For a client with diabetes mellitus, which new lab finding is the greatest concern?
Potassium 5.0 mEq/L.
Creatinine 4.4 mg/dL.
Hemoglobin 10.7 g/dL.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) 22 mg/dL.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason
A potassium level of 5.0 mEq/L is at the upper limit of the normal range, which is typically between 3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L. While this level should be monitored, especially in the context of diabetes where the patient may be at risk for hyperkalemia due to potential kidney issues, it is not immediately alarming¹.
Choice B Reason
A creatinine level of 4.4 mg/dL is significantly higher than the normal range of 0.6 to 1.2 mg/dL for males and 0.5 to 1.1 mg/dL for females. This indicates severe renal impairment or kidney failure, which is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus. Immediate intervention is required to address this critical issue¹.
Choice C Reason
A hemoglobin level of 10.7 g/dL is slightly below the normal range for adults, which is generally 13.8 to 17.2 g/dL for males and 12.1 to 15.1 g/dL for females. This could indicate mild anemia, which can be a complication of diabetes but is not as immediately concerning as a high creatinine level¹.
Choice D Reason
A Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) level of 22 mg/dL is within the normal range, which is typically between 7 and 20 mg/dL. This level does not indicate immediate concern and is not as critical as the elevated creatinine level¹.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
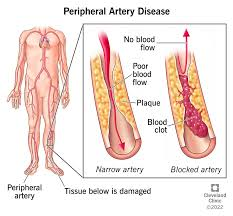
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason
While hypertension can contribute to the development of PAD, it does not directly cause fats to deposit in the arteries. Hypertension can damage the arterial walls, making them more susceptible to atherosclerosis, but it is not the primary mechanism of PAD development.
Choice B Reason
Excess fats in the diet can contribute to atherosclerosis, which is the accumulation of plaques in the arterial walls. However, the fats do not simply get stored; they combine with other substances, including calcium and inflammatory cells, to form plaques that can restrict blood flow.
Choice C Reason
This statement is the most accurate. PAD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaques formed by fats, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood. These plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the extremities. The process can be exacerbated by factors such as smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Arterial spasms can occur, but they are not the typical cause of chronic PAD. Spasms are more often associated with conditions like Raynaud's phenomenon or can be a response to stress or cold temperatures. PAD is usually a result of progressive atherosclerosis rather than intermittent spasms.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is characterized by challenges with social skills, repetitive behaviors, and communication difficulties. Jaw clenching and rocking are forms of self-stimulatory behavior (stimming) often observed in individuals with ASD¹³¹⁴. These behaviors can serve as a coping mechanism to manage sensory overload or express emotions.
Choice B Reason:
Stereotypic Movement Disorder involves repetitive, seemingly purposeless movements. While jaw clenching and rocking could be symptoms, they are more commonly associated with ASD. Stereotypic Movement Disorder is typically diagnosed when these behaviors interfere significantly with normal activities or result in self-harm, which is not mentioned in the child's description.
Choice C Reason:
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is marked by an ongoing pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development. The behaviors described, jaw clenching and rocking, are not typical indicators of ADHD, which more commonly includes symptoms like difficulty staying focused, hyperactivity, and impulsive actions.
Choice D Reason:
Intellectual Disability Disorder is characterized by limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior, which covers a range of everyday social and practical skills. The behaviors of jaw clenching and rocking do not directly indicate Intellectual Disability Disorder. This condition is usually identified by deficits in intellectual and adaptive functioning, not by specific behaviors like those described.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
