The community health nurse is performing a home visit for a 74-year-old client recovering from hip surgery. The nurse notes that the client seems uncharacteristically confused at times and has dry mucous membranes. The client states to stop drinking water early in the day because it's just too difficult to get up during the night to go to the bathroom. What would be the nurse's best response?
You need to have your medications adjusted so you need to be admitted to the hospital for a complete workup.
You build up too much urine in your bladder, which can cause you to get confused.
Dehydration can cause changes that can result in confusion, so let's try to increase your fluid intake.
Urinary tract infections are common and can cause confusion, so it's important not to urinate at night.
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason: This is not the best response because it is alarmist and does not address the client's concern. The nurse should not assume that the client needs to have their medications adjusted or be admitted to the hospital without further assessment.
Choice B reason: This is not the best response because it is inaccurate and does not explain the link between urine retention and confusion. The nurse should not imply that the client is causing their own confusion by not drinking enough water.
Choice C reason: This is the best response because it is accurate and educates the client on the effects of dehydration on the body. The nurse should encourage the client to drink more fluids throughout the day and offer strategies to make it easier for them to access the bathroom at night.
Choice D reason: This is not the best response because it is irrelevant and does not address the client's dehydration. The nurse should not suggest that the client has a urinary tract infection without evidence or testing. The nurse should also not discourage the client from urinating at night, as this can lead to other complications.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct finding for hypervolemia. Hypotension is a low blood pressure, which can be caused by hypovolemia (low blood volume) or other factors. Hypervolemia is an excess of fluid in the body, which can increase the blood pressure.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct finding for hypervolemia. Bradycardia is a slow heart rate, which can be caused by heart block, medication, or other factors. Hypervolemia can cause tachycardia (fast heart rate) as the heart tries to pump the excess fluid.
Choice C reason: This is a correct finding for hypervolemia. Peripheral edema is a swelling of the extremities due to fluid accumulation in the tissues. Hypervolemia can cause peripheral edema as the fluid leaks from the blood vessels into the interstitial spaces.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct finding for hypervolemia. Weight loss is a decrease in body weight, which can be caused by dehydration, malnutrition, or other factors. Hypervolemia can cause weight gain as the body retains more fluid.
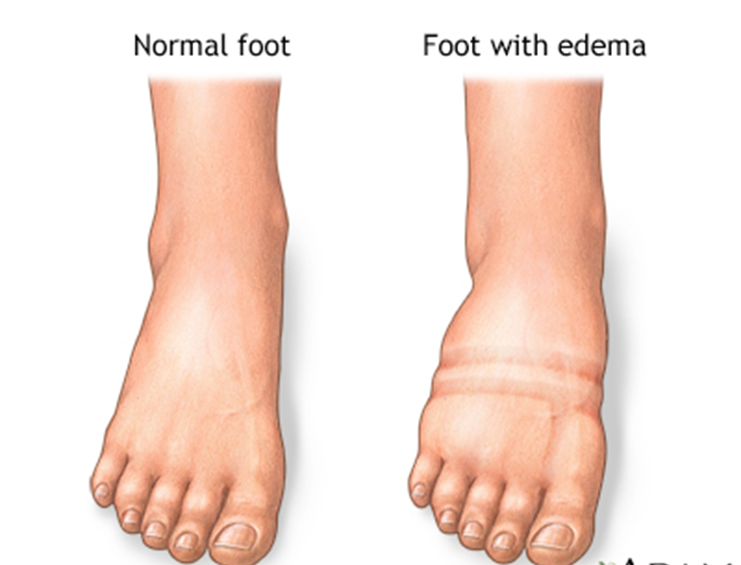
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: Active transport is the process of moving molecules across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient, requiring energy.
Choice B reason: Diffusion is the process of moving molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, without using energy.
Choice C reason: Filtration is the process of moving fluid and solutes through a membrane by a pressure gradient.
Choice D reason: Osmosis is the process of moving water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
