A client in her first trimester of pregnancy is scheduled for an ultrasound.
Which of the following would not be a reason for an ultrasound at this stage?
Determine fetal position.
Detect multiple gestations.
Detect maternal abnormalities.
Confirm pregnancy.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale:
Fetal position during the first trimester is not definitively determined through ultrasound. While the gestational sac and fetal pole can be visualized, the fetus is still quite small and has ample space to move within the amniotic sac. This makes it challenging to accurately ascertain its position.
Reliable assessment of fetal position typically occurs later in pregnancy, usually between 34 and 36 weeks gestation. At this point, the fetus is larger and less mobile, allowing for a clearer assessment of its position through ultrasound.
The early determination of fetal position in the first trimester is not a primary goal of ultrasound. It is more focused on establishing pregnancy viability, gestational age, and detecting any potential abnormalities.
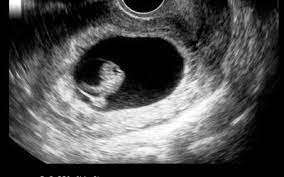
Choice B rationale:
Ultrasound in the first trimester can reliably detect multiple gestations. It can visualize the presence of multiple gestational sacs or fetal poles, clearly indicating whether a woman is carrying twins, triplets, or more.
Early identification of multiple gestations is crucial for optimal pregnancy management. It allows healthcare providers to tailor prenatal care, monitor for potential complications associated with multiple pregnancies, and plan for appropriate delivery. Choice C rationale:
Ultrasound in the first trimester can assist in detecting certain maternal abnormalities that could impact pregnancy. These may include:
Uterine abnormalities, such as fibroids or structural defects
Ovarian cysts
Ectopic pregnancies (where the embryo implants outside the uterus)
Gestational trophoblastic disease (abnormal growth of tissue inside the uterus)
Early identification of these maternal abnormalities allows for timely intervention and management, ensuring the best possible outcomes for both mother and fetus.
Choice D rationale:
Confirming pregnancy is a primary reason for ultrasound in the first trimester. It can visualize the gestational sac, which contains the developing embryo and confirms the presence of a pregnancy.
Ultrasound can also detect the fetal heartbeat, which typically becomes visible between 6 and 8 weeks gestation. This provides further confirmation of a viable pregnancy.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The correct answer is C. The test results are normal.
Choice A rationale:
A biophysical profile (BPP) score of 8 does not necessarily indicate a need for immediate cesarean delivery.
Cesarean delivery is typically reserved for cases where there is a clear and urgent risk to the health of the mother or fetus, such as severe fetal distress or placental abruption.
A score of 8, while not the highest possible score, is still within the normal range and does not, by itself, constitute a reason for immediate surgical intervention.
Choice B rationale:
Additional tests may be considered in certain cases, such as when the BPP score is borderline or when there are other risk factors present.
However, a score of 8 is generally considered reassuring and does not typically warrant further testing.
It's essential to evaluate the BPP score in the context of the overall clinical picture, including the gestational age, maternal health, and fetal history.
Choice D rationale:
While an obstetric specialist may review the BPP results and discuss delivery options with the patient, this is not typically done within a week for a score of 8.
A score of 8 indicates reassuring fetal well-being, and there is usually no need for such urgent consultation or decision-making.
The timing of delivery discussions would depend on the overall clinical situation and the patient's individual preferences.
Choice C rationale:
A BPP score of 8 is considered normal.
It suggests that the fetus is well-oxygenated and has normal heart rate, breathing movements, muscle tone, and amniotic fluid levels.
This score does not raise immediate concerns about fetal well-being and does not typically require any immediate interventions.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Fetal heart rate of 90 beats per minute is a sign of fetal bradycardia, which is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. It indicates that the fetus is not getting enough oxygen, and it can lead to fetal distress, brain damage, or even death.
Oxytocin can cause uterine hyperstimulation, which can reduce blood flow to the placenta and cause fetal bradycardia. Therefore, if the nurse observes a fetal heart rate of 90 beats per minute, it is essential to discontinue the oxytocin infusion immediately and notify the healthcare provider.
Choice B rationale:
Increased urinary output is not a direct contraindication to oxytocin administration. In fact, oxytocin can sometimes cause a decrease in urinary output due to its antidiuretic effects.
While a significant increase in urinary output could be a sign of fluid overload, it would not necessarily indicate that the oxytocin infusion needs to be discontinued. The nurse would need to assess the patient's overall fluid status and other clinical indicators to make this determination.
Choice C rationale:
Three contractions occurring within a 10-minute period is considered a normal contraction pattern during labor. It is not a sign of uterine hyperstimulation or fetal distress.
In fact, the goal of oxytocin administration is to achieve regular contractions that are occurring every 2-3 minutes and lasting 40-60 seconds. Therefore, this finding would not indicate that the oxytocin infusion needs to be discontinued.
Choice D rationale:
Adequate resting tone of the uterus palpated between contractions is a normal finding during labor. It indicates that the uterus is contracting effectively and is not at risk for uterine atony (lack of muscle tone).
This finding would not be a reason to discontinue the oxytocin infusion.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
