe and nutritious option for individuals with celiac disease. Other gluten-free options include corn, quinoa, oats (certified gluten-free oats), potatoes, and many fruits and vegetables.
A. Barley: Barley contains gluten, which is harmful to individuals with celiac disease. It should be avoided in the child's diet.
C. Rye: Rye also contains gluten and should be avoided in the child's diet. It can cause damage to the small intestine in individuals with celiac disease.
D. Wheat: Wheat is a primary source of gluten and is strictly off-limits for individuals with celiac disease. It is essential to avoid all wheat-containing products, including bread, pasta, and baked goods.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["260"]
Explanation
To calculate the total fluid intake, we need to convert all the measurements to milliliters (mL) and then add them up:
1 cup = 240 mL
1 oz = 30 mL
Given fluid intake:
Juice: ½ cup = 0.5 * 240 mL = 120 mL
Gelatin: 3 oz = 3 * 30 mL = 90 mL
Ice pop: 1 oz = 1 * 30 mL = 30 mL
Ginger ale: 20 mL
Total fluid intake = 120 mL + 90 mL + 30 mL + 20 mL = 260 mL
So, the nurse should record 260 mL as the child's fluid intake.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
For a 6-month-old infant who has undergone the repair of an intussusception, the nurse should select an oral electrolyte solution. This solution is specifically designed to replace lost fluids and electrolytes due to vomiting or diarrhea, which is crucial in preventing dehydration in infants.
Options A, B, and C are not suitable choices for an infant in this situation:
A. Half-strength orange juice: Citrus juices, including orange juice, are not recommended for infants under 12 months old. They are acidic and may cause stomach upset or diarrhea.
B. Sterile water: Sterile water does not contain the necessary electrolytes, and offering plain water to an infant after surgery or during an illness can lead to electrolyte imbalances and further dehydration.
C. Half-strength infant formula: Diluting infant formula can lead to inadequate nutrition for the infant. The baby requires appropriate nutrition to support recovery after surgery, and diluting formula can be harmful.
D. An oral electrolyte solution is the best choice as it helps maintain proper hydration and electrolyte balance in the infant's body during the recovery period. If the infant tolerates the oral electrolyte solution well and is not at risk for aspiration, the healthcare provider may gradually advance the diet to include other clear liquids and then slowly reintroduce regular infant formula or breast milk as appropriate. The healthcare provider's instructions should be followed carefully to support the infant's recovery and ensure adequate nutrition.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
