A 46-year-old female patient returns to the clinic with continued dysuria after being treated with trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole for 3 days. Which action will the nurse plan to take?
Remind the patient about the need to drink 1000 mL of fluids daily.
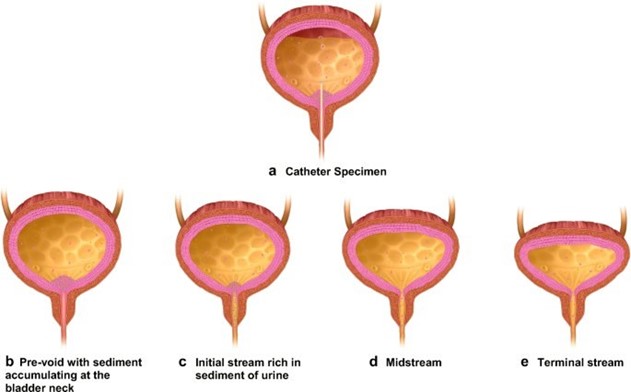
Obtain a midstream urine specimen for culture and sensitivity testing.
Suggest that the patient use acetaminophen (Tylenol) to relieve symptoms.
Tell the patient to take trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole for 3 days.
The Correct Answer is B
This is because the persistent dysuria suggests that the initial treatment was not effective, and there may be a possibility of a resistant organism. Obtaining a midstream urine specimen for culture and sensitivity testing will help identify the specific microorganism causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic to use. The nurse should also instruct the patient to continue to drink plenty of fluids, as this will help flush out the bacteria and relieve symptoms. The nurse may suggest the use of acetaminophen (Tylenol) to relieve discomfort, but this should not be the only action taken, as treating the underlying infection is crucial. The nurse should not tell the patient to take trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole for an additional three days, as the initial treatment was not effective, and a different course of treatment may be required based on the results of the urine culture and sensitivity testing.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A decrease in the level of consciousness is a serious sign and could be an indication of worsening conditions. It is essential for the nurse to ensure that the patient's airway is open and clear, as a compromised airway can lead to hypoxia and a further decrease in consciousness. Therefore, maintaining a patent airway should be the nurse's priority action in this situation.
While monitoring blood pressure and restricting oral intake may be important interventions in certain situations, they are not the priority actions in this scenario. Administering SQ insulin may not be necessary for a patient with hypothyroidism and acute appendicitis.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Based on the assessment findings presented, the nurse would suspect a urinary tract infection (UTI). The client's symptoms of acute confusion, urinary frequency and incontinence, and elevated WBC count with bands suggest a possible infection. Dehydration or diabetic ketoacidosis could also cause confusion and fatigue, but these conditions are less likely given the normal BMP and CBC results.
Hepatitis would not typically present with these specific symptoms.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
