The client inquires what the positive result from the potassium hydroxide (KOH) test indicates. Which of the following is an accurate response by the nurse?
You have a virus.
You have a fungal infection.
You have a bacterial infection.
You have cancer.
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A Reason: A virus is not detected by the KOH test, which is used to diagnose fungal infections of the skin, hair, or nails. A virus can be detected by other tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or viral culture.
Choice B Reason: A fungal infection is detected by the KOH test, which dissolves the skin cells and leaves behind the fungal elements that can be seen under a microscope. A fungal infection can cause symptoms such as itching, scaling, redness, or blisters.
Choice C Reason: A bacterial infection is not detected by the KOH test, which is specific for fungi. A bacterial infection can be detected by other tests, such as gram stain or culture.
Choice D Reason: Cancer is not detected by the KOH test, which is not a screening tool for malignancy. Cancer can be detected by other tests, such as biopsy or imaging.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This choice is incorrect. Inability to read is not a finding that the nurse should expect in a client who has meningitis, but rather a possible finding in a client who has a stroke or a brain tumor. Meningitis does not affect the language or cognitive functions, but rather the meninges or the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord.
Choice B Reason: This choice is incorrect. Bruising around the eyes is not a finding that the nurse should expect in a client who has meningitis, but rather a possible finding in a client who has a basilar skull fracture or a head trauma. Meningitis does not cause bleeding or bruising, but rather inflammation and infection of the meninges.
Choice C Reason: This is the correct choice. A throbbing headache is a finding that the nurse should expect in a client who has meningitis, as it is one of the most common and characteristic symptoms. A throbbing headache is caused by increased intracranial pressure and irritation of the meninges due to inflammation and infection.
Choice D Reason: This choice is incorrect. A heart rate of 50 is not a finding that the nurse should expect in a client who has meningitis, but rather a possible finding in a client who has bradycardia or a slow heart rate. Meningitis does not affect the heart rate, but rather the temperature and blood pressure. The nurse should expect to see fever and hypotension in a client who has meningitis.
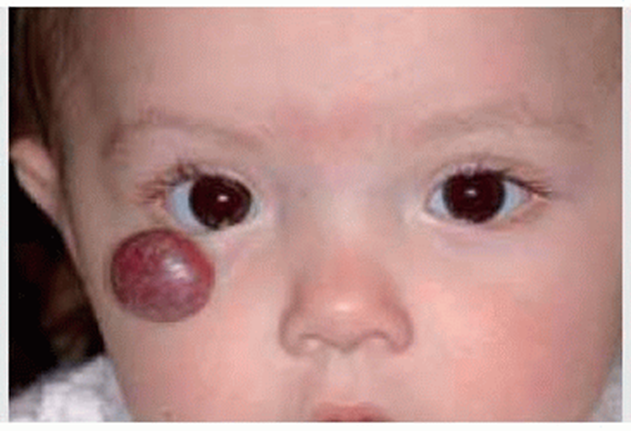
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is correct because the lesion on the child's head is most likely a hemangioma, which is a benign tumor of blood vessels that appears as a red or purple mark on the skin. Hemangiomas are common in newborns and usually grow during the first year of life, then shrink and fade over several years. The nurse should reassure the client that hemangiomas are harmless and do not require treatment unless they interfere with vision, breathing, or feeding.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because the lesion on the child's head will not spread, but rather grow and shrink within a limited area. The nurse should not alarm the client by suggesting that the lesion will spread to other parts of the body or become malignant. The nurse should explain that hemangiomas are not contagious or infectious and do not affect the child's overall health or development.
Choice C reason: This is incorrect because the lesion on the child's head is not caused by scarring from the birth process, but rather by abnormal growth of blood vessels in the skin. The nurse should not confuse or misinform the client about the cause of the lesion. The nurse should explain that hemangiomas are not related to trauma, infection, or genetics, but rather to unknown factors that influence blood vessel formation during fetal development.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because the lesion on the child's head is not a precancerous lesion and does not need a referral to a dermatologist. The nurse should not scare or mislead the client by suggesting that the lesion is a sign of cancer or requires further evaluation or treatment. The nurse should explain that hemangiomas are benign and usually resolve on their own without any complications or sequelae.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
