Fetal well-being during labor is assessed by:
accelerations in the FHR.
maternal pain control
the response of the fetal heart rate (FHR) to uterine contractions (UCs).
an FHR above 110 beats/min.
The Correct Answer is C
Fetal well-being during labor is assessed by the response of the fetal heart rate (FHR) to uterine contractions (UCs). During labor, the fetal heart rate is monitored to assess the well-being of the fetus. The fetal heart rate should increase in response to fetal movement and contractions, which indicates that the fetus is receiving adequate oxygenation and blood flow. This response is called an "acceleration" in the FHR. However, accelerations alone are not enough to assess fetal well-being during labor. It is the combination of the FHR pattern with the uterine contractions pattern that provides the most information.
In addition to the FHR response to UCs, other factors that may be used to assess fetal well-being during labor include fetal scalp blood sampling, fetal pulse oximetry, and fetal ultrasound. Maternal pain control may help to decrease maternal stress and anxiety during labor, but it is not directly related to fetal well-being. An FHR above 110 beats/min is within the normal range for a fetal baseline heart rate, but it is not enough to assess fetal well-being during labor.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
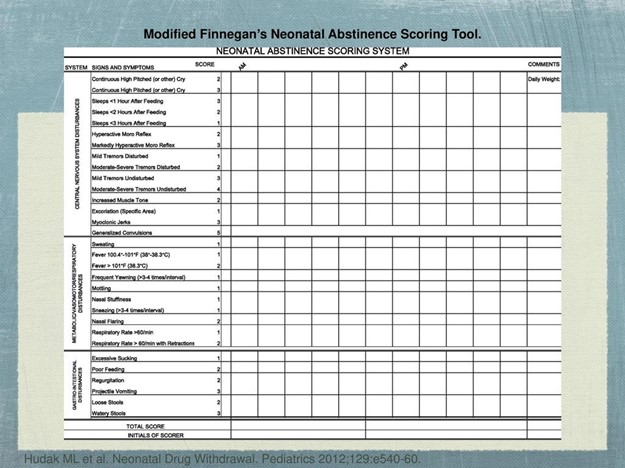
The Finnegan score is a tool used to assess and monitor newborns for withdrawal symptoms related to maternal substance use during pregnancy.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Surveillance is the ongoing and systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of health data for the purpose of monitoring health problems and trends. The Department of Health collects data on reportable diseases, including hepatitis B, to monitor disease incidence and inform public health interventions.
Descriptive epidemiology involves the study of the distribution and determinants of
health-related states or events in populations, while the epidemiological triangle is a model that describes the relationships among the agent, host, and environment in the development of disease.
Incident reporting refers to the documentation of adverse events or errors in healthcare settings.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
