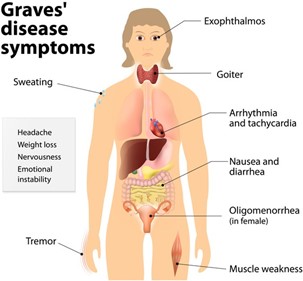
During the nursing assessment of a patient with Graves' disease. The nurse notes a bounding, rapid pulse and systolic hypertension. Based on these assessment data, which question is important for the nurse to ask the patient?
“Do you ever have any chest pain?'
“Have you noticed any recent decrease in your appetite?”
“Do you have any problem with frequent constipation?”
The Correct Answer is A
The patient's bounding, rapid pulse and systolic hypertension may indicate cardiovascular complications associated with Graves' disease, such as tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, or congestive heart failure, which can cause chest pain. It is important for the nurse to assess for any symptoms of cardiovascular distress and report any abnormal findings to the healthcare provider for prompt intervention. Questions about appetite and constipation may be relevant to the patient's overall health status, but they are not the most important concern in this situation.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
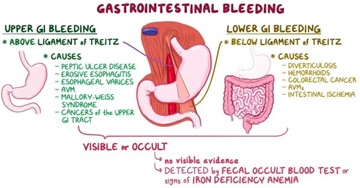
Coffee-ground material in the NG suction indicates that there is active bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, which could be a life-threatening situation. This requires immediate medical attention and intervention to control the bleeding and stabilize the patient.
Options A, B, and C are also important assessment data, but they are not as urgent as option D in this scenario.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
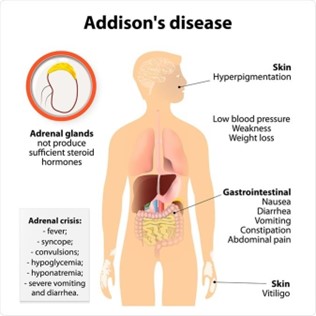
The statement "I had the stomach flu earlier this week and couldn't take the hydrocortisone" indicates that the patient may not be adhering to their prescribed medication regimen, which can lead to an Addisonian crisis. Therefore, the nursing diagnosis of ineffective therapeutic regimen management related to lack of knowledge of management of the condition is appropriate.
Addison’s disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. Hydrocortisone is a glucocorticoid medication that is often used to replace the cortisol that the adrenal glands are not producing. In the Addisonian crisis, the body is unable to produce the necessary levels of cortisol and aldosterone, which can lead to potentially life-threatening complications such as hypotension, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances.
The other statements may indicate areas where patient education is needed, but they do not directly relate to the immediate risk of an Addisonian crisis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
